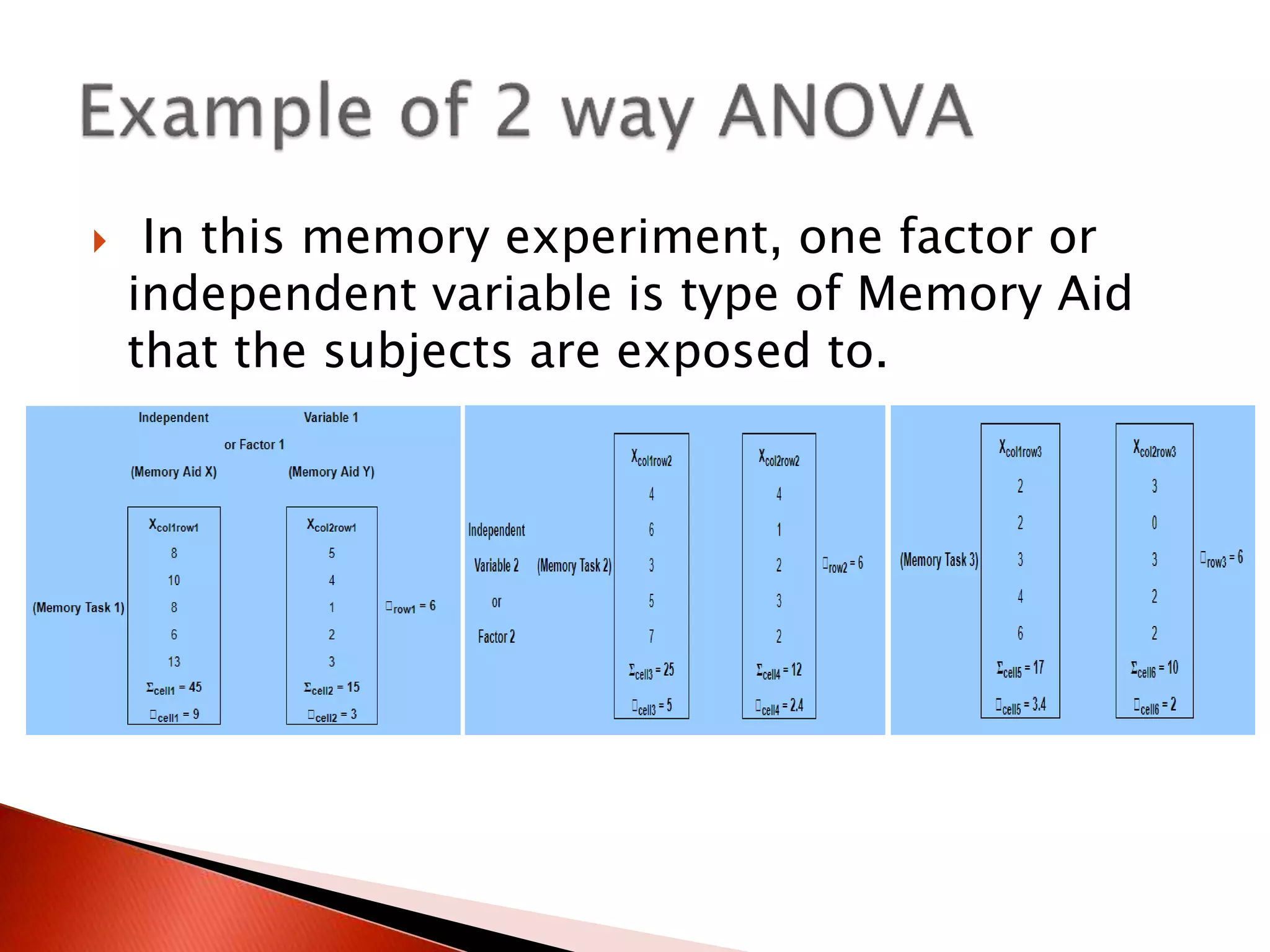
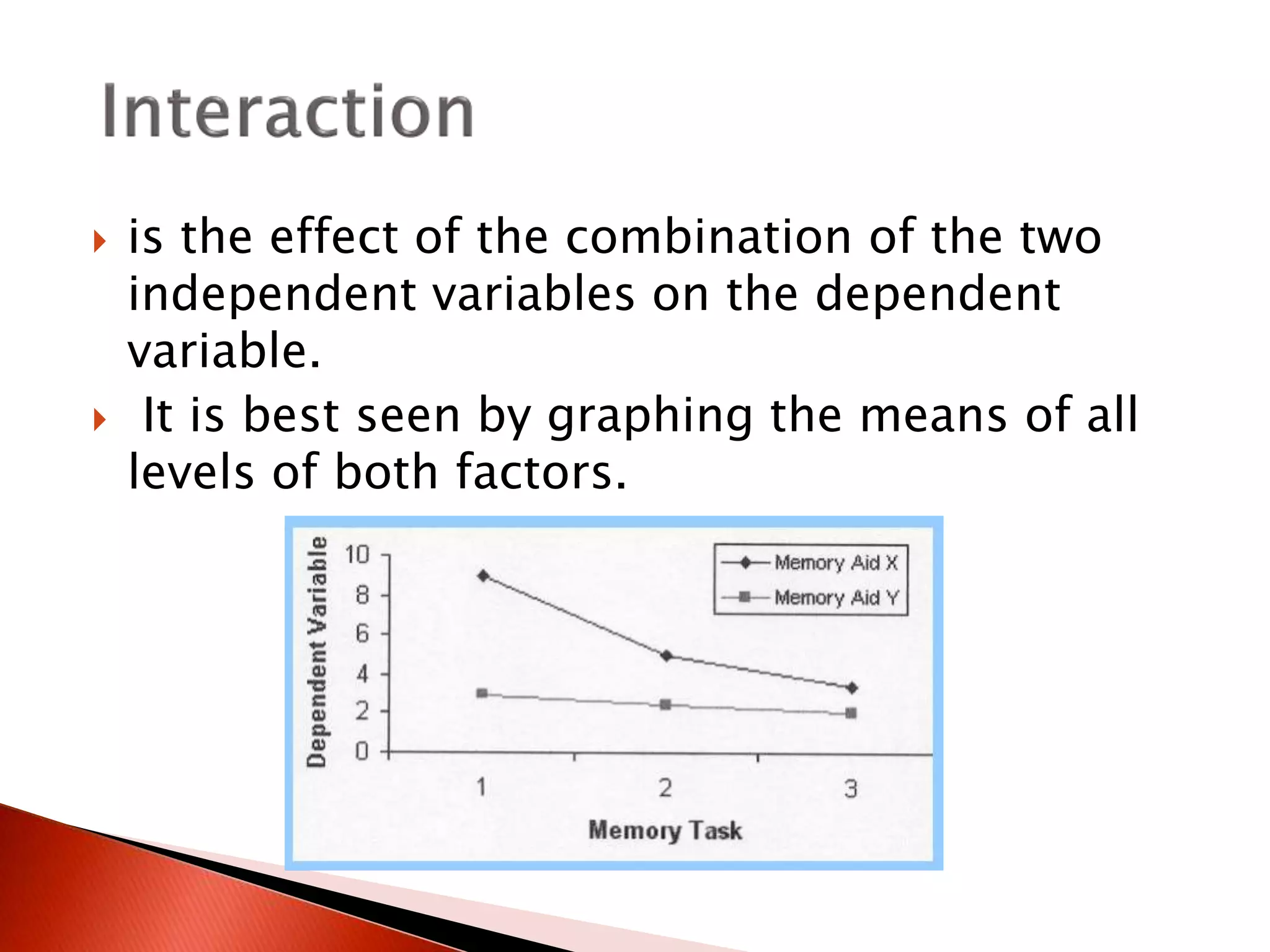
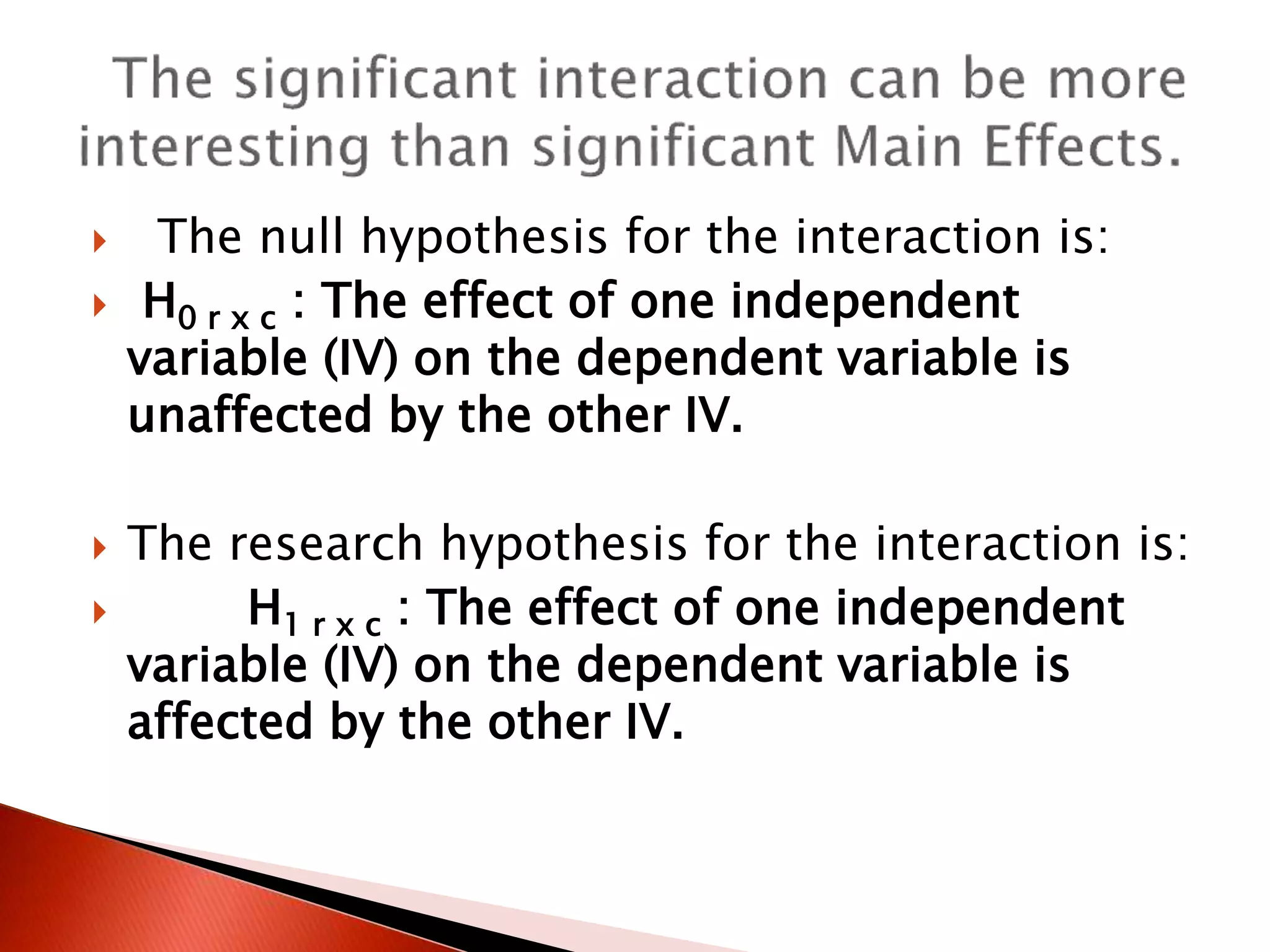
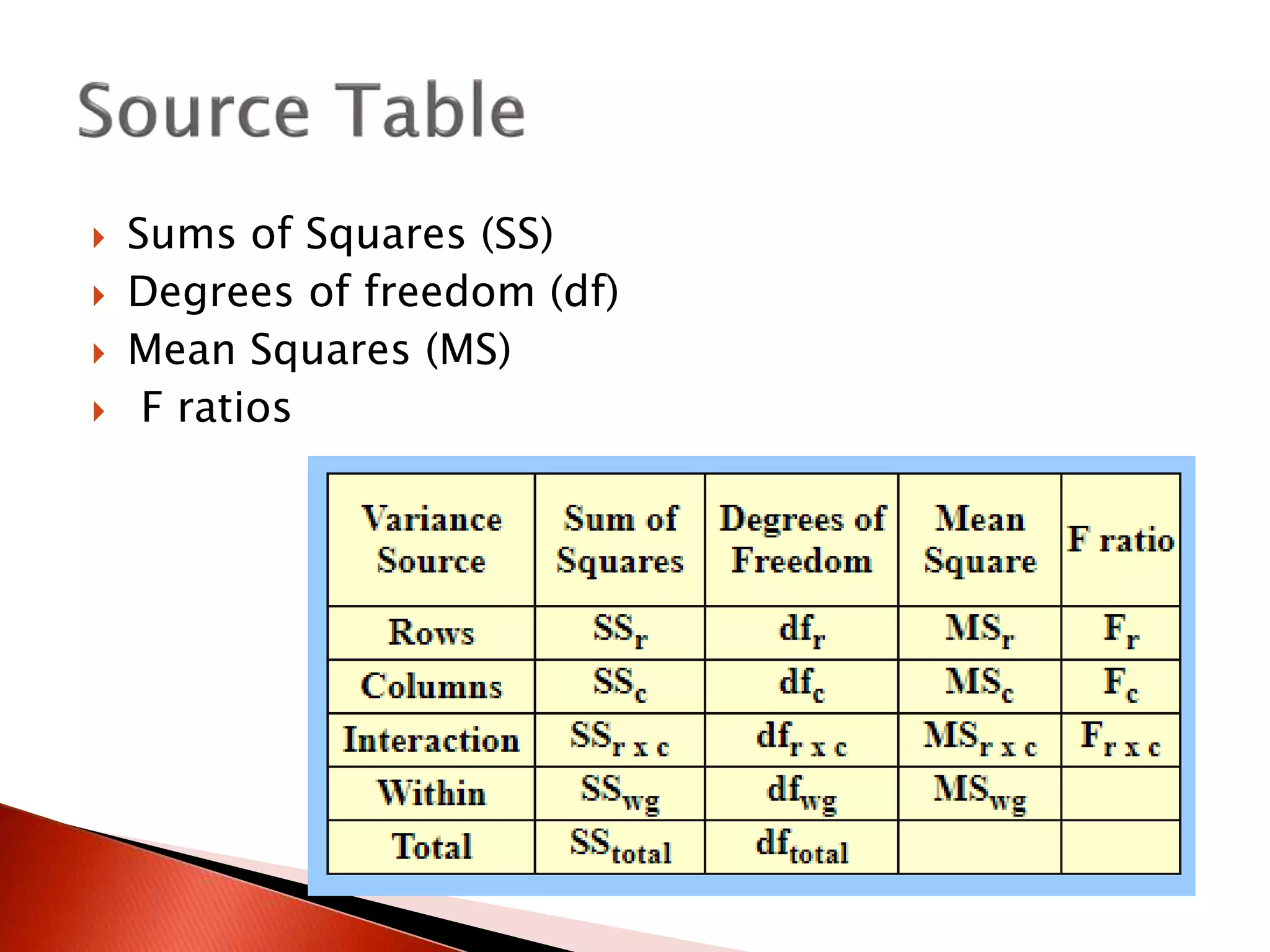
