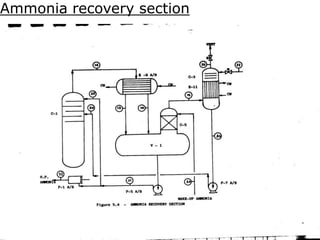
The document outlines the urea production process at NFL Vijaipur, detailing the two lines of urea plants commissioned in 1987 and 1997, and the unique Snamprogetti technology implemented. It describes the main operations involved in the urea synthesis, purification, and prilling stages, emphasizing high pressure synthesis loops and medium to low pressure recovery sections. The process encompasses CO2 compression, ammonia distribution, and urea concentration through vacuum evaporation, culminating in the production of solid urea prills for storage.