The document summarizes a case study report on implementing value management in a construction project in Malaysia. It discusses:
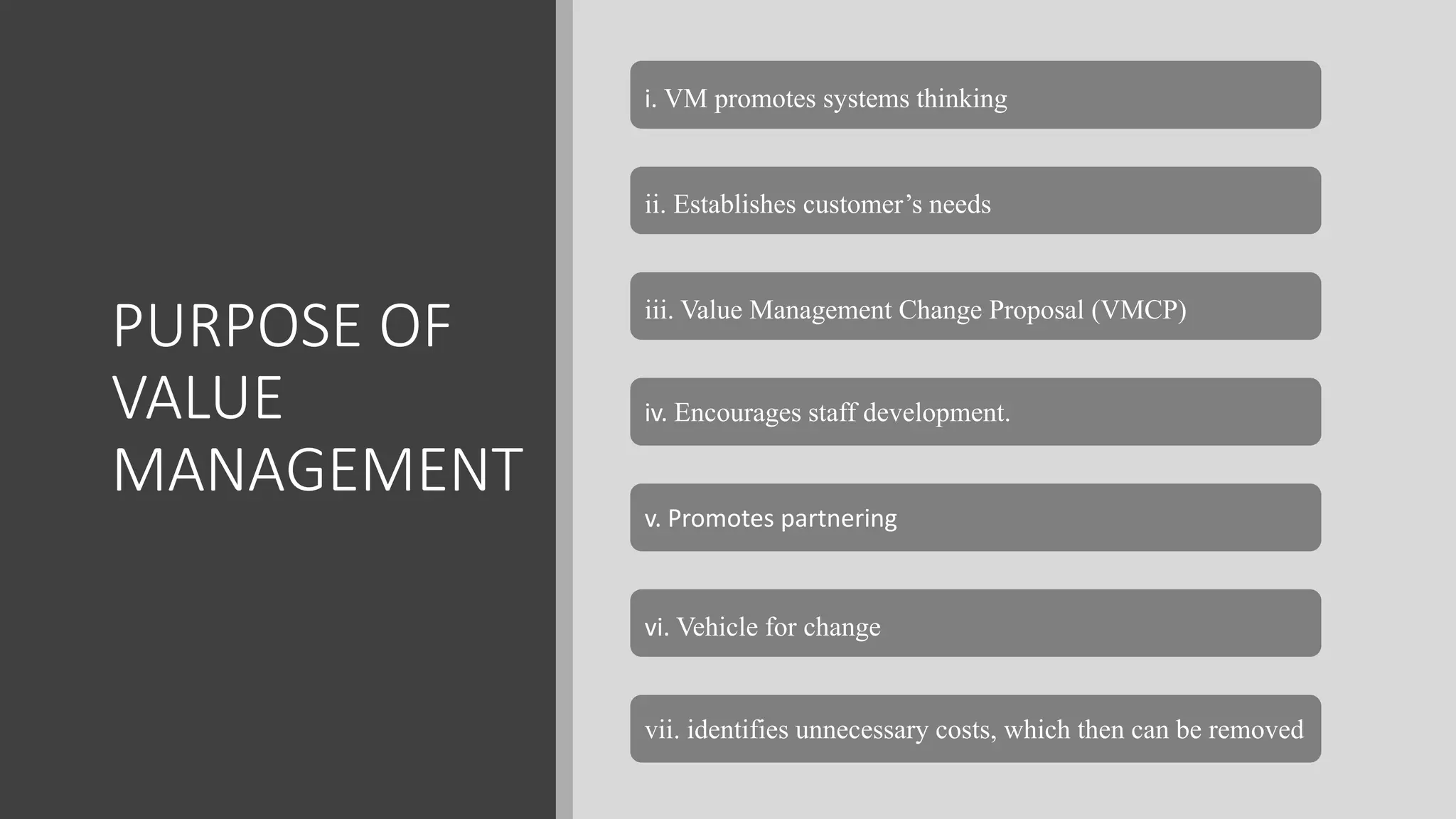
1) An introduction to value management, its process and purpose.
