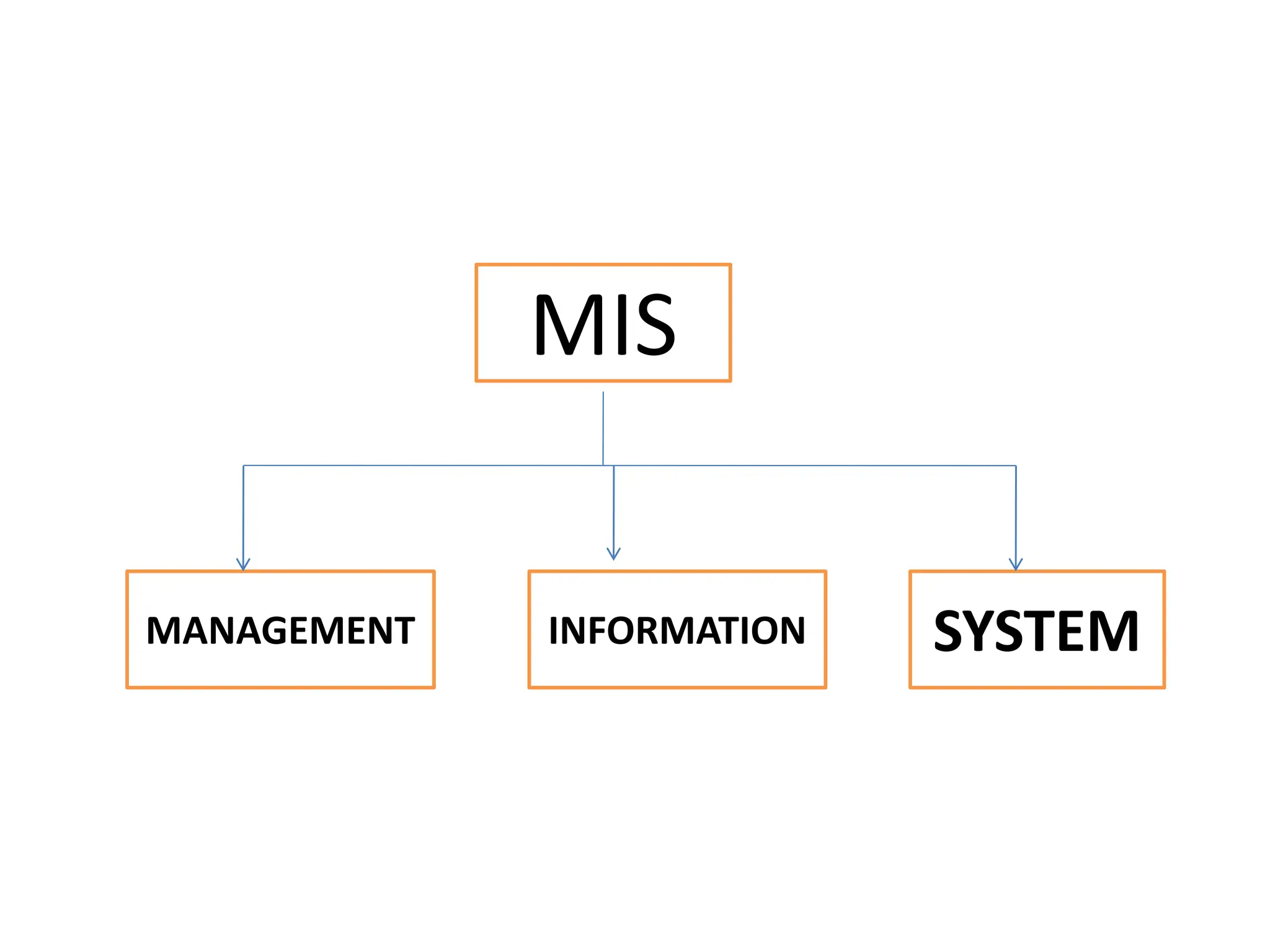
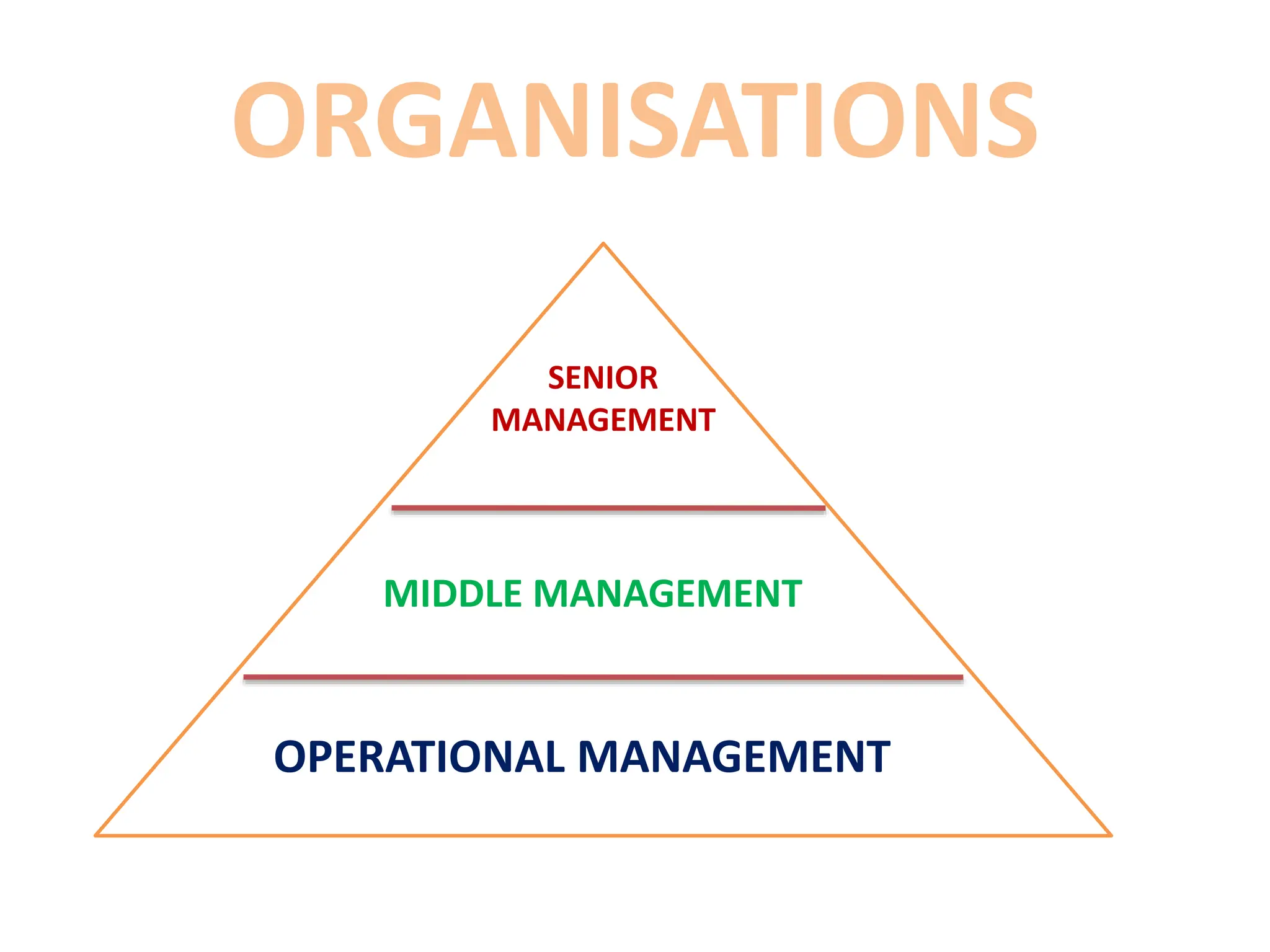
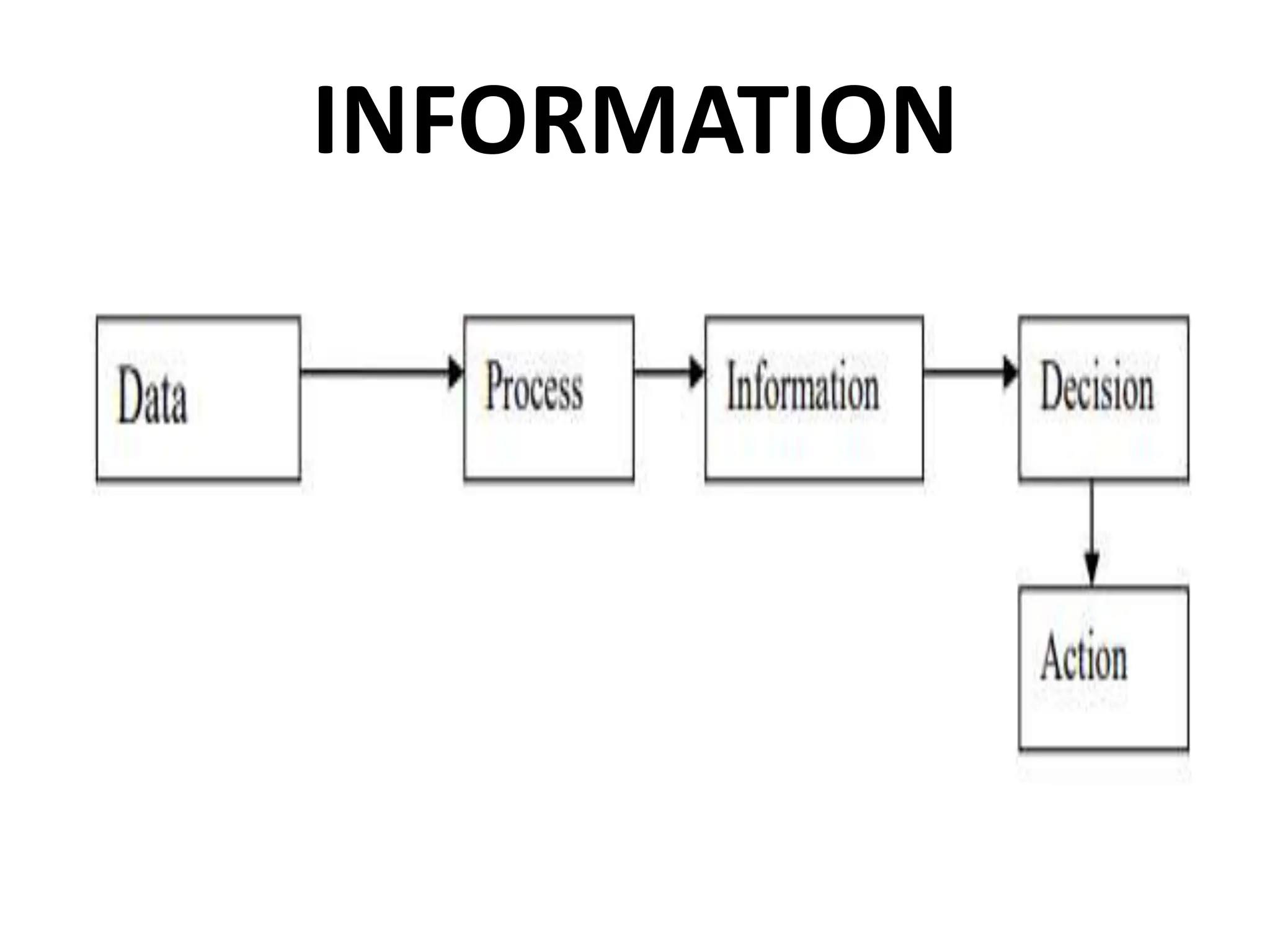
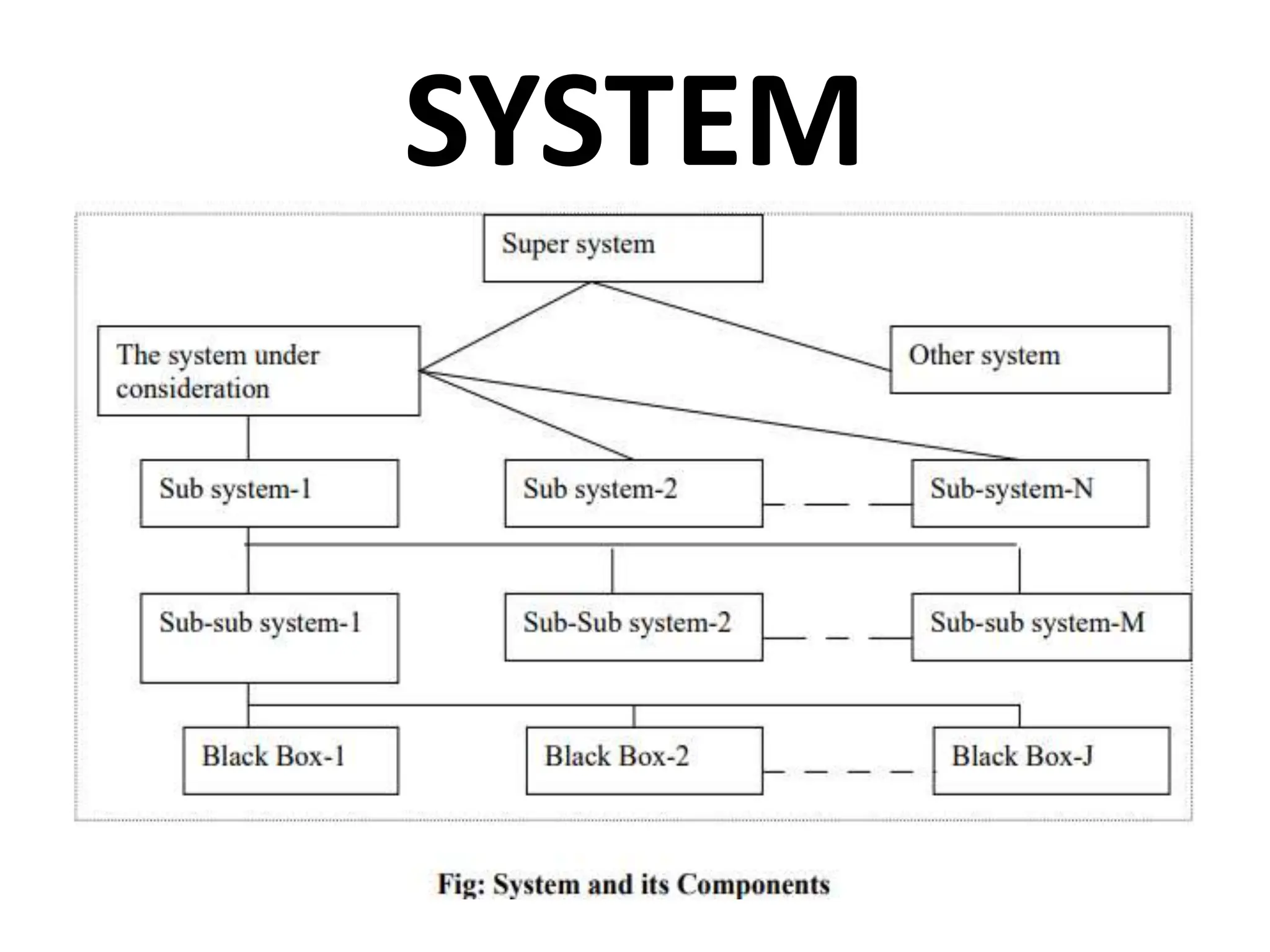
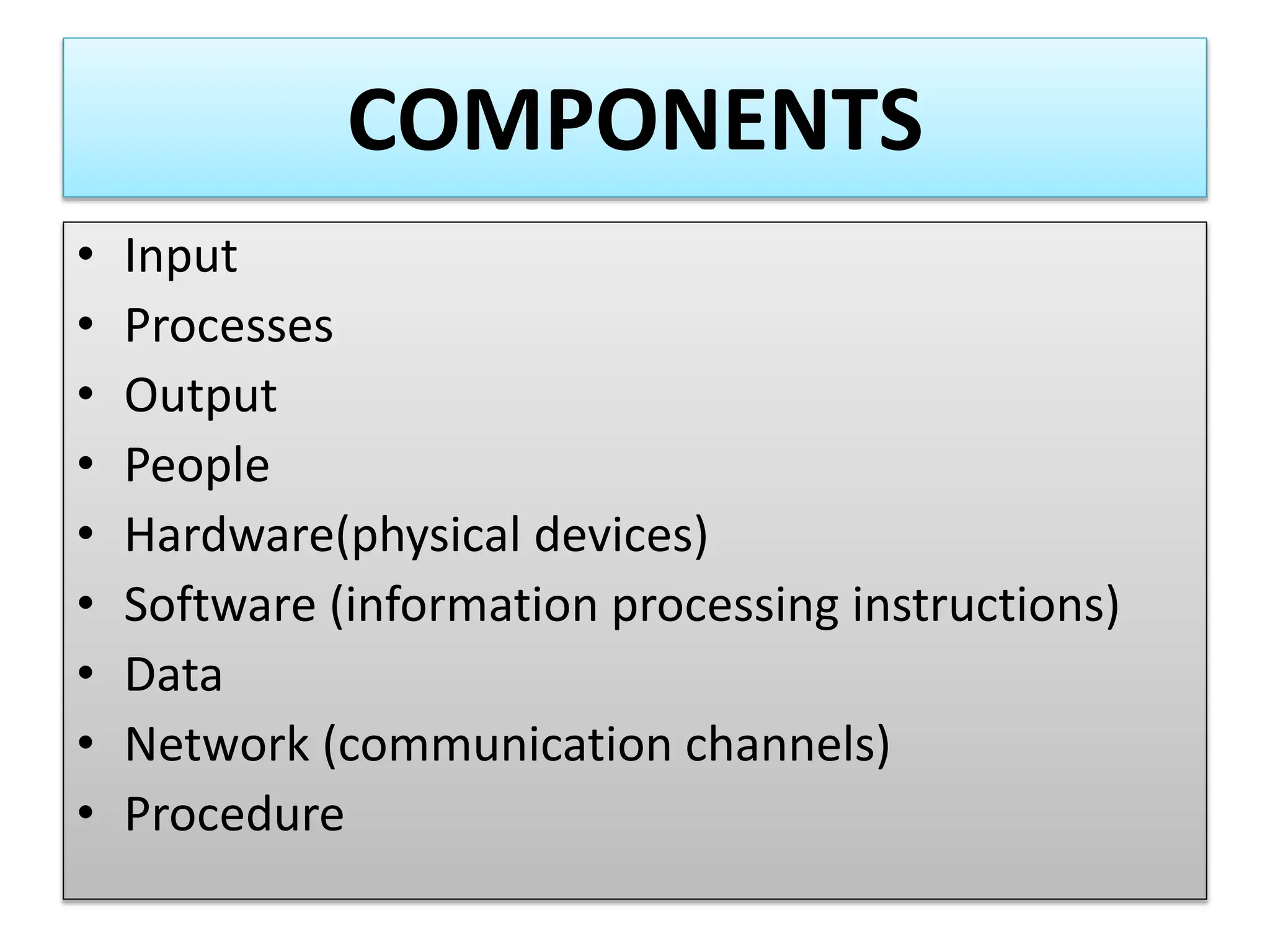
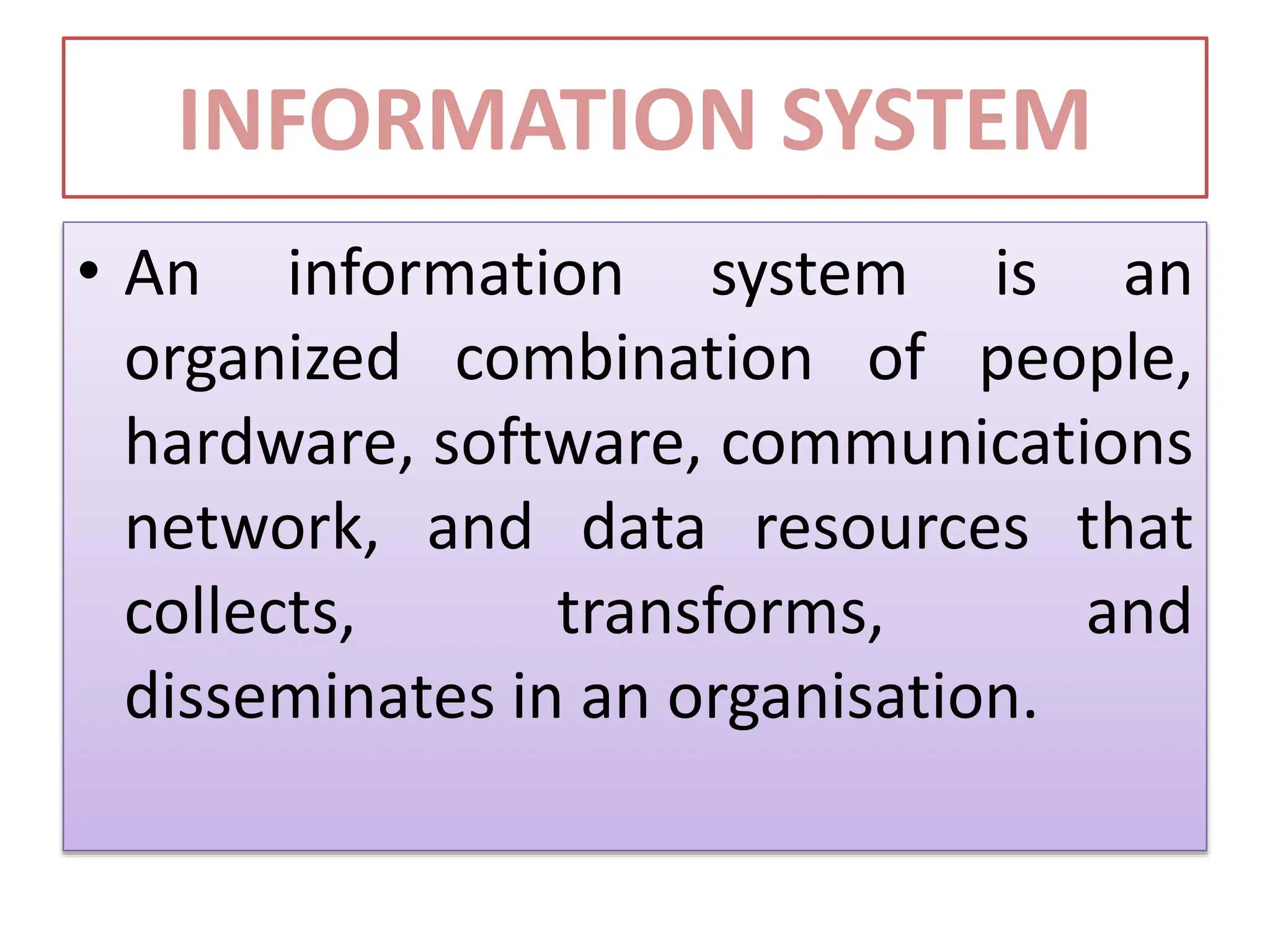
