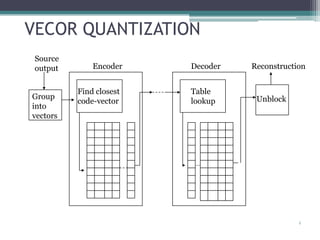
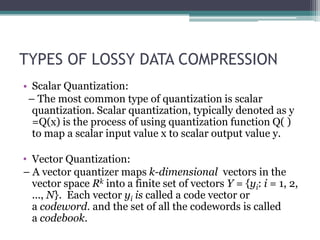
The document discusses efficient codebook design for image compression using vector quantization. It introduces data compression techniques, including lossless compression methods like dictionary coders and entropy coding, as well as lossy compression methods like scalar and vector quantization. Vector quantization maps vectors to codewords in a codebook to compress data. The LBG algorithm is described for generating an optimal codebook by iteratively clustering vectors and updating codebook centroids.





![VECTOR QUANTIZATION
• The amount of compression will be described in
terms of the rate, which will be measured in bits
per sample. Suppose we have a codebook of size
k, and the input vector is of dimension L. We
need to use [log 2 k] bits to specify which of the
code-vectors was selected. The rate for an L-
dimensional vector quantizer with a codebook of
size K is [log 2 k]/L .](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/vq-111117050703-phpapp02/85/Vector-quantization-7-320.jpg)