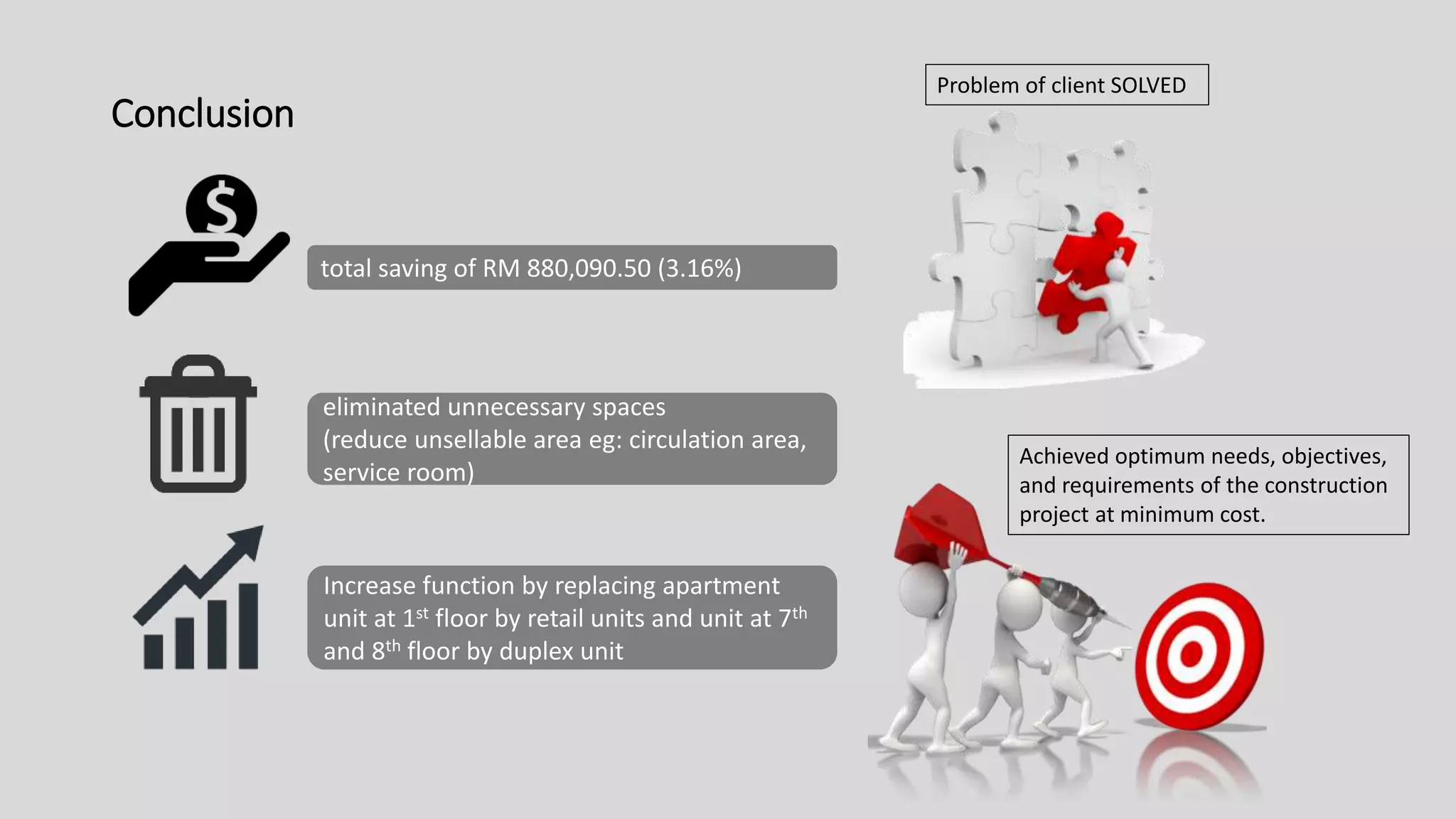
2) A description of the project - an 8-storey apartment building in Subang Jaya, Selangor with residential units from first to eighth floor and basement car park.
