Unit 5 discusses file handling in C programming. It defines a file as a collection of bytes stored on disk where related data is stored. There are two main types of file accessing: sequential and random. Sequential files are processed line-by-line while random accessing allows accessing any point in the file. Common file handling functions in C include fopen(), fclose(), fread(), fwrite(), fseek(), ftell() among others. Files are needed to permanently store data for programs to access even after terminating. Reading from files uses functions like fscanf() while writing uses fprintf(). The key aspects of files, records and fields are also discussed along with examples of reading and writing to files in C.
![Unit 5
Part –A
1. Define file.
A file represents a sequence of bytes on the disk where a group of related data is
stored. (Or)
A file is a collection of records.
2. Mentiondifferenttype of file accessing.
SequentialaccessandRandomaccess
When dealing with files, there are two types of files they are:
1. Text files and 2. Binary files.
3. DistinguishbetweenSequentialaccessandRandomaccess.
Sequential files are generally used in cases where the program processes the data in
a sequential fashion – i.e. counting words in a text file
True random access file handling, however, only accesses the file at the point at
which the data should be read or written, rather than having to process it sequentially.
4. What ismeantby commandline argument.?Give anexample.
Command-line arguments are given after the name of the program in command-line
shell of Operating Systems. To pass command line arguments, we typically define main()
with two arguments : first argument is the number of command line arguments and
second is list of command-line arguments.