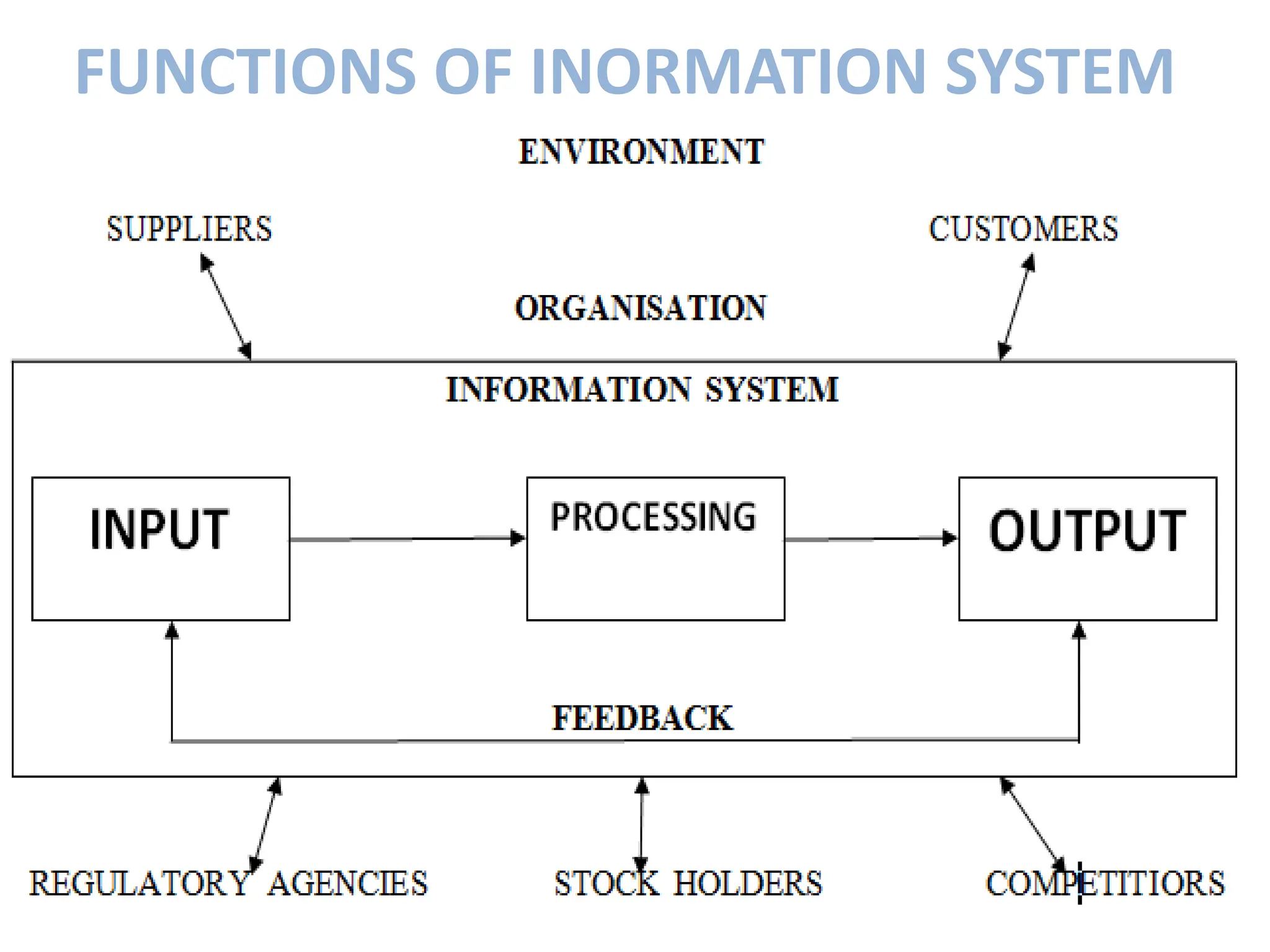
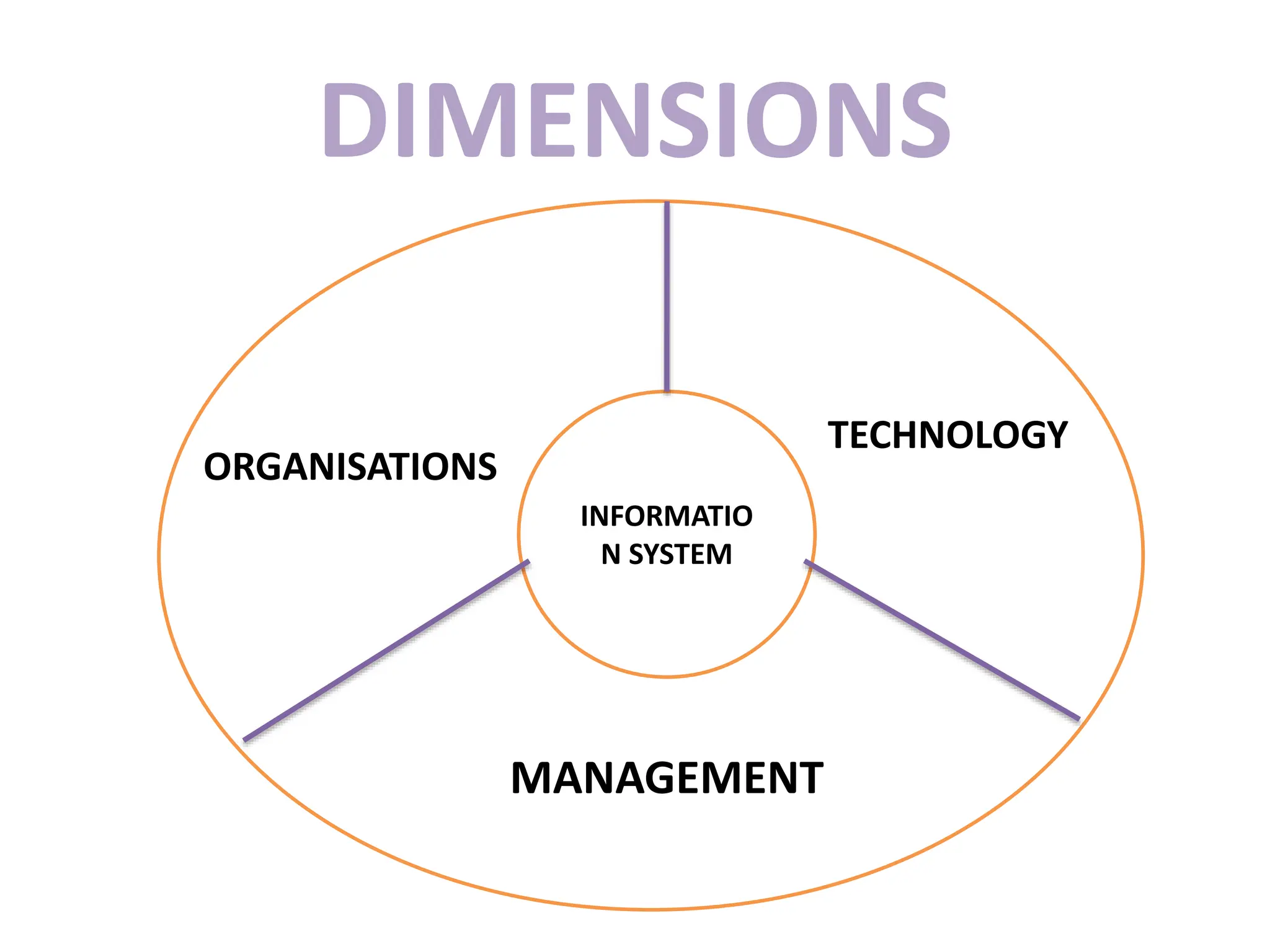
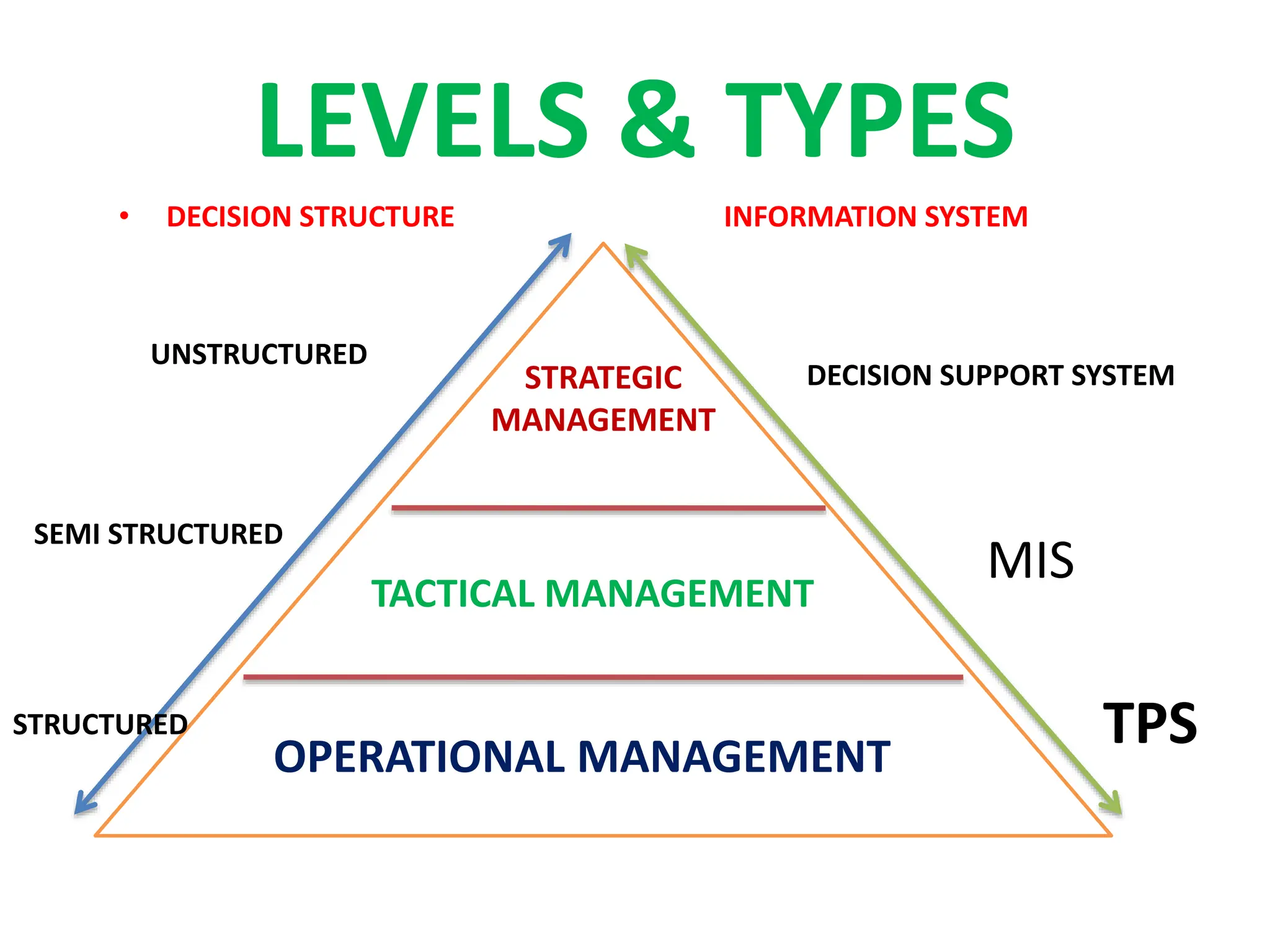
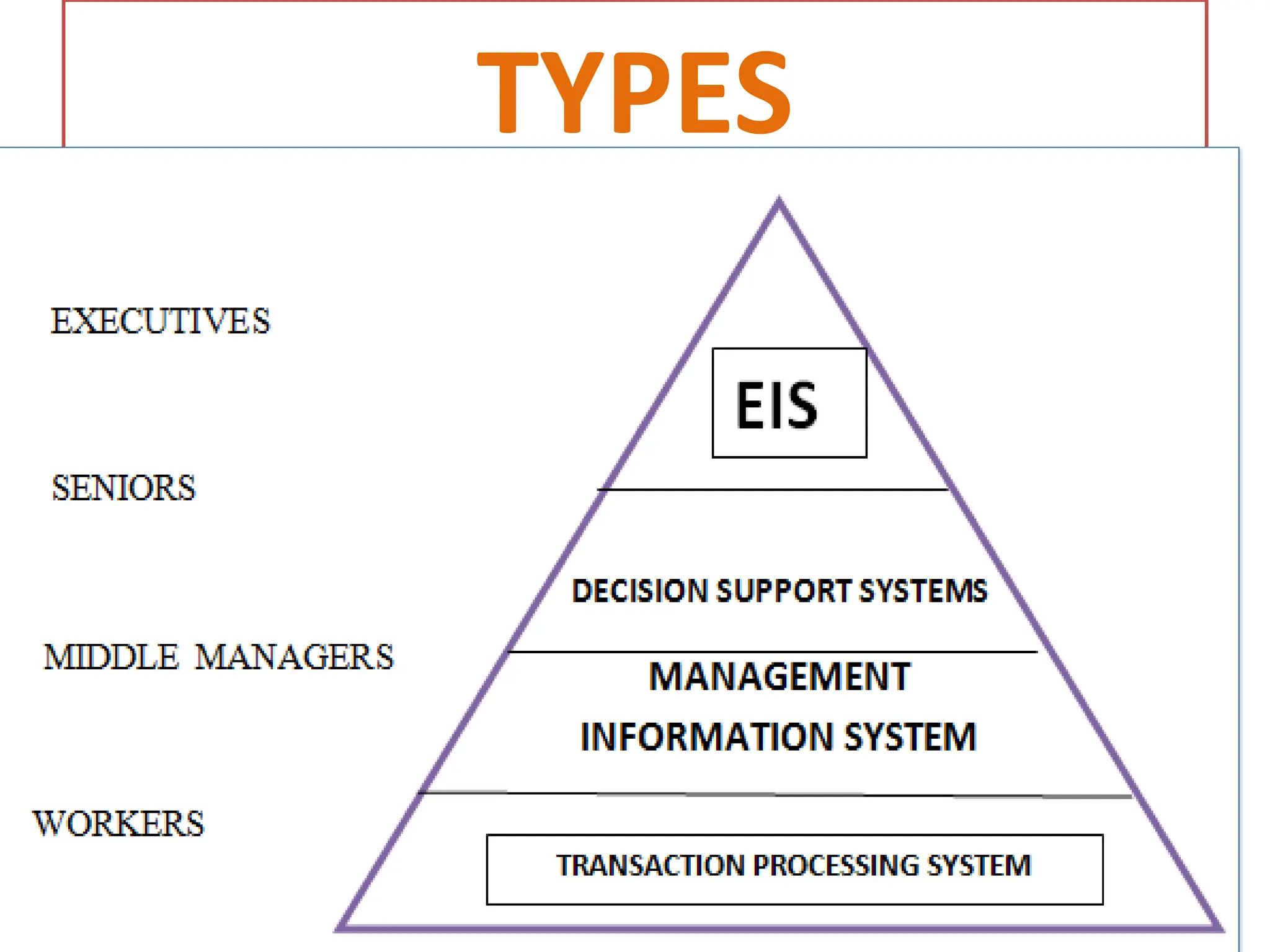
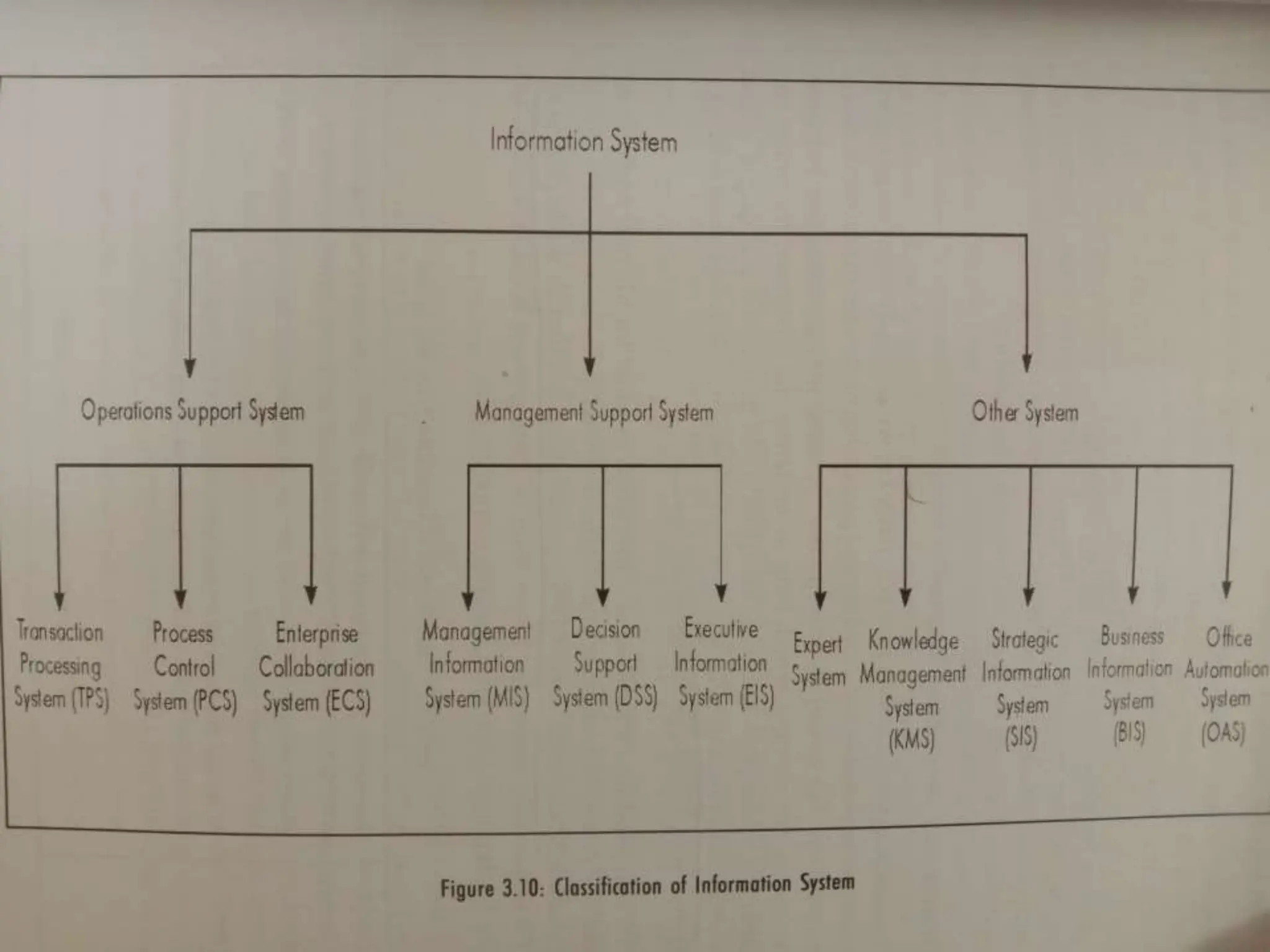
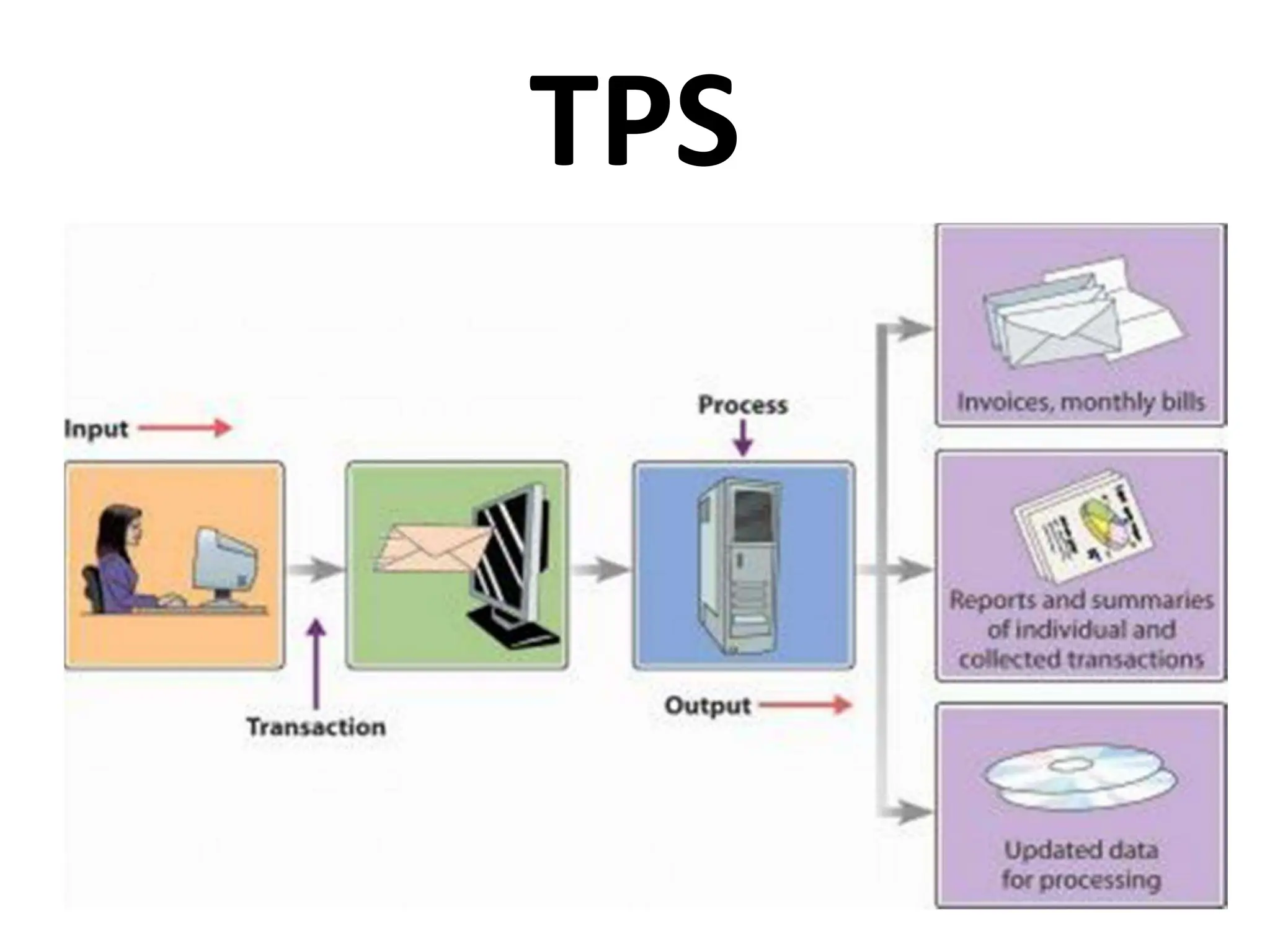