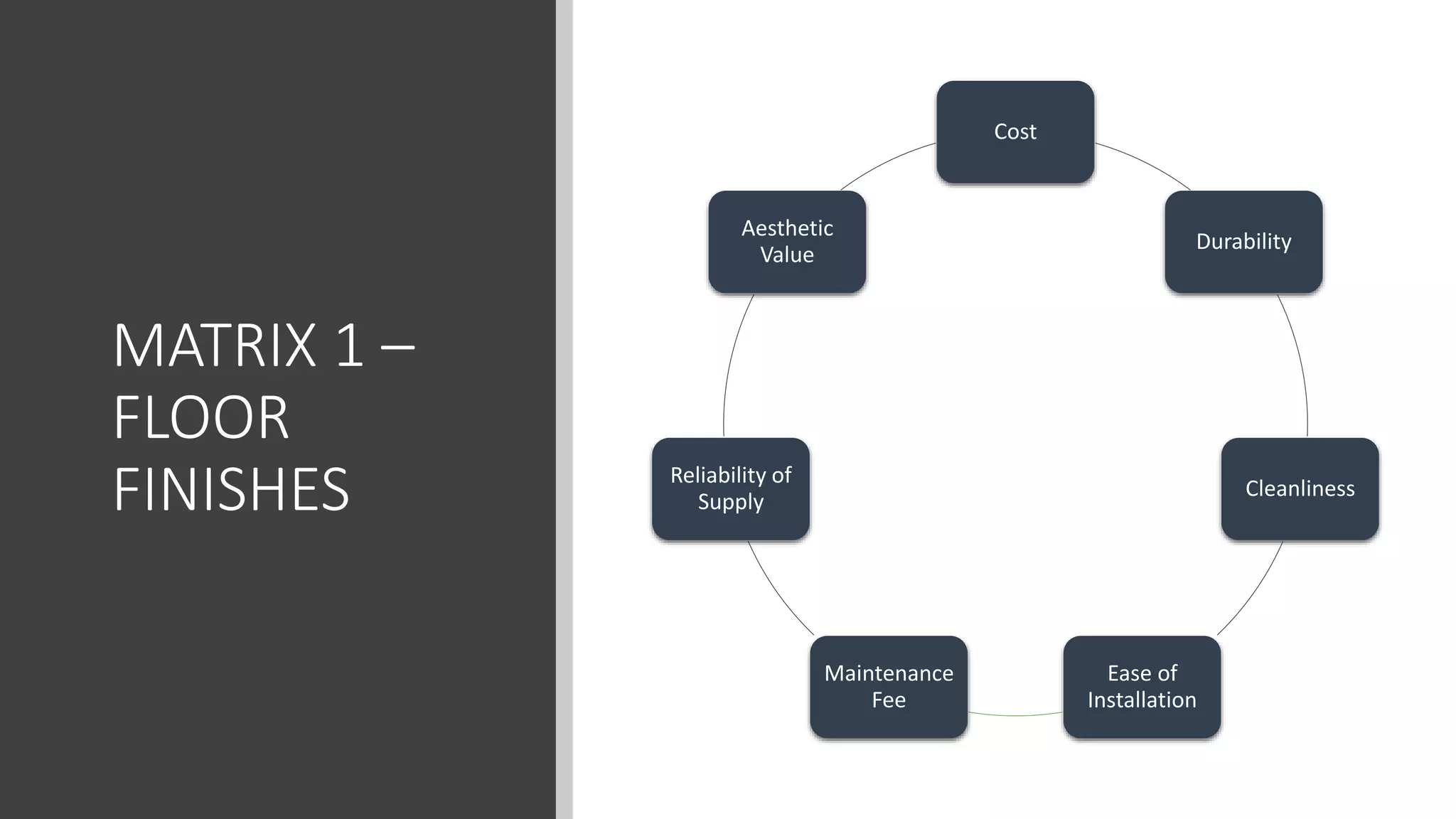
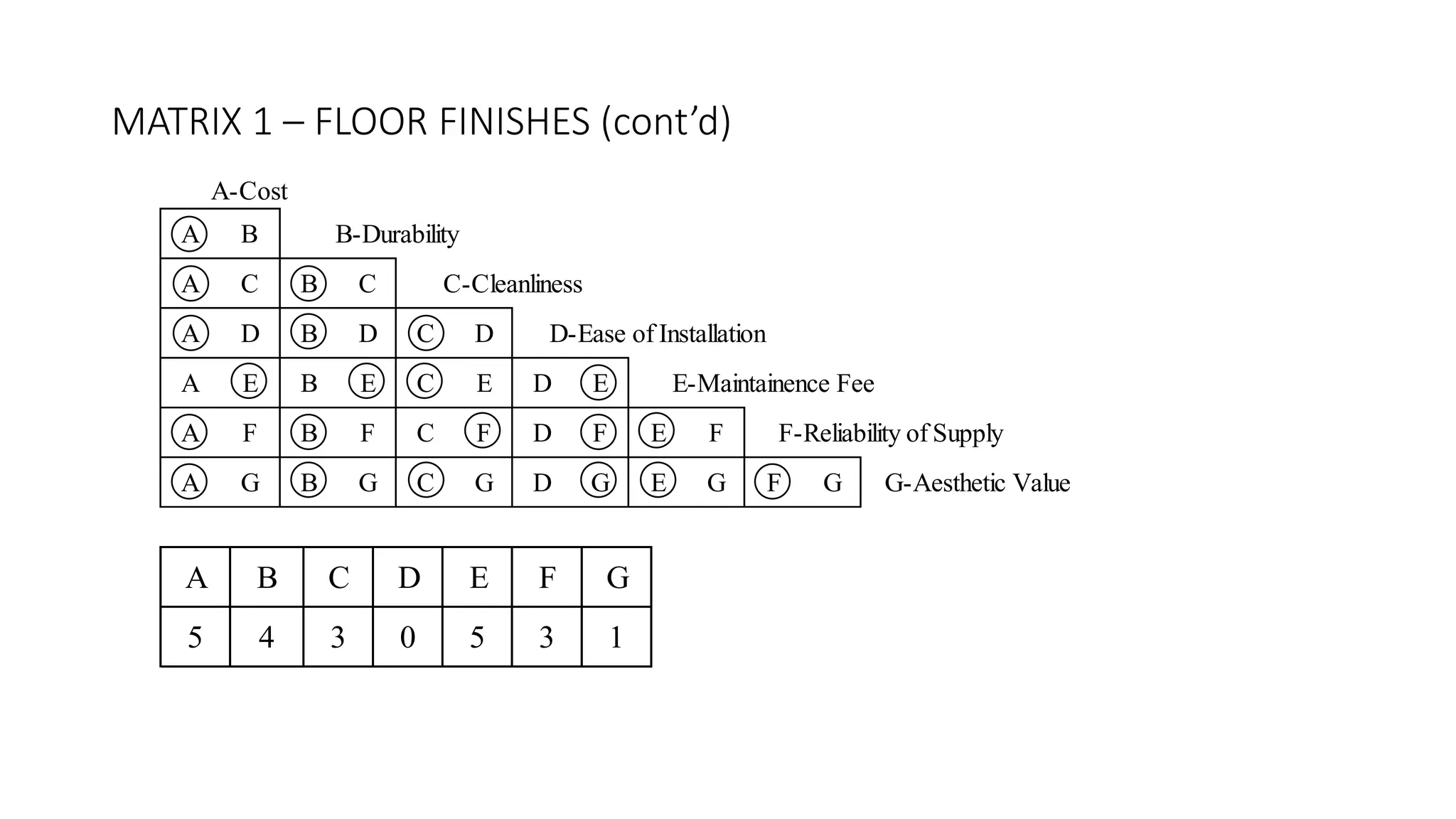
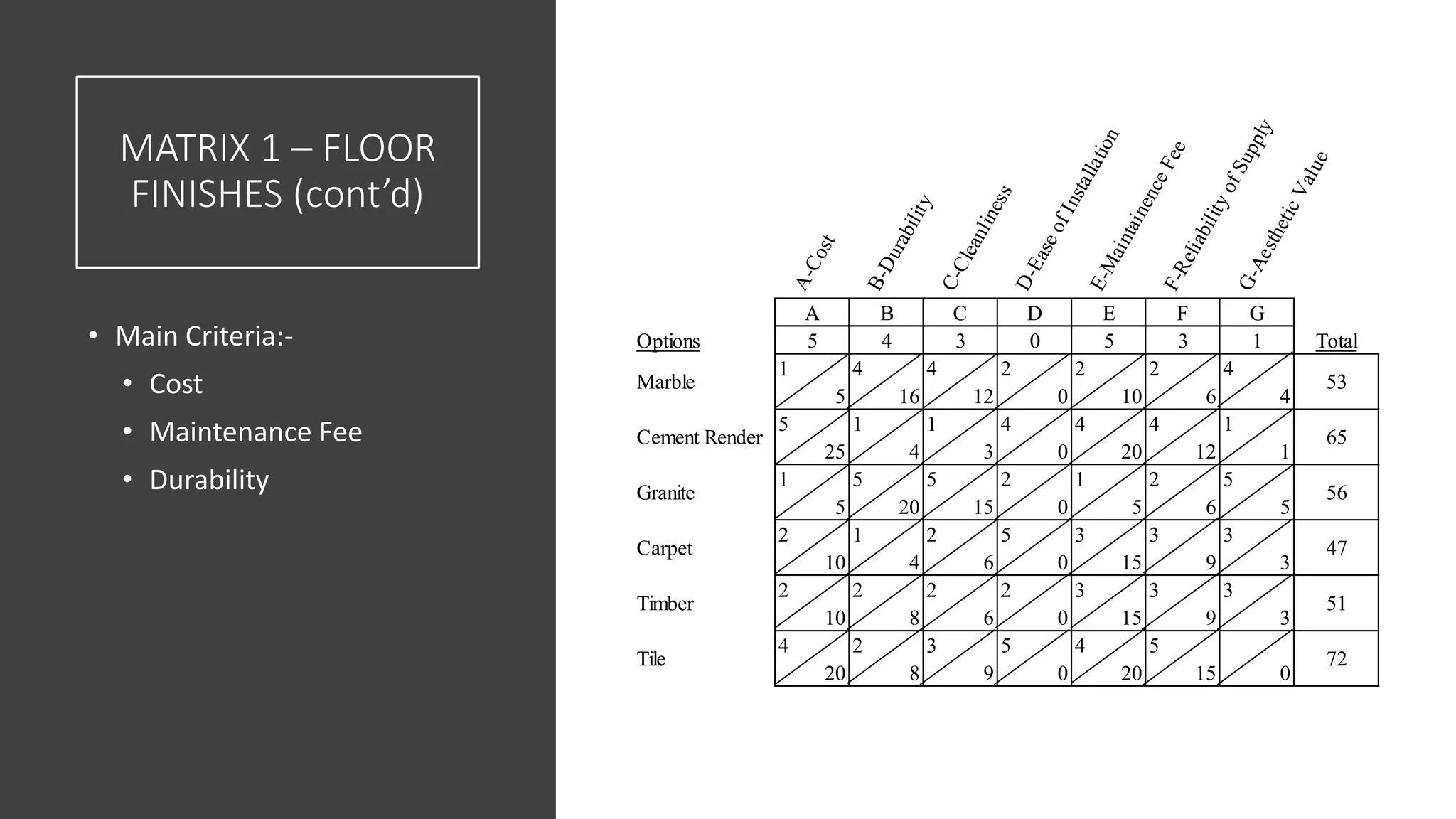
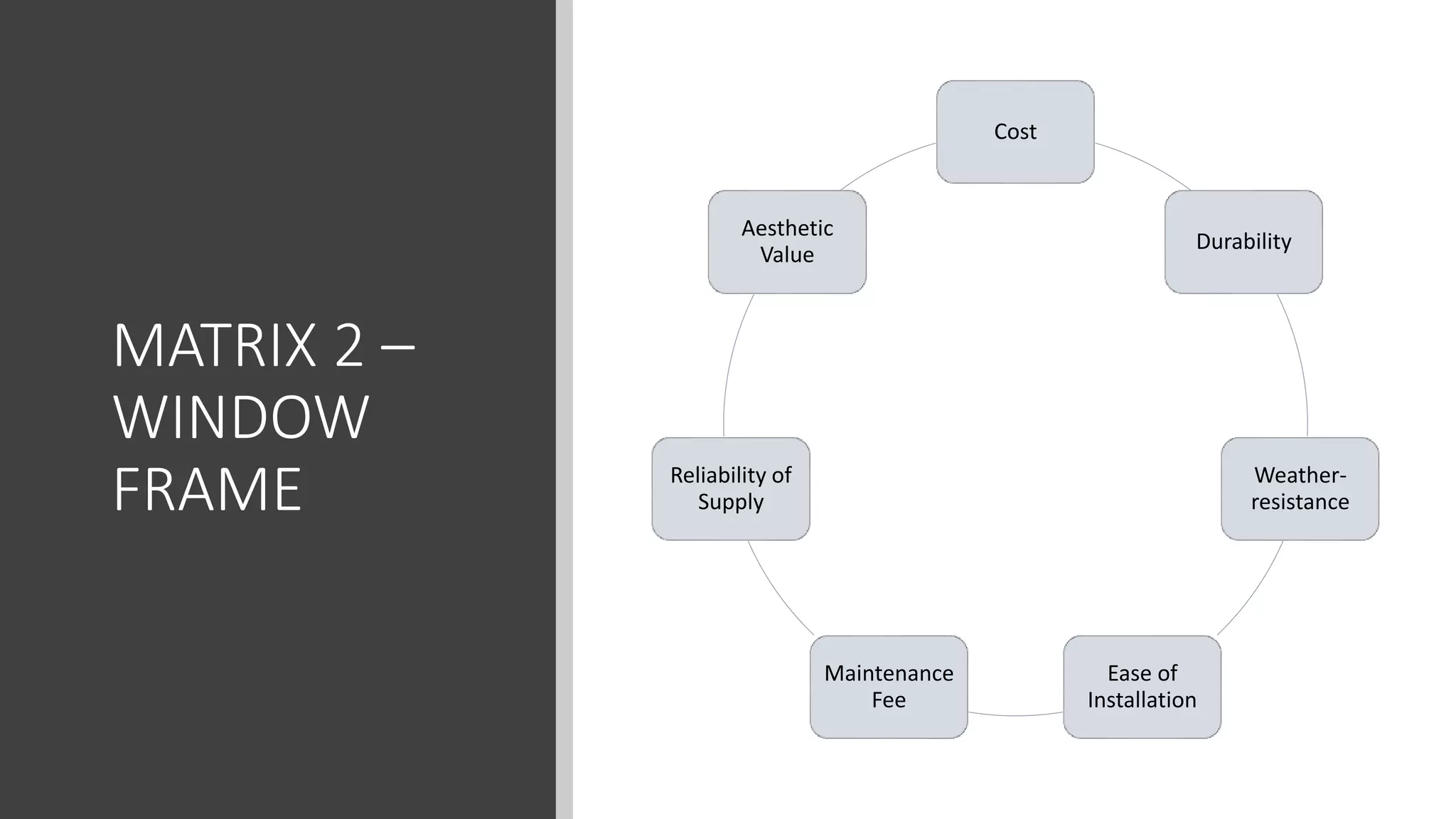
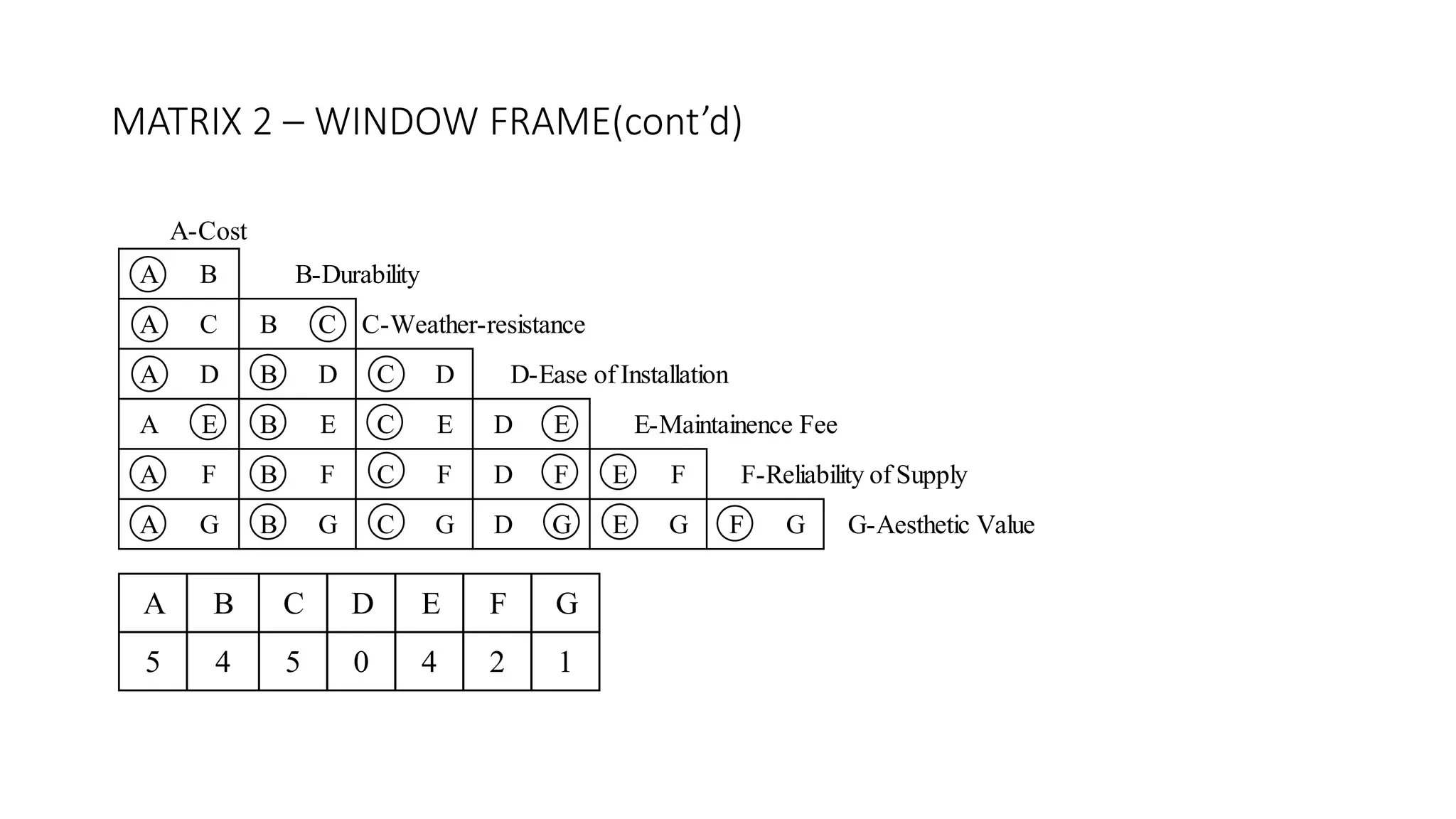