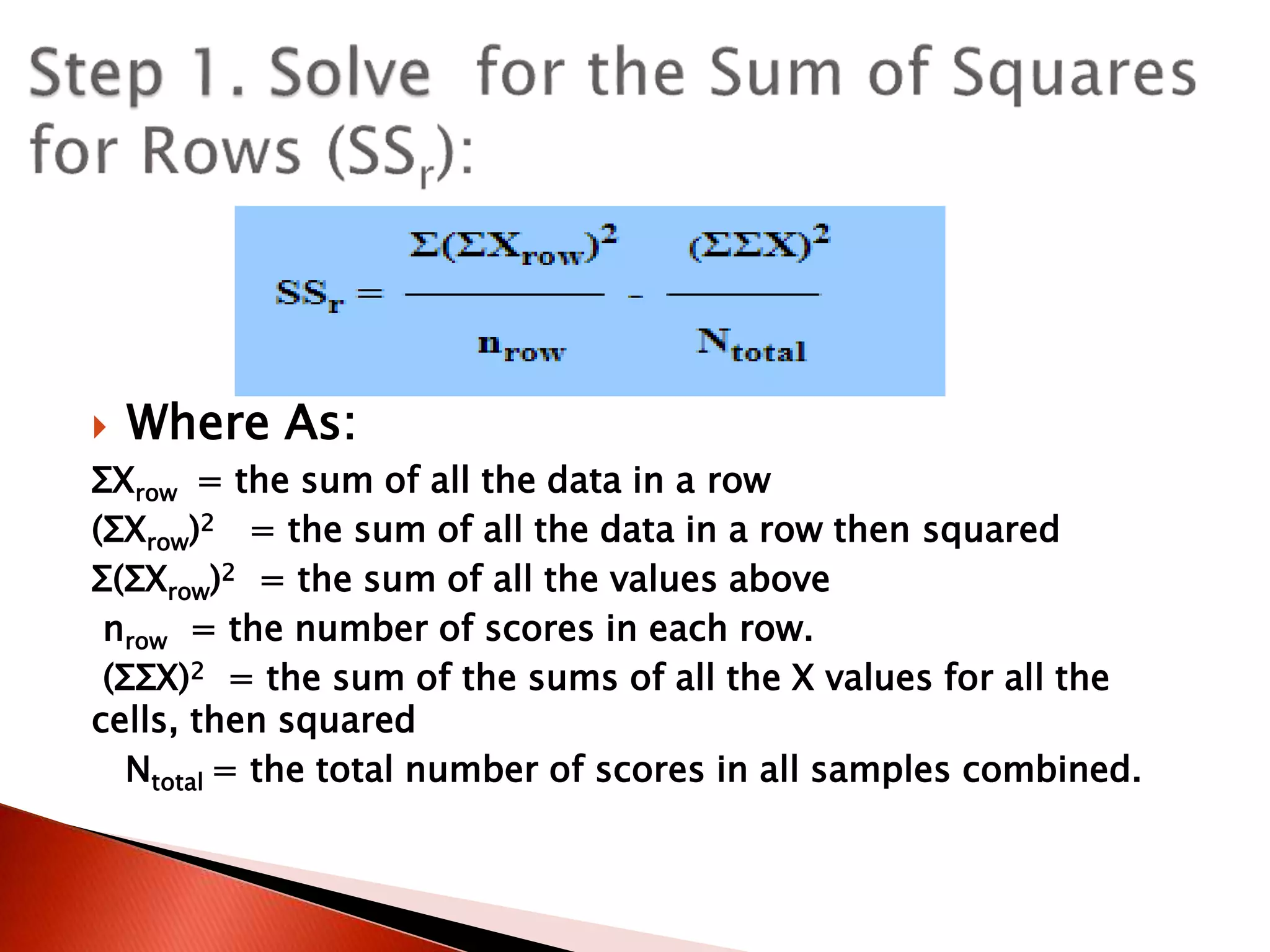
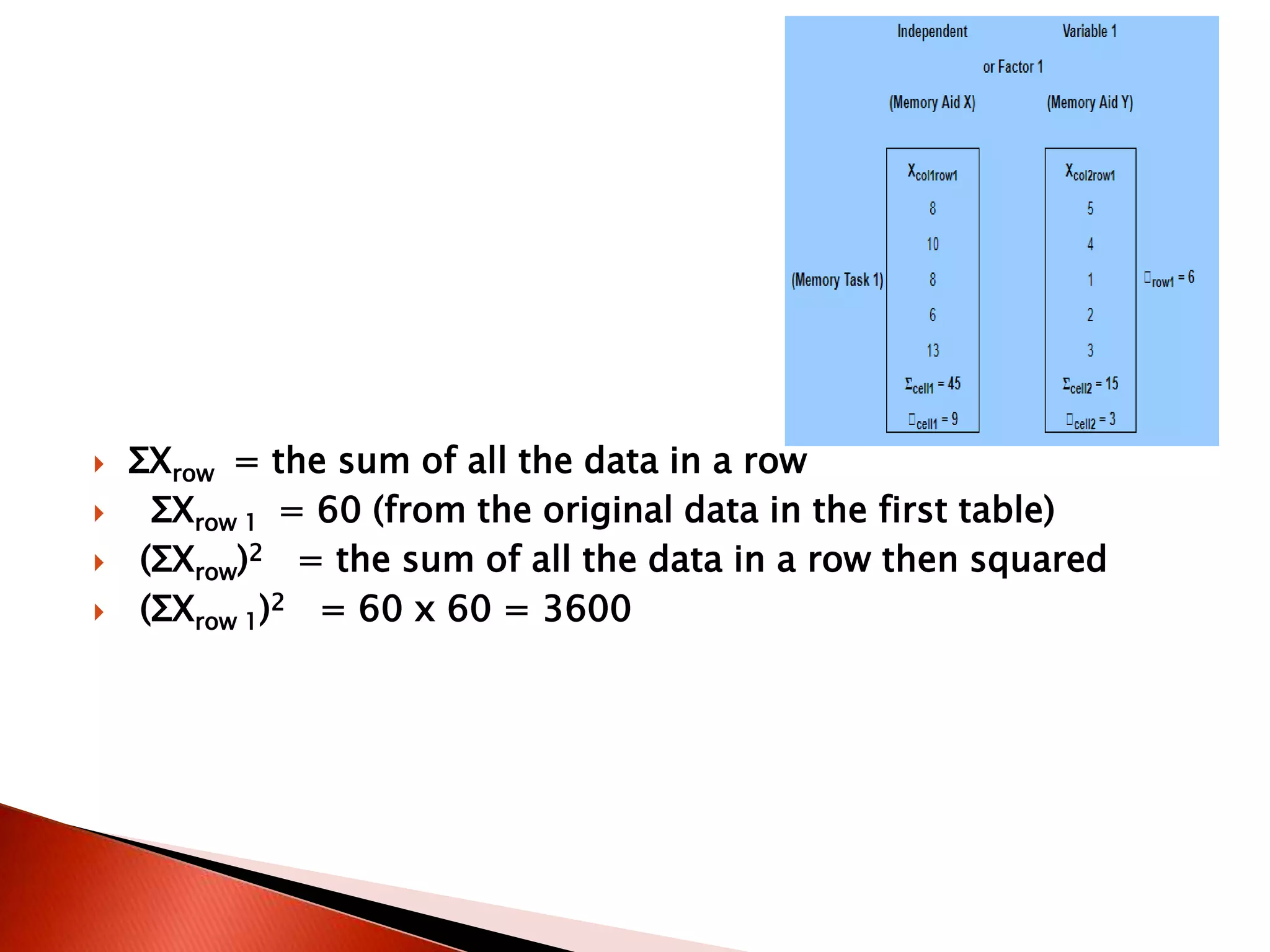
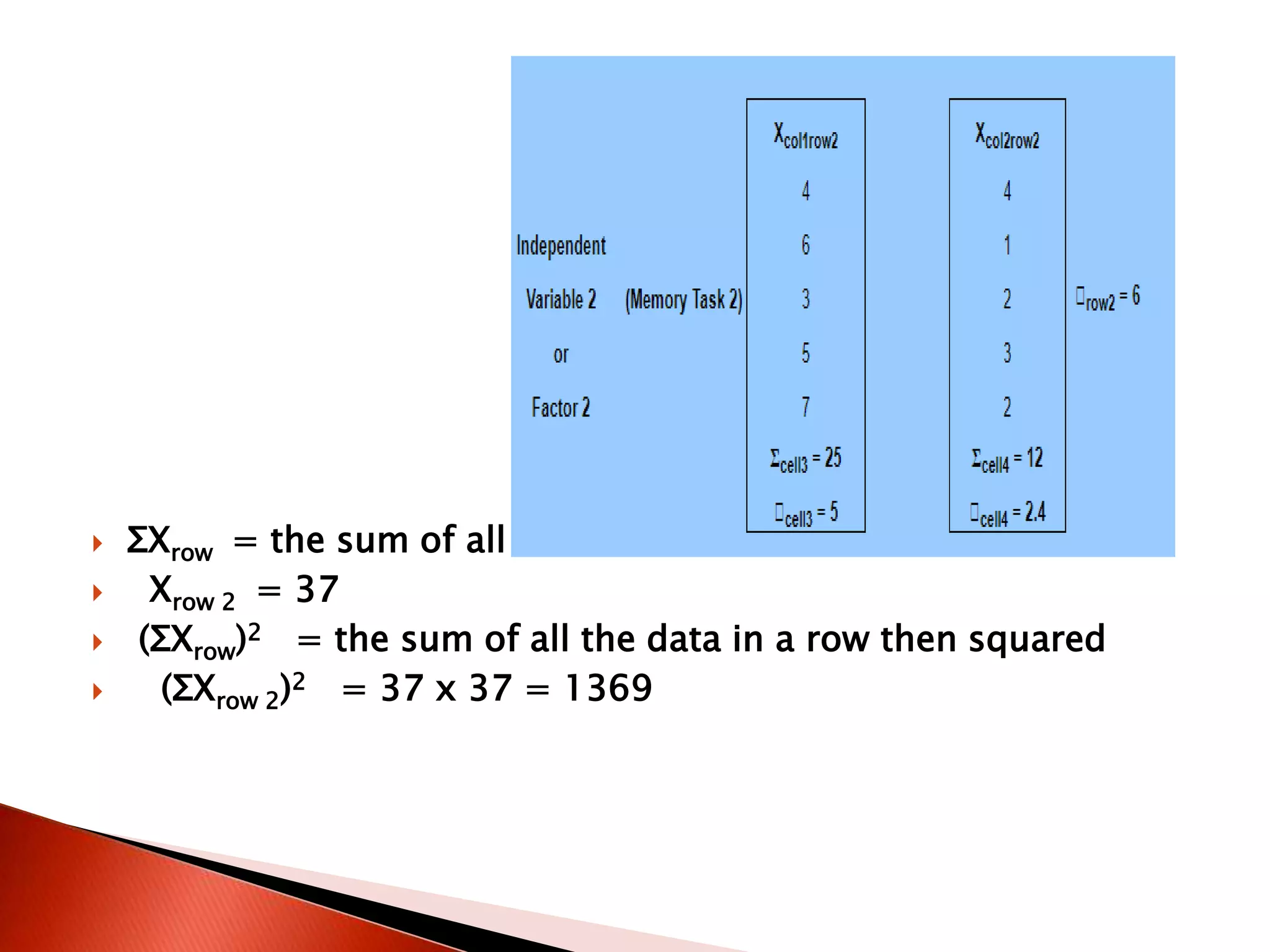
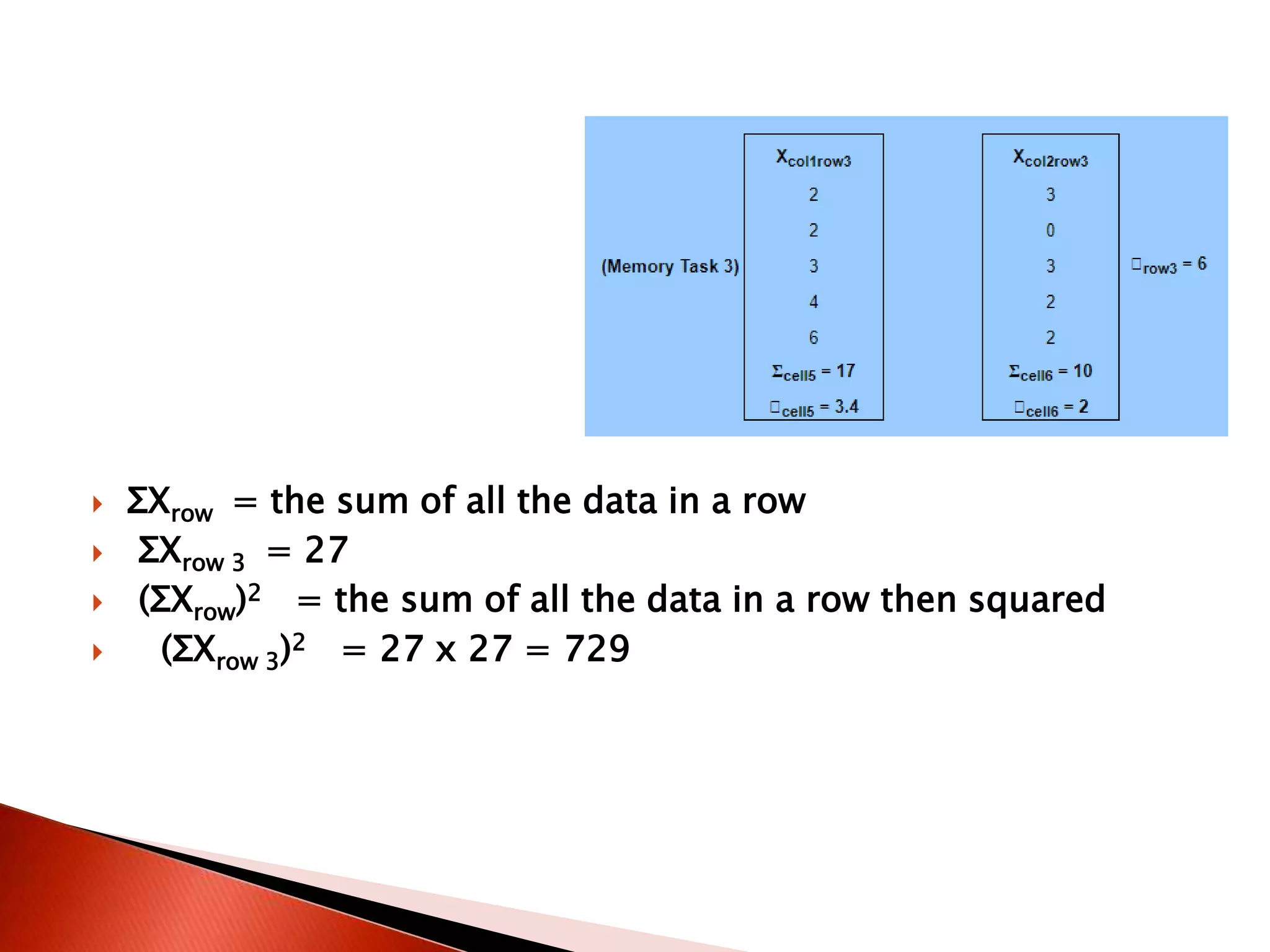