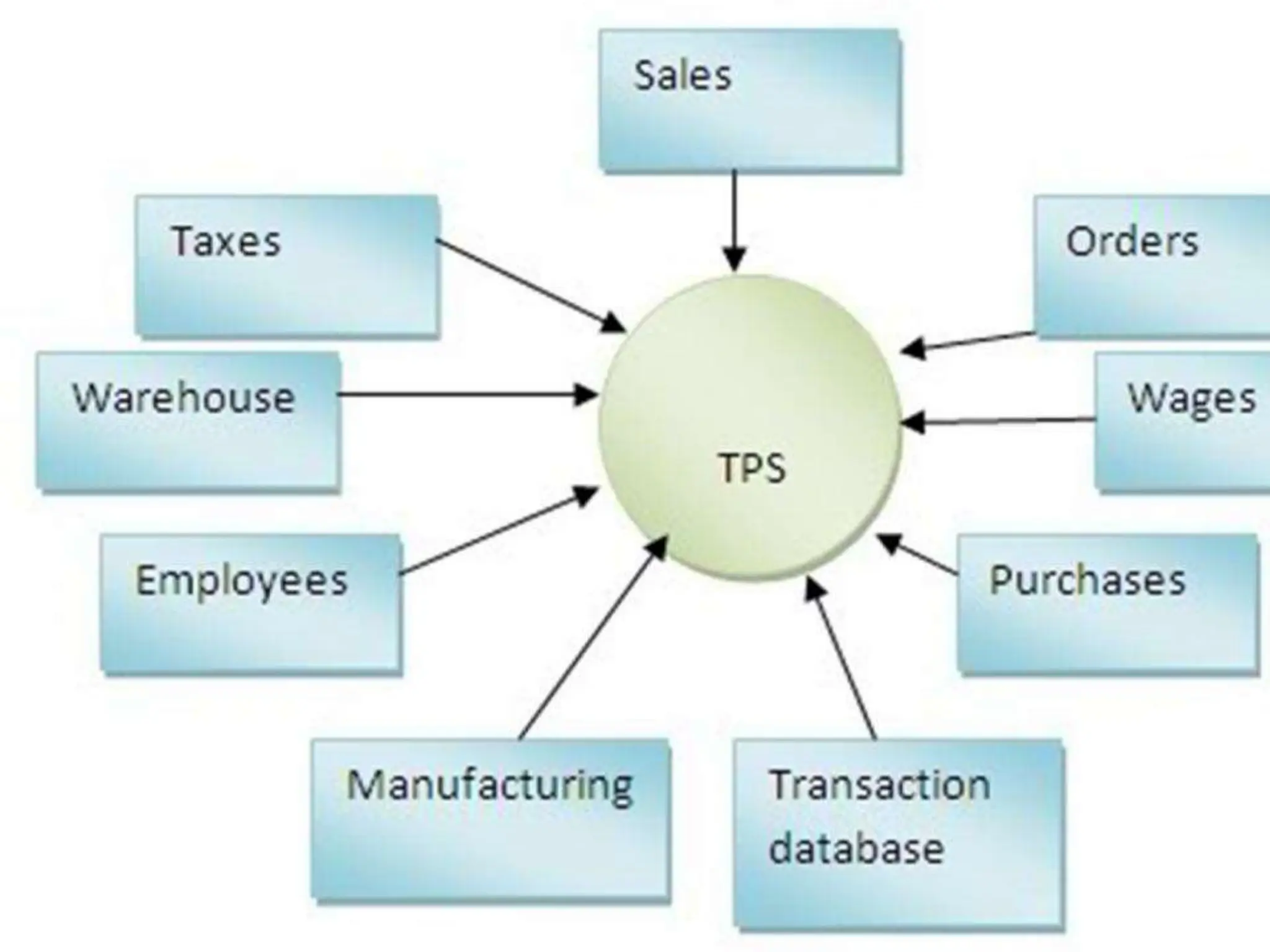
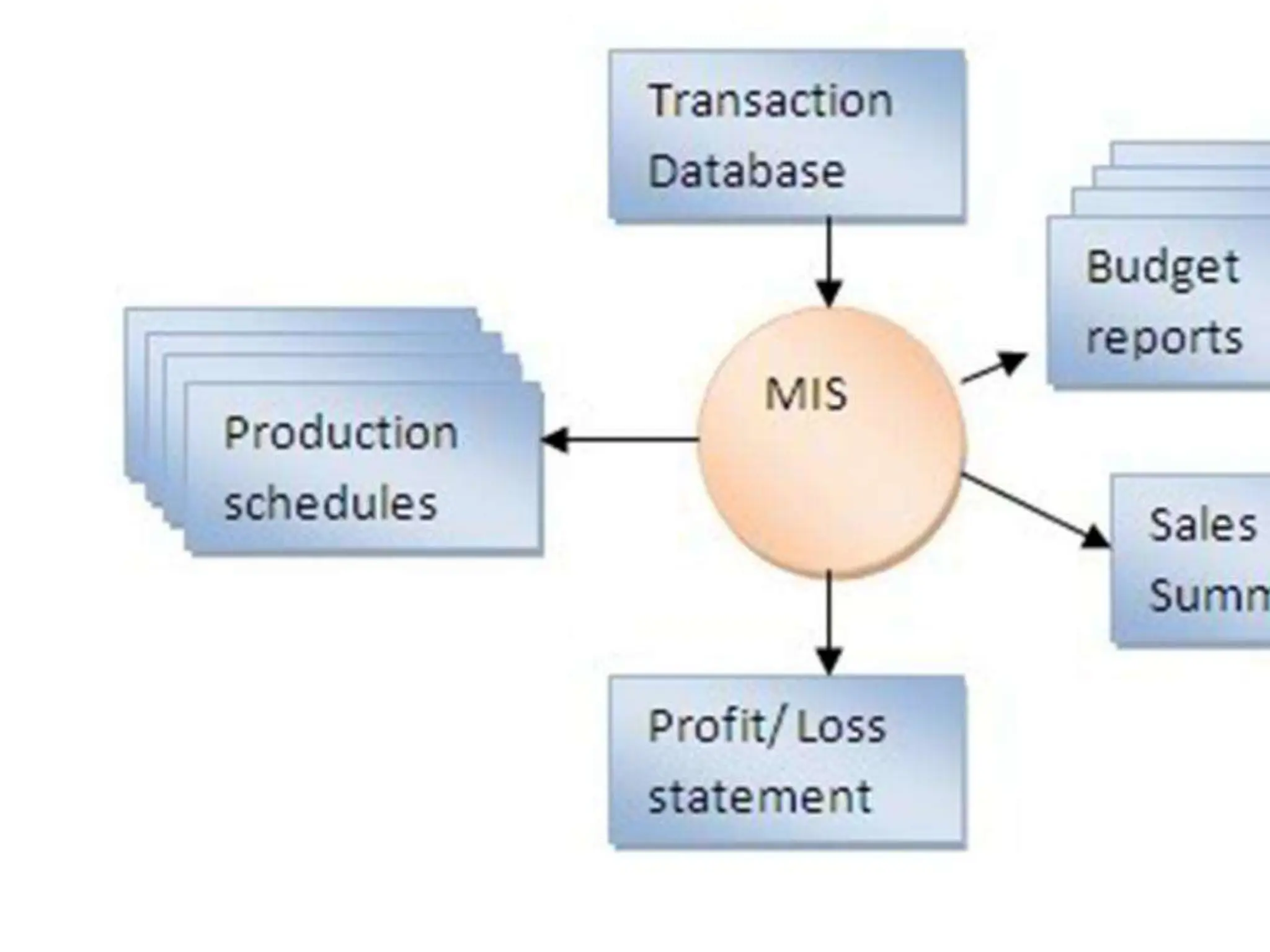
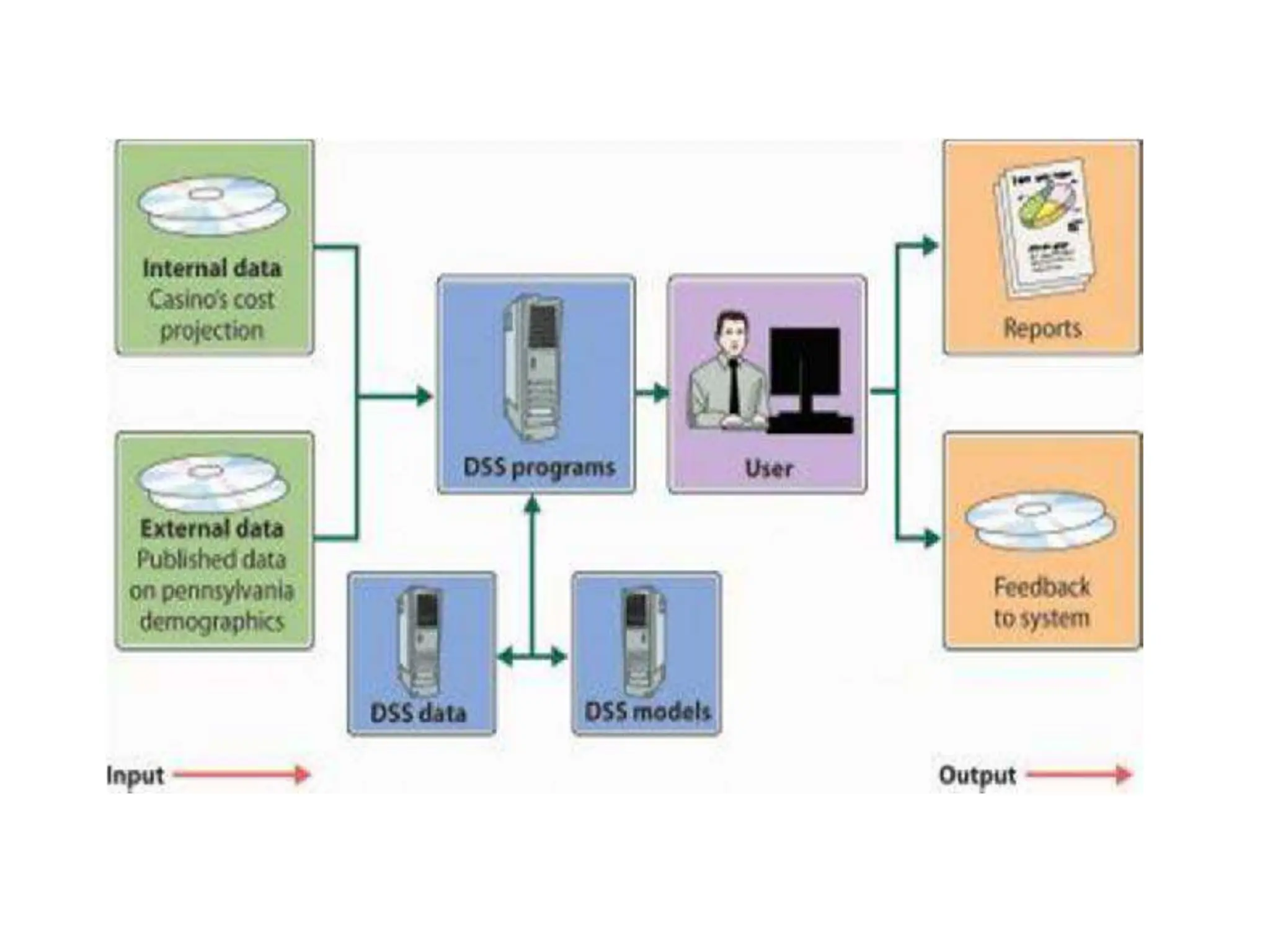
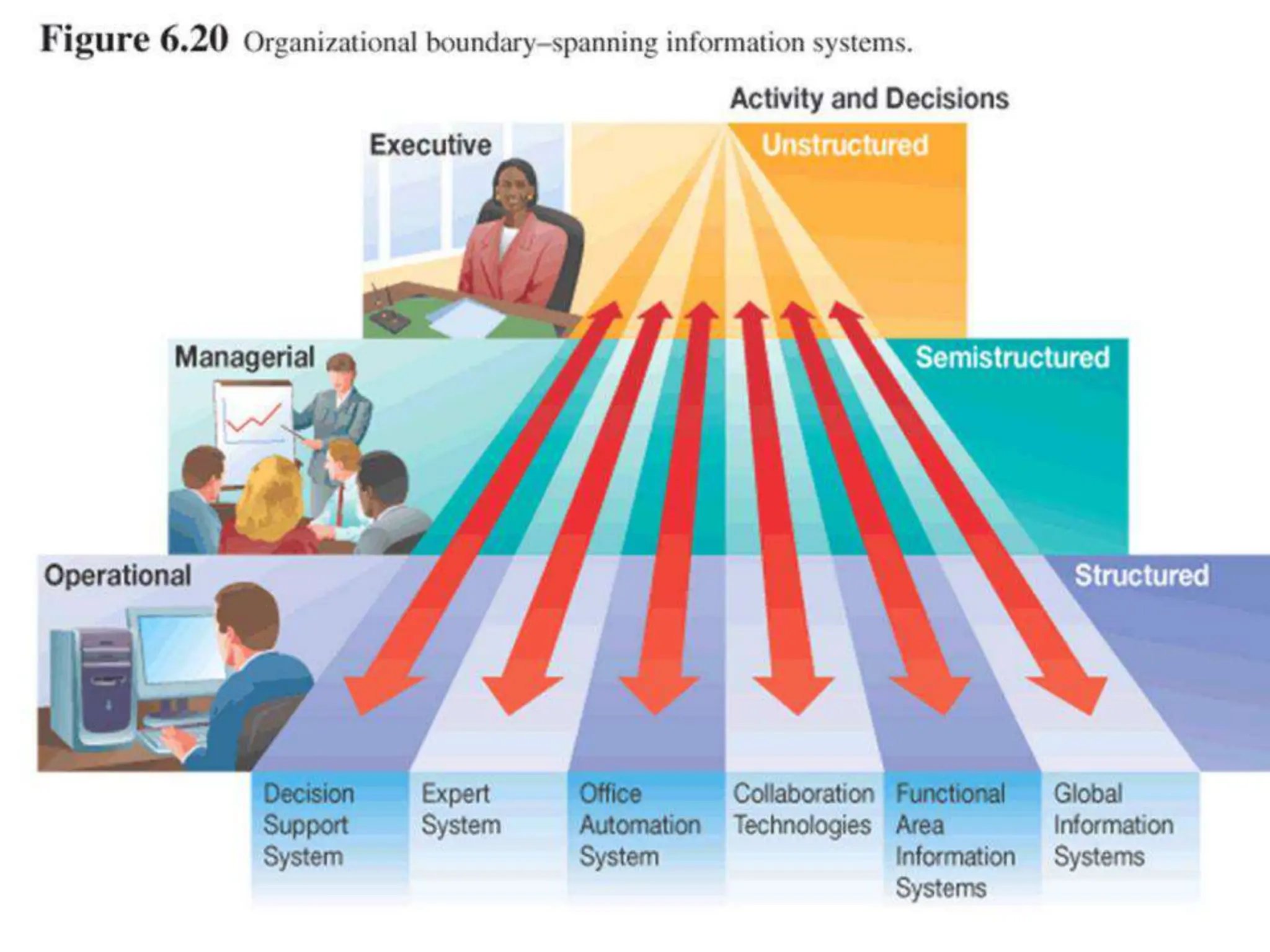
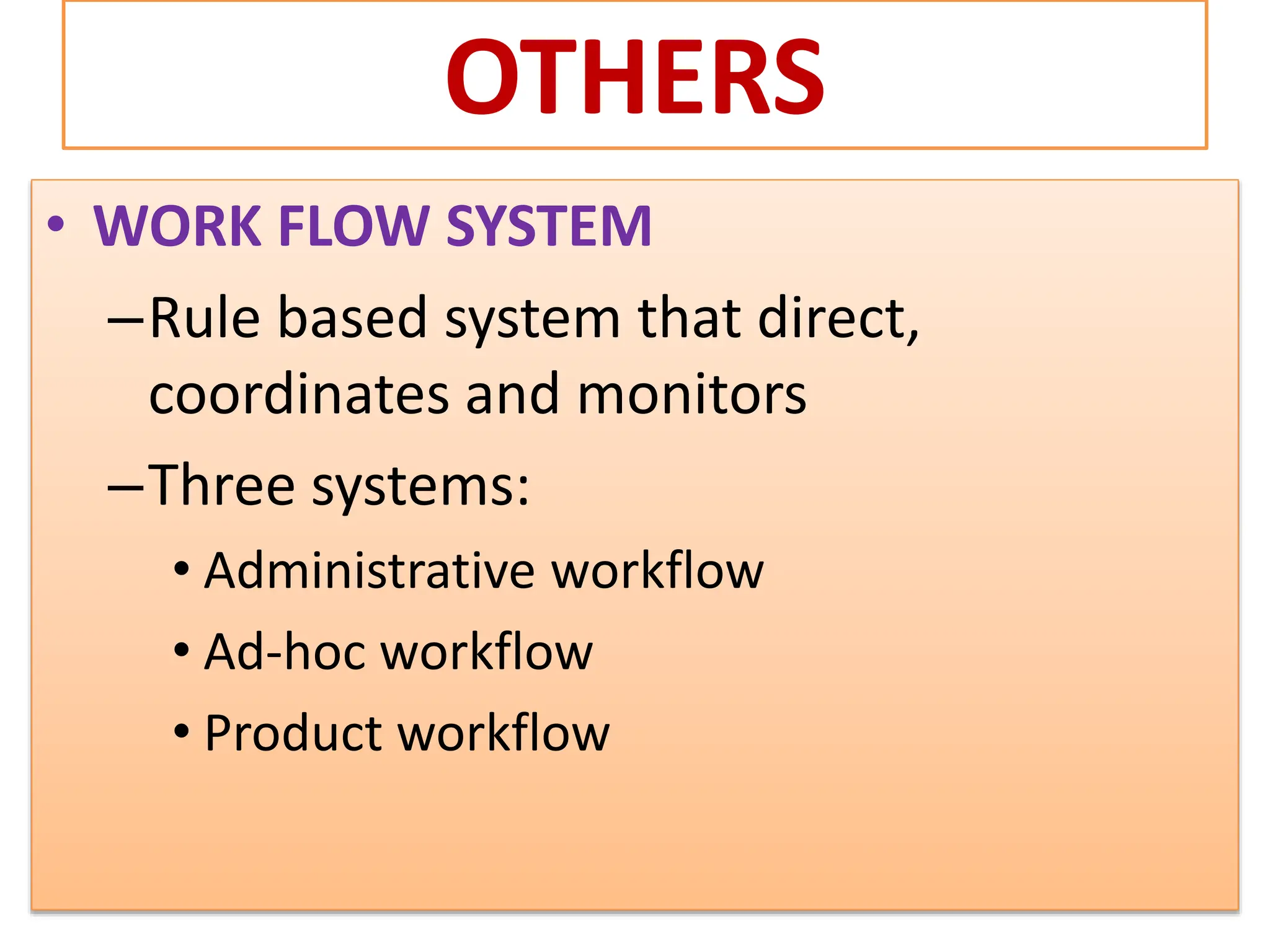
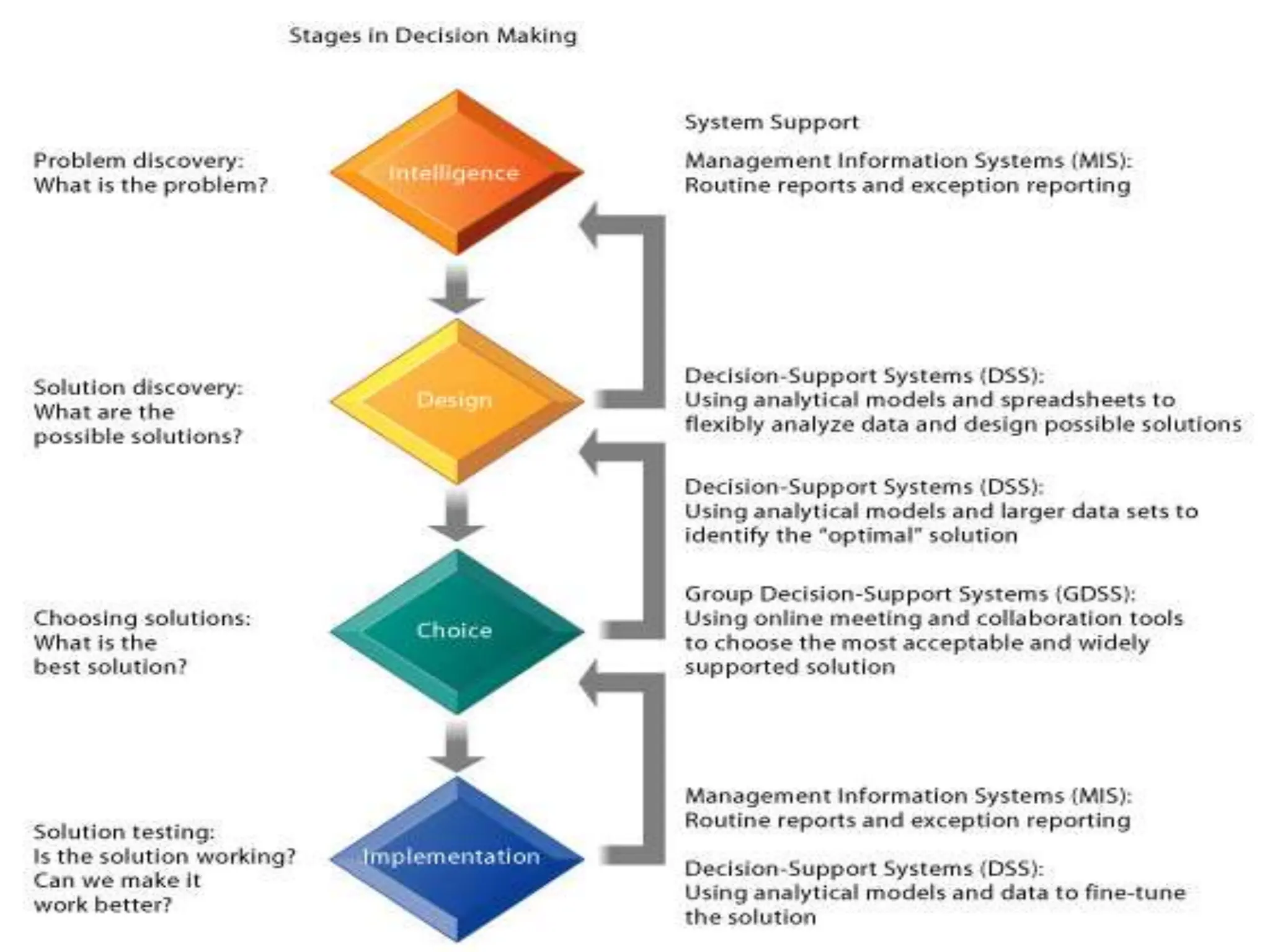
