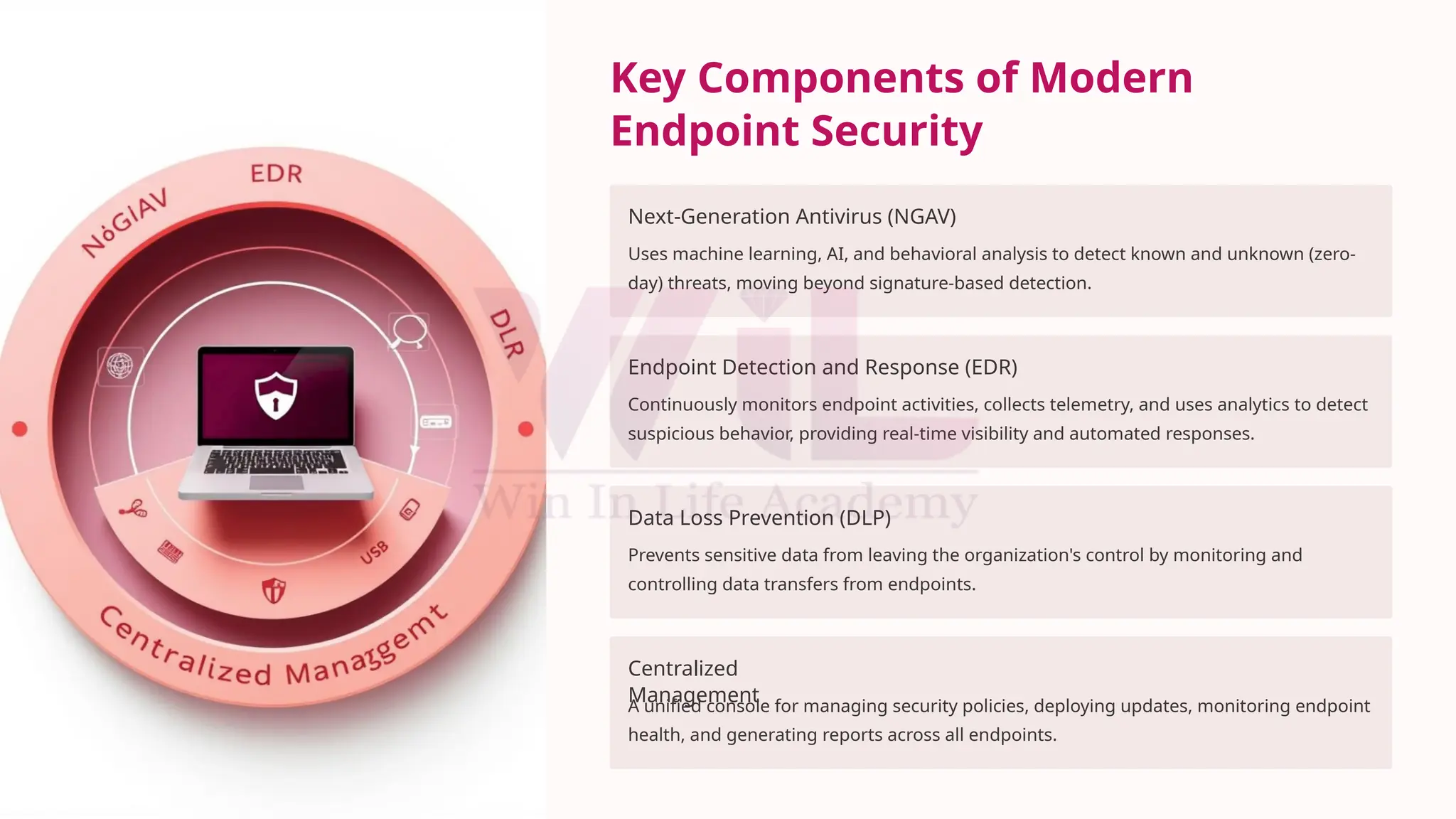
This presentation provides a focused overview of endpoint security within the framework of a Security Operations Center (SOC). It highlights how endpoints—such as laptops, mobile devices, and servers—are prime targets for cyberattacks and how SOC teams monitor, protect, and respond to threats targeting these endpoints. The content covers endpoint detection and response (EDR), antivirus solutions, behavioral monitoring, and the integration of endpoint data into SIEM systems to enhance threat visibility and rapid incident response.