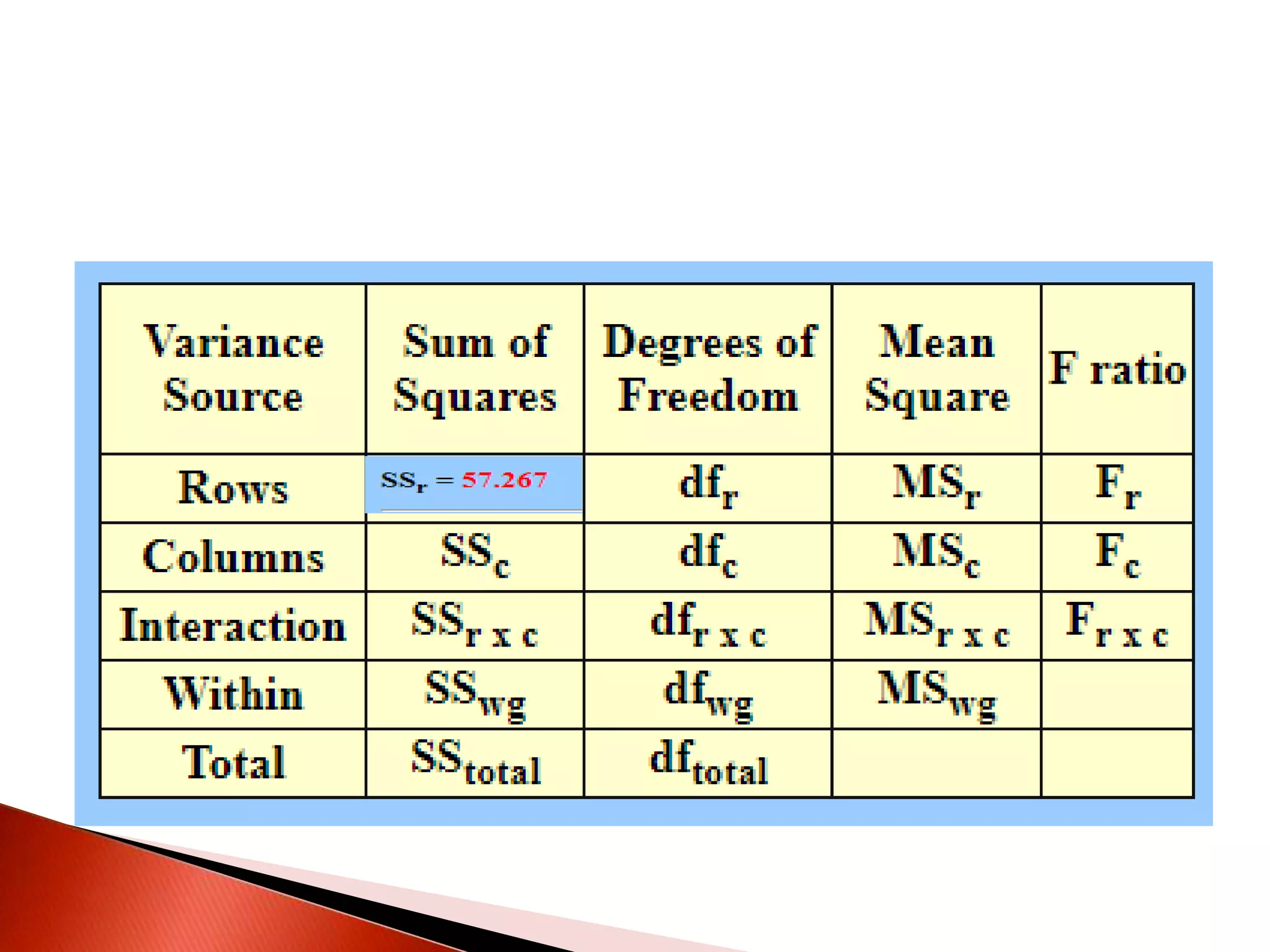
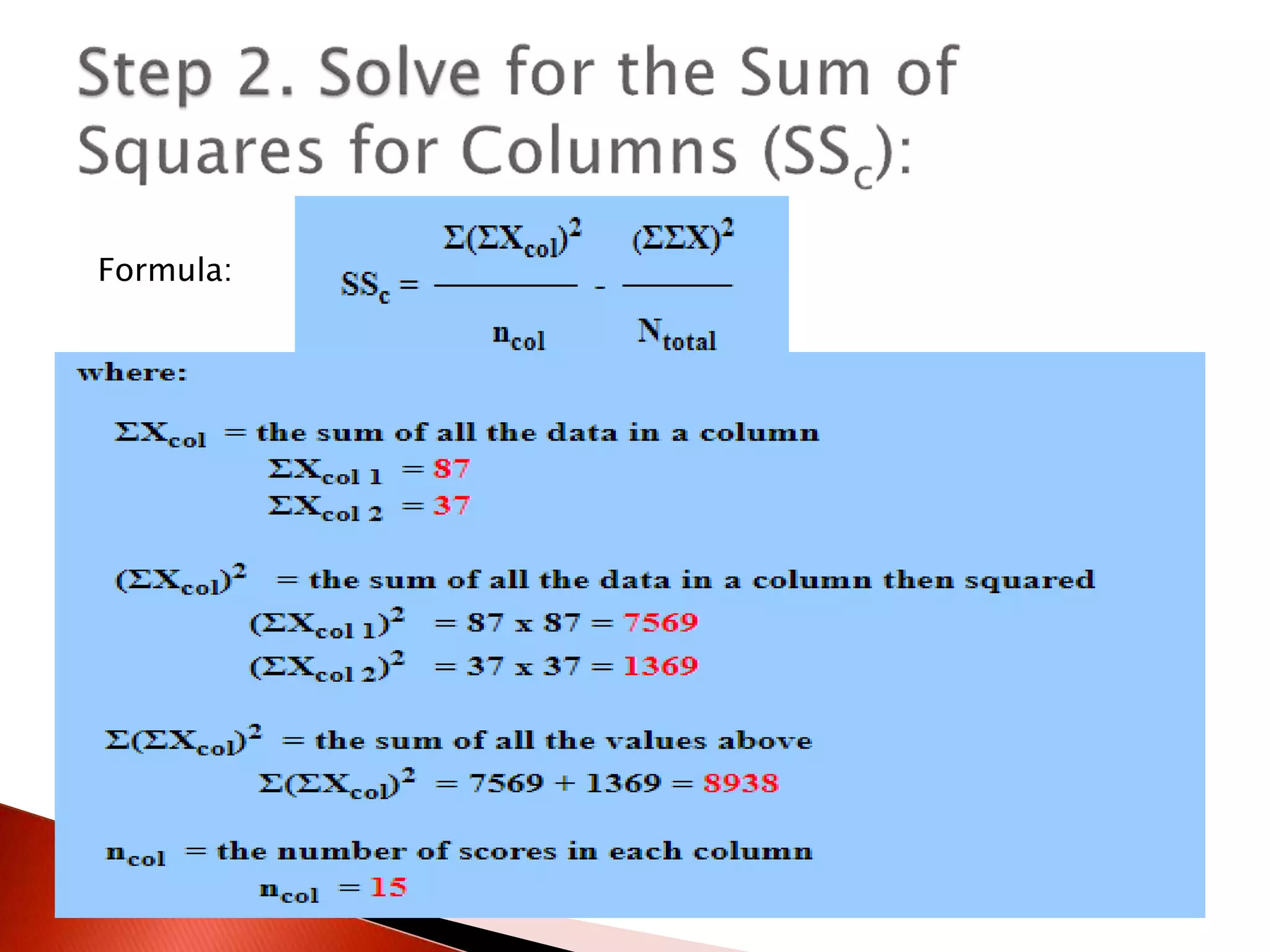
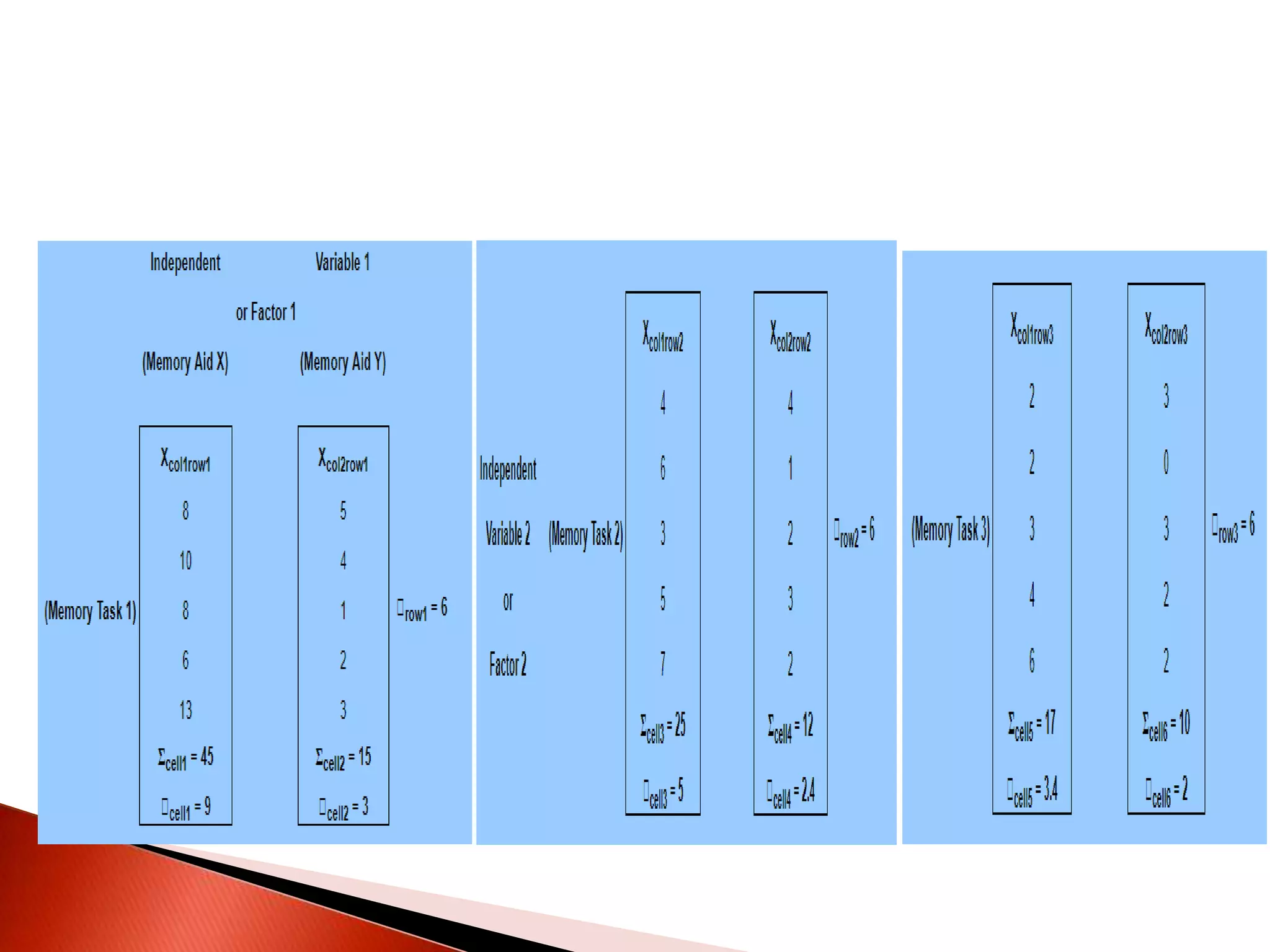
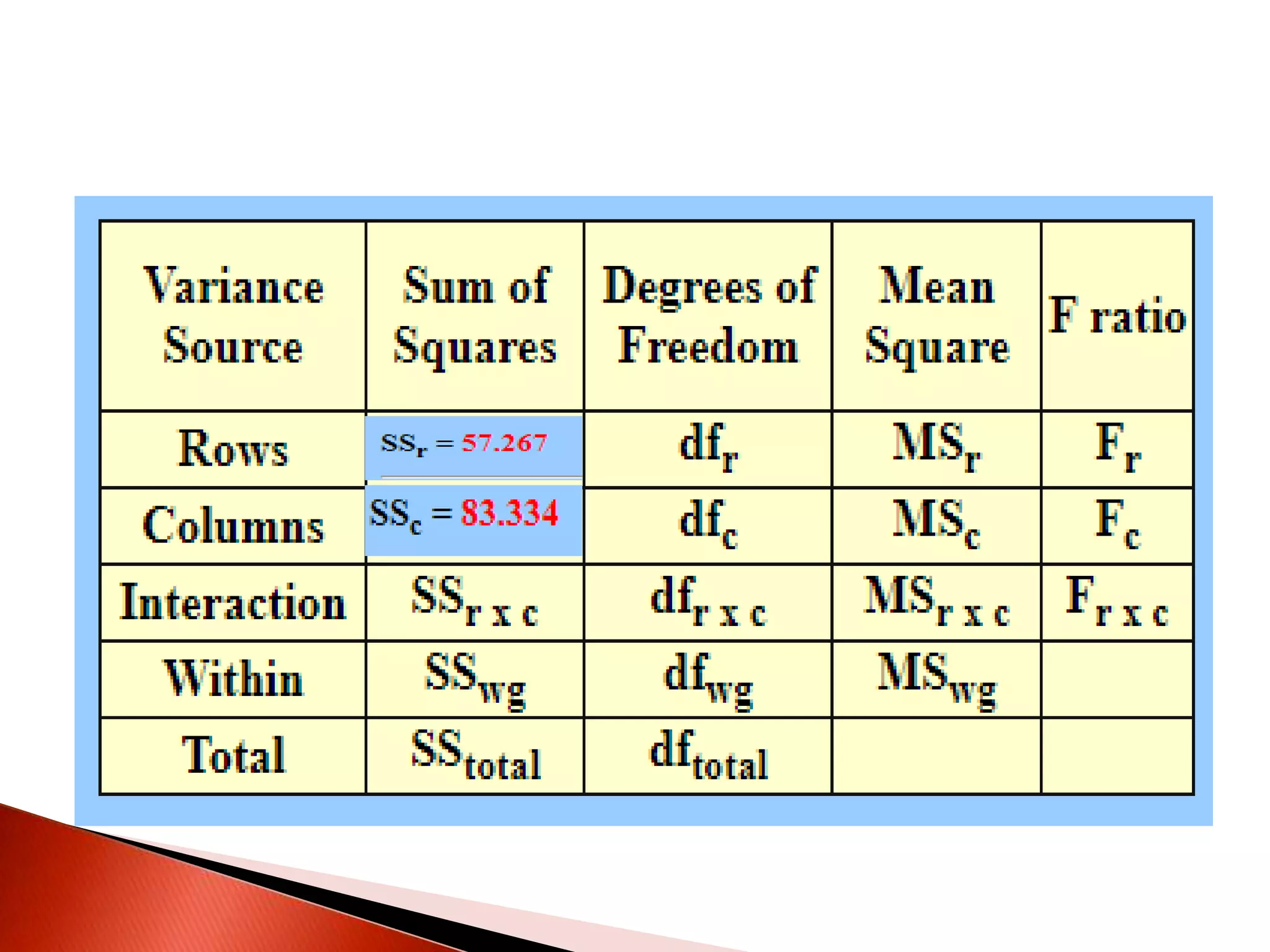