int main(int argc, char *argv[]) { /* ... */ }
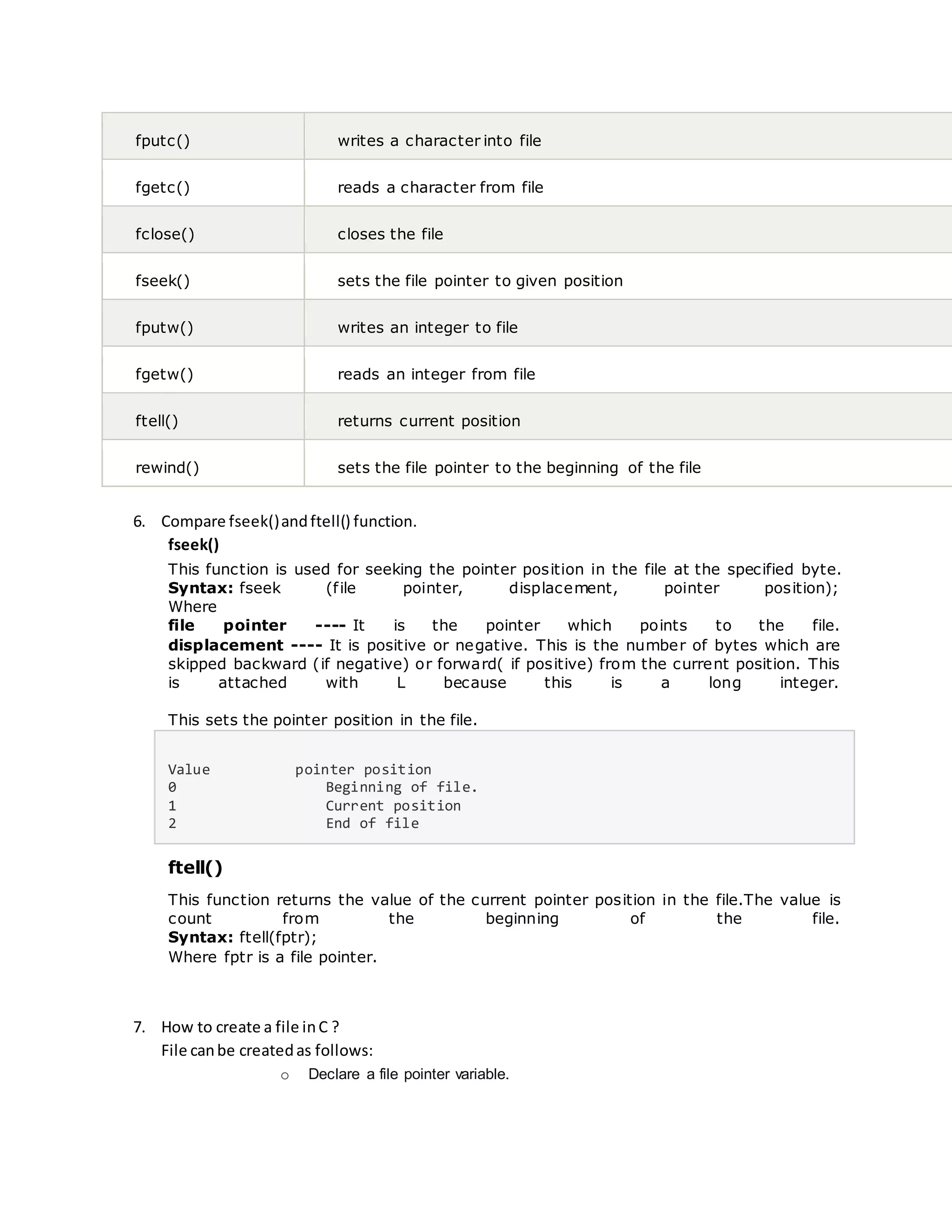
5. List outthe variousfile handlingfunction.
There are many functions in C library to open, read, write, search and close
file. A list of file functions are given below:
Function Description
fopen() opens new or existing file
fprintf() write data into file
fscanf() reads data from file](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/unit5pcqbans-201123143932/75/Unit-5-dwqb-ans-1-2048.jpg)



![is, whenyouopena file inthe write mode,the file isreset,resultingindeletionof anydataalready
presentinthe file.Whileinappendmode thiswill nothappen.Appendmode isusedtoappendoradd
data to the existingdataof file,if any.Hence,whenyouopenafile inAppend(a) mode,the cursoris
positionedatthe endof the presentdatainthe file.
16. What isthe use of rewind() functions.
The rewind function sets the file position to the beginning of the file for the stream pointed to
by stream. It also clears the error and end-of-file indicators for stream.
Syntax
The syntax for the rewind function in the C Language is:
void rewind(FILE *stream);
17. Write a C Program to findthe Size of a File.
Here is source code of the C Program to find the size of file using file handling function.
1. #include <stdio.h>
2. void main(int argc, char **argv)
3. {
4. FILE *fp;
5. char ch;
6. int size = 0;
7. fp = fopen(argv[1], "r");
8. if (fp == NULL)
9. printf("nFile unable to open ");
10. else
11. printf("nFile opened ");
12. fseek(fp, 0, 2); /* file pointer at the end of file */
13. size = ftell(fp); /* take a position of file pointer */
14. printf("The size of given file is : %dn", size);
15. fclose(fp);
16. }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/unit5pcqbans-201123143932/75/Unit-5-dwqb-ans-6-2048.jpg)

![i) rename().(3)
ii) remove().(5)
iii) fflush().(5)
i) rename()’ function can be called to change the name of a file from oldname to newname. If
the file with newname is already existing while ‘rename()’ was called, behaviour is
implementation defined. Both the functions return ZERO when succeed and non-zero value
when they fail. If ‘rename()’ fails, file with original name is yet accessible.
For example, for an existing file “hello.txt”,
rename("hello.txt", "byebye.txt");
They are prototypedbelow:
int rename(char const *oldname, char const *newname);
ii) remove()’ functioncanbe usedtoexplicitlyclose/deleteafile specifiedbyargument.If the specified
file isopenwhile remove() wascalled,behaviourisimplementationdefined.
For example, for an existing file “hello.txt”,
remove("hello.txt");
Theyare prototypedbelow:
int remove(char const *filename);
iii) fflush() is typically used for output stream only. Its purpose is to clear (or flush) the output
buffer and move the buffered data to console (in case of stdout) or disk (in case of file output
stream). Below is its syntax.
fflush(FILE *ostream);
Example:
#include <stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
int main()
{
char str[20];
int i;
for (i=0; i<2; i++)
{
scanf("%[^n]s", str);
printf("%sn", str);
// fflush(stdin);](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/unit5pcqbans-201123143932/75/Unit-5-dwqb-ans-8-2048.jpg)


![int scanf(const char *format, ...) reads formatted input from stdin.