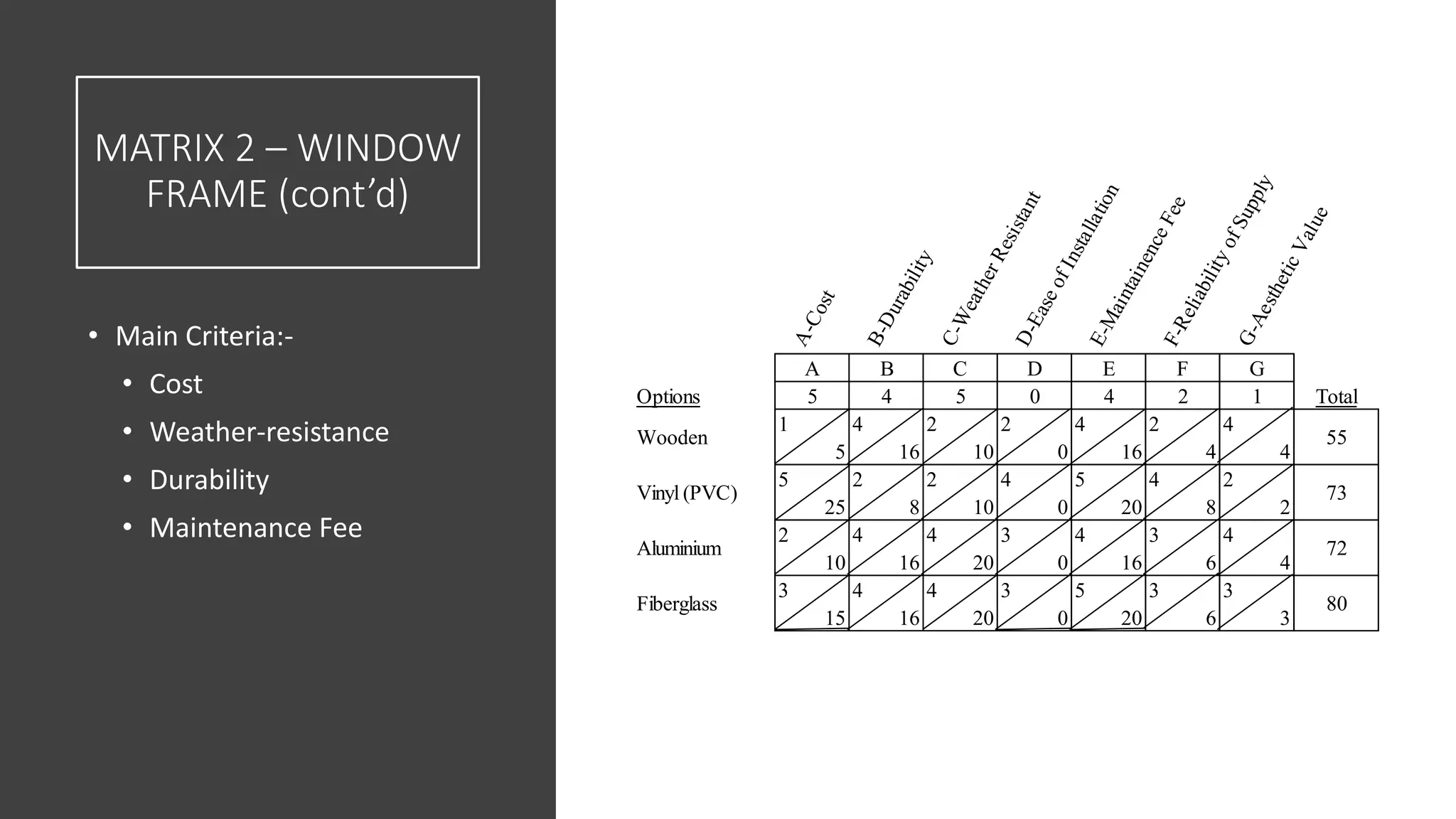
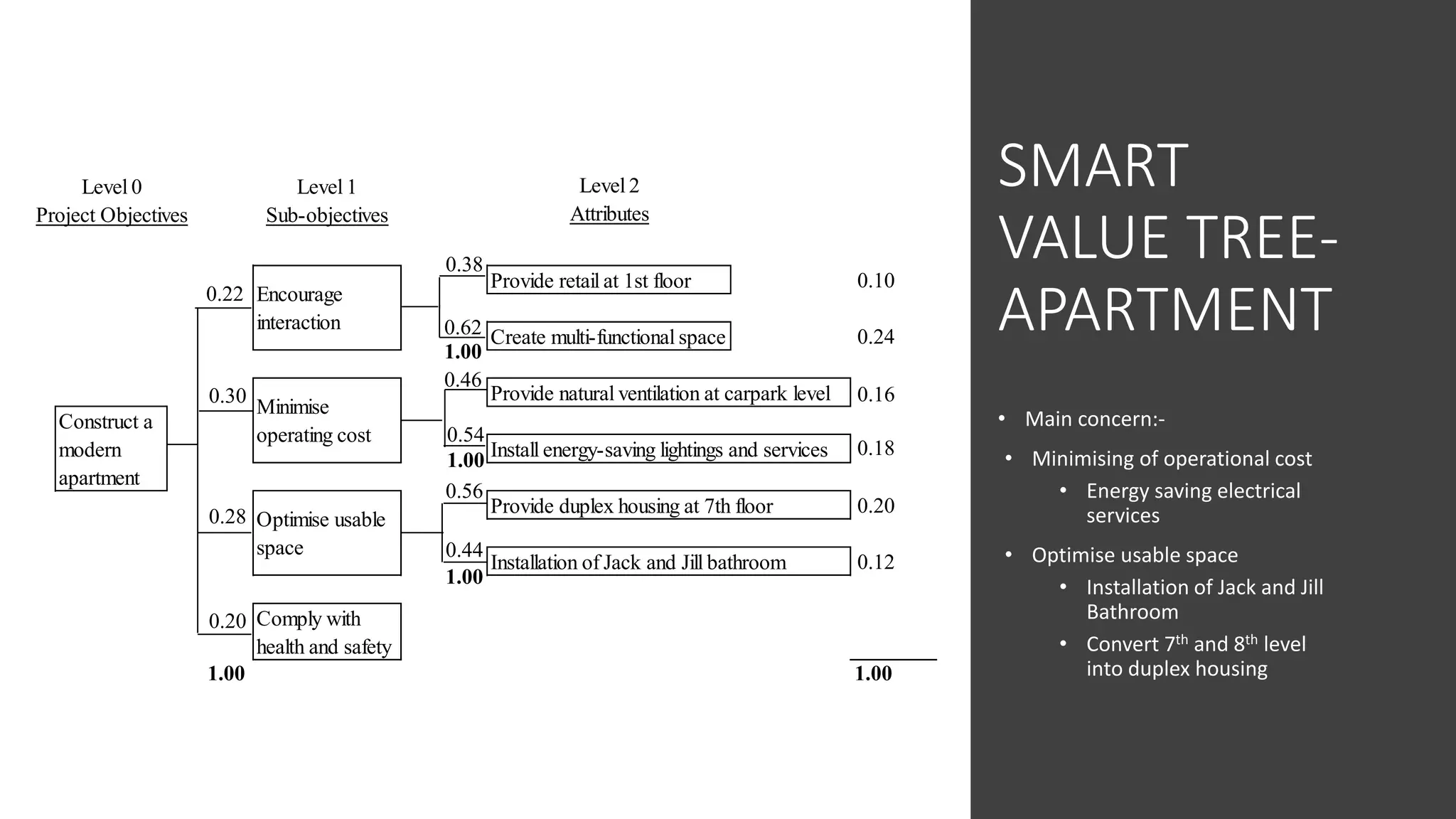
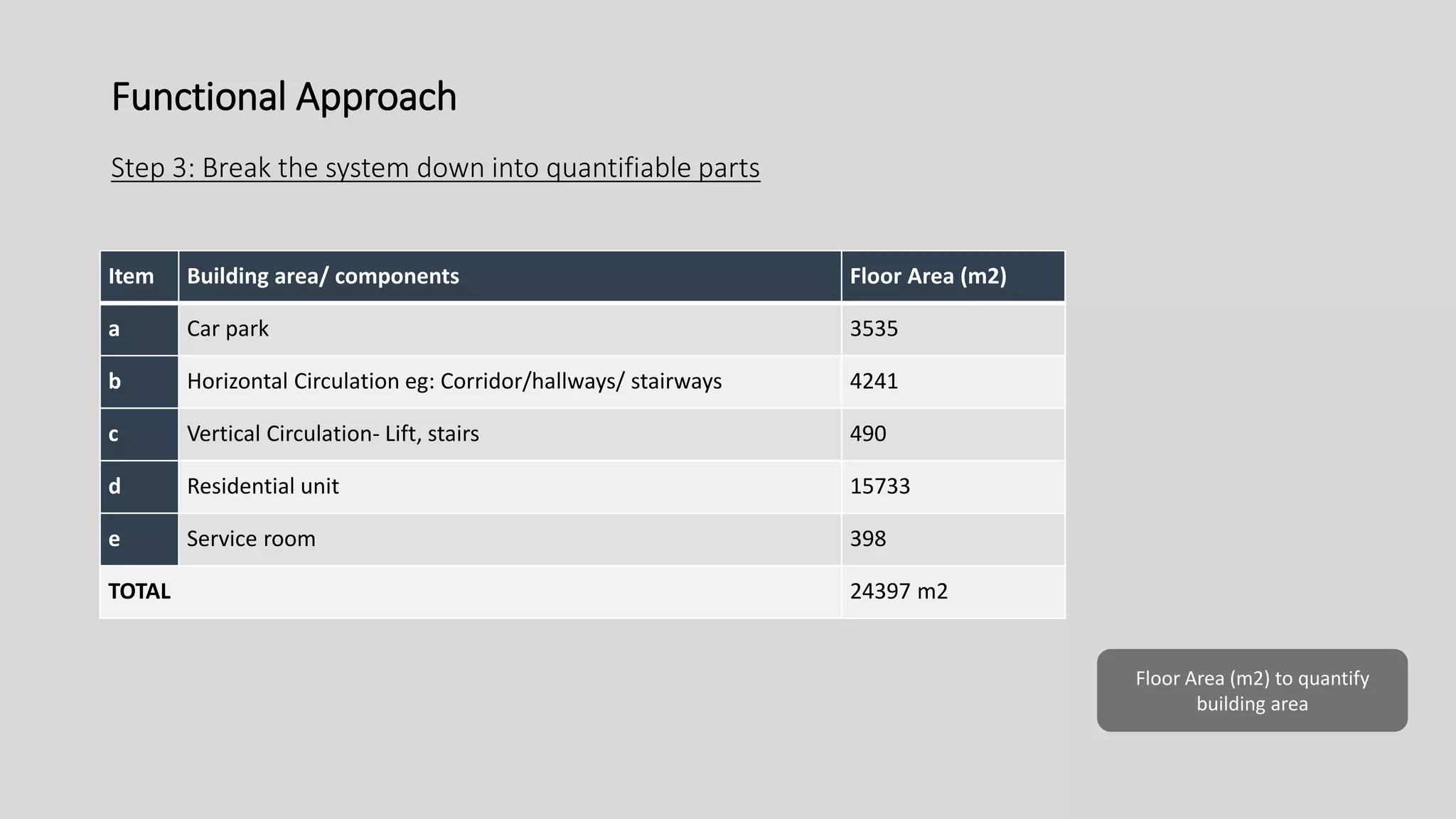
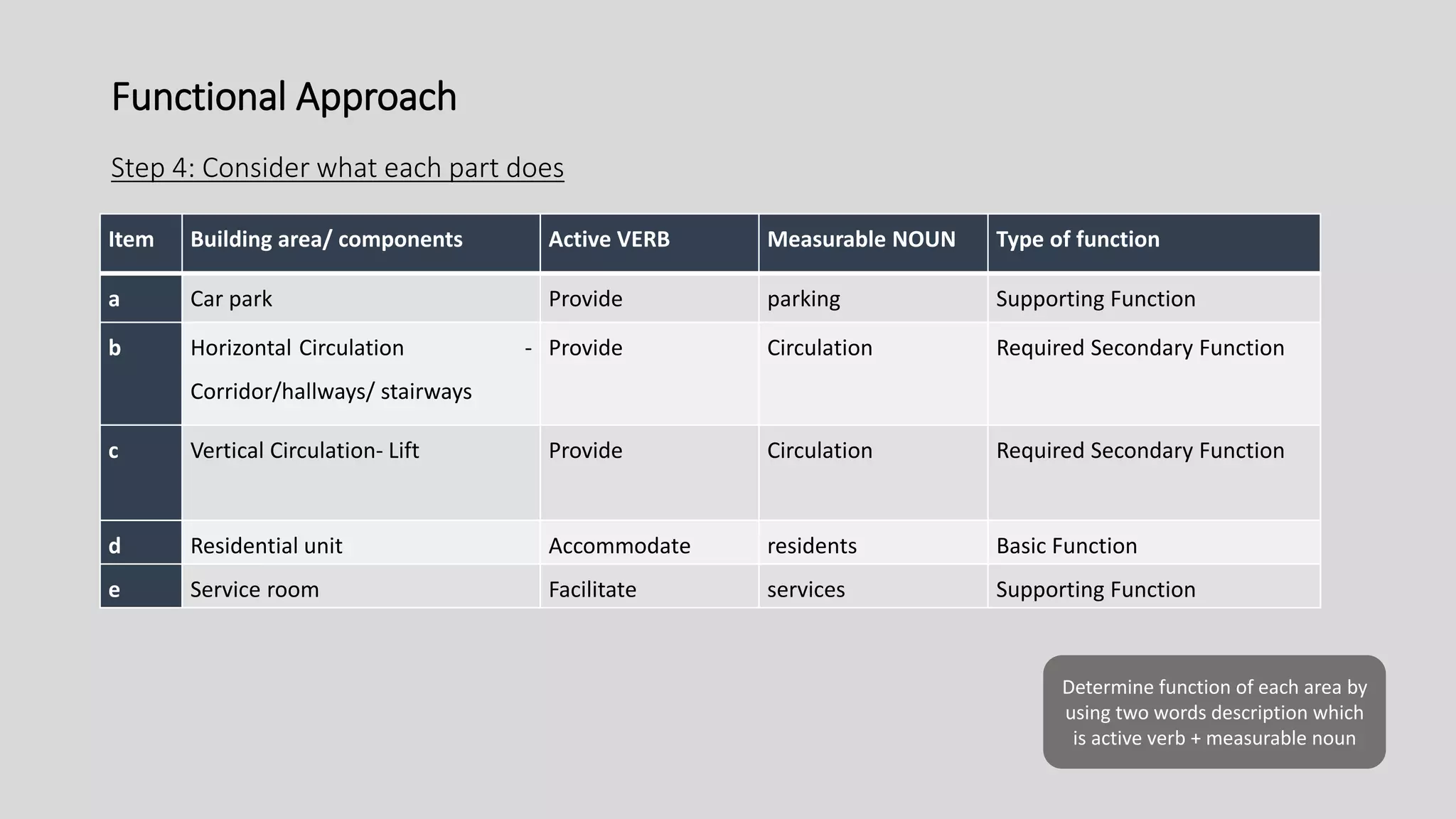
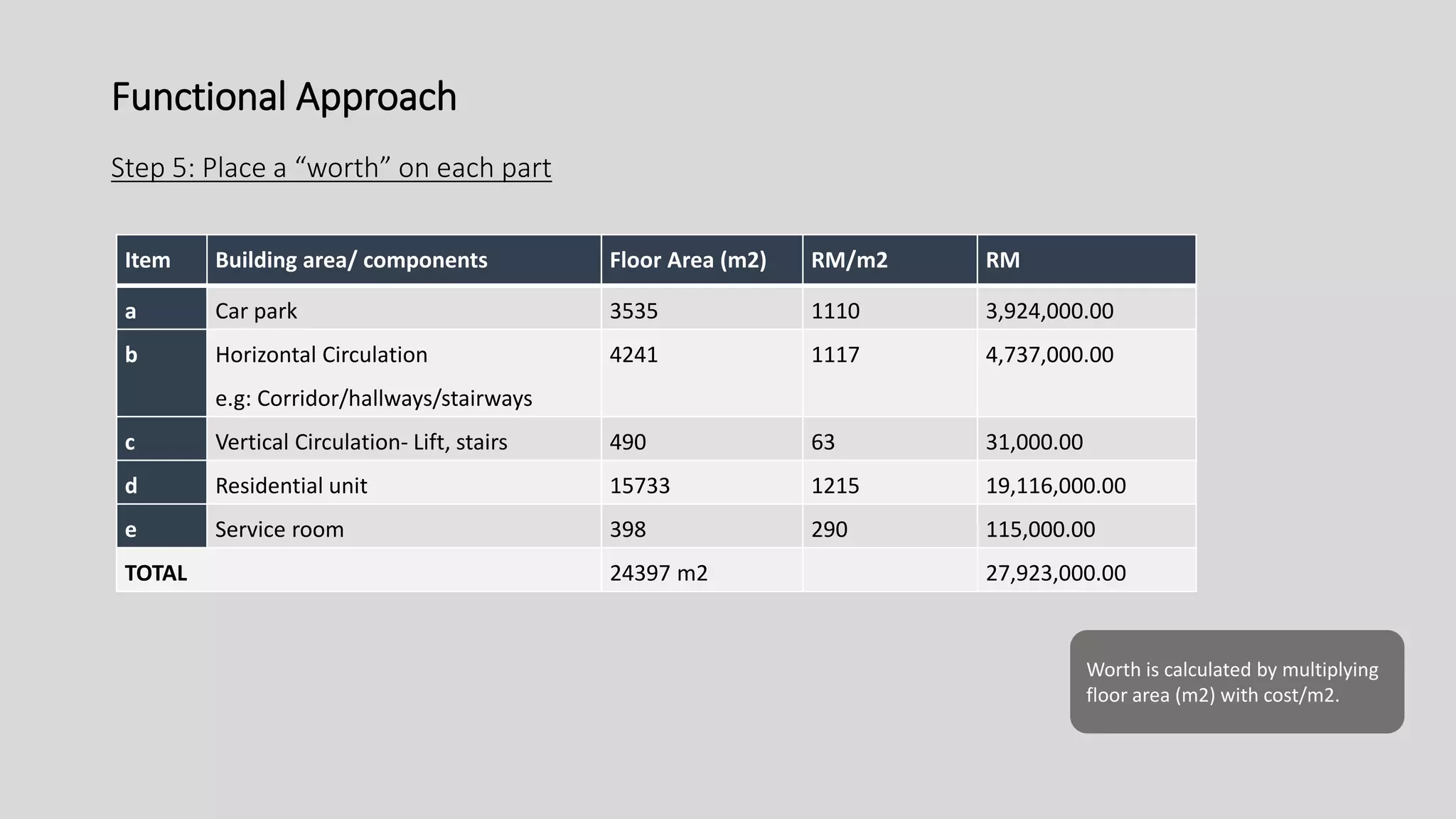
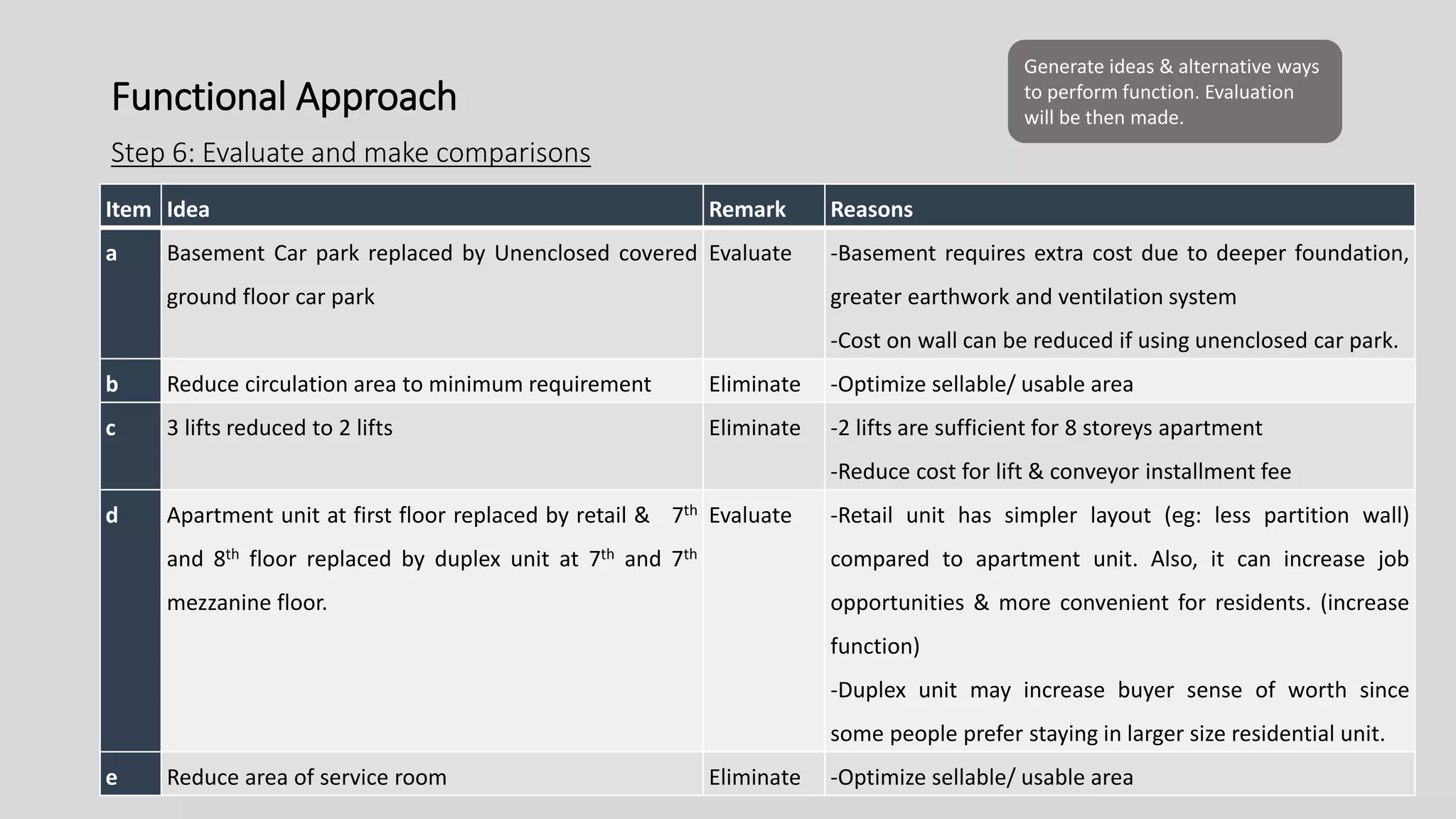
