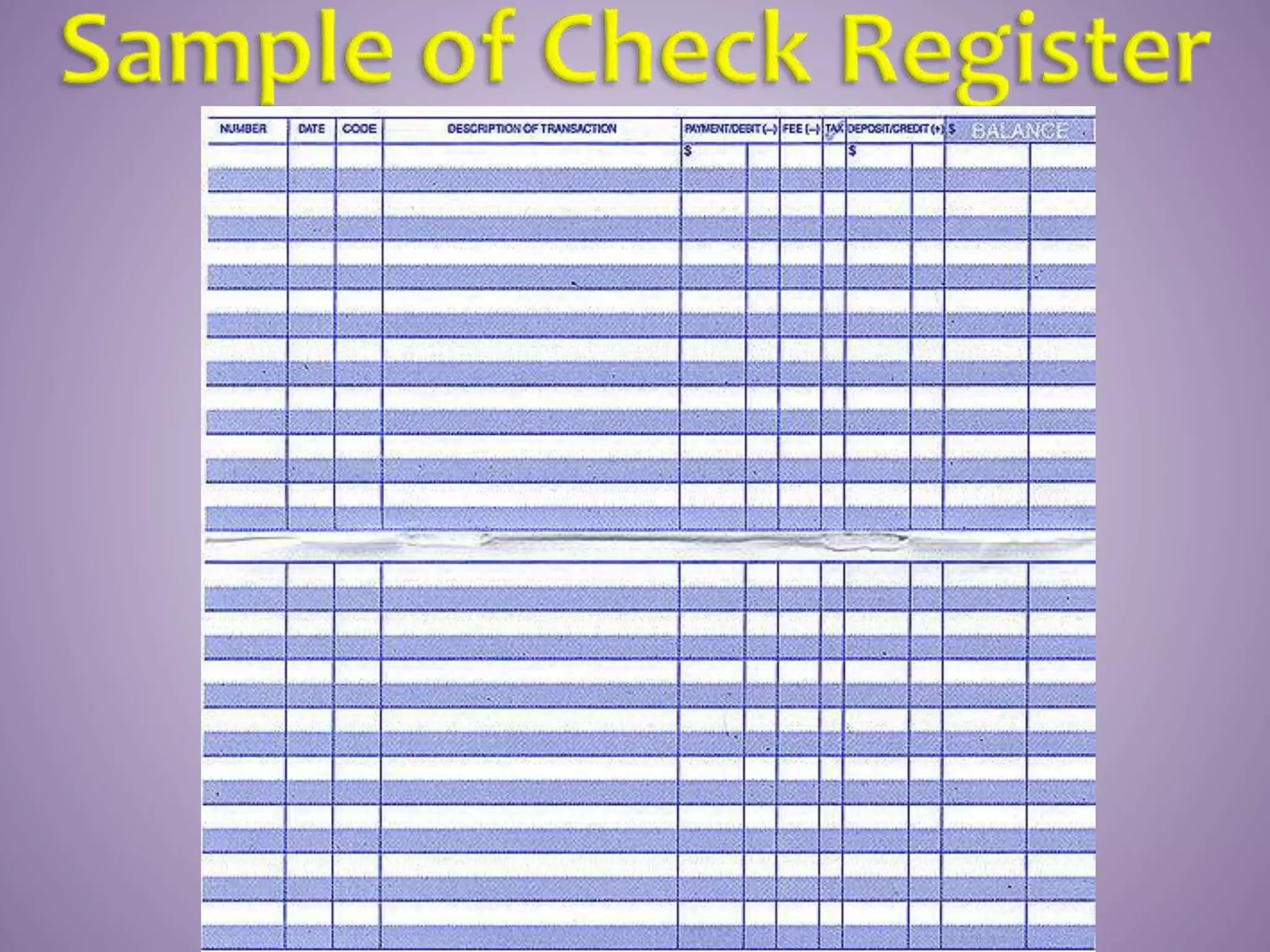
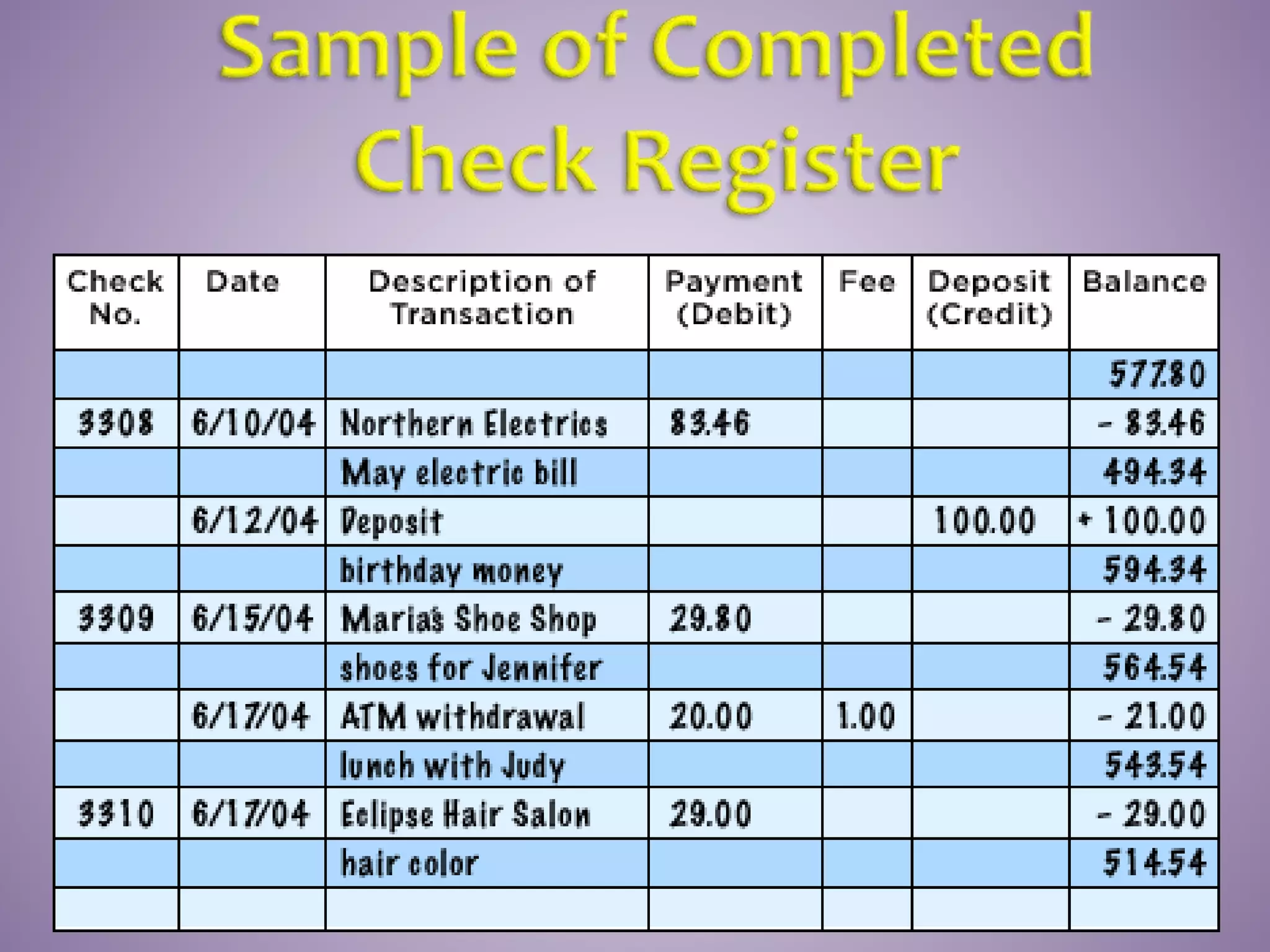
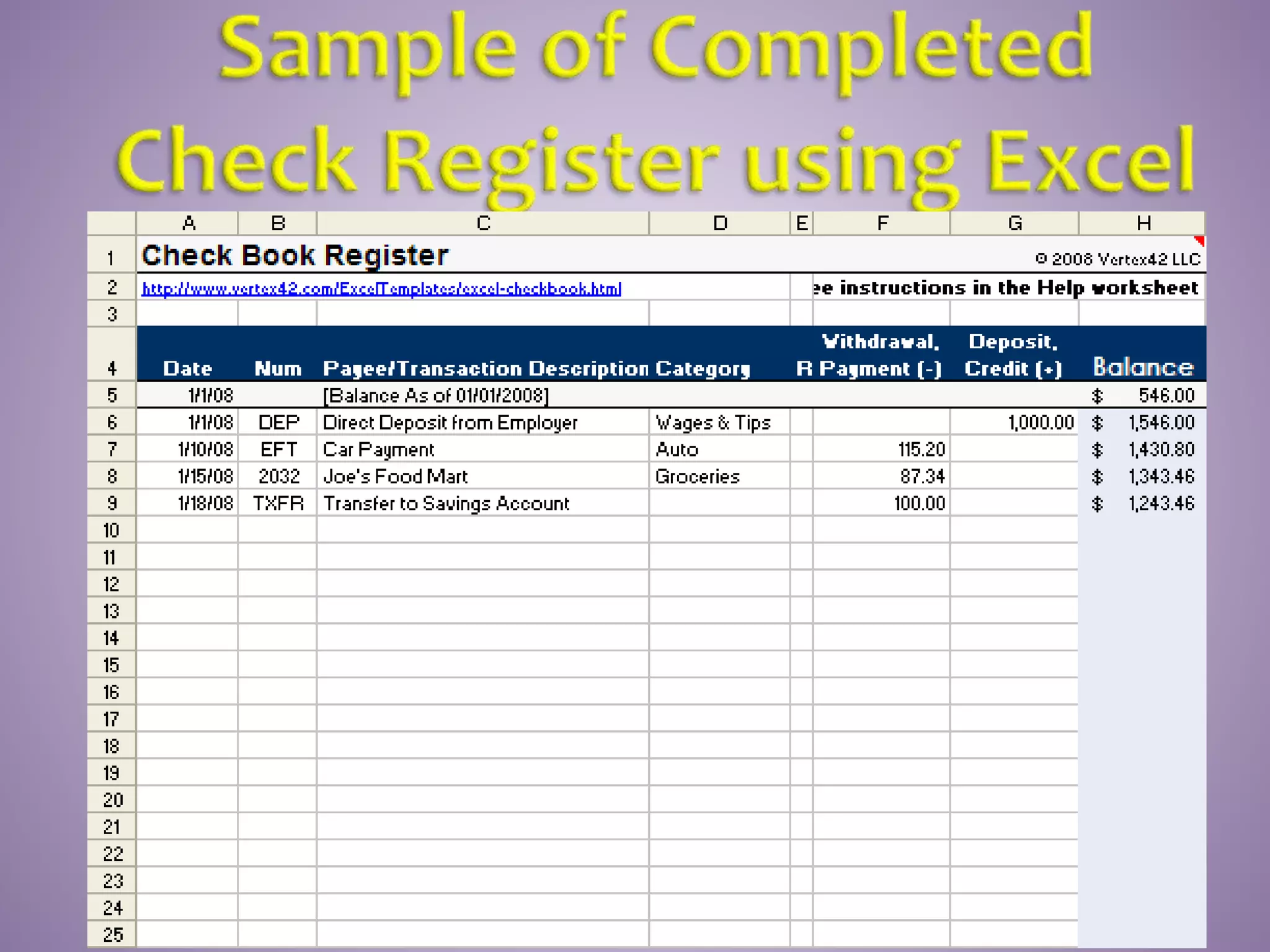
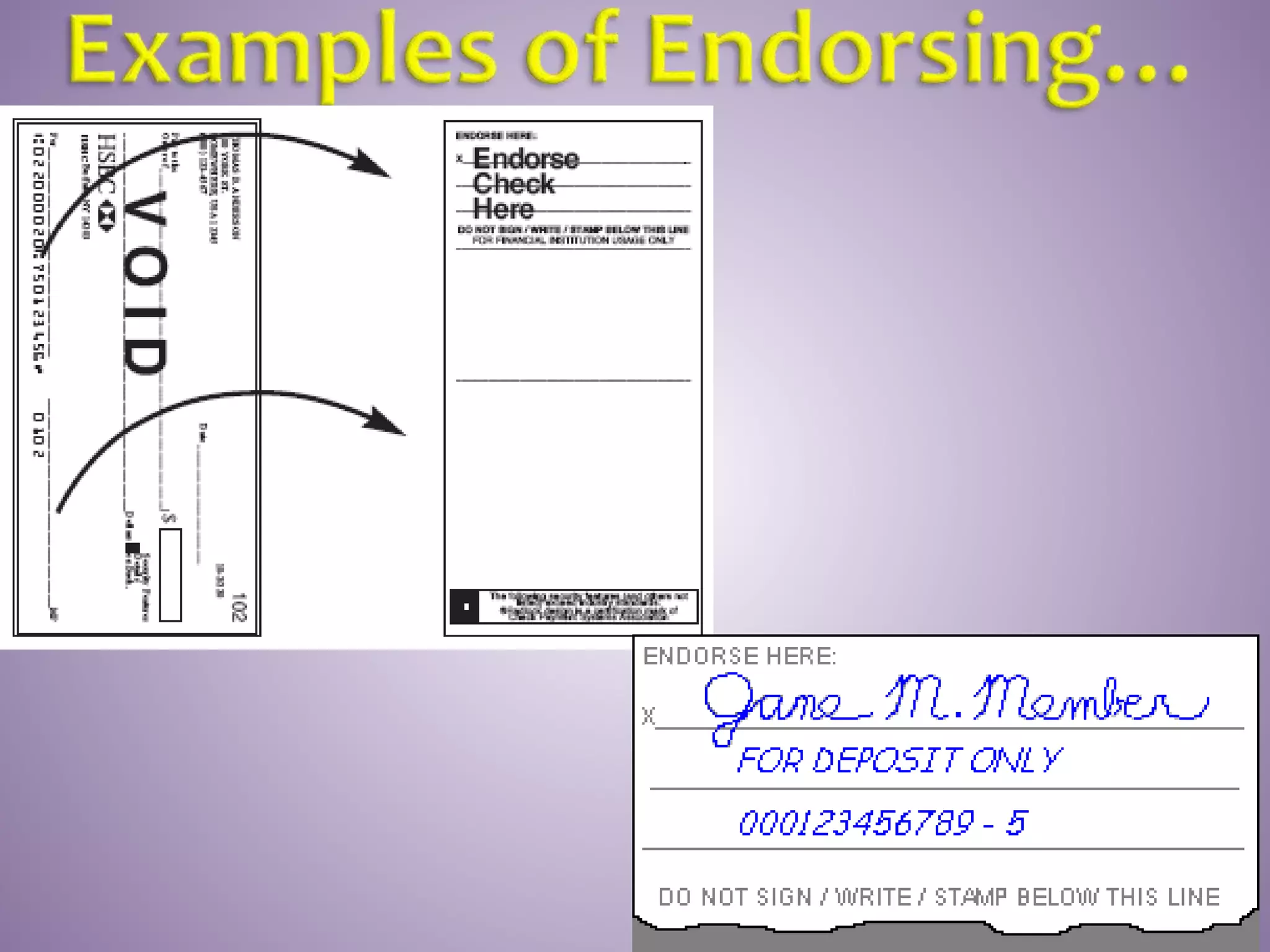
This document provides instructions on how to properly manage and use a checking account. It explains the key parts of a check, how to correctly write checks including spelling out numeric amounts, the importance of avoiding writing checks to cash, how to record checks in a check register, how to reconcile the register with bank statements each month, how to endorse checks, and what overdraft protection is and how it works to protect against insufficient funds.