Declaration
Following is the declaration for scanf() function.
int scanf(const char *format, ...)
Example
The following example shows the usage of scanf() function.
#include <stdio.h>
int main () {
char str1[20], str2[30];
printf("Enter name: ");
scanf("%s", str1);
printf("Enter your website name: ");
scanf("%s", str2);
printf("Entered Name: %sn", str1);
printf("Entered Website:%s", str2);
return(0);
}
C)(i).printf:
printf function is used to print character stream of data on stdout console.
Syntax:
Example:
printf("hello geeksquiz");
fprintf:
fprintf is used to print the sting content in file but not on stdout console.
Example:
fprintf(fptr,"%d.%sn", i, str);
D)(ii). feof():
It checks ending of a file. It continuously return zero value until end of file not come and return non
zero value when end of file comes.
Syntax:
feof(file pointer);](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/unit5pcqbans-201123143932/75/Unit-5-dwqb-ans-11-2048.jpg)

![ Check whether character is “End Character of File” or not , if yes then Terminate Loop
“putc” will write Single Character on File Pointed by “fp2” pointer
Program:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h> // For exit()
int main()
{
FILE *fptr1, *fptr2;
char filename[100], c;
printf("Enter the filename to open for reading n");
scanf("%s", filename);
// Open one file for reading
fptr1 = fopen(filename, "r");
if (fptr1 == NULL)
{
printf("Cannot open file %s n", filename);
exit(0);
}
printf("Enter the filename to open for writing n");
scanf("%s", filename);
// Open another file for writing
fptr2 = fopen(filename, "w");
if (fptr2 == NULL)
{
printf("Cannot open file %s n", filename);
exit(0);
}
// Read contents from file
c = fgetc(fptr1);
while (c != EOF)
{
fputc(c, fptr2);
c = fgetc(fptr1);
}
printf("nContents copied to %s", filename);
fclose(fptr1);
fclose(fptr2);
return 0;
}
Output:
Enter the filename to open for reading](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/unit5pcqbans-201123143932/75/Unit-5-dwqb-ans-13-2048.jpg)





![If a file is removed from or added to the directory after the most recent call to opendir() or
rewinddir(), whether a subsequent call to readdir() returns an entry for that file is unspecified.
The readdir() function may buffer several directory entries per actual read operation; readdir()
marks for update the st_atime field of the directory each time the directory is actually read.
7. Write aC Program to readcontent of a File anddisplay it. (13)
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h> // For exit() function
int main()
{
char c[1000];
FILE *fptr;
if ((fptr = fopen("program.txt", "r")) == NULL)
{
printf("Error! opening file");
// Program exits if file pointer returns NULL.
exit(1);
}
// reads text until newline
fscanf(fptr,"%[^n]", c);
printf("Data from the file:n%s", c);
fclose(fptr);
return 0;
}
If the file program.txt is not found, this program prints error message.
If the file is found, the program saves the content of the file to a string c until 'n' newline is
encountered.
Suppose, the program.txt file contains following text.
C programming is awesome.
I love C programming.
How are you doing?
The output of the program will be:
Data from the file: C programming is awesome.
8. Write aC Program to print the contents of a File inreverse.(13)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/unit5pcqbans-201123143932/75/Unit-5-dwqb-ans-20-2048.jpg)
![#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
FILE *fp1;
int cnt = 0;
int i = 0;
if( argc < 2 )
{
printf("Insufficient Arguments!!!n");
printf("Please use "program-name file-name" format.n");
return -1;
}
fp1 = fopen(argv[1],"r");
if( fp1 == NULL )
{
printf("n%s File can not be opened : n",argv[1]);
return -1;
}
//moves the file pointer to the end.
fseek(fp1,0,SEEK_END);
//get the position of file pointer.
cnt = ftell(fp1);
while( i < cnt )
{
i++;
fseek(fp1,-i,SEEK_END);
printf("%c",fgetc(fp1));
}
printf("n");
fclose(fp1);
return 0;
}
Actual file contents:
This is line1.
