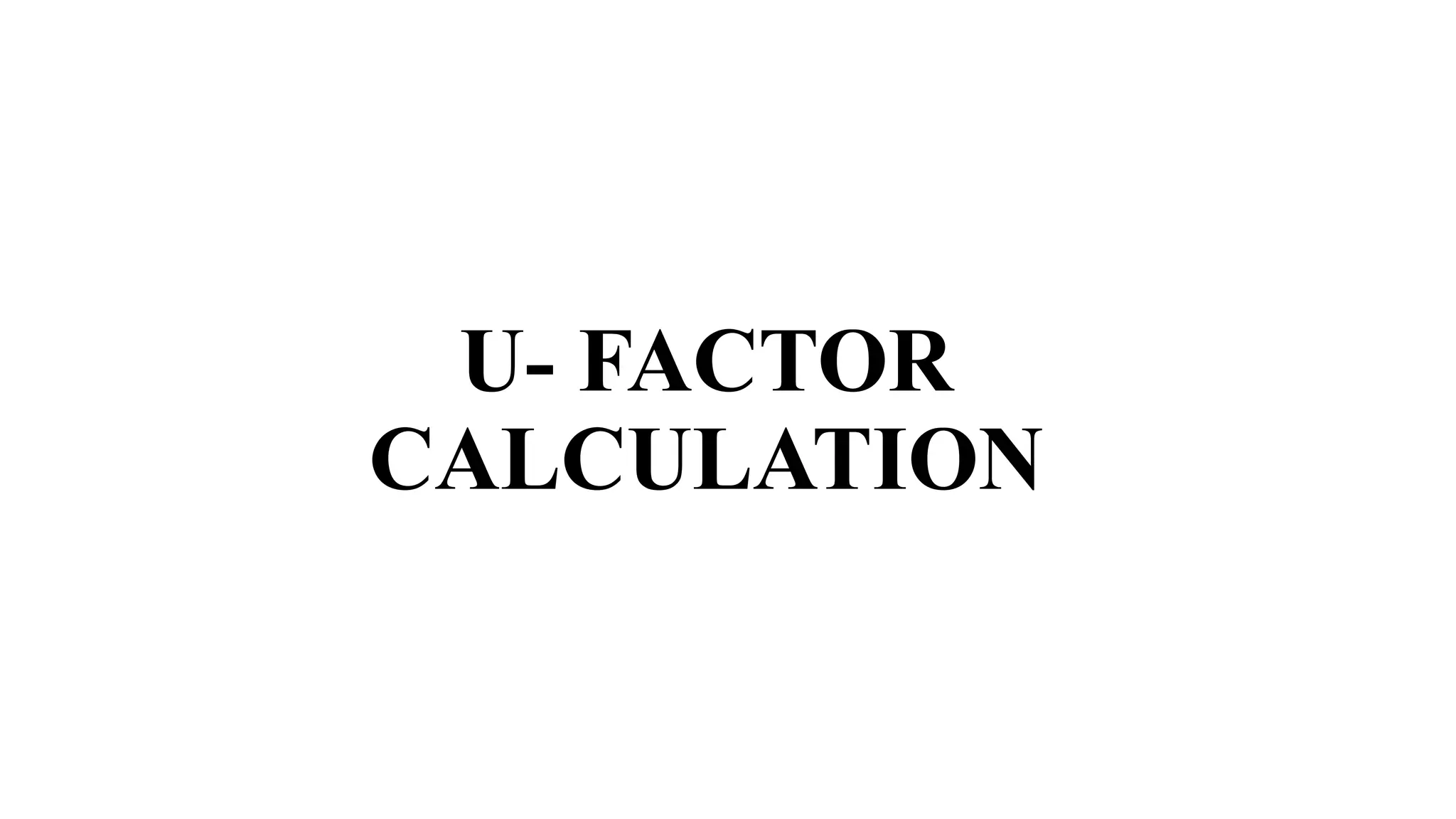
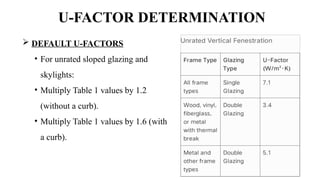
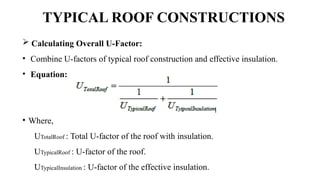
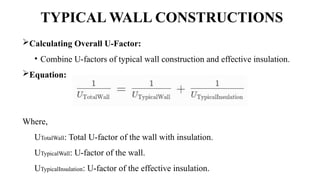
The u-factor quantifies the thermal transmittance of materials, reflecting how much heat passes through a square meter per degree Celsius temperature difference. A lower u-factor indicates better insulation, making it essential for evaluating and selecting energy-efficient building components like windows and walls. Calculations of u-factor consider various factors including material properties and environmental conditions, following specific standards outlined in ISO 15099.