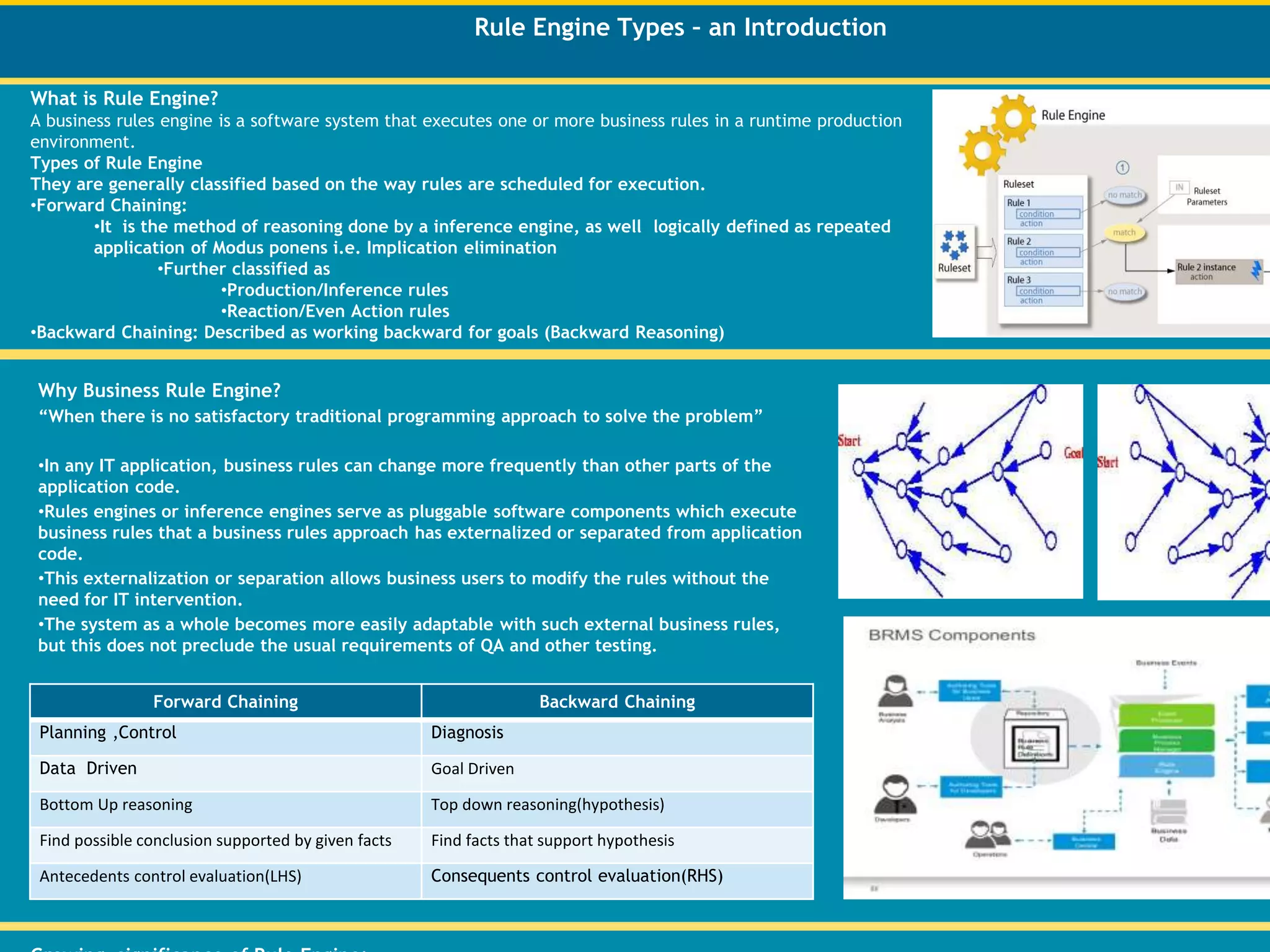
A rule engine is a software system that executes business rules in a production environment. There are two main types of rule engines: forward chaining, which repeatedly applies rules to infer new facts from existing facts, and backward chaining, which works backwards from goals to find facts that support those goals. Business rule engines are useful when traditional programming cannot easily adapt to changing business rules, as they allow non-technical users to modify rules without requiring code changes.