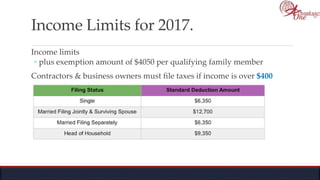
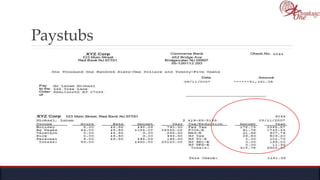
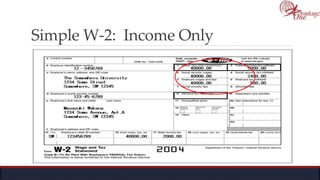
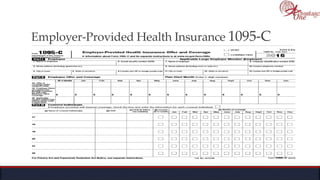
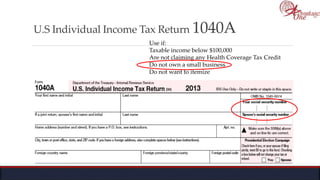
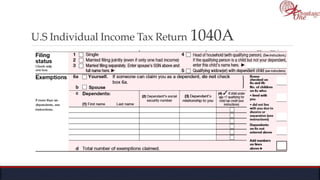
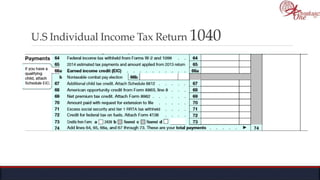
The document outlines the roles and responsibilities of tax professionals, including enrolled agents, who can represent taxpayers before the IRS. It also details the necessary tax information and documents needed for various taxpayer situations, as well as tasks for both individuals and business owners regarding tax preparation and record-keeping. Additionally, it highlights the Taxpayer Bill of Rights, ensuring taxpayers understand their rights in dealing with the IRS.