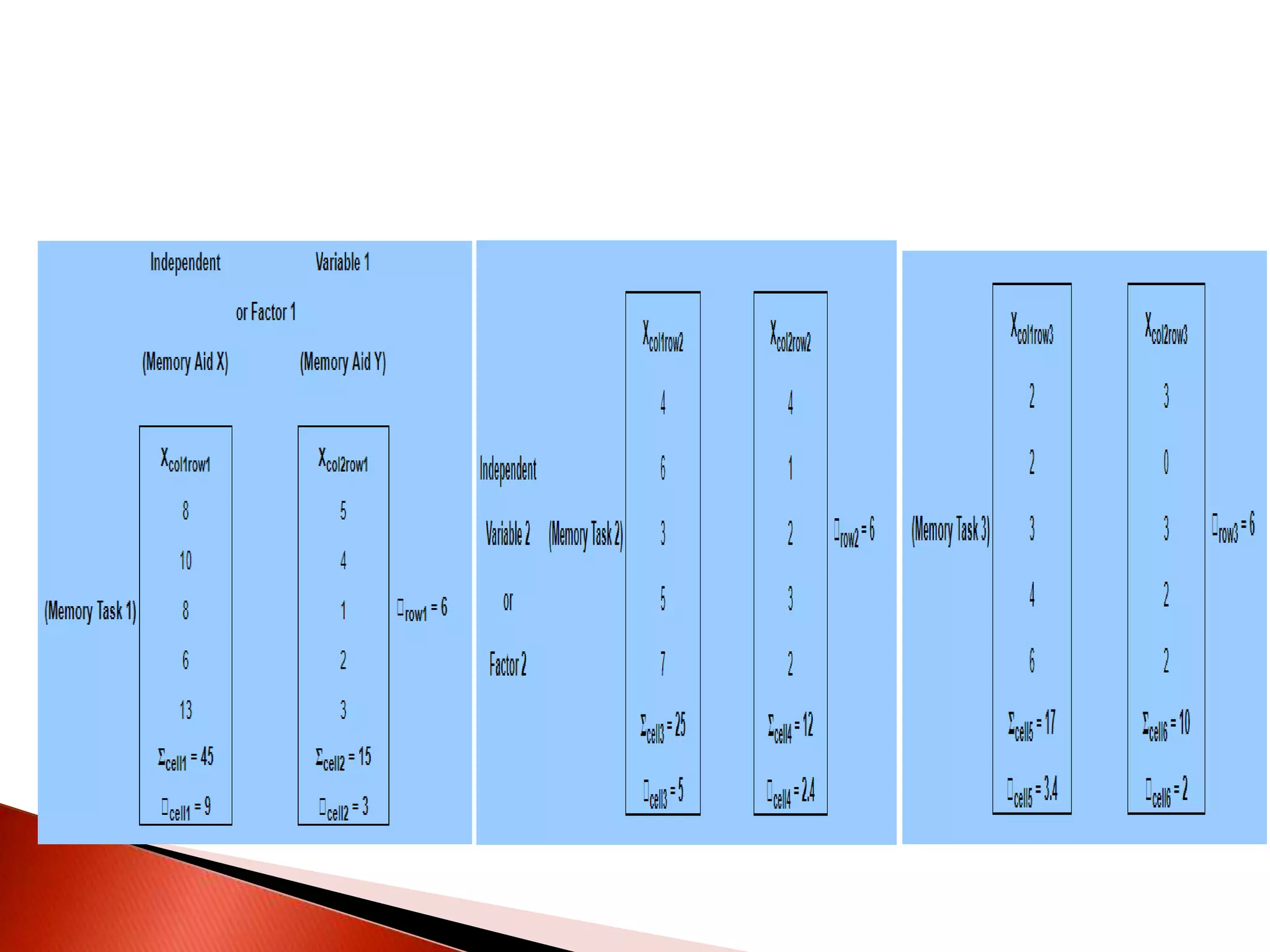
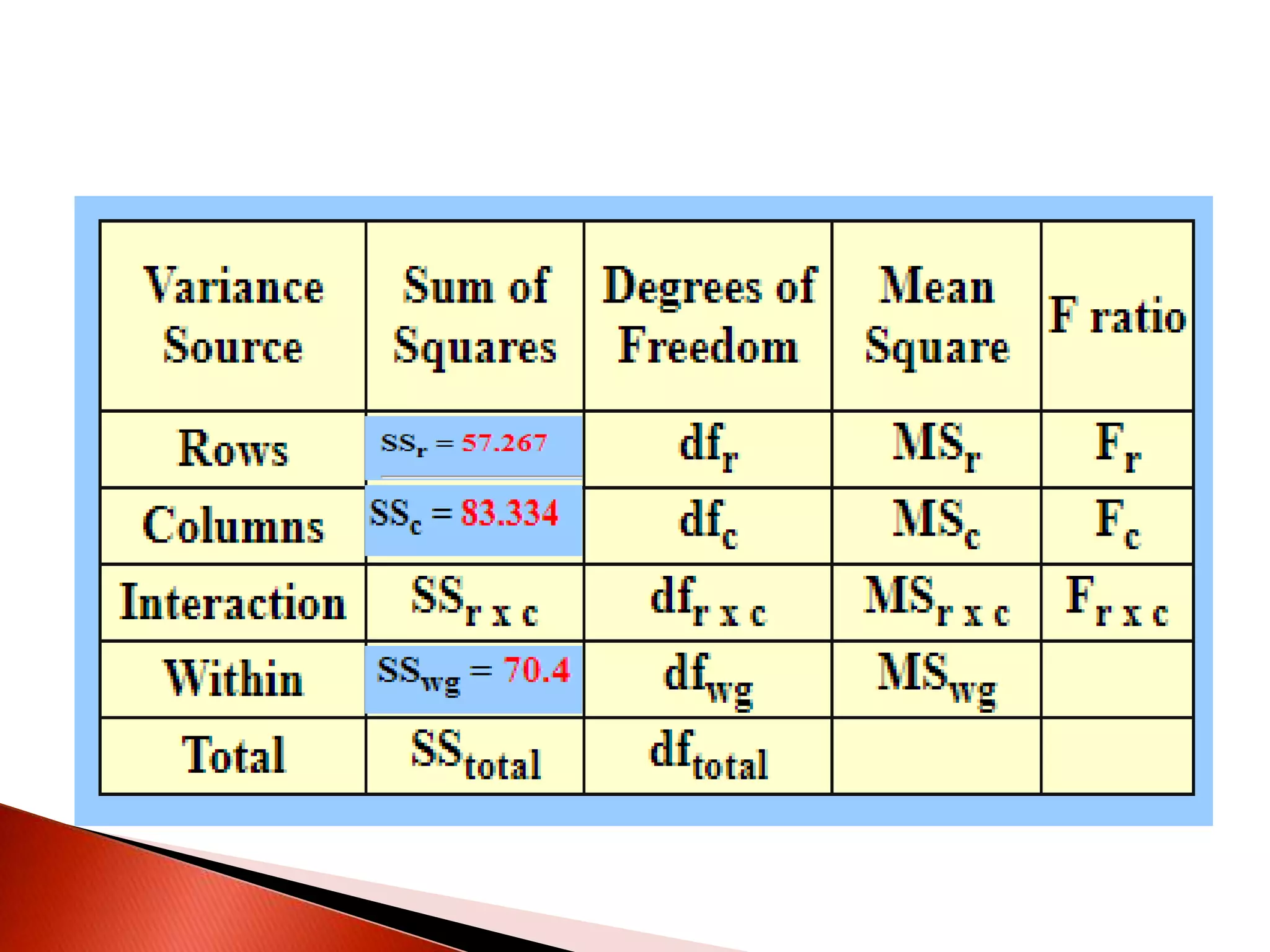
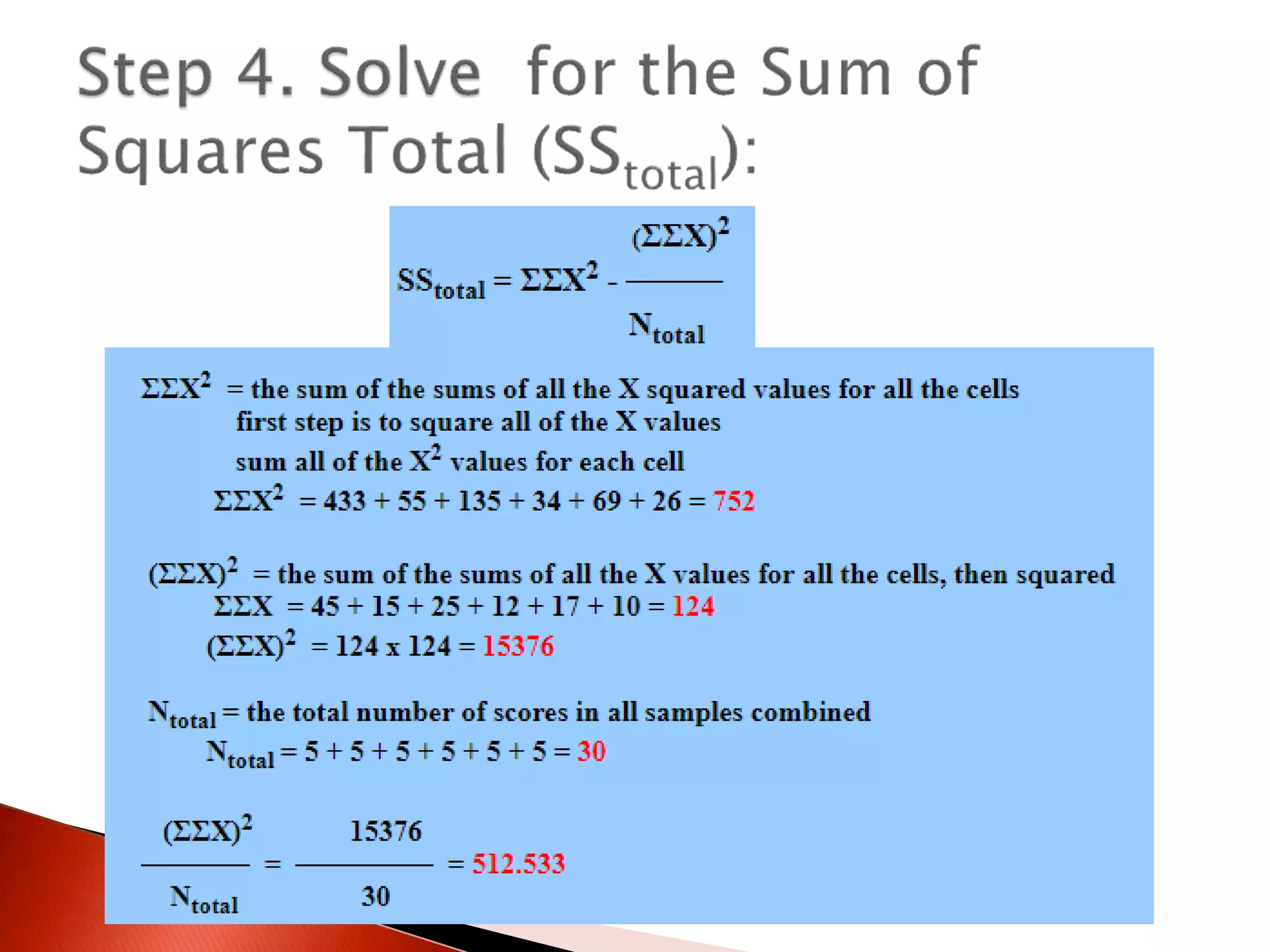
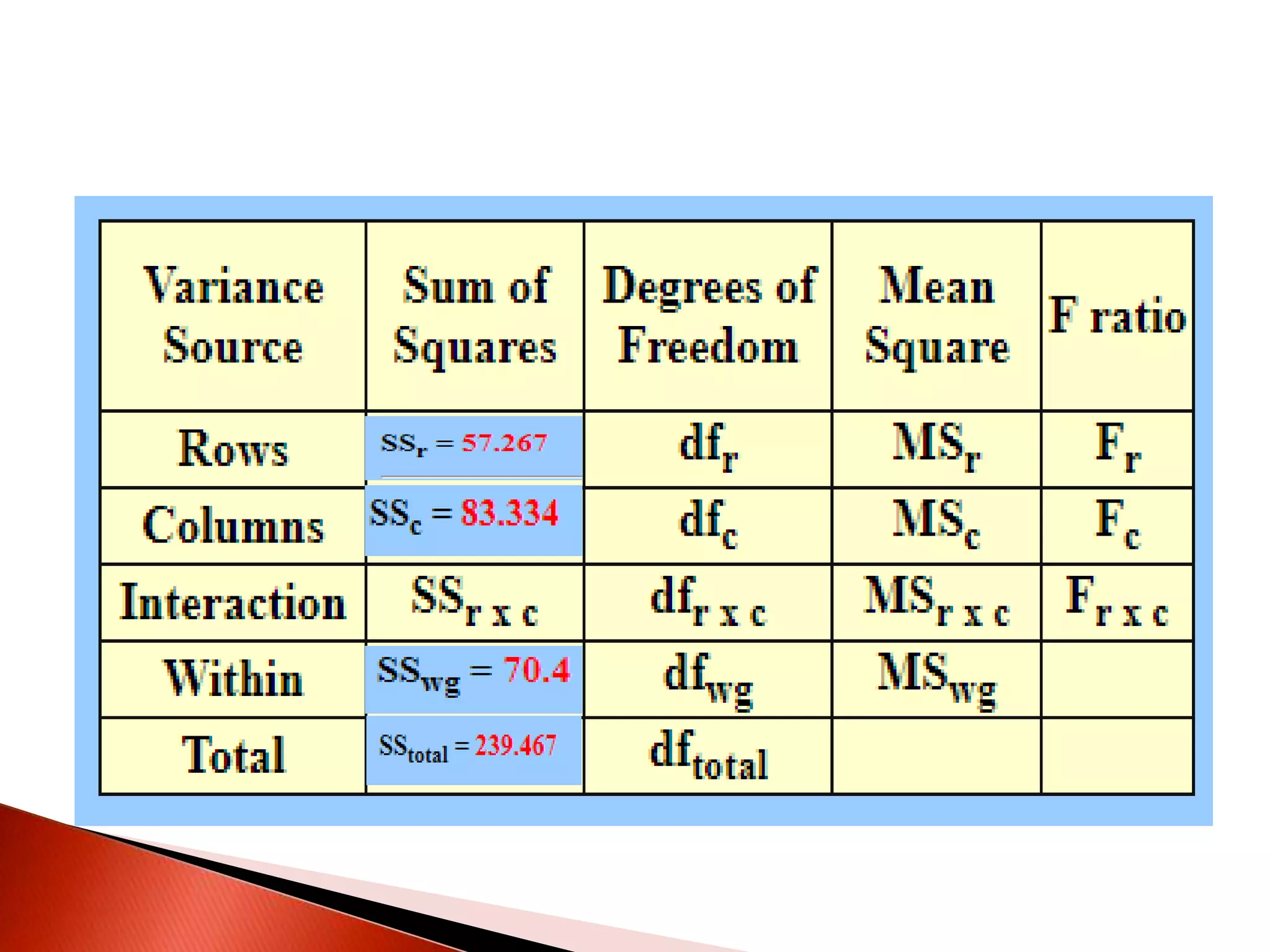
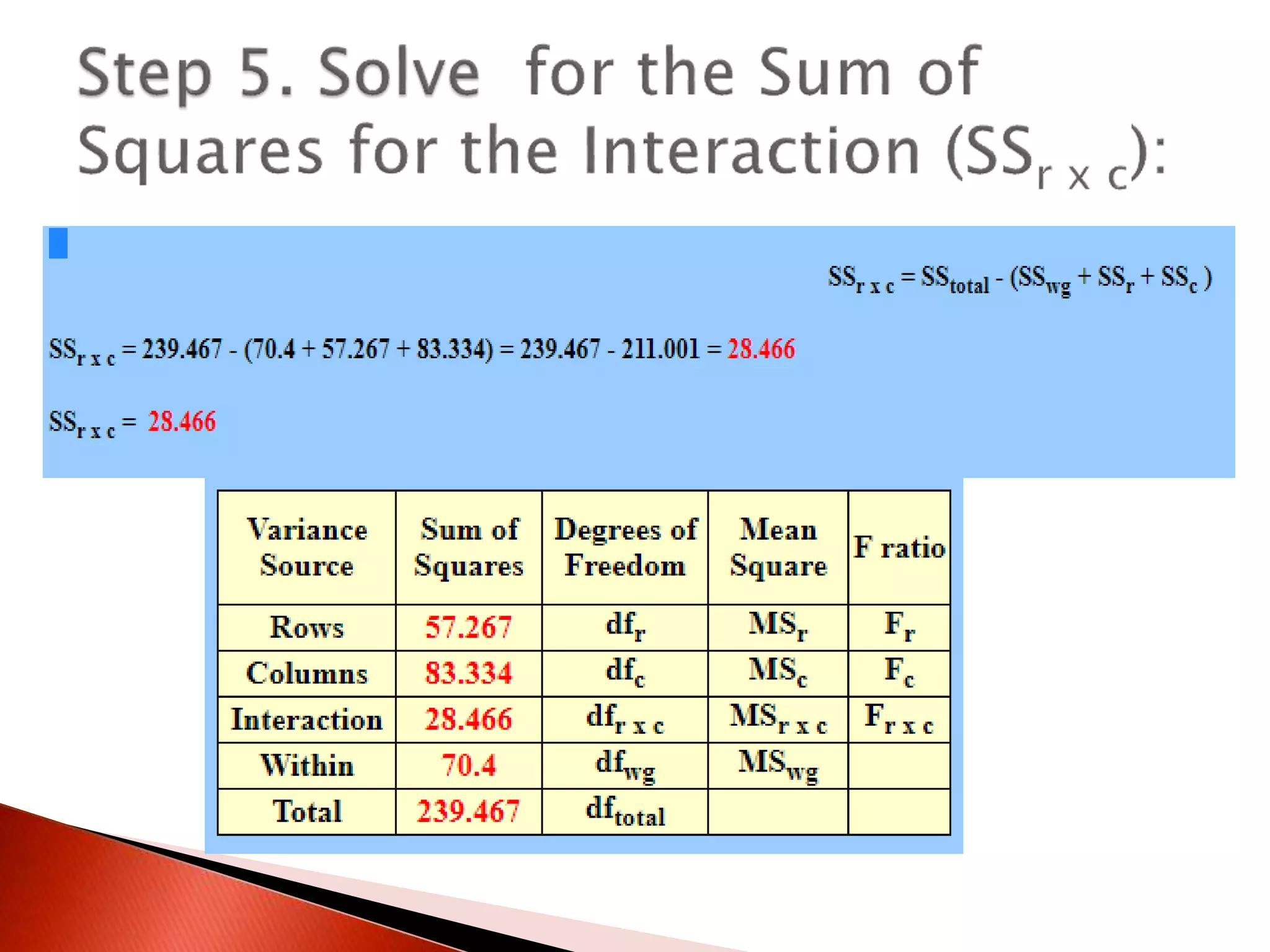