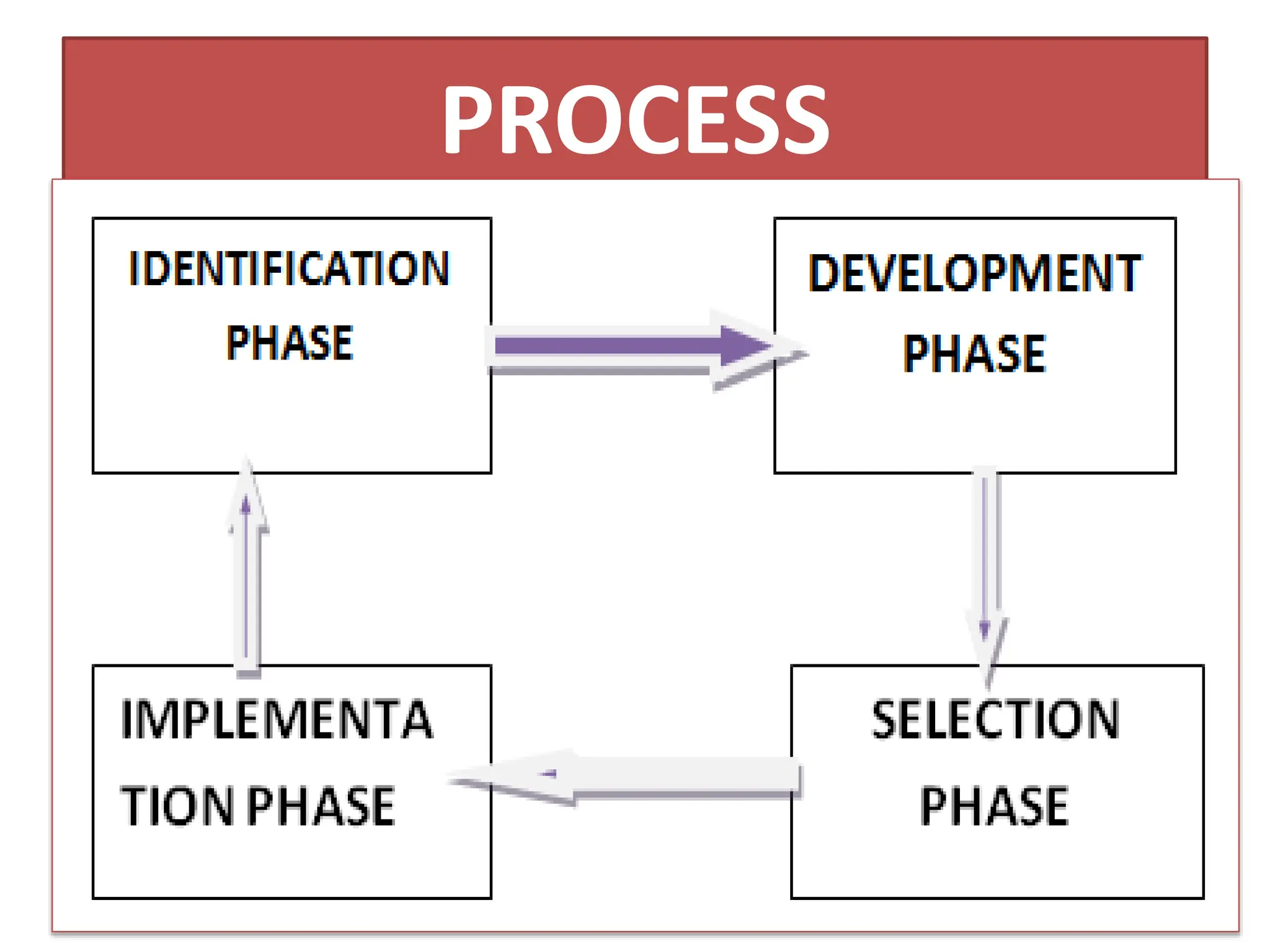
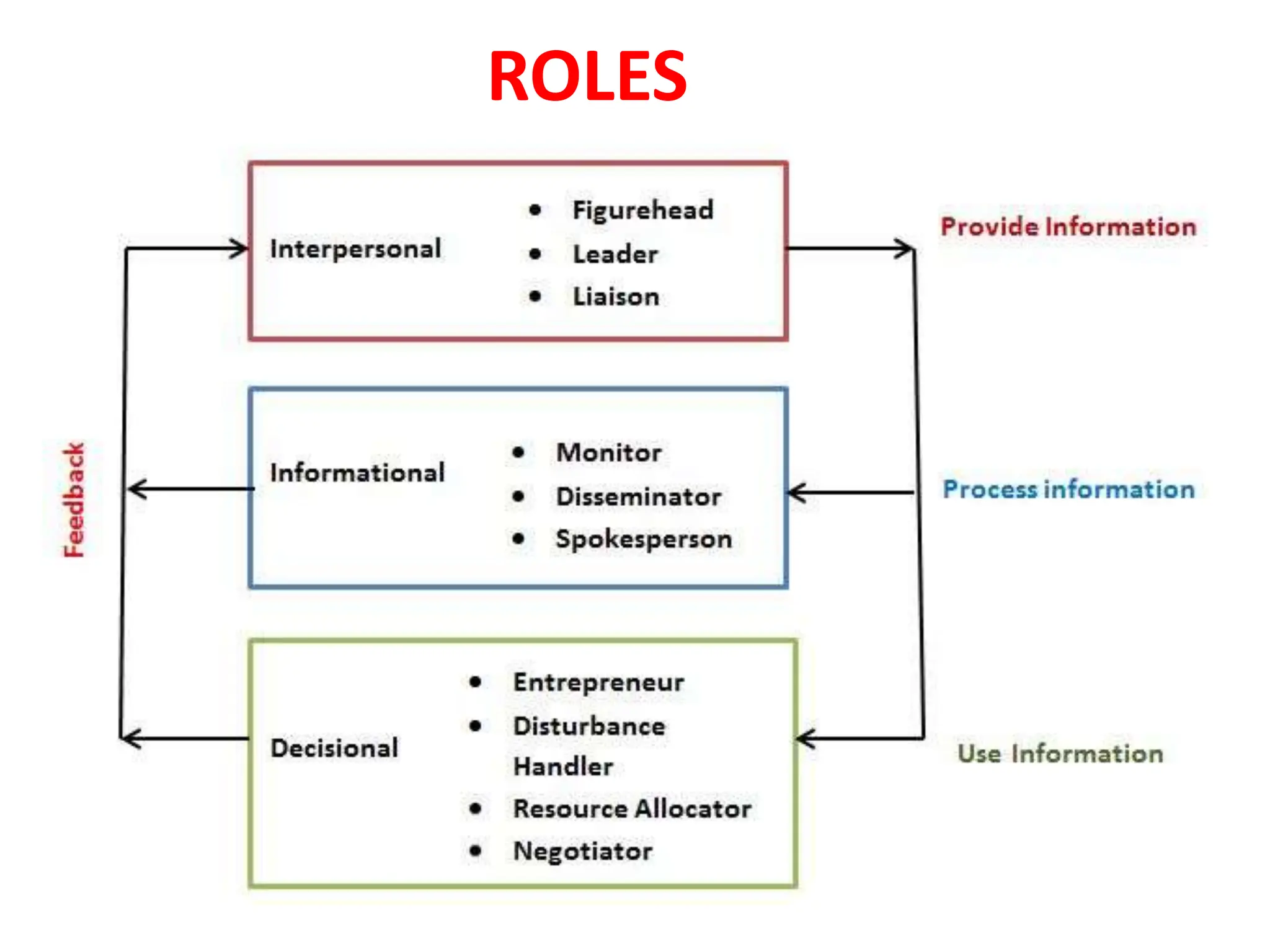
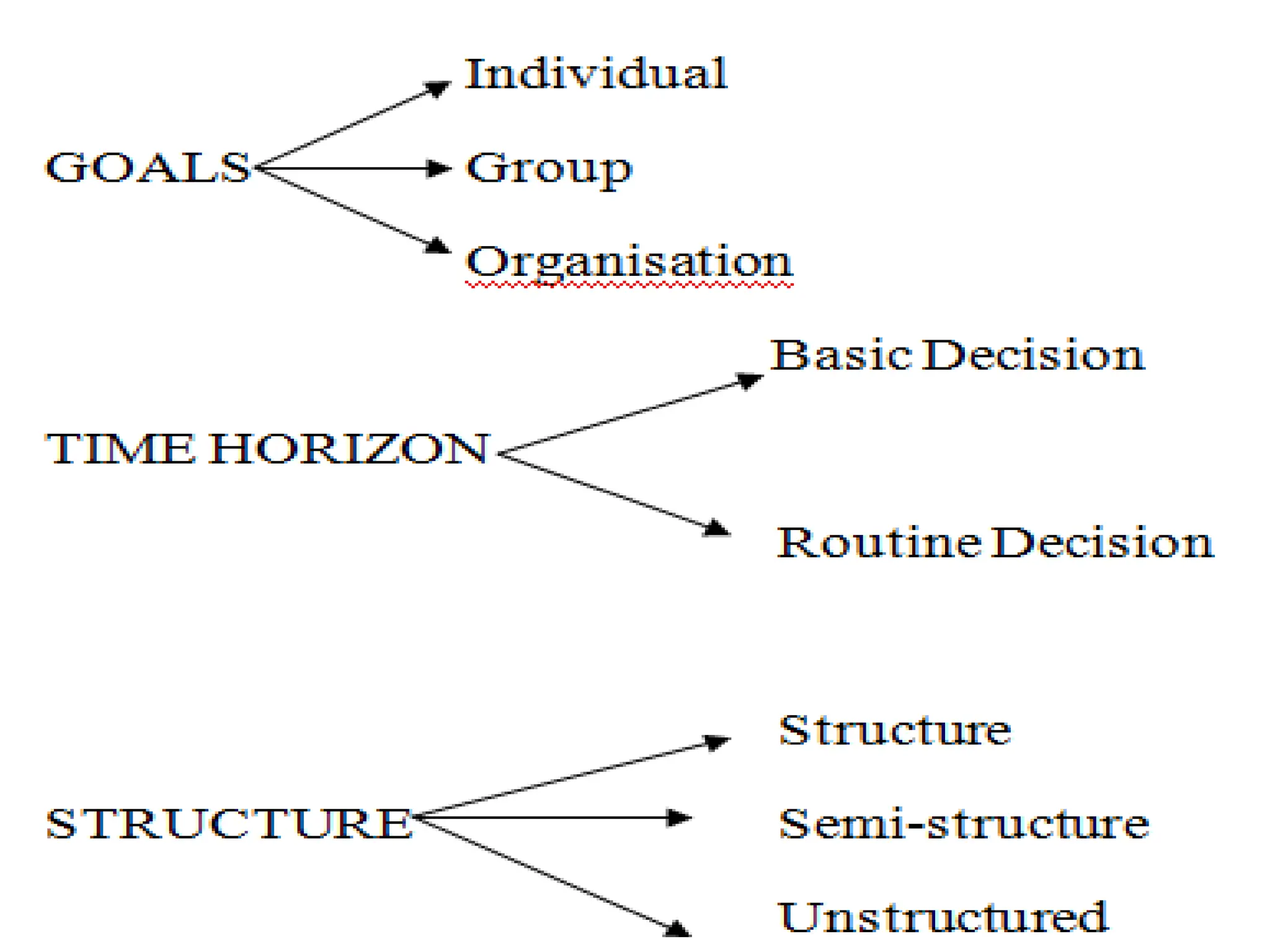
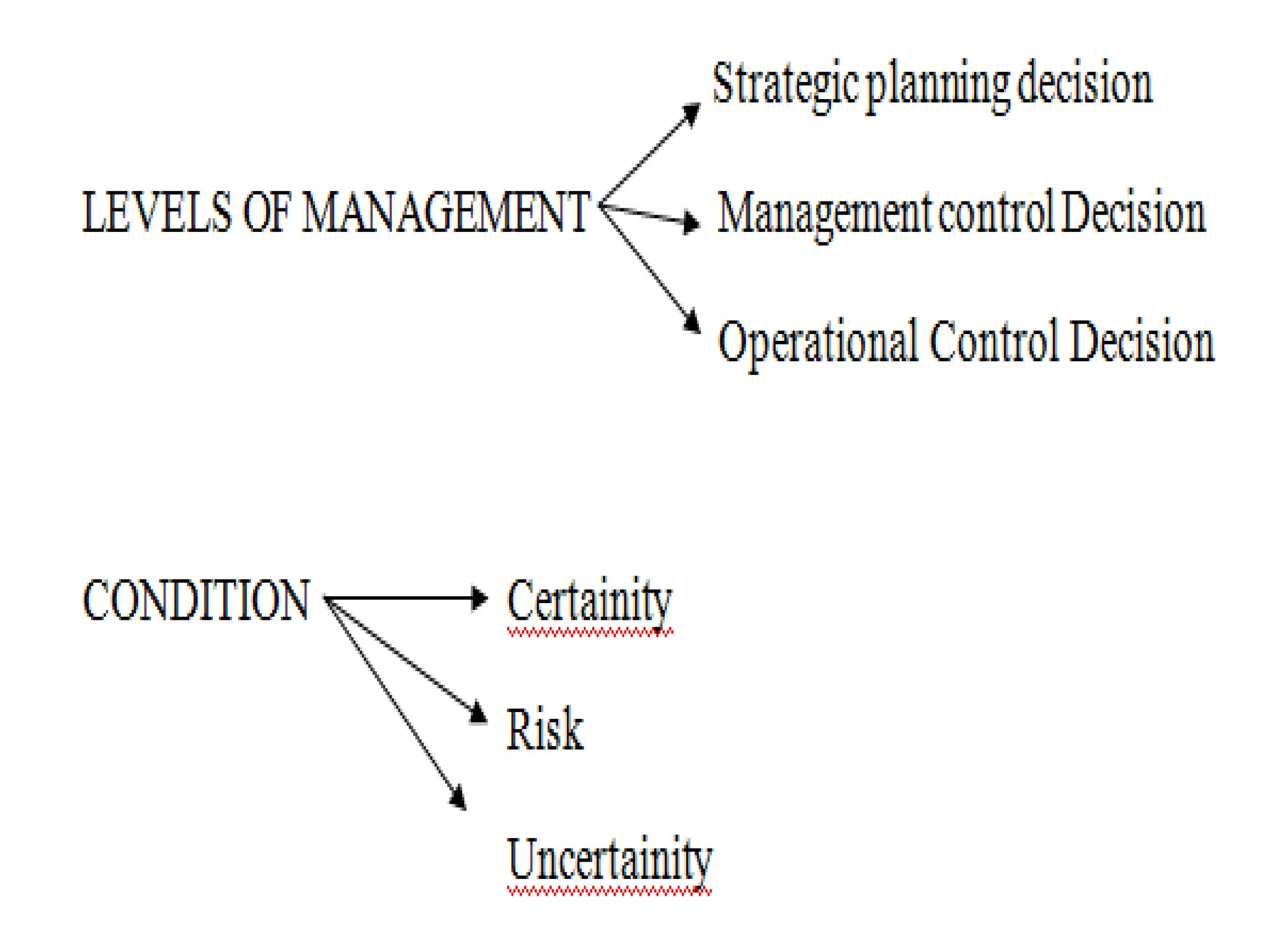
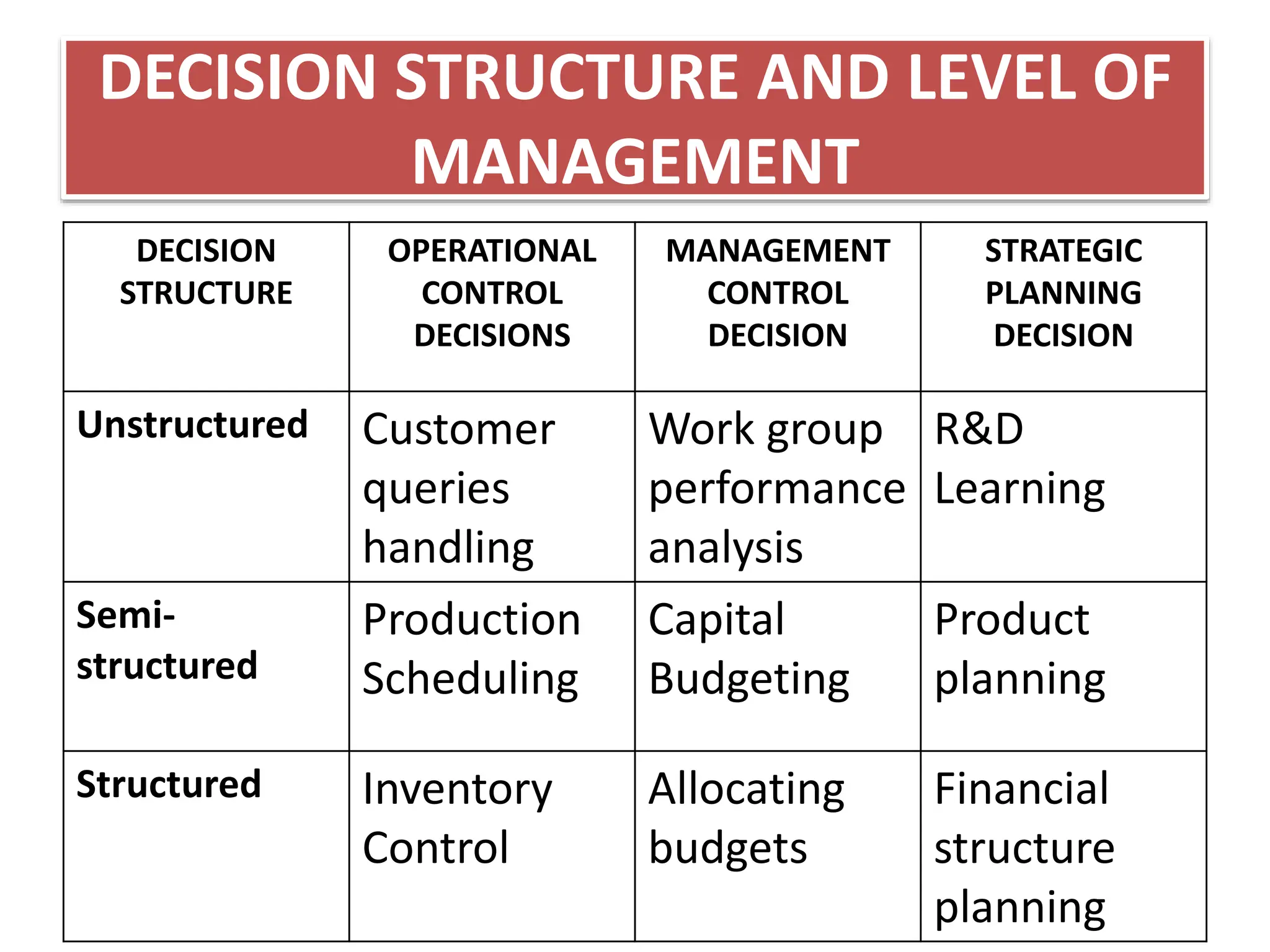
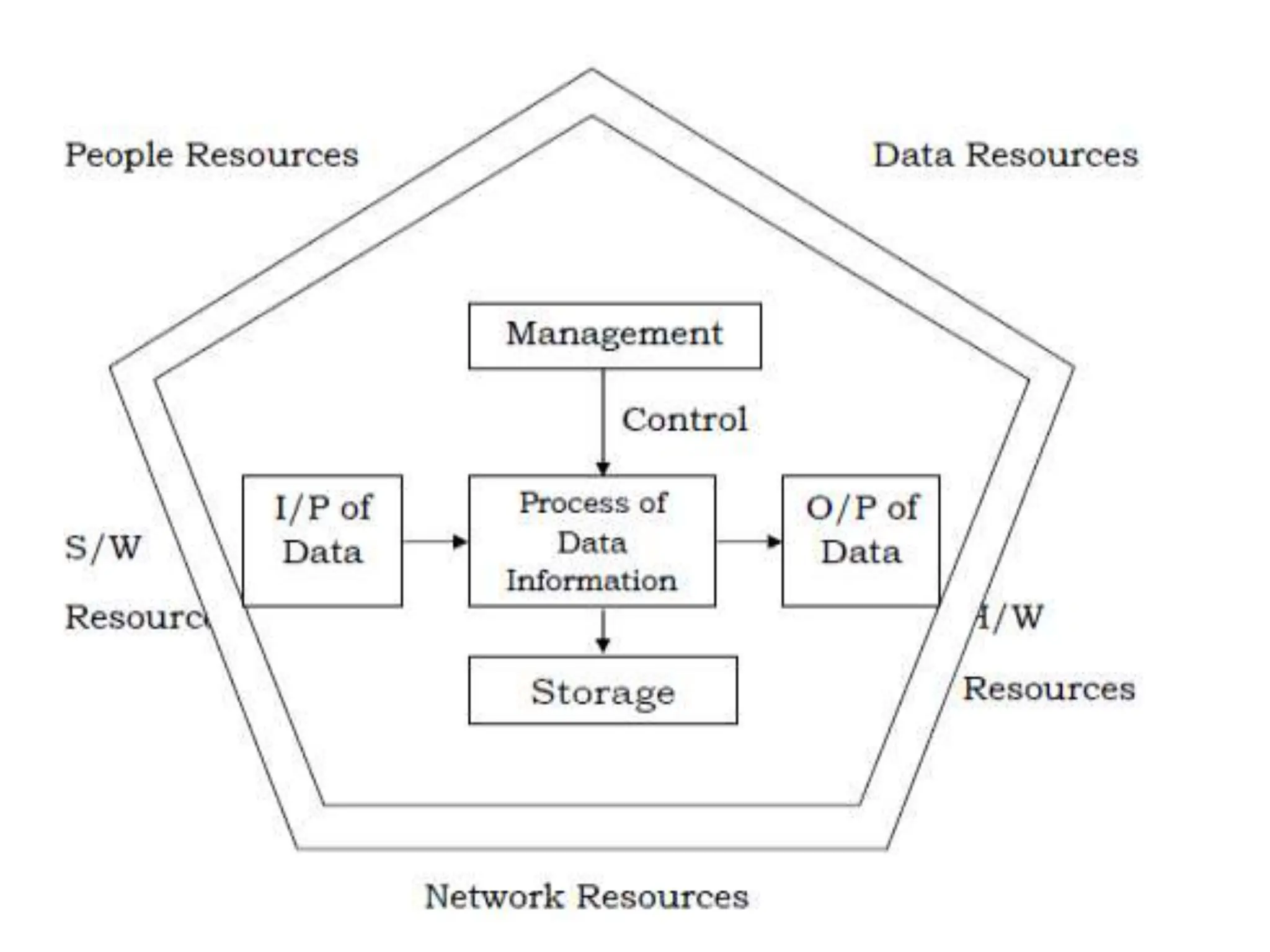