This is line2.
This is line3.
This is line4.
This is line5.
This is line6.
Terminal command: ./prg2 file1.txt
.6enil si sihT
.5enil si sihT
.4enil si sihT
.3enil si sihT
.2enil si sihT
.1enil si sihT
9.Write aC Program Transactionprocessing using randomaccess files.(13)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/unit5pcqbans-201123143932/75/Unit-5-dwqb-ans-21-2048.jpg)
![9. Write aC Program Transactionprocessing using randomaccess files.(16)
1 /* Fig. 11.16: fig11_16.c
2 This program reads a random access file sequentially,
3 updates data already written to the file, creates new
4 data to be placed in the file, and deletes data
5 already in the file. */
6 #include <stdio.h>
7
8 struct clientData {
9 int acctNum;
10 char lastName[ 15 ];
11 char firstName[ 10 ];
12 double balance;
13 };
14
15 int enterChoice( void );
16 void textFile( FILE * );
17 void updateRecord( FILE * );
18 void newRecord( FILE * );
19 void deleteRecord( FILE * );
20
21 int main()
22 {
23 FILE *cfPtr;
24 int choice;
25
26 if ( ( cfPtr = fopen( "credit.dat", "r+" ) ) == NULL )
27 printf( "File could not be opened.n" );
28 else {
29
30 while ( ( choice = enterChoice() ) != 5 ) {
31
32 switch ( choice ) {](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/unit5pcqbans-201123143932/75/Unit-5-dwqb-ans-22-2048.jpg)





![10. Write a C program Finding average of numbers stored in sequentialaccess file.(13)
#include <stdio.h>
int main (int argc, const char * argv[])
{
FILE *input;
int term, sum,i=0;
char c=’y’;
float avg;
input = fopen("data.txt","w");
while(c==’y’)
{printf(“enter a no”);
Scanf(“%d”,&term);
fprintf(input,"%d",&term);
printf(“Continue y or n: “);
scanf(“%c”,c);
}
fclose(input);
sum = 0;
input = fopen("data.txt","r");
while(!feof(input))
{
fscanf(input,"%d",&term);
sum = sum + term;
i++;
}
fclose(input);
printf("The Avg of the numbers is %f.n",sum/i);
return 0;
}
11. Explain about command line argument with suitable example.(13)
Command line argument is a parameter supplied to the program when it is invoked. Command
line argument is an important concept in C programming. It is mostly used when you need to
control your program from outside. Command line arguments are passed to the main() method.
parameters/argumentssuppliedtothe programwhenitisinvoked.Theyare usedto
control program fromoutside insteadof hard coding those valuesinside the code.
In real time application,itwill happentopassargumentstothe mainprogram itself.
These argumentsare passedtothe main() functionwhile executing binary filefrom
commandline.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/unit5pcqbans-201123143932/75/Unit-5-dwqb-ans-28-2048.jpg)
![Syntax:
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
Here argc counts the number of arguments on the command line and argv[ ] is a pointer array
which holds pointers of type char which points to the arguments passed to the program.
ExampleforCommandLineArgument
#include <stdio.h>
#include <conio.h>
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
int i;
if( argc >= 2 )
{
printf("The arguments supplied are:n");
for(i = 1; i < argc; i++)
{
printf("%st", argv[i]);
}
}
else
{
printf("argument list is empty.n");
}
return 0;
}
Remember that argv[0] holds the name of the program and argv[1] points to the first
command line argument and argv[n] gives the last argument. If no argument is supplied, argc
will be 1.
12. Developa C Program tofind the number of lines ina text file.(13)
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
FILE *fileptr;
int count_lines = 0;
char filechar[40], chr;
printf("Enter file name: ");
scanf("%s", filechar);
fileptr = fopen(filechar, "r");](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/unit5pcqbans-201123143932/75/Unit-5-dwqb-ans-29-2048.jpg)

![4 */
5 int main(int agrc, char** argv)
6 {
7 /*
8 * Declarations.