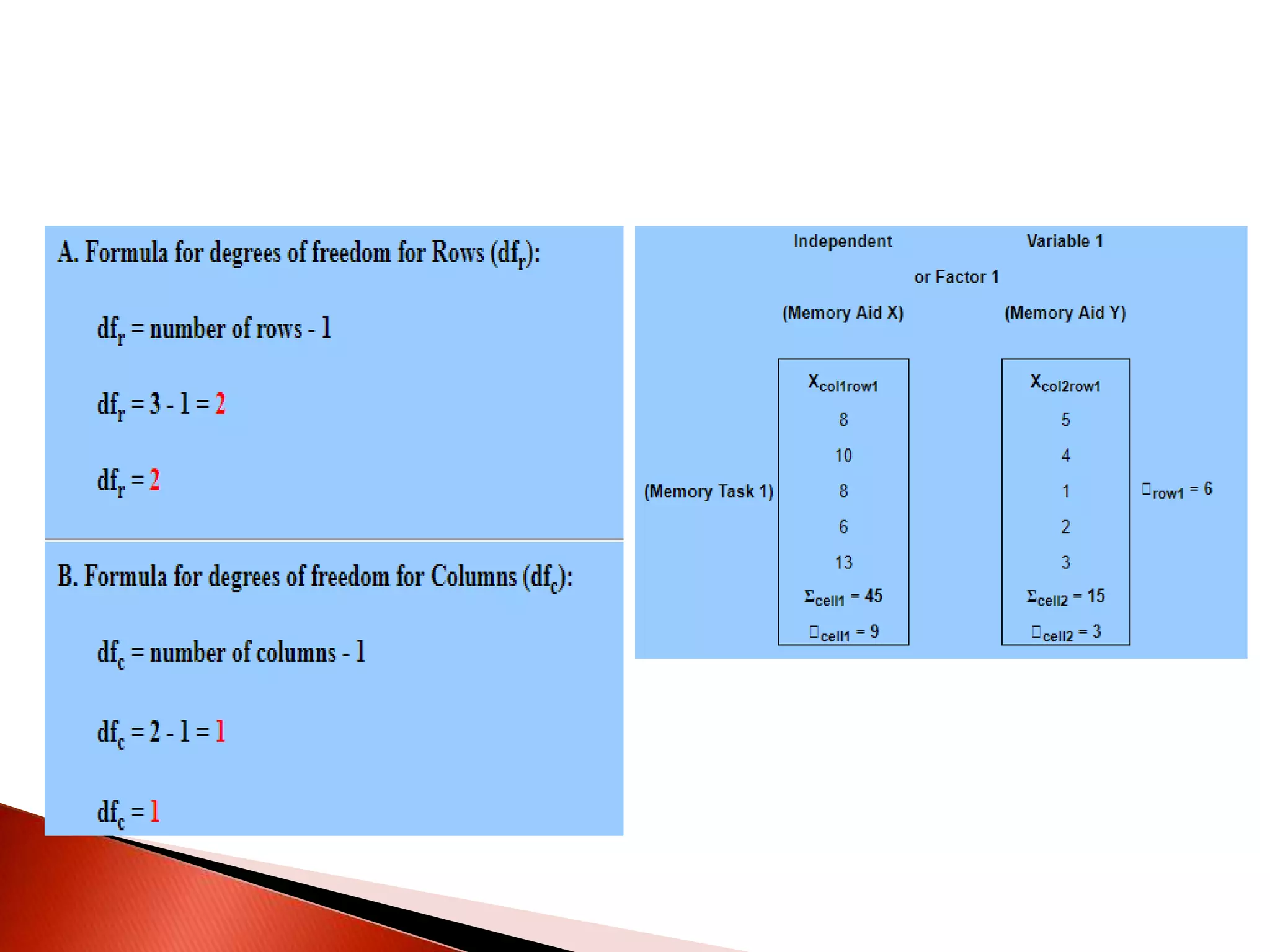
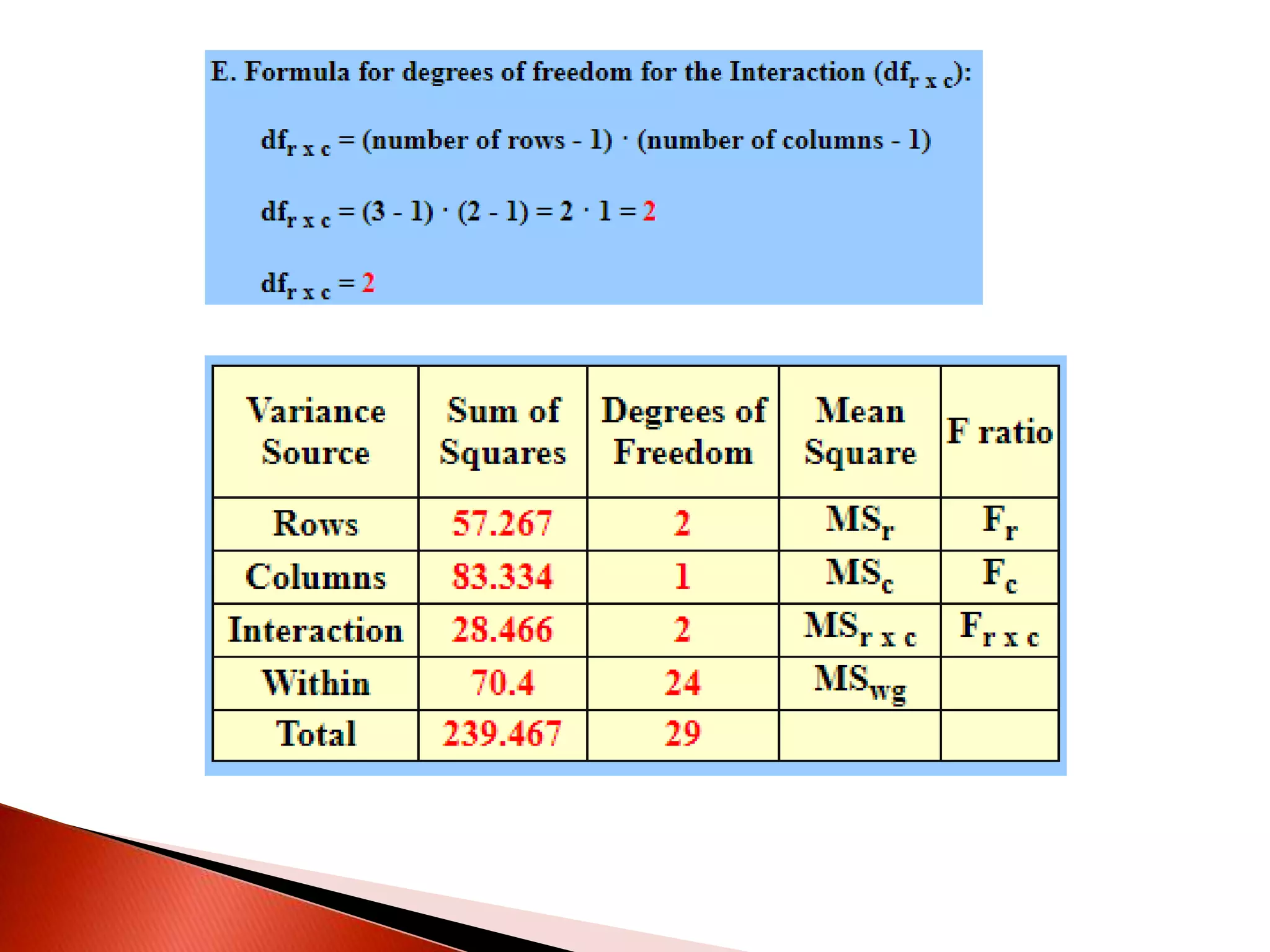
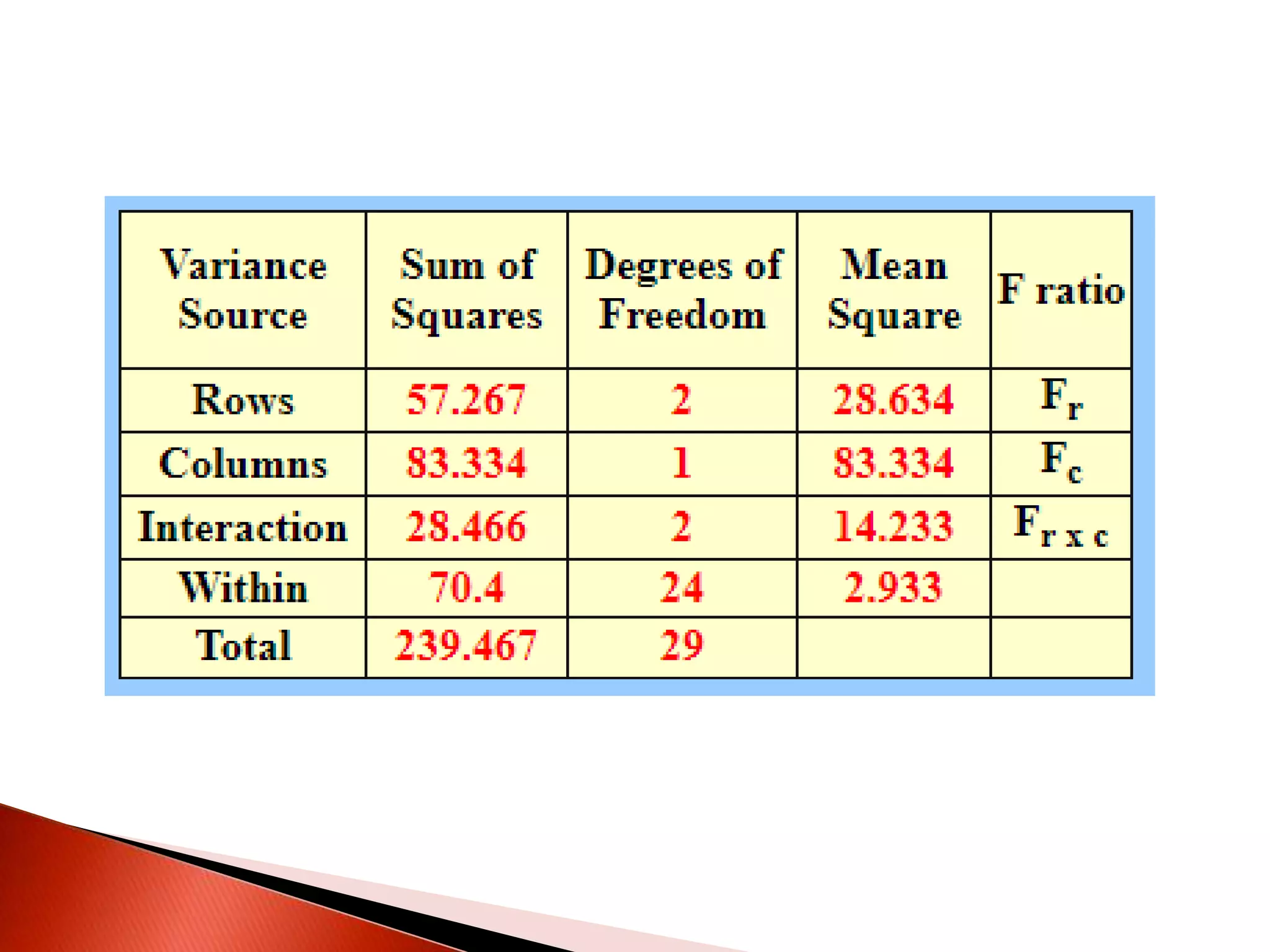
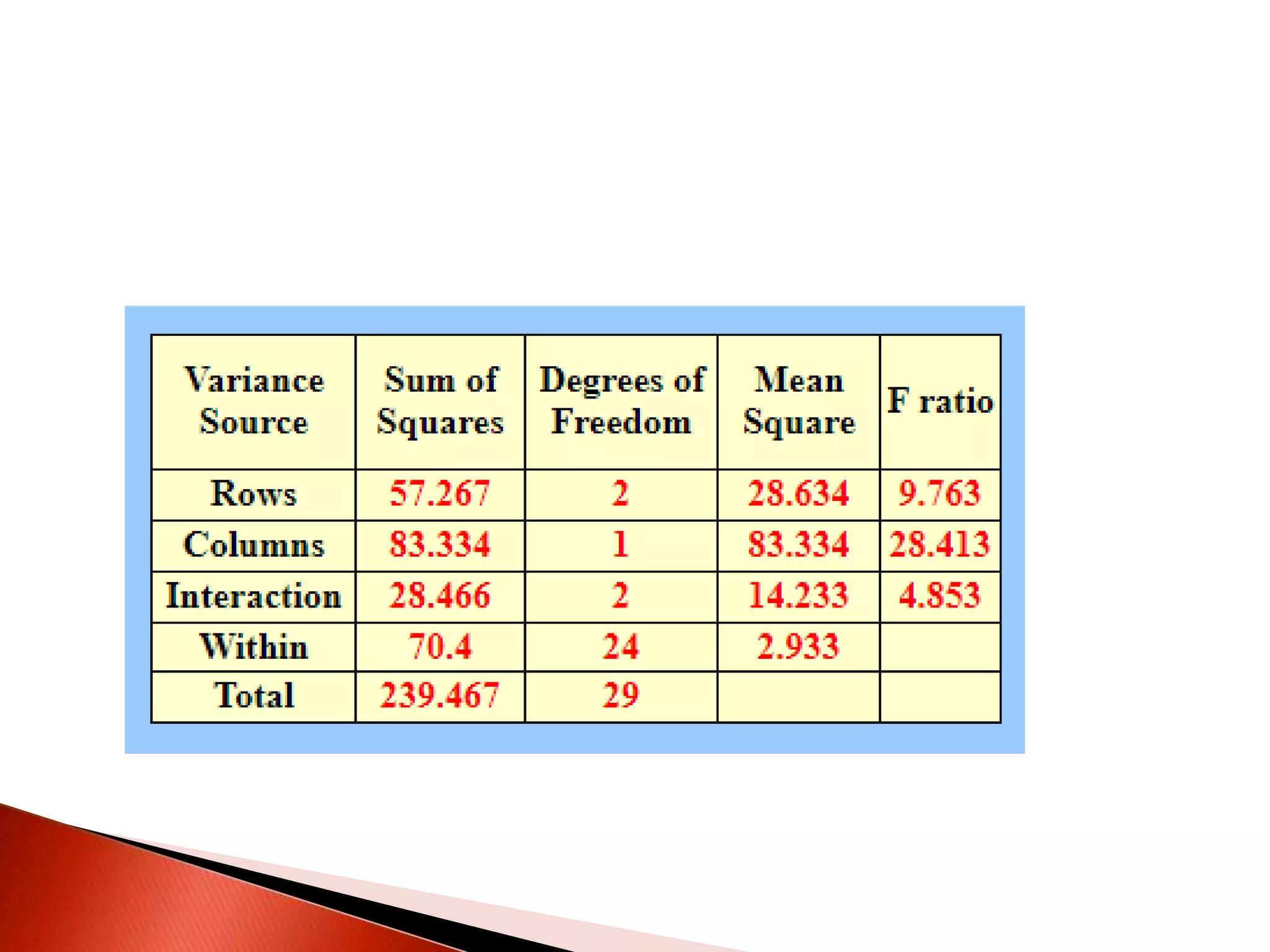
Two-way ANOVA is used to analyze data with two independent variables that have multiple levels. This document describes a memory experiment with two independent variables: type of memory aid and memory task. It provides the null and research hypotheses for the main effects of each independent variable and their interaction. Formulas are given for calculating sums of squares, degrees of freedom, mean squares, and F-ratios to determine if the main effects or interaction are statistically significant.