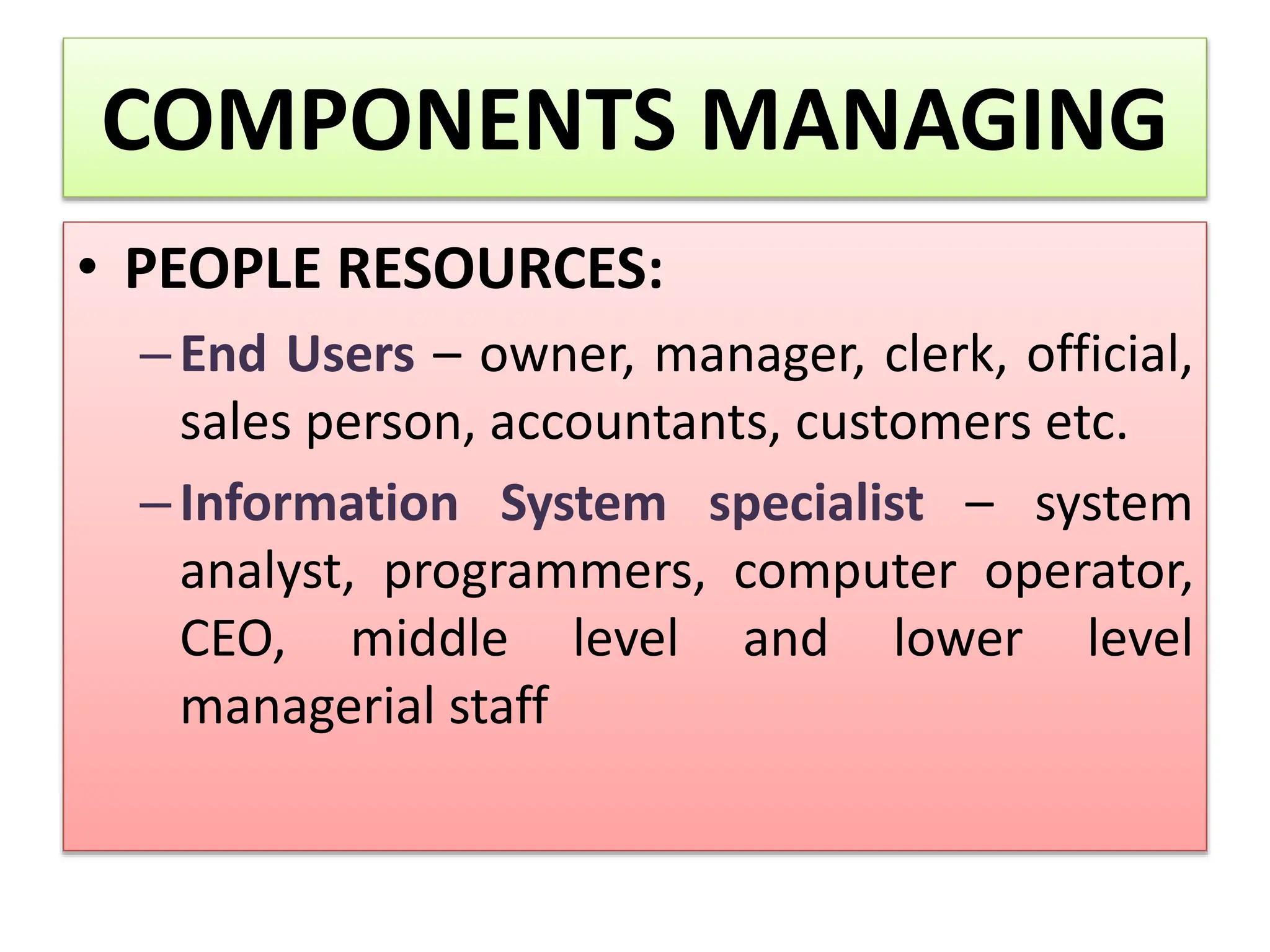
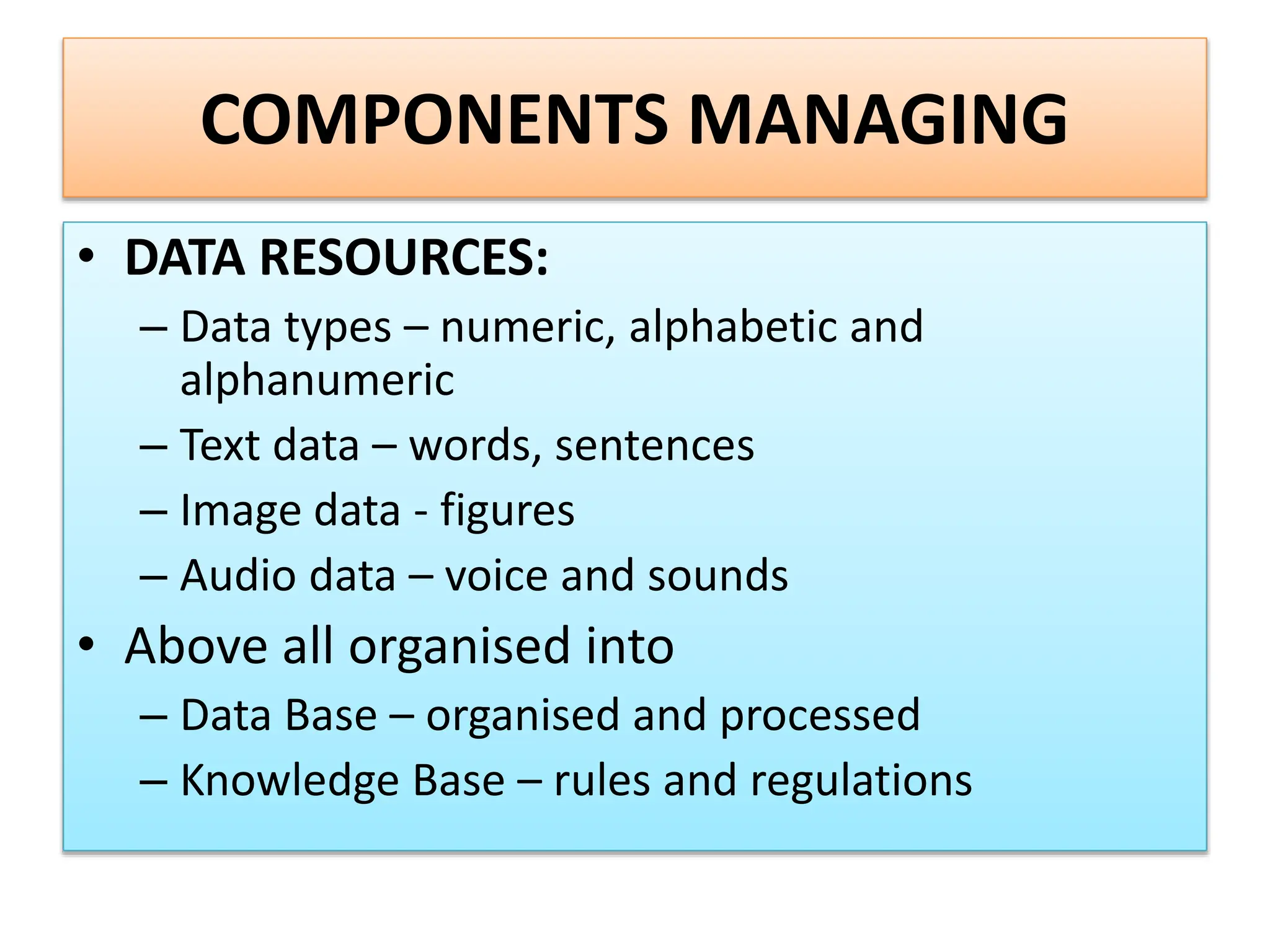
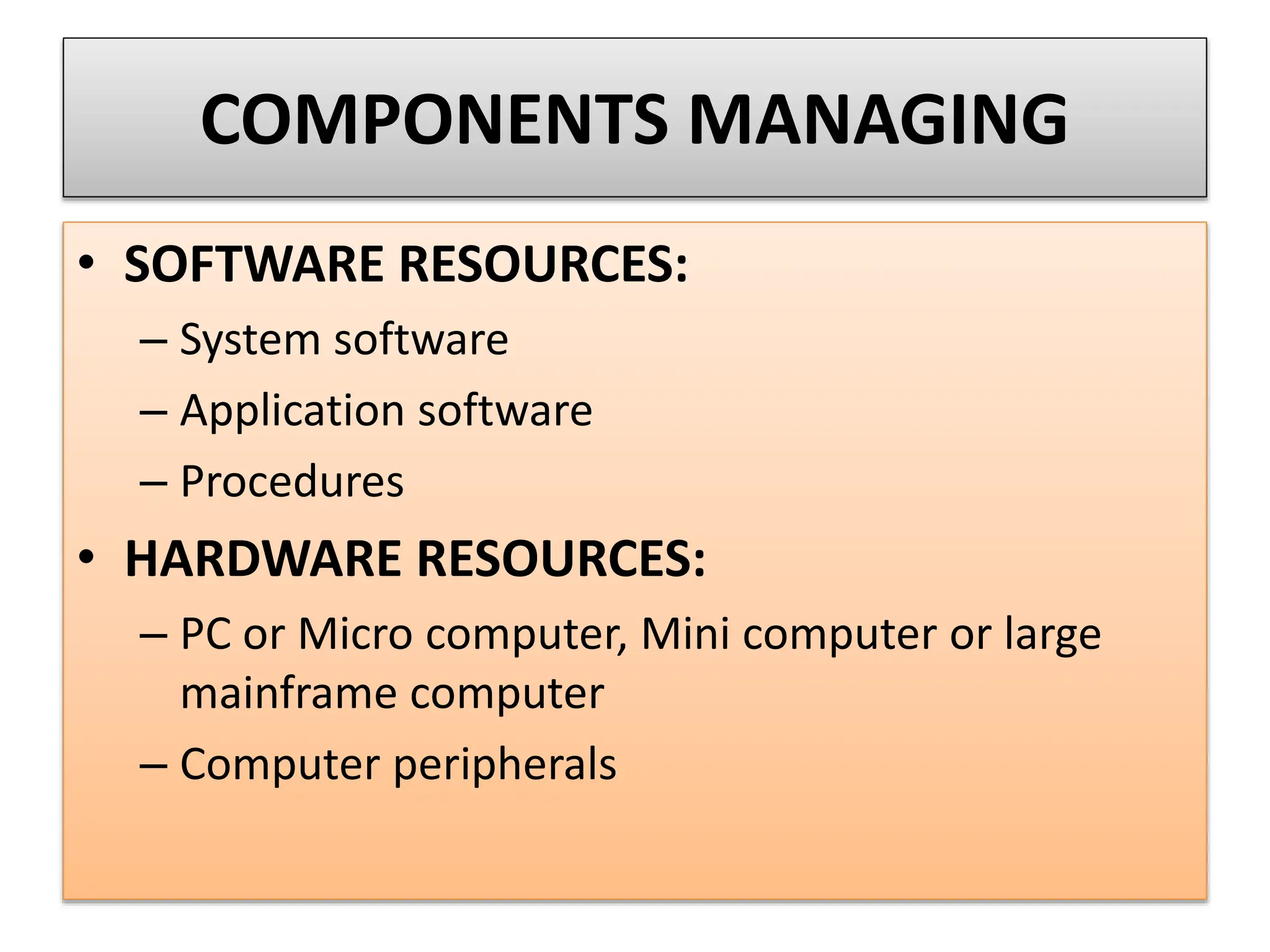
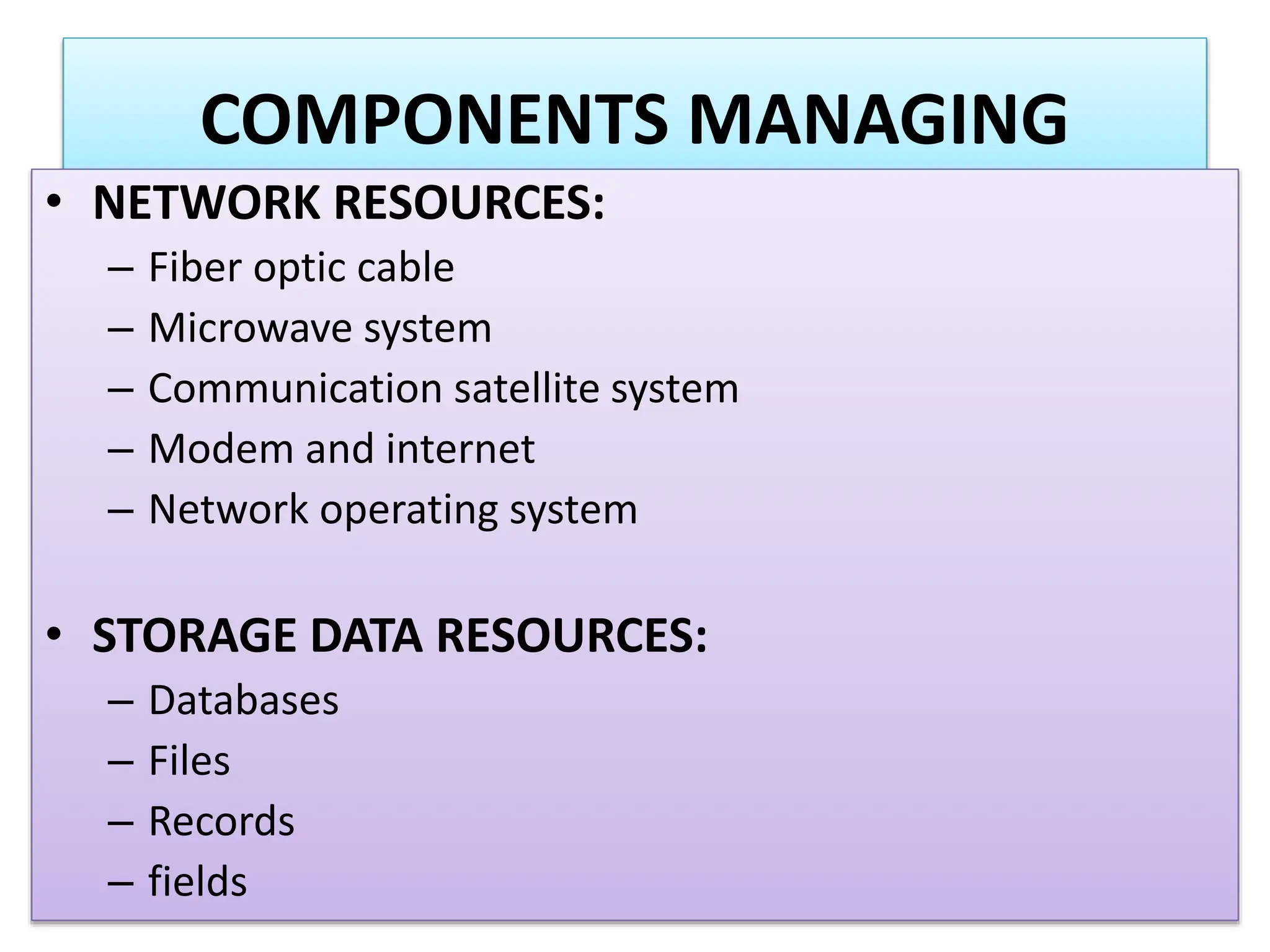
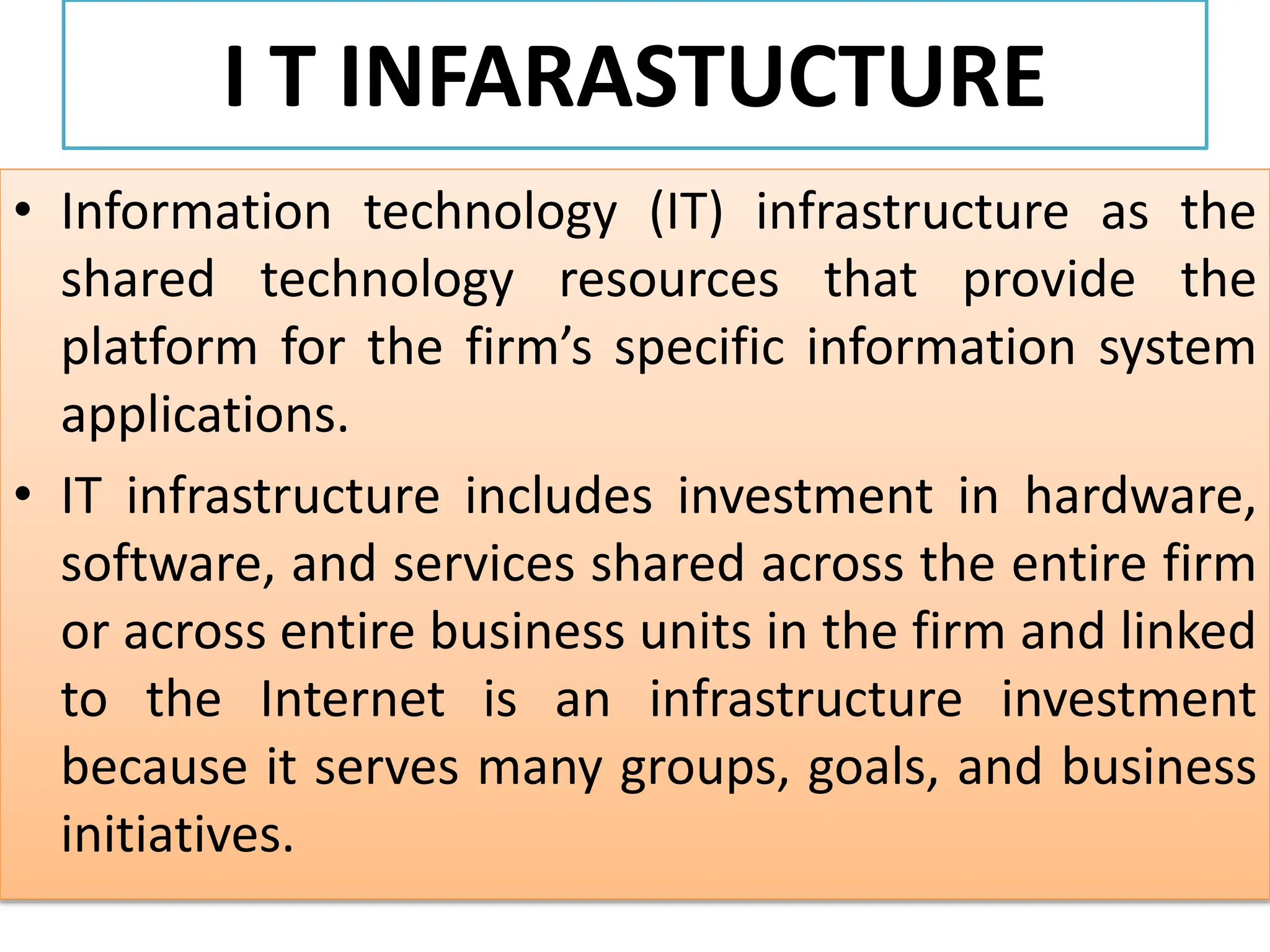
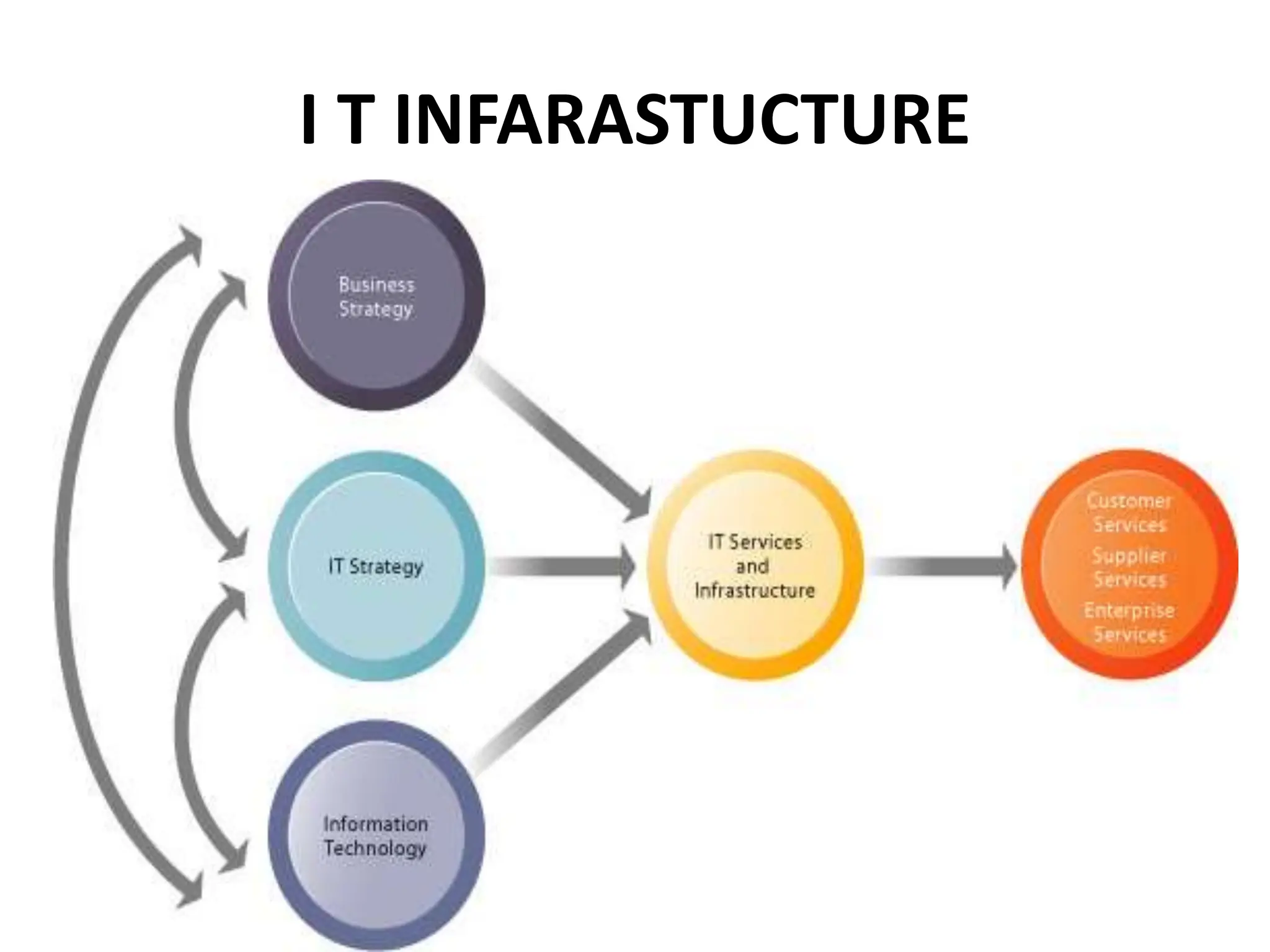