9 */
10 int n;
11 double factorial;
12 int counter;
13
14 /*
15 * Initializations.
16 */
17 n = atoi(argv[1]);
18 factorial = 1.0;
19
20 /*
21 * Calculation of factorial.
22 */
23 for (counter = 1; counter <= n; counter = counter +1)
24 {
25 factorial = factorial * counter;
26 }
27
28 /*
29 * Print out the result.
30 */
31 printf("n!= %f n", factorial);
32 }
convert the command line argument “n” to an integer value by using standard library function called
atoi(char* s).](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/unit5pcqbans-201123143932/75/Unit-5-dwqb-ans-31-2048.jpg)
![14. Write a C Program to generate Fibonacci series by using command line arguments.(13)
Hence a C Program computes first N fibonacci numbers using command line arguments.
Here is source code of the C Program to compute first N fibonacci numbers using command line
arguments.
#include <stdio.h>
/* Global Variable Declaration */
int first = 0;
int second = 1;
int third;
/* Function Prototype */
void rec_fibonacci(int);
void main(int argc, char *argv[])/* Command line Arguments*/
{
int number = atoi(argv[1]);
printf("%dt%d", first, second); /* To print first and second number
of fibonacci series */
rec_fibonacci(number);
printf("n");
}
/* Code to print fibonacci series using recursive function */
void rec_fibonacci(int num)
{
if (num == 2) /* To exit the function as the first two numbers are
already printed */
{
return;
}
third = first + second;
printf("t%d", third);
first = second;
second = third;
num--;
rec_fibonacci(num);
}
Output:
$ cc arg6.c
$ a.out 10
0 1 1 2 3 5 8 13 21 34
PART-C
1.(i) Write the case study of “How sequential accessfile isdifferfrom Random access file”.(10)
Sequential accessfile :
– Cannotbe modifiedwithoutthe riskof destroyingotherdata](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/unit5pcqbans-201123143932/75/Unit-5-dwqb-ans-32-2048.jpg)

![1 /* Fig. 11.3: fig11_03.c
2 Create a sequential file */
3 #include <stdio.h>
4
5 int main()
6 {
7 int account;
8 char name[ 30 ];
9 double balance;
10 FILE *cfPtr; /* cfPtr = clients.dat file pointer */
11
12 if ( ( cfPtr = fopen( "clients.dat", "w" ) ) == NULL )
13 printf( "File could not be openedn" );
14 else {
15 printf( "Enter the account, name, and balance.n" );
16 printf( "Enter EOF to end input.n" );
17 printf( "? " );
18 scanf( "%d%s%lf", &account, name, &balance );
19
20 while ( !feof( stdin ) ) {
21 fprintf( cfPtr, "%d %s %.2fn",
22 account, name, balance );
23 printf( "? " );
24 scanf( "%d%s%lf", &account, name, &balance );
25 }
26
27 fclose( cfPtr );
28 }
29
30 return 0;
31 }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/unit5pcqbans-201123143932/75/Unit-5-dwqb-ans-34-2048.jpg)
![1 /* Fig. 11.11: fig11_11.c
2 Creating a randomly accessed file sequentially */
3 #include <stdio.h>
4
5 struct clientData {
6 int acctNum;
7 char lastName[ 15 ];
8 char firstName[ 10 ];
9 double balance;
10 };
11
12 int main()
13 {
14 int i;
15 struct clientData blankClient = { 0, "", "", 0.0 };
16 FILE *cfPtr;
17
18 if ( ( cfPtr = fopen( "credit.dat", "w" ) ) == NULL )
19 printf( "File could not be opened.n" );
20 else {
21
22 for ( i = 1; i <= 100; i++ )
23 fwrite( &blankClient,
24 sizeof( struct clientData ), 1, cfPtr );
25
26 fclose( cfPtr );
27 }
28
29 return 0;
30 }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/unit5pcqbans-201123143932/75/Unit-5-dwqb-ans-35-2048.jpg)
![(ii) Write a C program to write all the membersof an array ofstructures to a file usingfwrite().Read
the array from the file anddisplay on the screen.(5)
#include <stdio.h>
struct s
{
char name[50];
int height;
};
int main(){
struct s a[5],b[5];
FILE *fptr;
int i;
fptr=fopen("file.txt","wb");
for(i=0;i<5;++i)
{
fflush(stdin);
printf("Enter name: ");
gets(a[i].name);
printf("Enter height: ");
scanf("%d",&a[i].height);
}
fwrite(a,sizeof(a),1,fptr);
fclose(fptr);
fptr=fopen("file.txt","rb");
fread(b,sizeof(b),1,fptr);
for(i=0;i<5;++i)
{
printf("Name: %snHeight: %d",b[i].name,b[i].height);
}
fclose(fptr);
}
2. Summarize the various file openingmodeswiththeirdescriptions.(15)
File Modes
r Open a text file for reading.