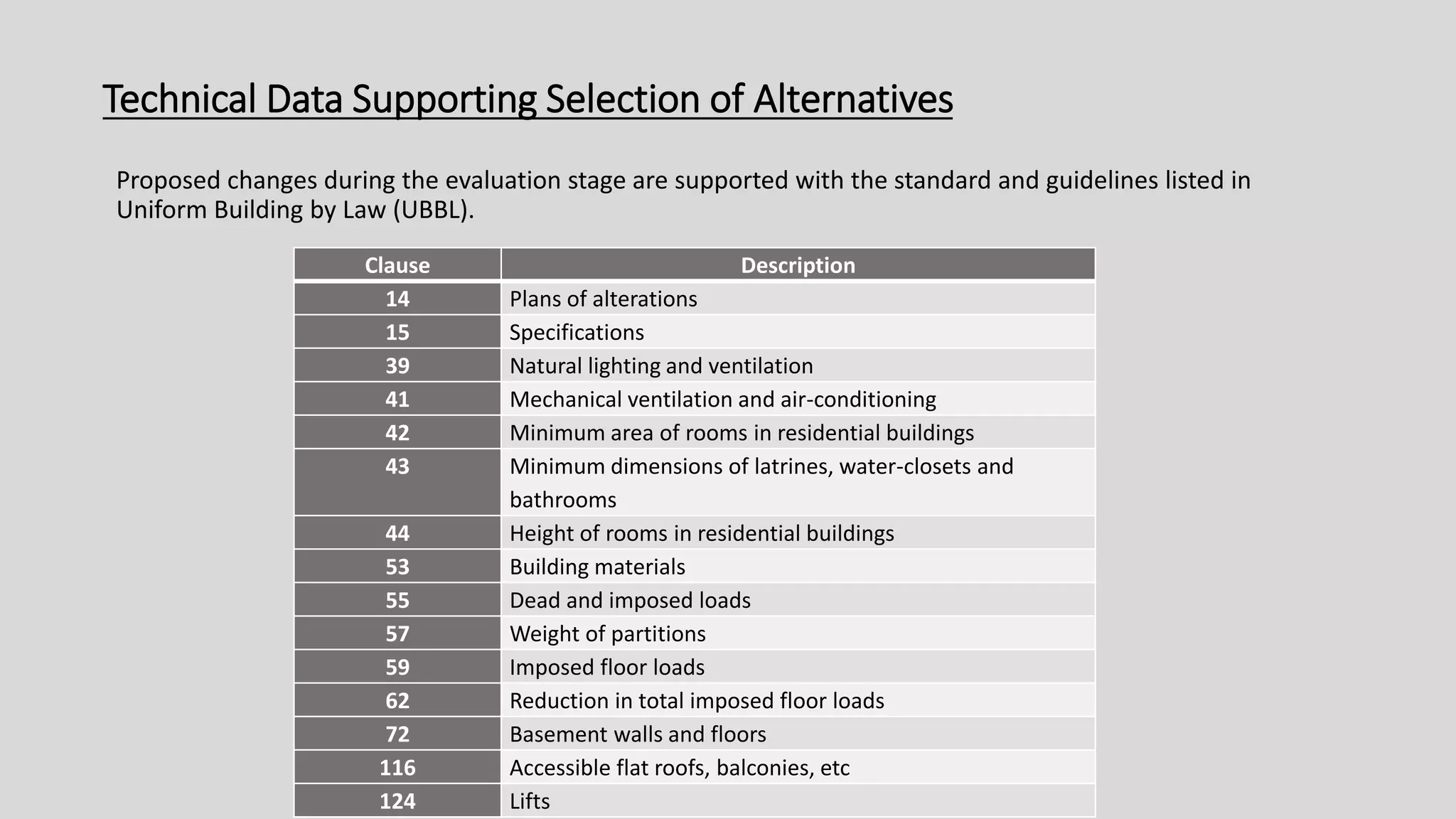
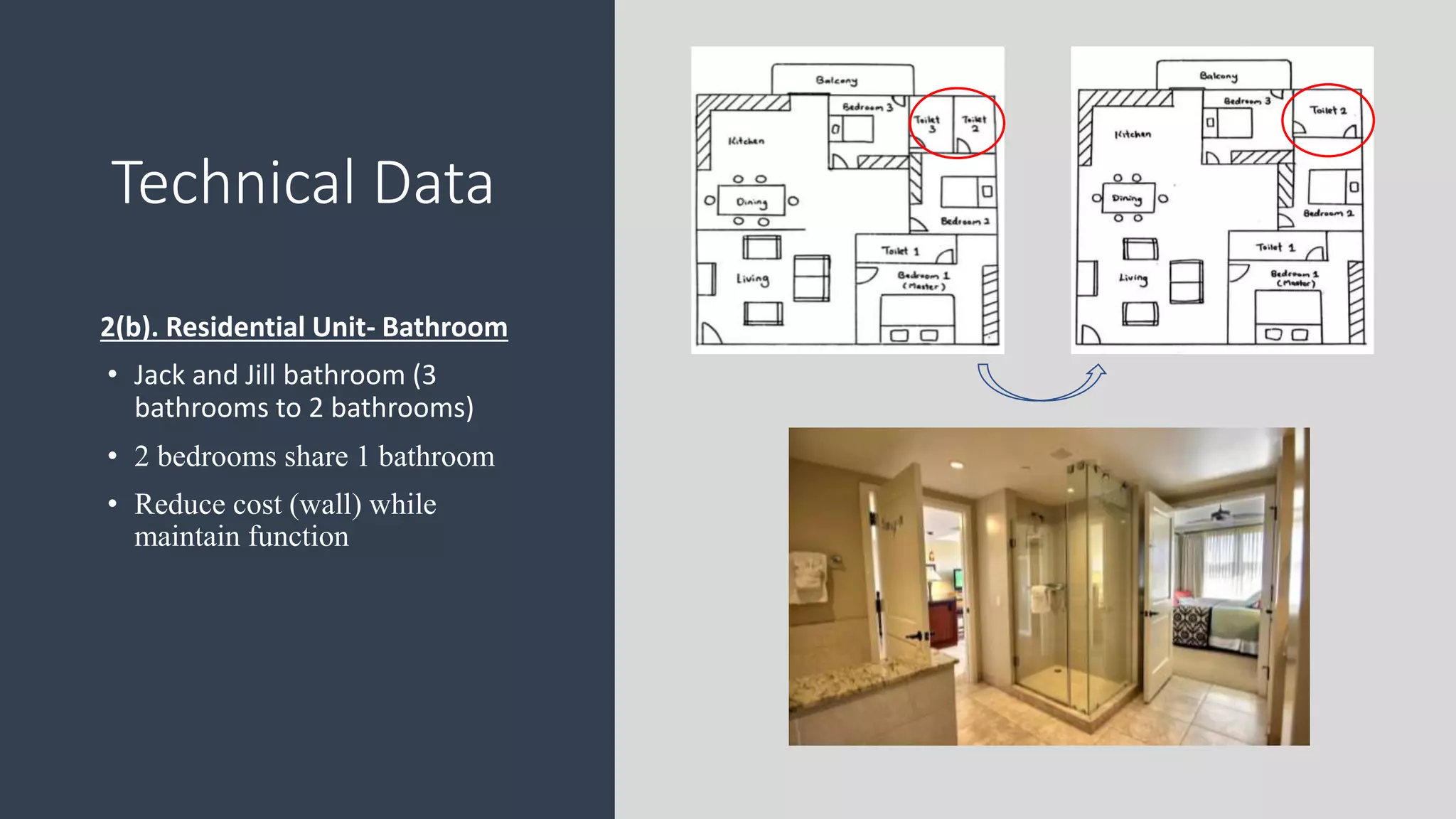
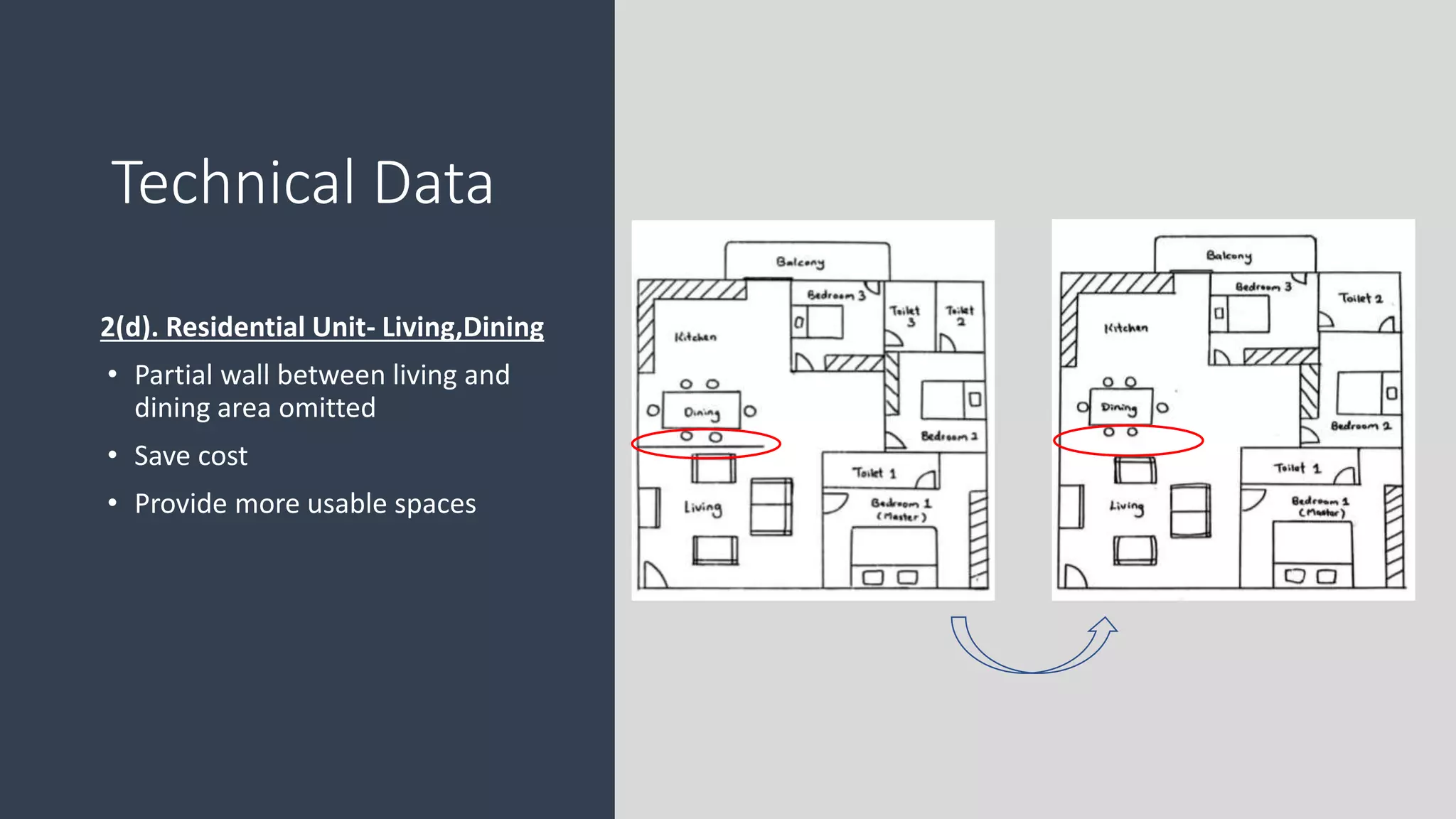
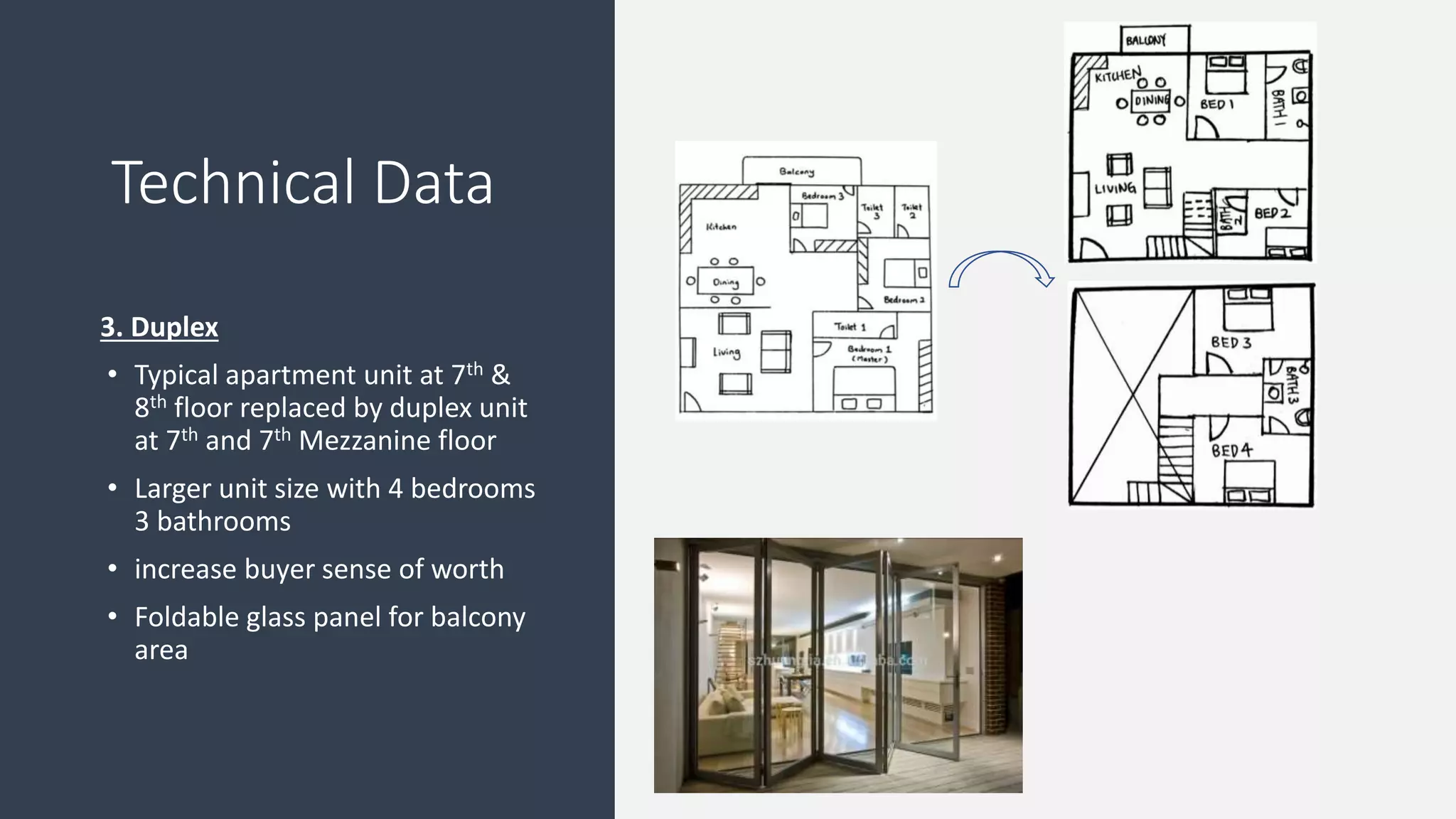
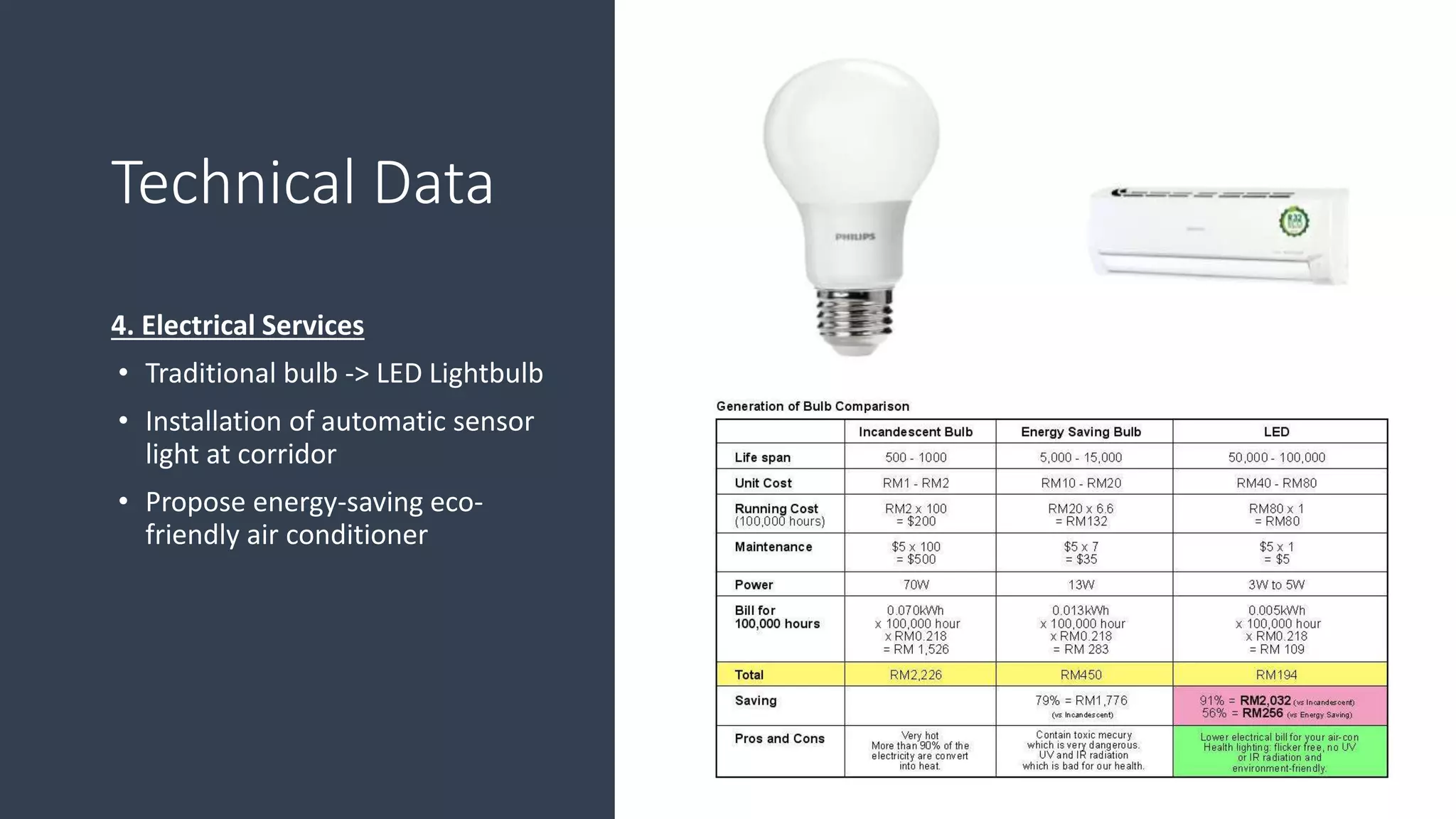
