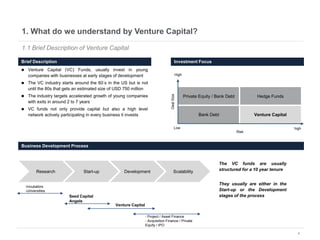
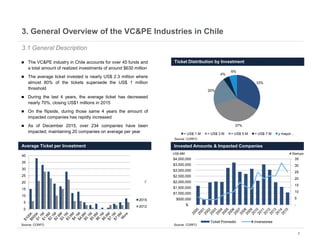
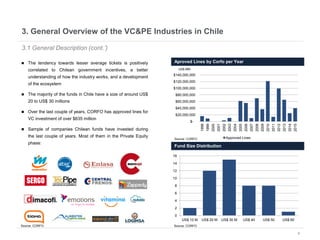
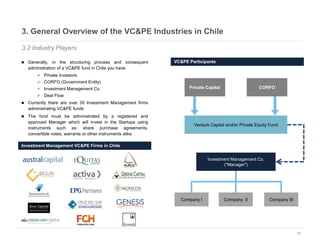
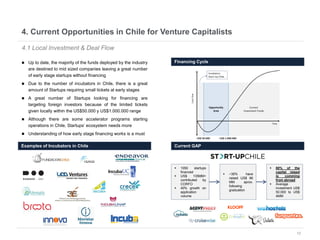
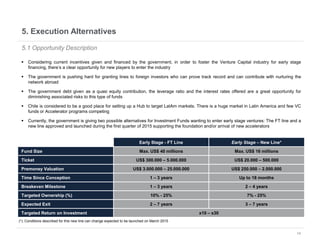
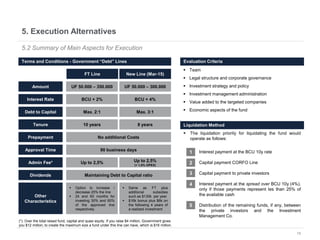
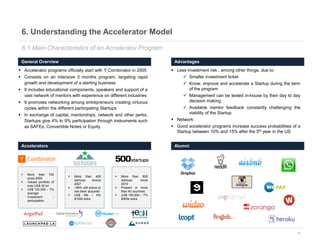
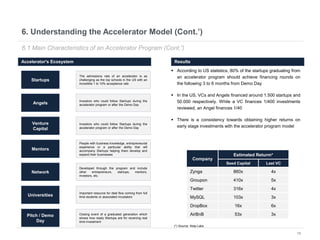
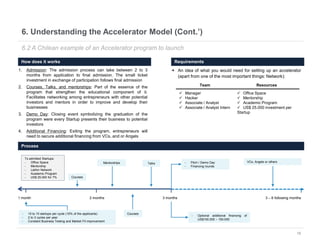
This document provides an overview of venture capital opportunities in Chile. It discusses the history of VC in Chile, the current state of the industry, and opportunities for new VC funds. Specifically, it notes that while most investments have been in later stages, there is an opportunity to fund early stage startups. The Chilean government is incentivizing new VC funds through programs like the FT line and a new early stage line to close current funding gaps for startups and help foster Chile's startup ecosystem.