w Create a text file for writing. If the file exists, it is overwritten.
a Open a text file in append mode. Text is added to the end of the
file.
rb Open a binary file for reading.
wb Create a binary file for writing. If the file exists, it is overwritten.
ab Open a binary file in append mode. Data is added to the end of](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/unit5pcqbans-201123143932/75/Unit-5-dwqb-ans-36-2048.jpg)
![the file.
r+ Open a text file for reading and writing.
w+ Create a text file for reading and writing. If the file exists, it is
overwritten.
a+ Open a text file for reading and writing at the end.
r+b or
rb+
Open binary file for reading and writing.
w+b or
wb+
Create a binary file for reading and writing. If the file exists, it is
overwritten.
a+b or
ab+
Open a text file for reading and writing at the end.
3. Developa C Program to merge two files.(15)
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
int main()
{
FILE *fs1, *fs2, *ft;
char ch, file1[20], file2[20], file3[20];
printf("Enter name of first filen");
gets(file1);
printf("Enter name of second filen");
gets(file2);
printf("Enter name of file which will store contents of two filesn");
gets(file3);
fs1 = fopen(file1,"r");
fs2 = fopen(file2,"r");
if( fs1 == NULL || fs2 == NULL )
{
perror("Error ");
printf("Press any key to exit...n");
getch();
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
ft = fopen(file3,"w");
if( ft == NULL )
{
perror("Error ");](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/unit5pcqbans-201123143932/75/Unit-5-dwqb-ans-37-2048.jpg)
![printf("Press any key to exit...n");
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
while( ( ch = fgetc(fs1) ) != EOF )
fputc(ch,ft);
while( ( ch = fgetc(fs2) ) != EOF )
fputc(ch,ft);
printf("Two files were merged into %s file successfully.n",file3);
fclose(fs1);
fclose(fs2);
fclose(ft);
return 0;
}
4. Examine with example forthe functionsrequiredin binary file I/O operations.(15)
Binary File I/O uses fread and fwrite.
The declarations for each are similar:
size_t fread(void *ptr, size_t size_of_elements, size_t number_of_elements, FILE
*a_file);
size_t fwrite(const void *ptr, size_t size_of_elements, size_t number_of_elements,
FILE *a_file);
Both of these functions deal with blocks of memories - usually arrays. Because they accept pointers,
you can also use these functions with other data structures; you can even write structs to a file or a
read struct into memory.
Example Program:
#include <stdio.h>
struct s
{
char name[50];
int height;
};
int main(){
struct s a[5],b[5];
FILE *fptr;
int i;
fptr=fopen("file.txt","wb");
for(i=0;i<5;++i)
{](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/unit5pcqbans-201123143932/75/Unit-5-dwqb-ans-38-2048.jpg)
![fflush(stdin);
printf("Enter name: ");
gets(a[i].name);
printf("Enter height: ");
scanf("%d",&a[i].height);
}
fwrite(a,sizeof(a),1,fptr);
fclose(fptr);
fptr=fopen("file.txt","rb");
fread(b,sizeof(b),1,fptr);
for(i=0;i<5;++i)
{
printf("Name: %snHeight: %d",b[i].name,b[i].height);
}
fclose(fptr);
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/unit5pcqbans-201123143932/75/Unit-5-dwqb-ans-39-2048.jpg)