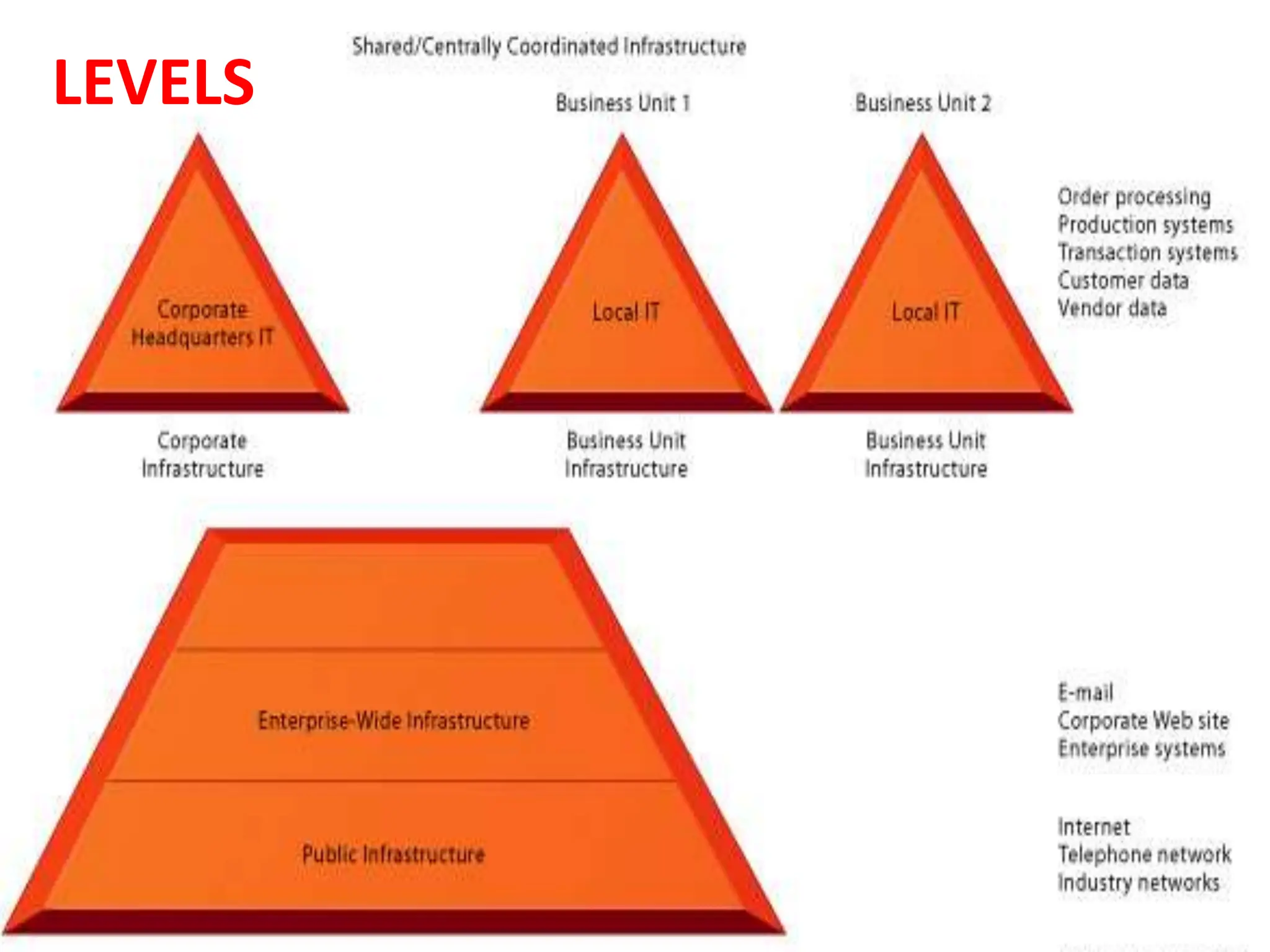
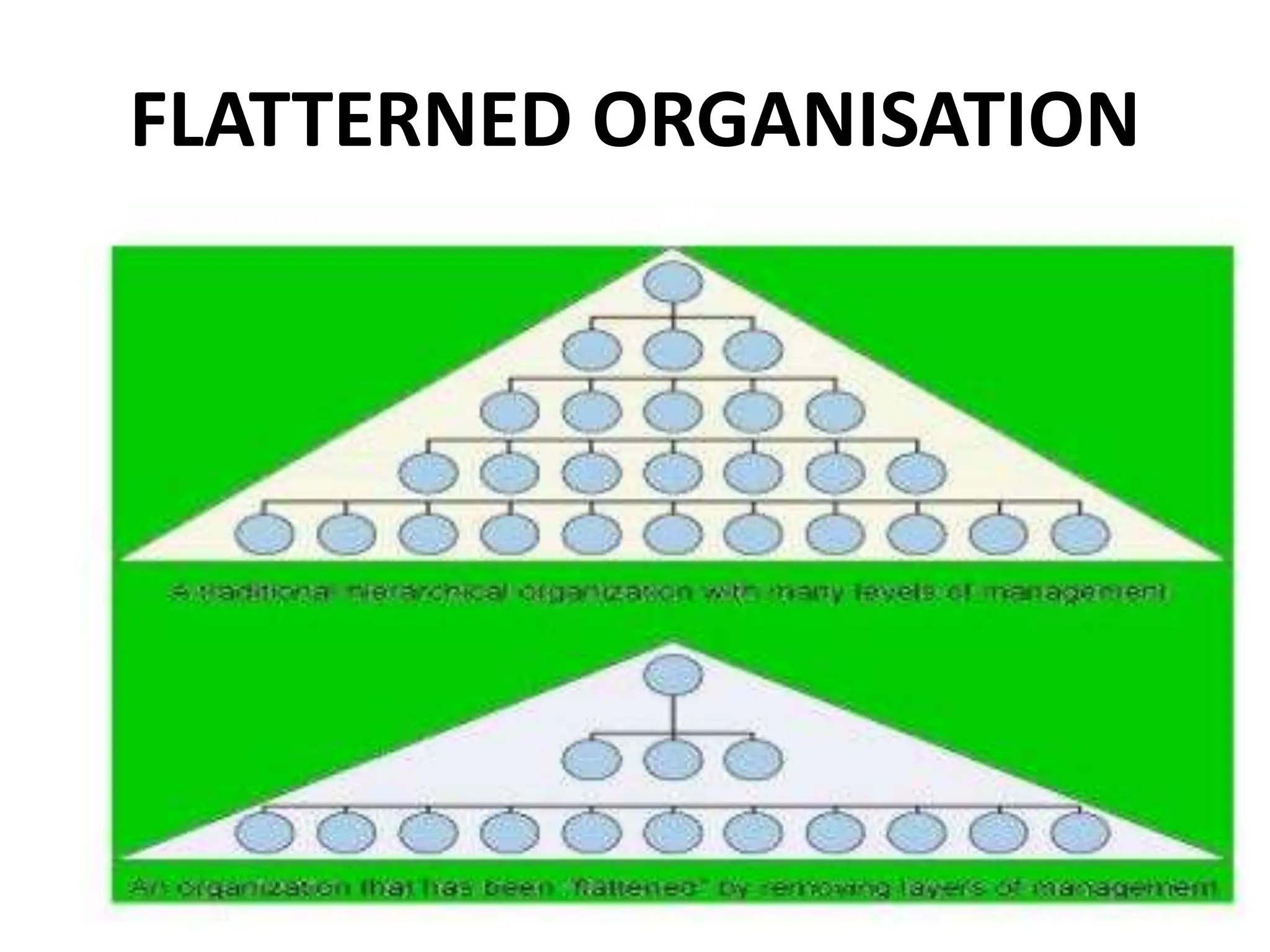
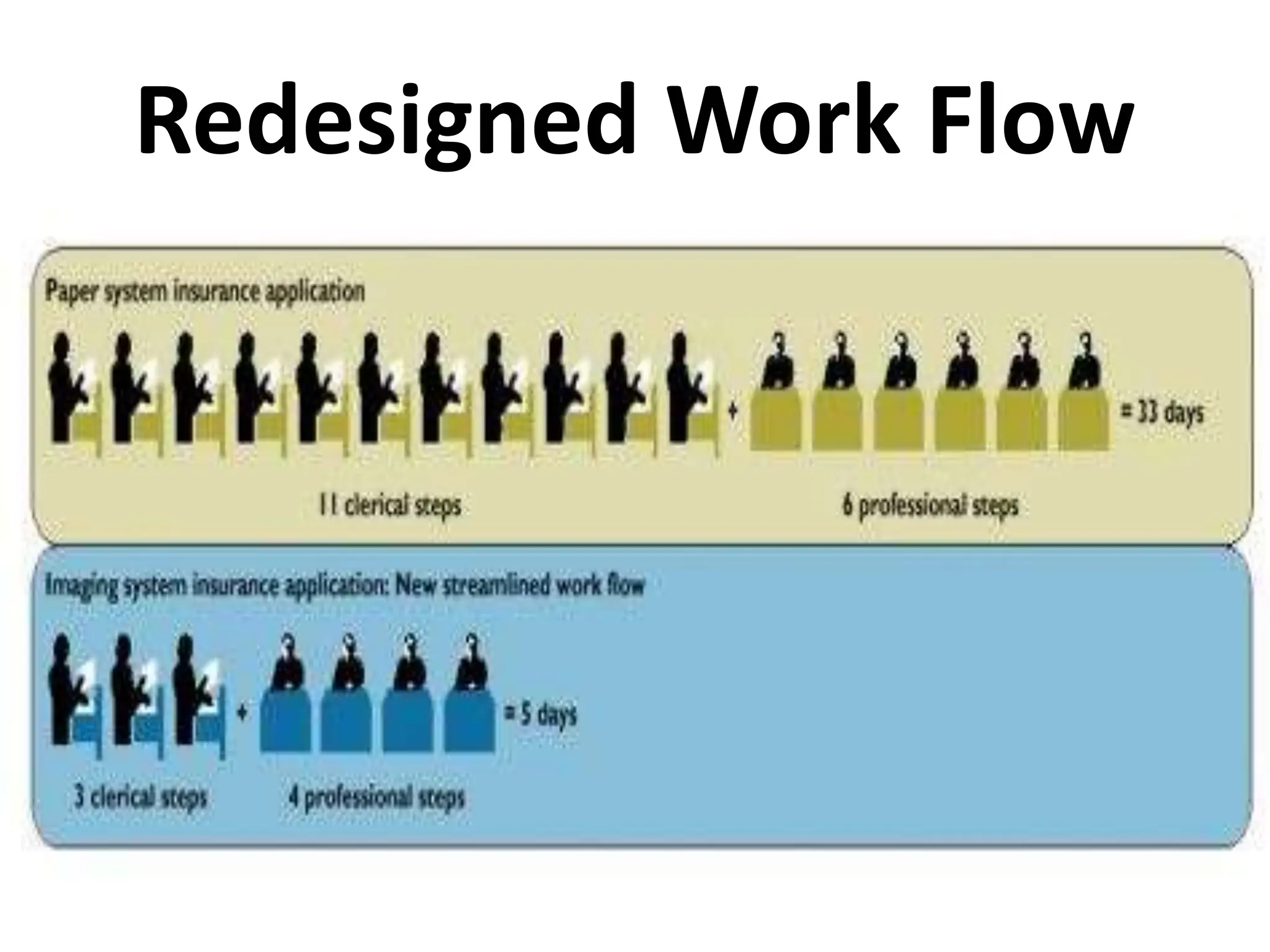
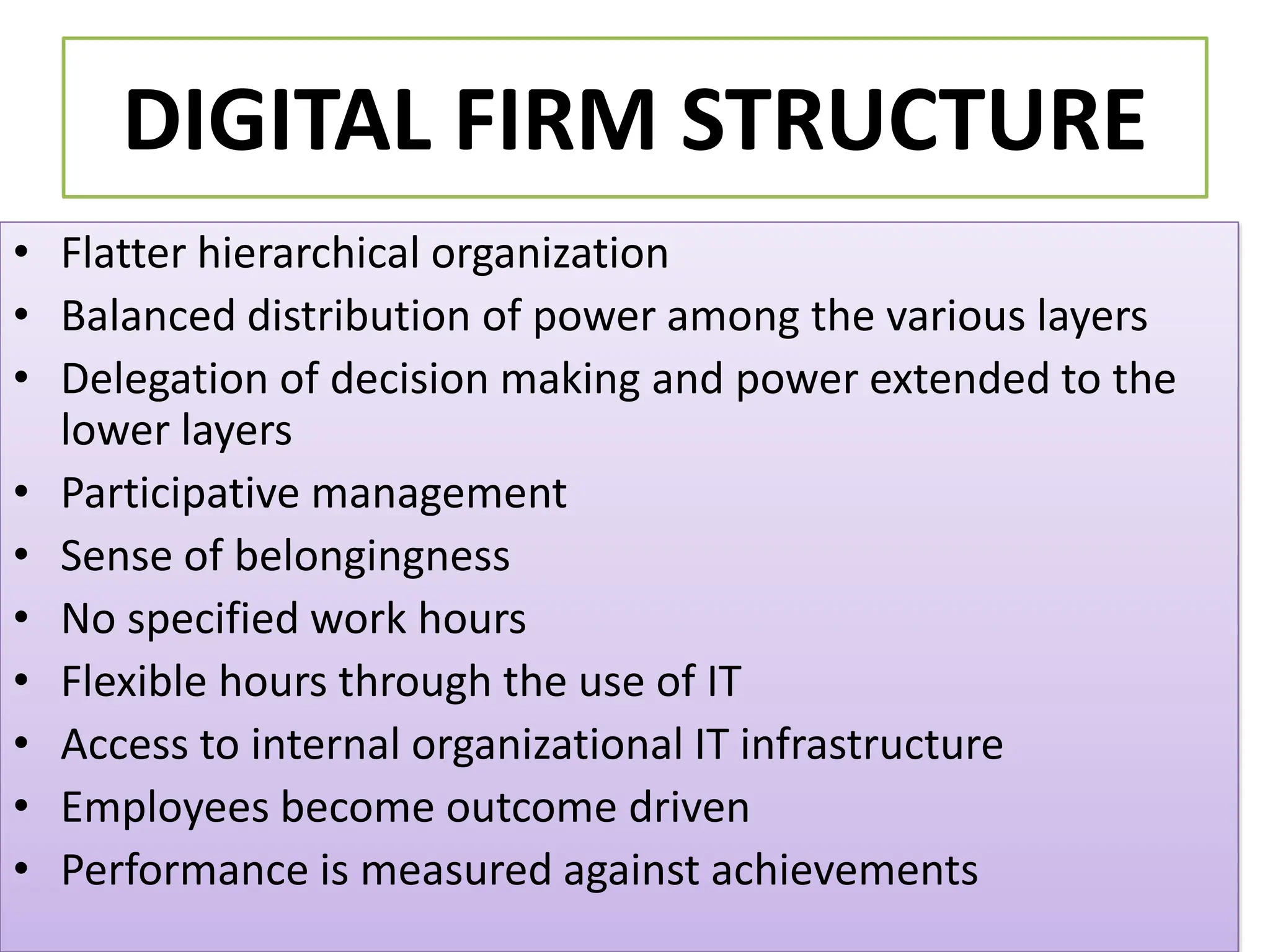
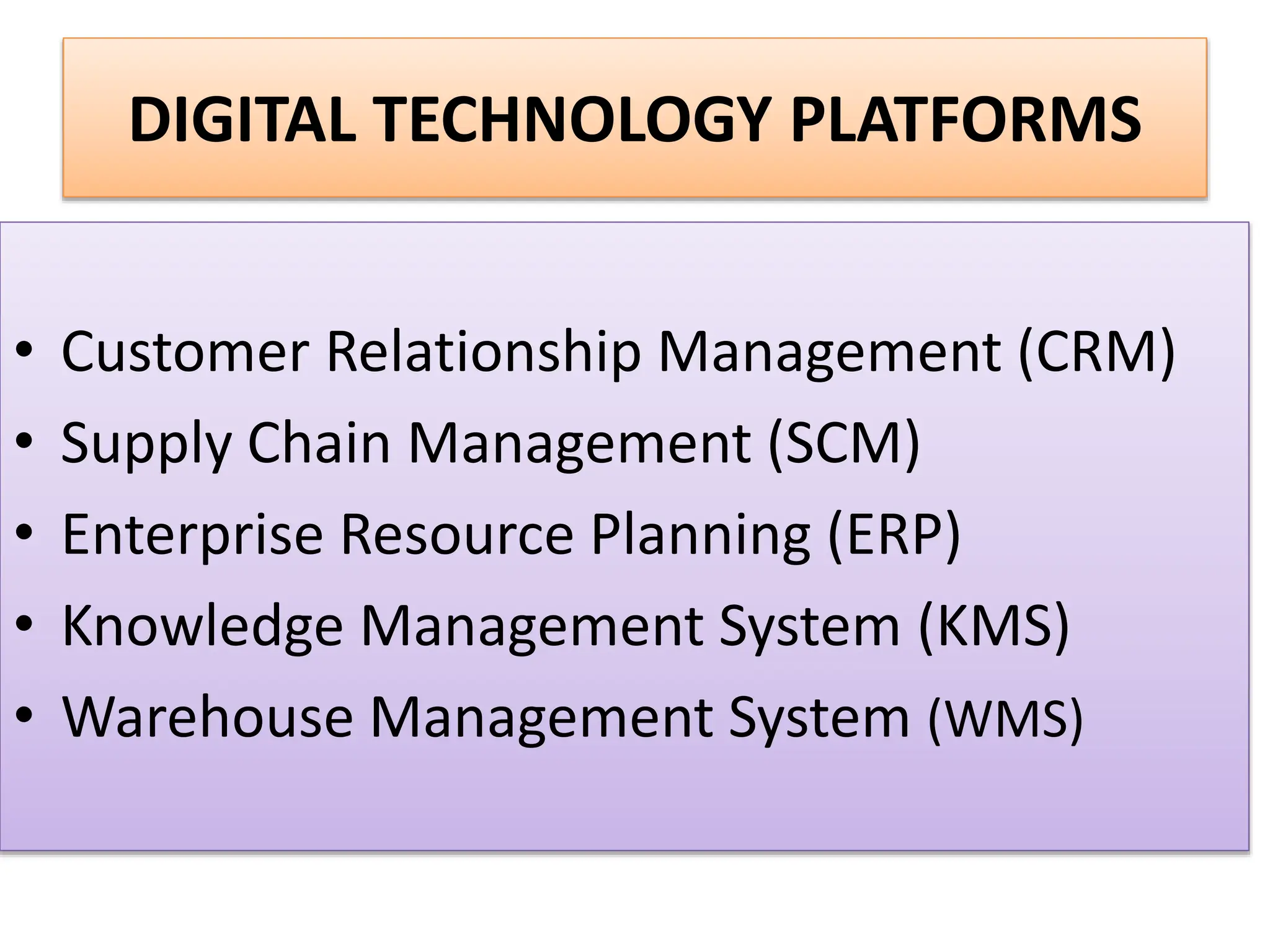
The document provides an extensive overview of Management Information Systems (MIS) and their role in organizations, highlighting their structure, components, types, and functions. It discusses various systems, including decision support systems (DSS), executive information systems (EIS), and expert systems, as well as the importance of information technology infrastructure in enhancing business processes. Furthermore, it explores the shift towards digital firms, emphasizing the benefits of digital relationships and flexible organizational structures.