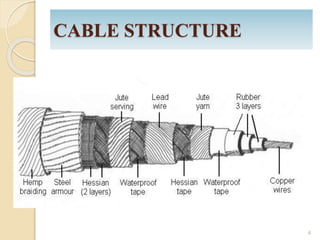
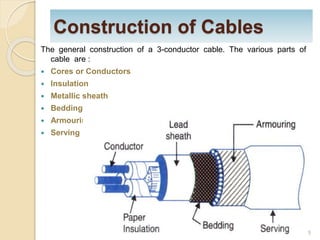
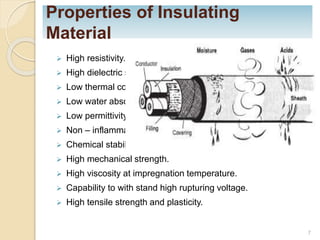
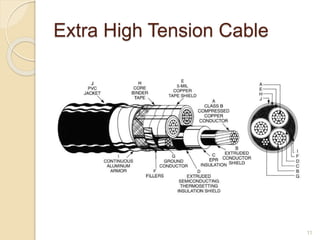
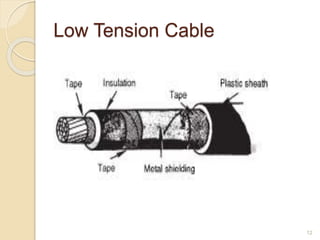
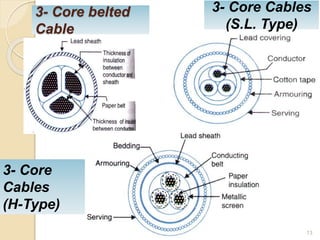
This document provides information on underground cables, including their construction, classification, insulating materials, and types. It discusses how underground cables consist of conductors covered with insulating material and a protective covering to reduce interference from external disturbances. The general construction of a 3-conductor cable is described, including its cores or conductors, insulation, metallic sheath, bedding, armouring, and serving. Various types of cables are classified based on voltage levels. Key properties and examples of insulating materials used in cables are also outlined, along with the advantages and disadvantages of underground cables compared to overhead systems.