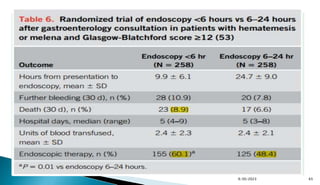
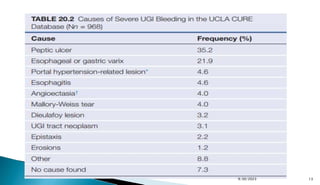
This document summarizes a presentation on the epidemiology, definition, etiologies, risk stratification, and management of upper gastrointestinal bleeding (UGIB). Some key points:
- UGIB accounts for 50% of GI bleeding admissions and has a mortality rate of 5-10% despite medical advances.
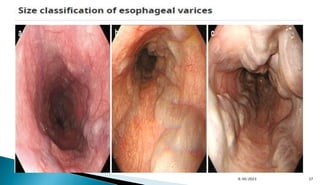
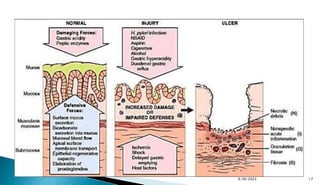
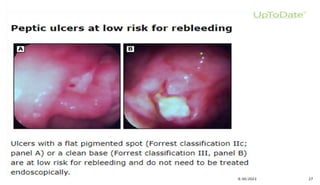
- Peptic ulcer disease, esophageal/gastric varices, Mallory-Weiss tears, and Dieulafoy's lesions are common causes.
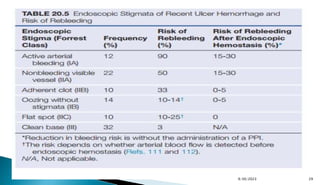
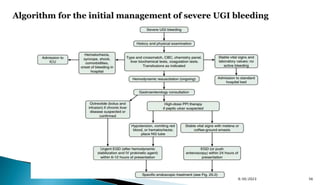
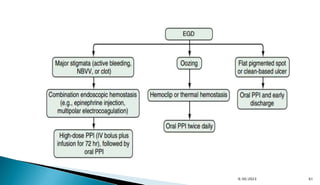
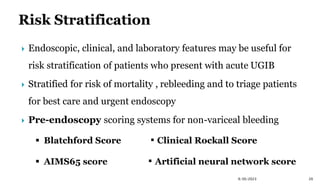
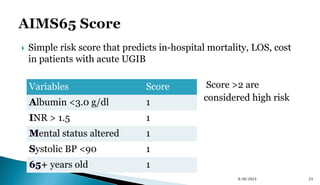
- Risk scoring systems like Glasgow-Blatchford and Rockall are used to predict outcomes and guide management. High-risk stigmata on endoscopy indicate need for intervention.
- Prevention focuses on H. pylori



















![ Passed through the working channel of an endoscope & applied to an
ulcer to determine if blood flow is present beneath the ulcer base.
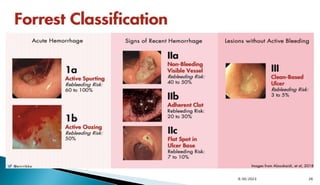
DEP has been utilized to risk stratify patients with SRH into:
High risk: active arterial bleeding [FIA], NBVV [FIIA] &
adherent clot [FIIB]
Intermediate risk: oozing bleeding [FIB], & flat spots [FIIC]
Low risk: clean ulcer base [FIII])
9/30/2023 28](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ugib-seminar-230930111023-f466b58a/85/UGIB-Seminar-pptx-28-320.jpg)