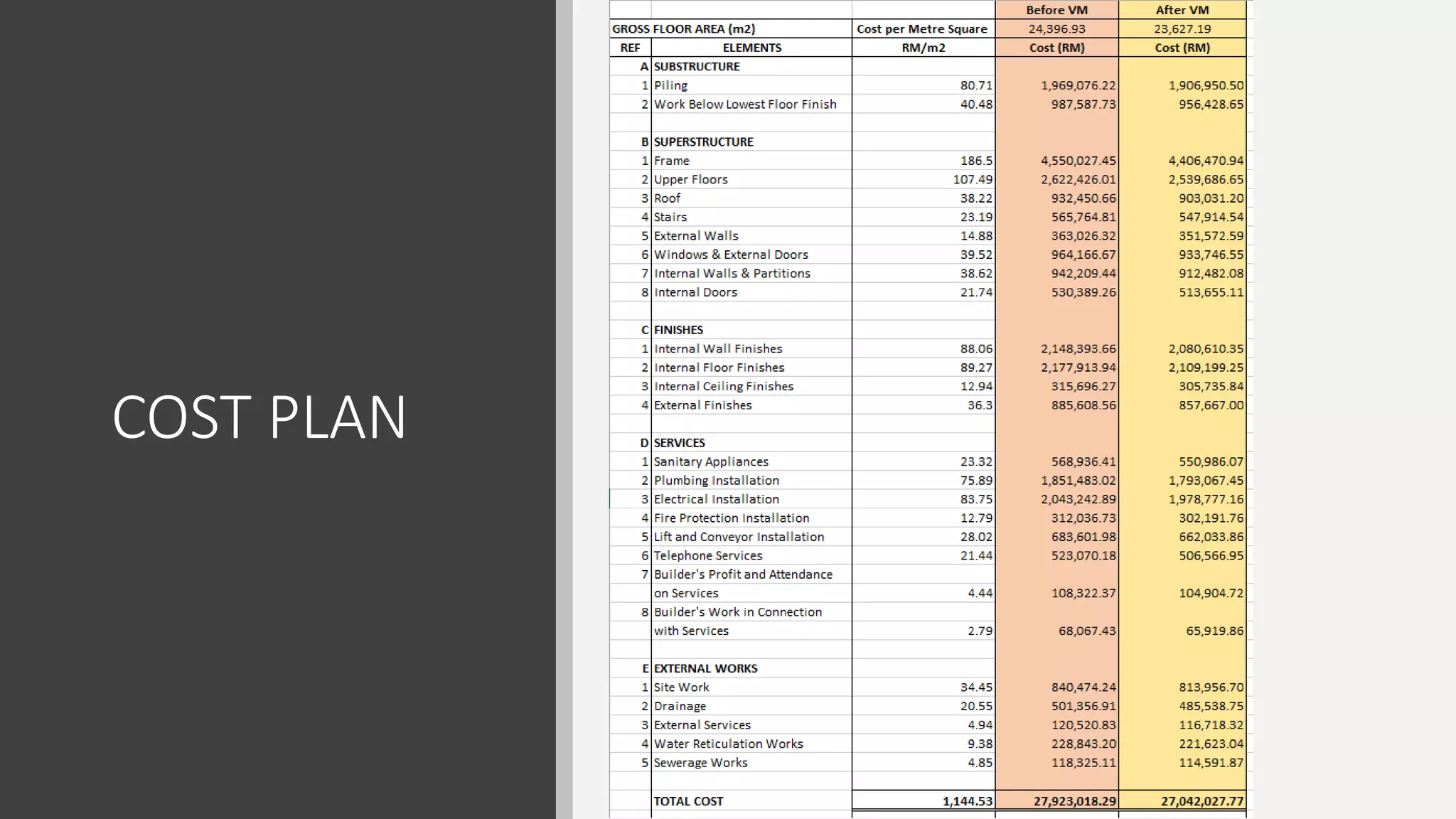
3) Value management tools that were used - priority setting matrix, smart value tree, functional approach - to identify unnecessary costs that could be removed from the project.
