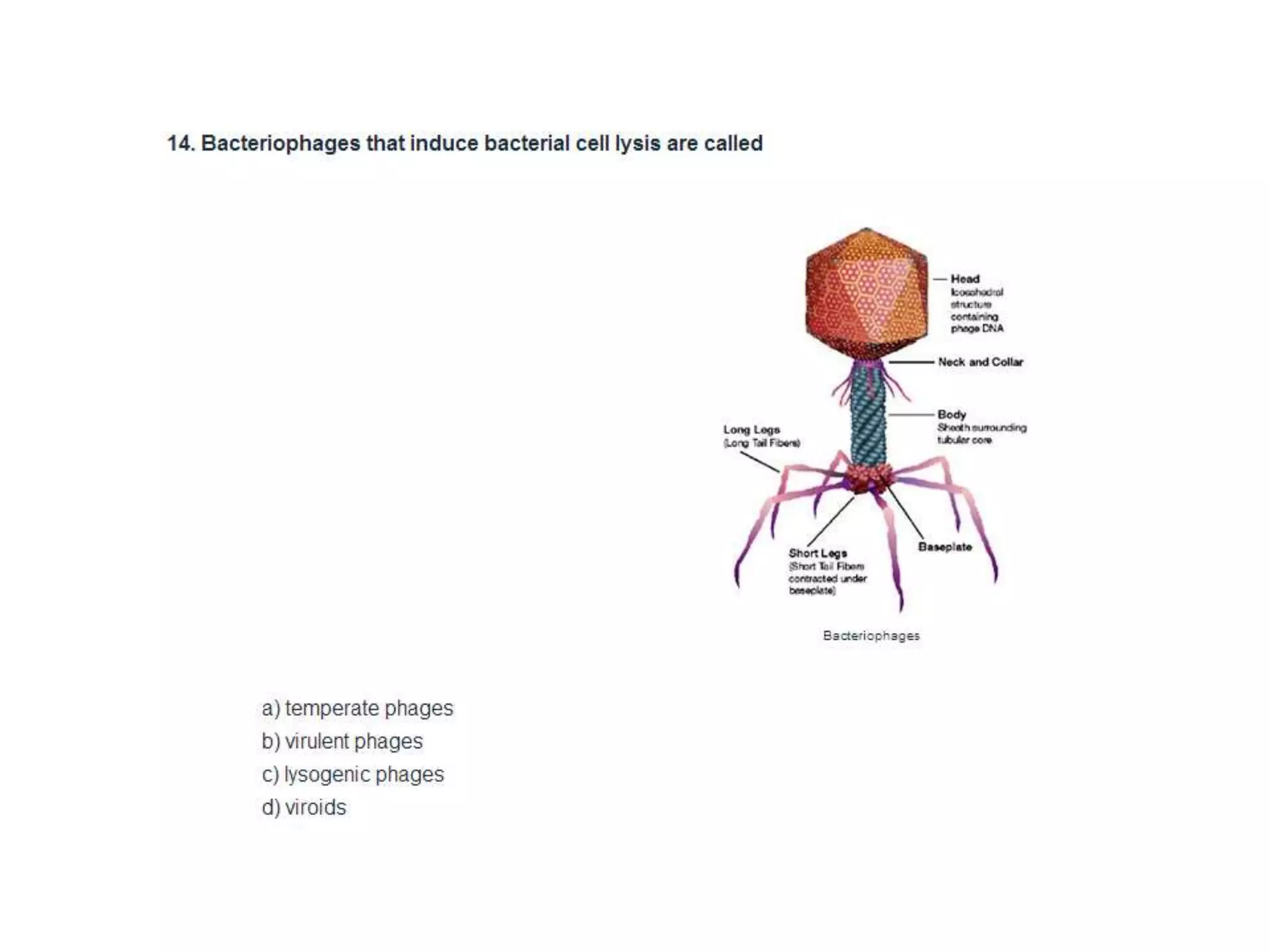
Viruses are submicroscopic infectious agents that lack cellular organization and require a host cell to replicate. They contain either DNA or RNA surrounded by a protein coat called a capsid. Viruses have different structures depending on their symmetry - icosahedral, helical, or complex. They multiply through lytic or lysogenic cycles, depending on if they cause host cell lysis or integrate into the host genome. Important plant, animal, and bacterial viruses are described along with their structures and life cycles. Viruses, viroids, and prions are compared in terms of their genetic material and ability to infect hosts.