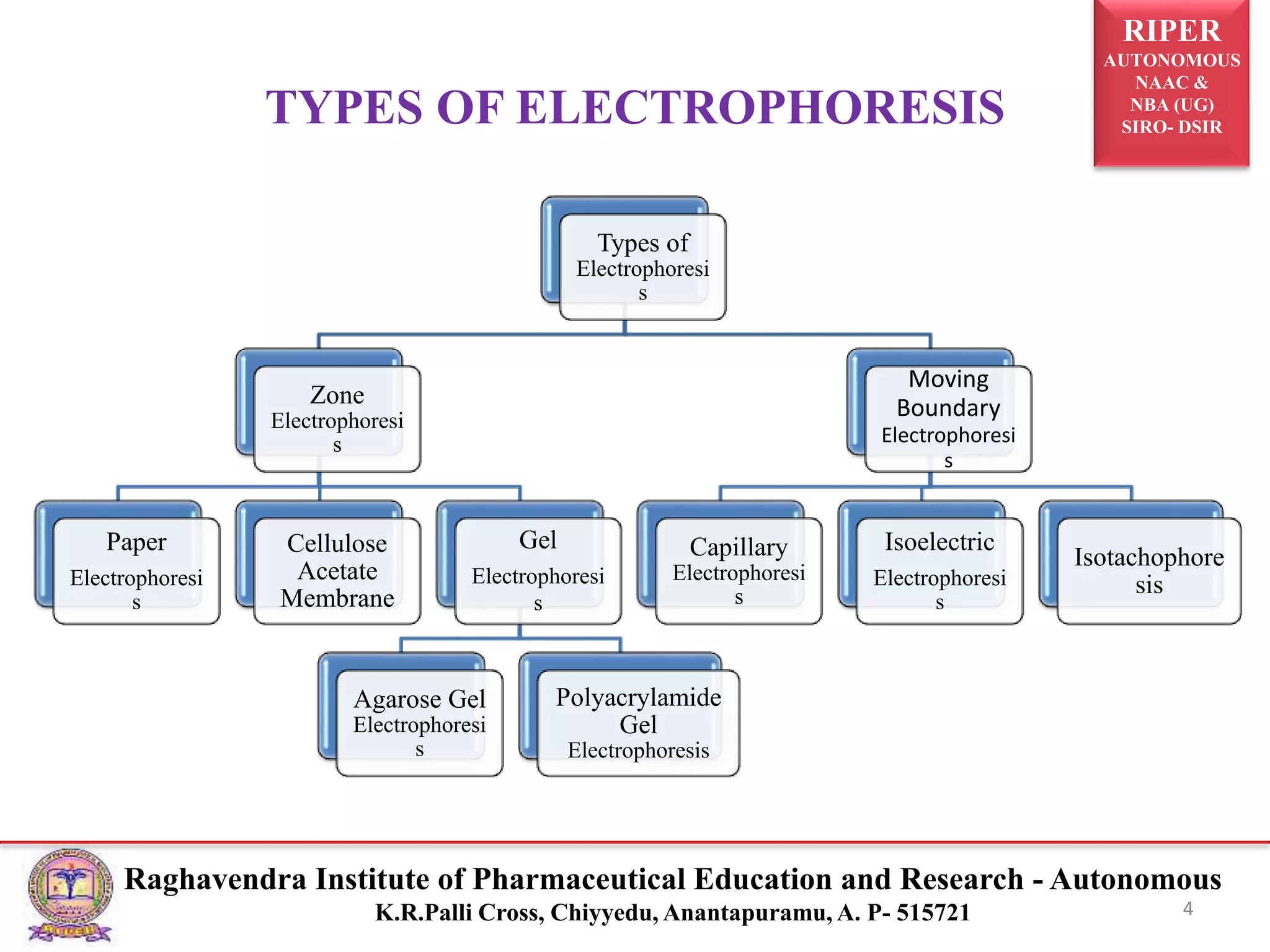
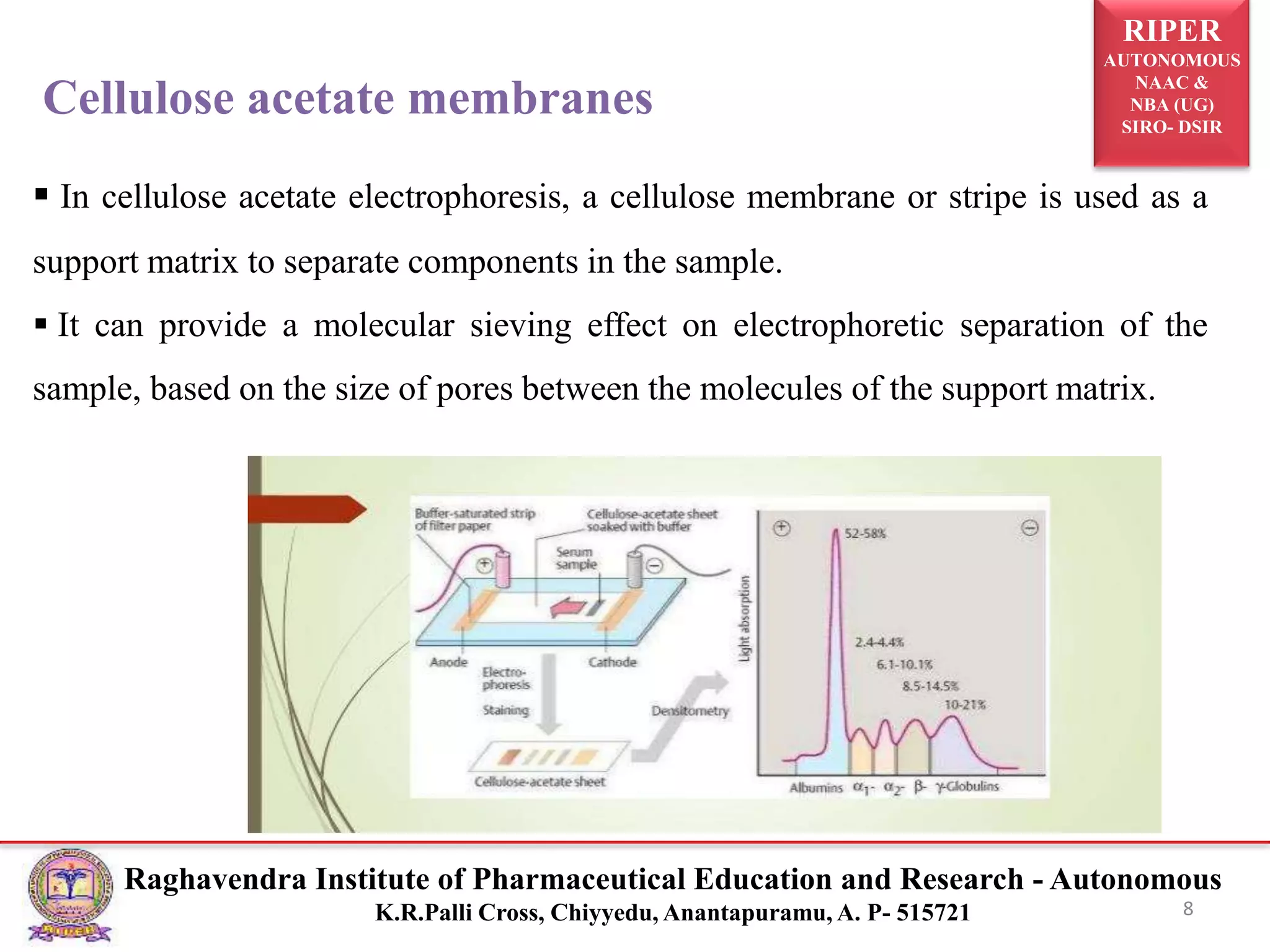
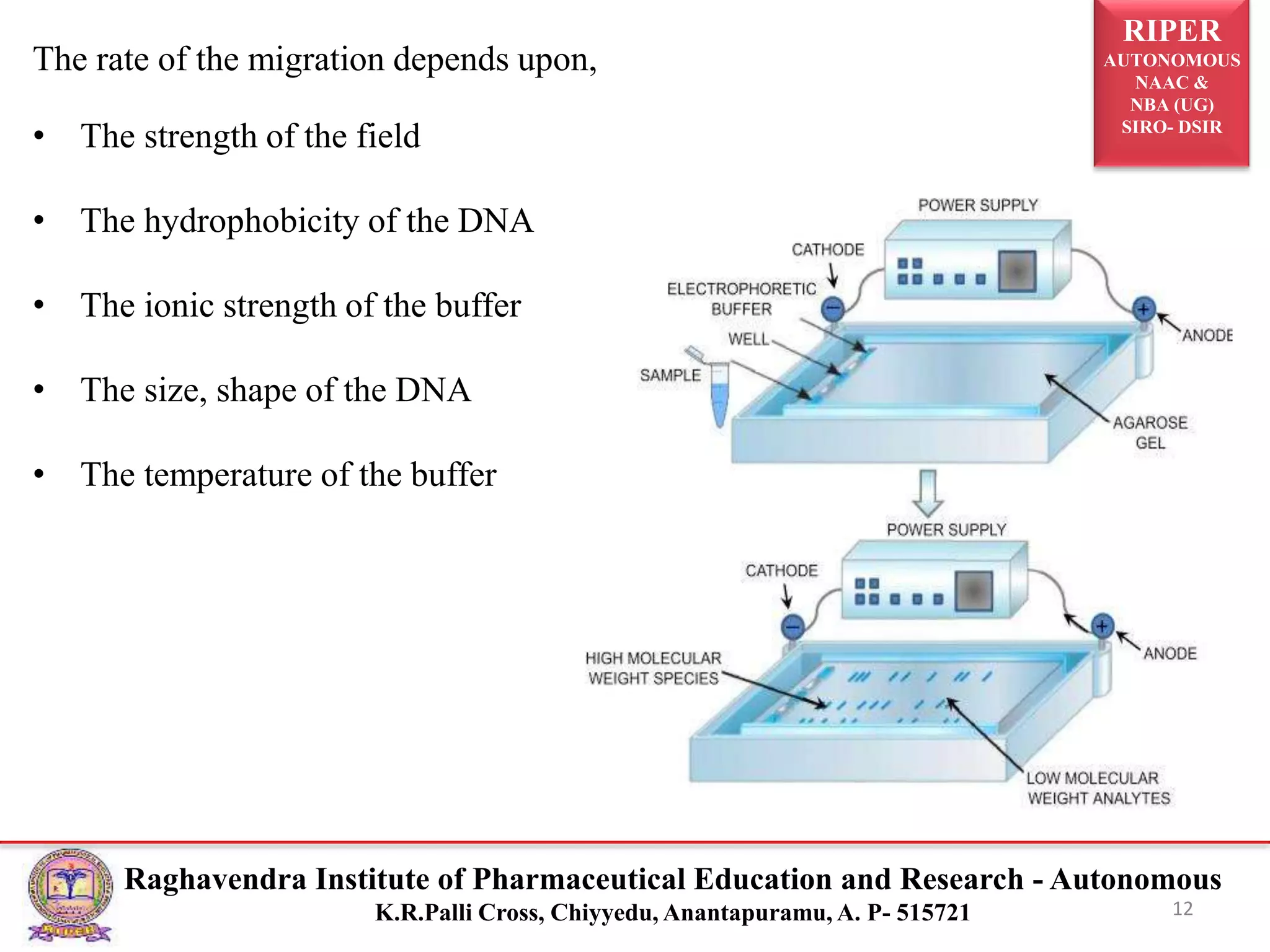
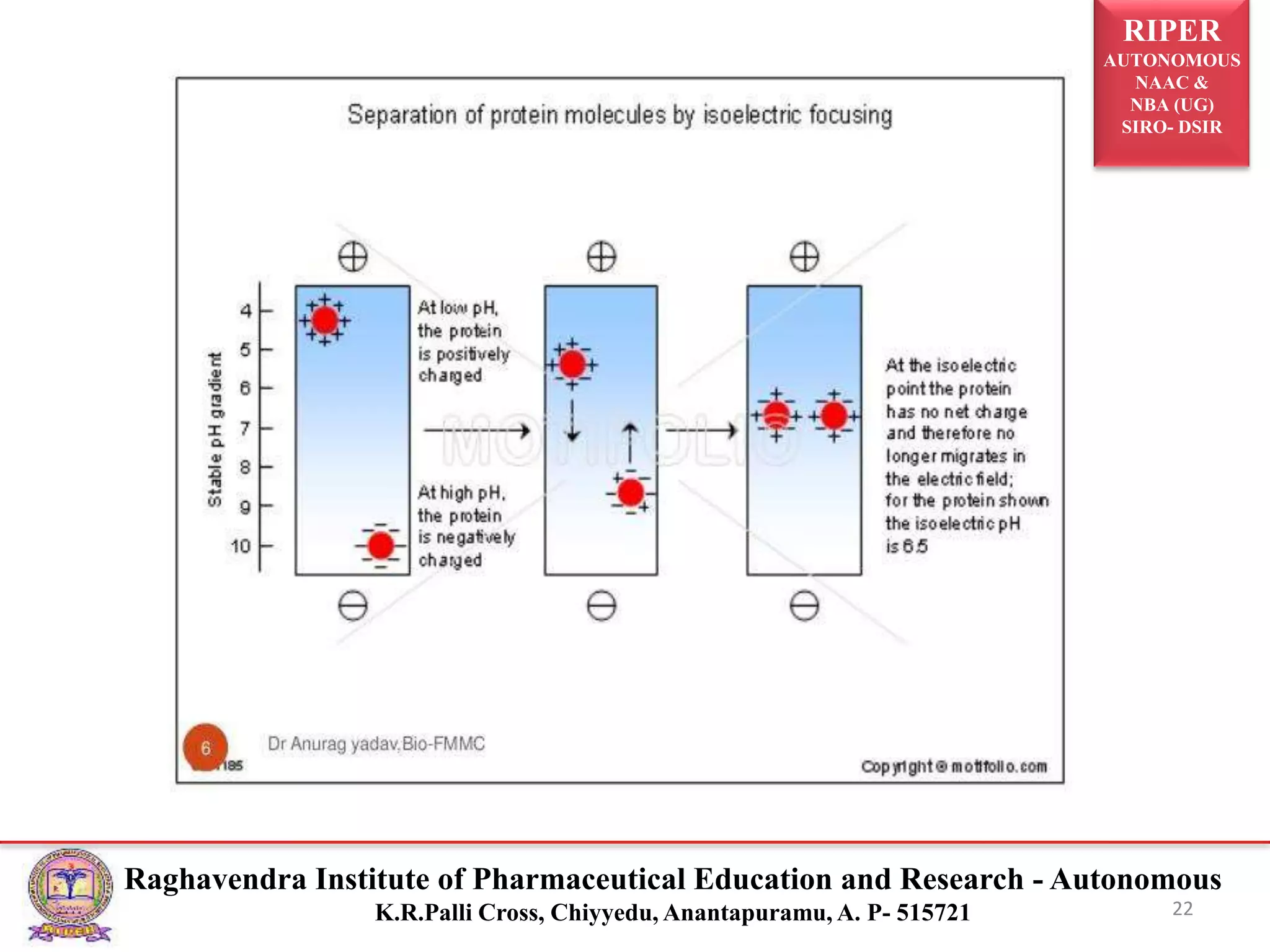
The document presents a seminar on electrophoresis as part of the M. Pharmacy program, detailing various types and techniques, including zone electrophoresis, gel electrophoresis, and capillary electrophoresis. It explains the principles, applications, and methods of separation for different charged molecules, along with their relevance in molecular genetics and disease diagnosis. Key references and educational context are also provided.