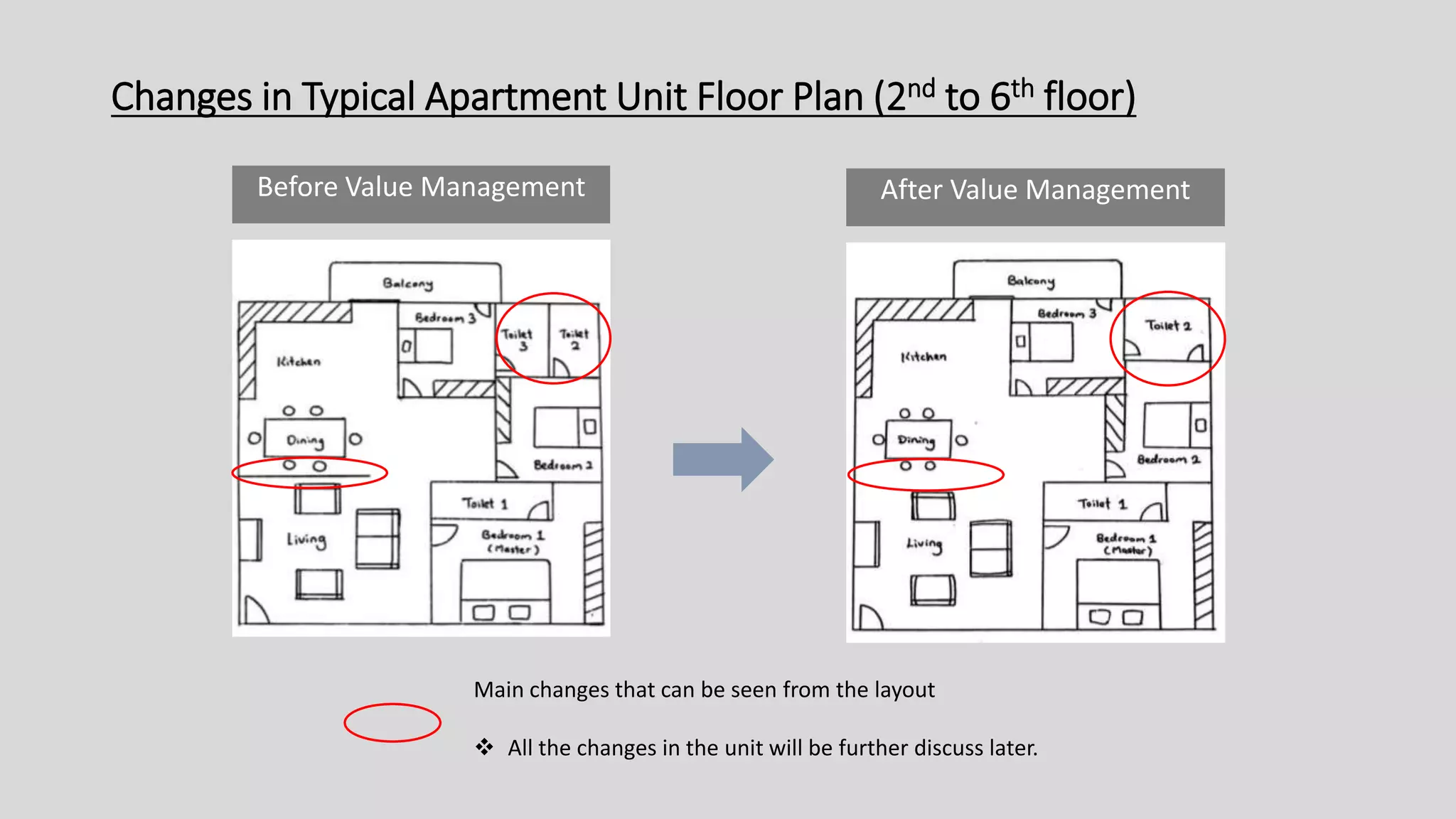
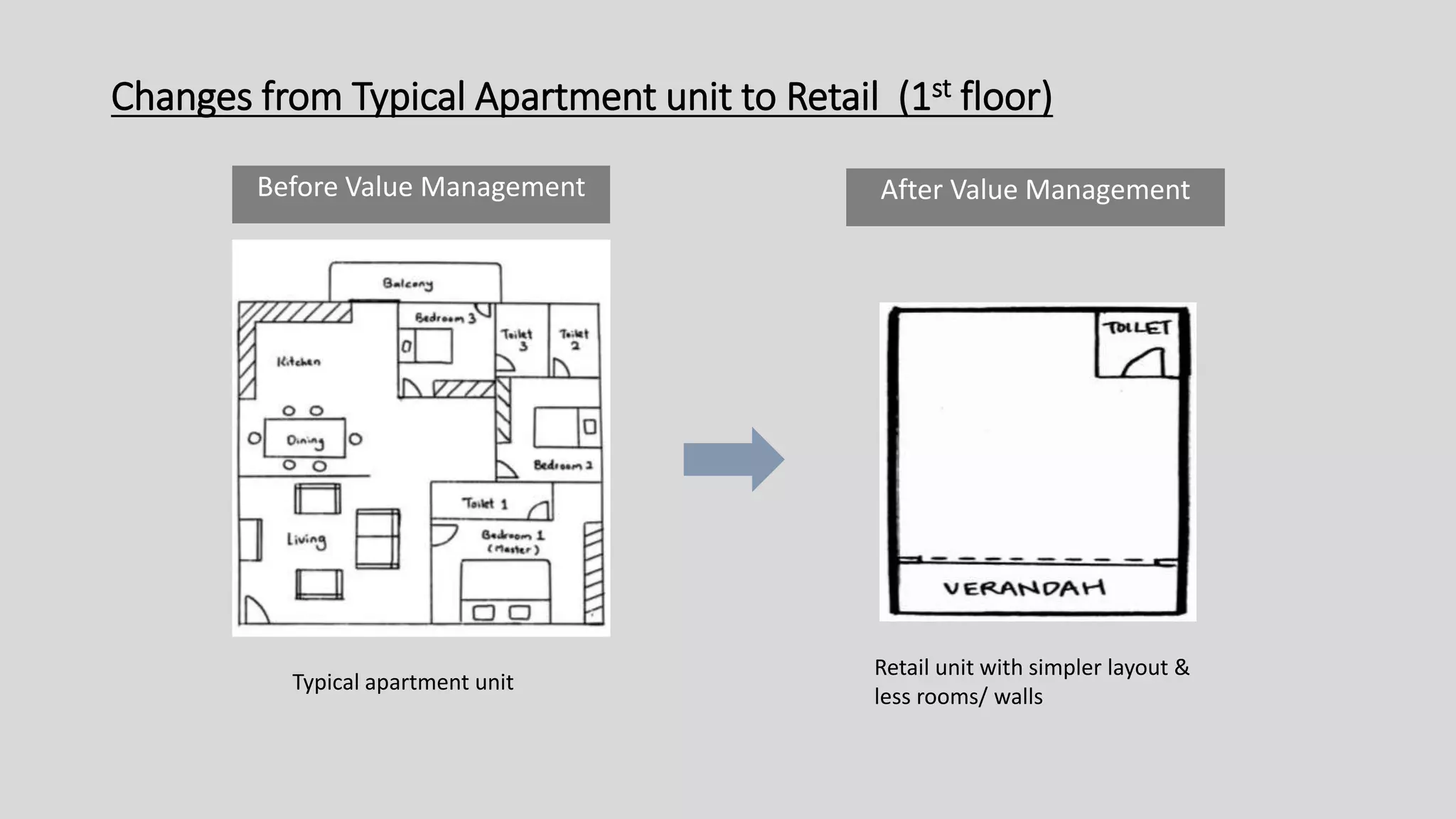
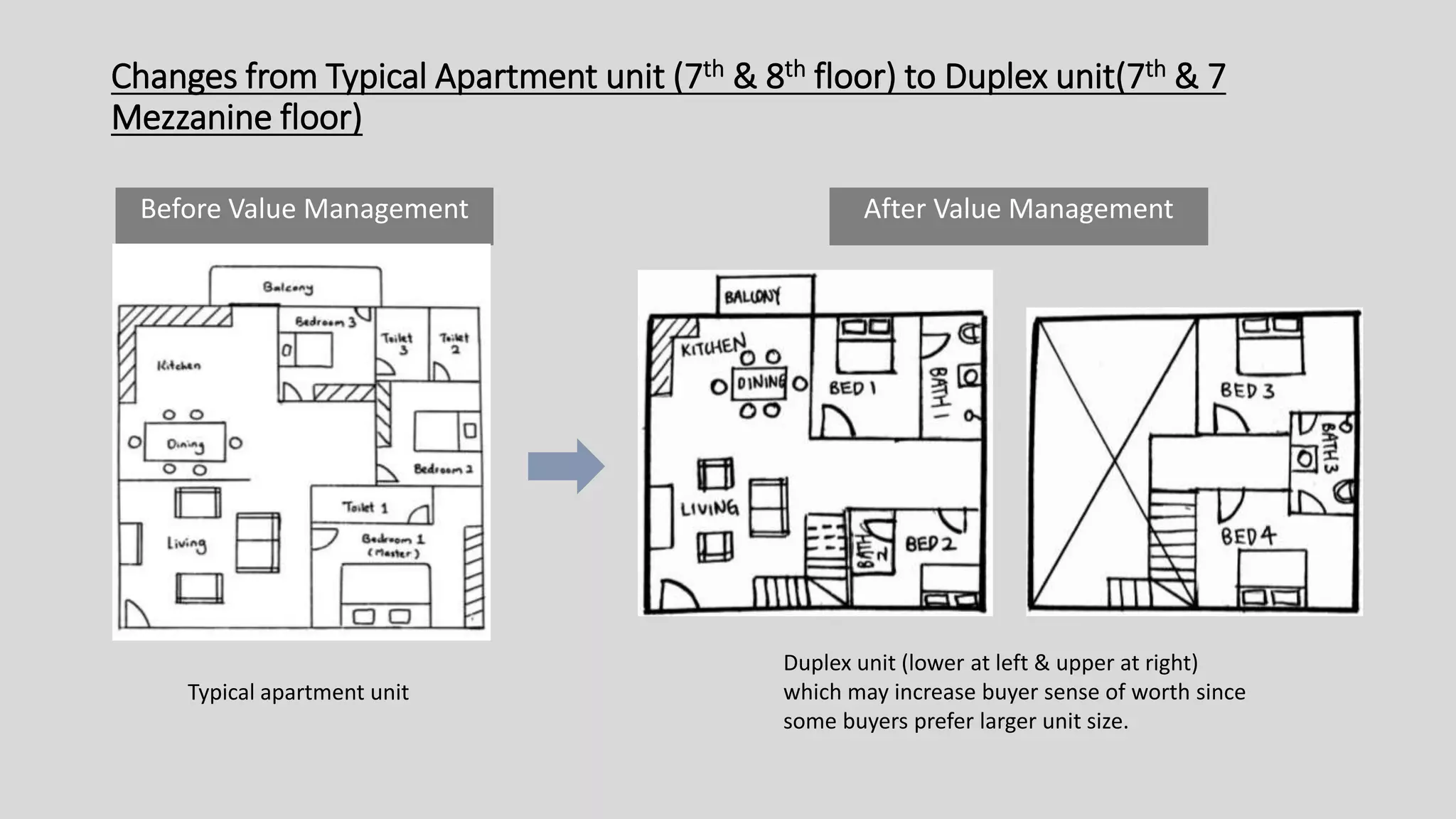
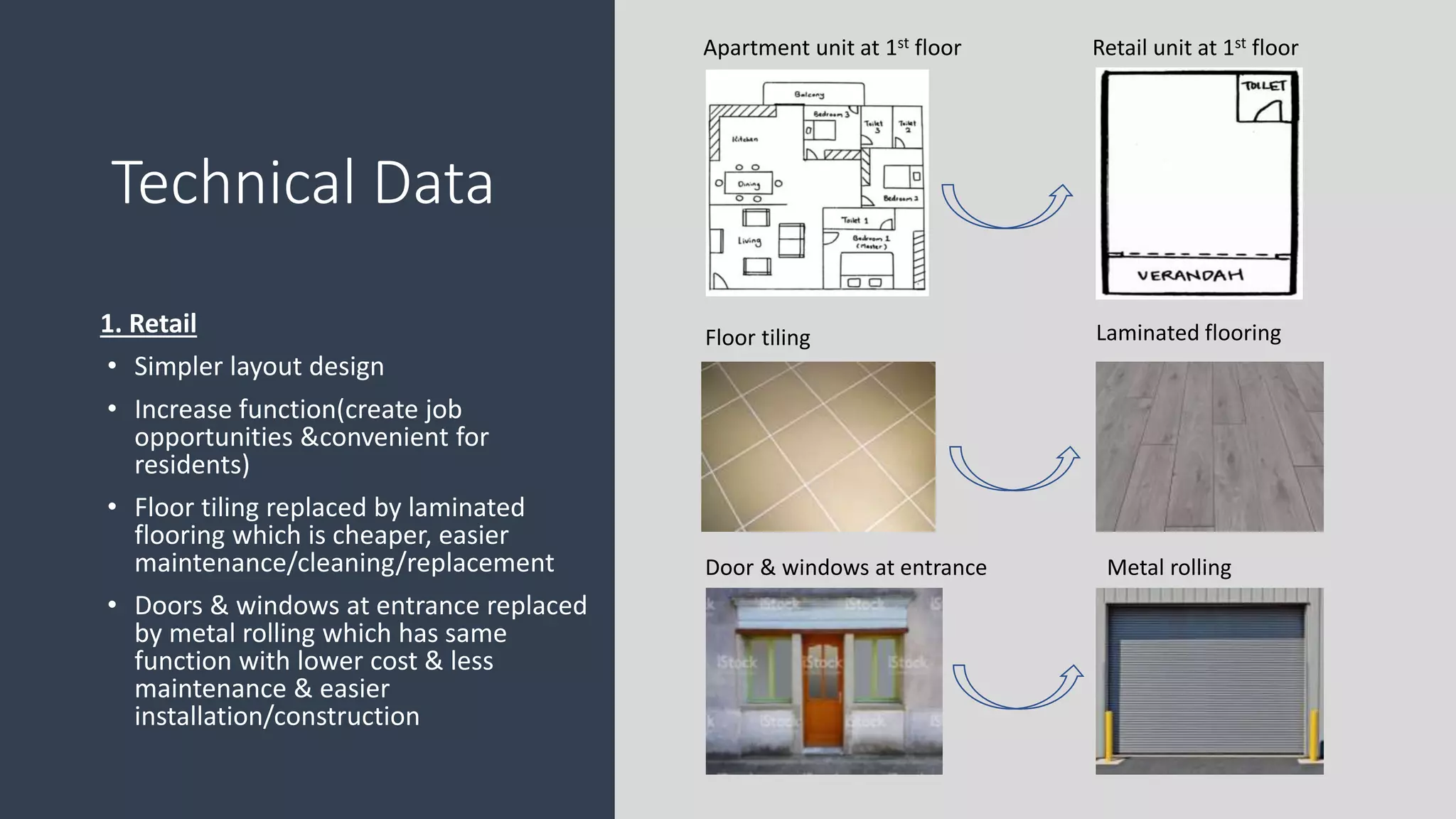
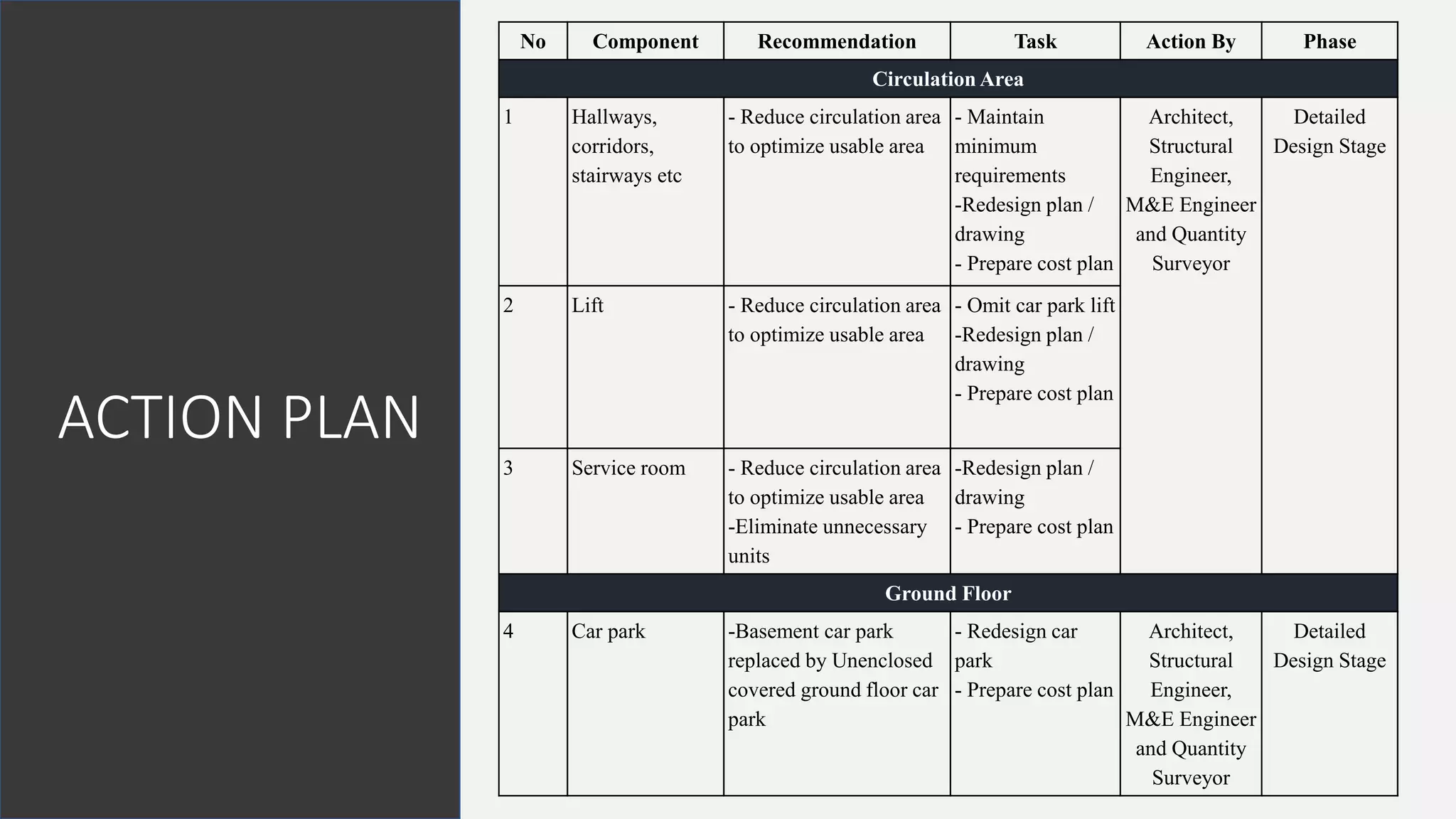
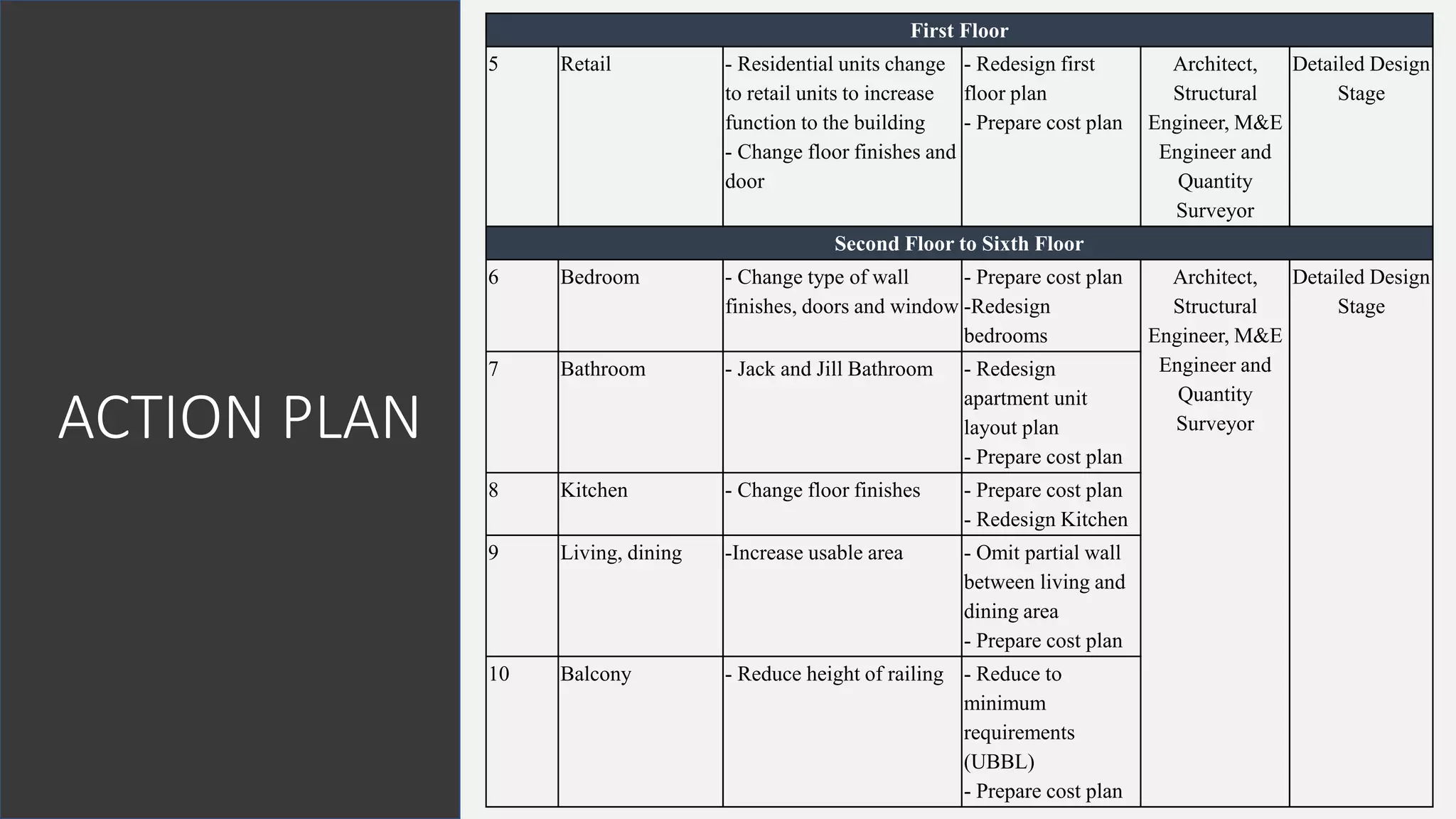
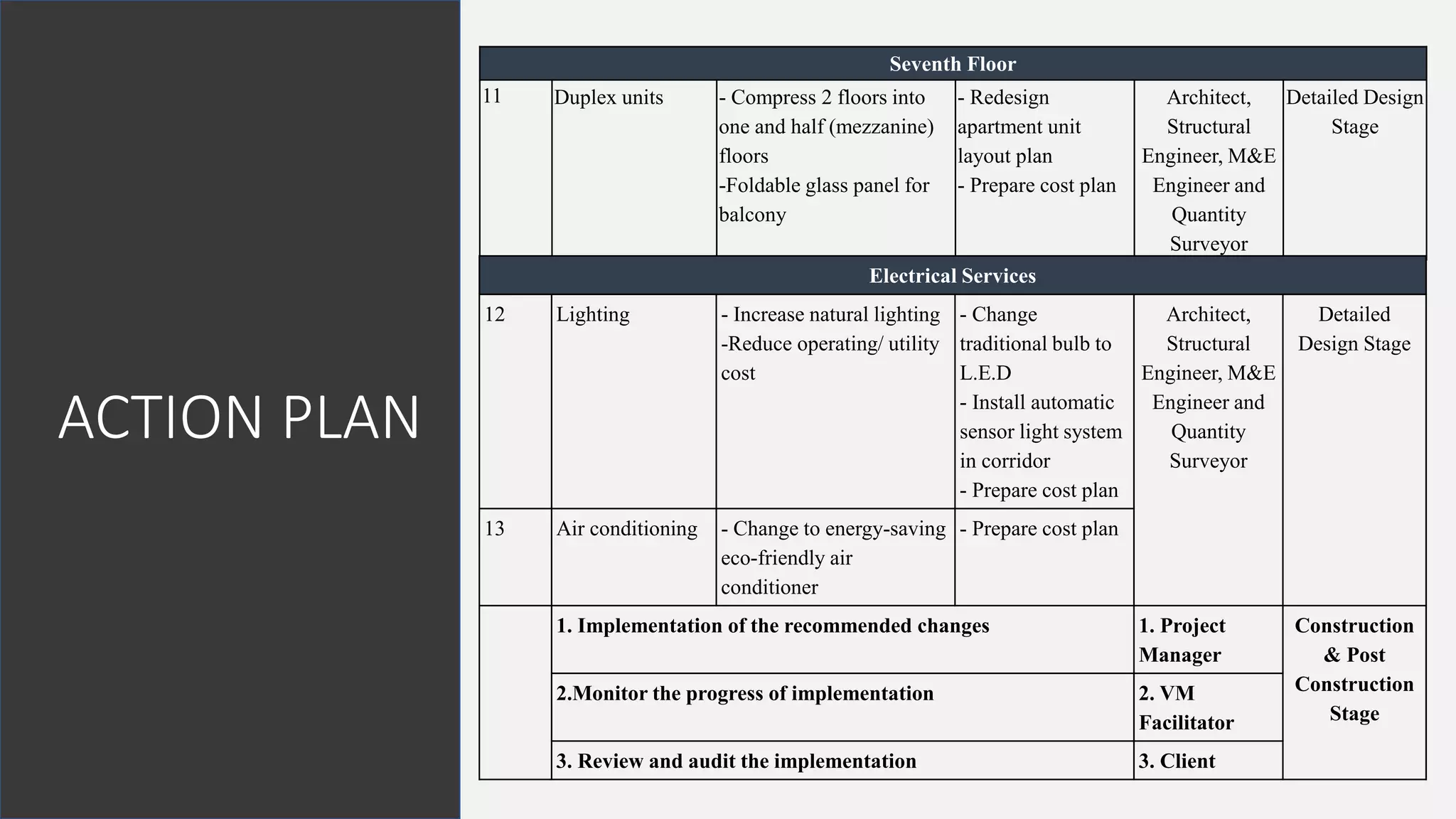
The value management process identified potential changes to the design like replacing the basement car park with ground floor car park, reducing circulation areas, changing some units to retail on the first