Embed presentation
Downloaded 346 times


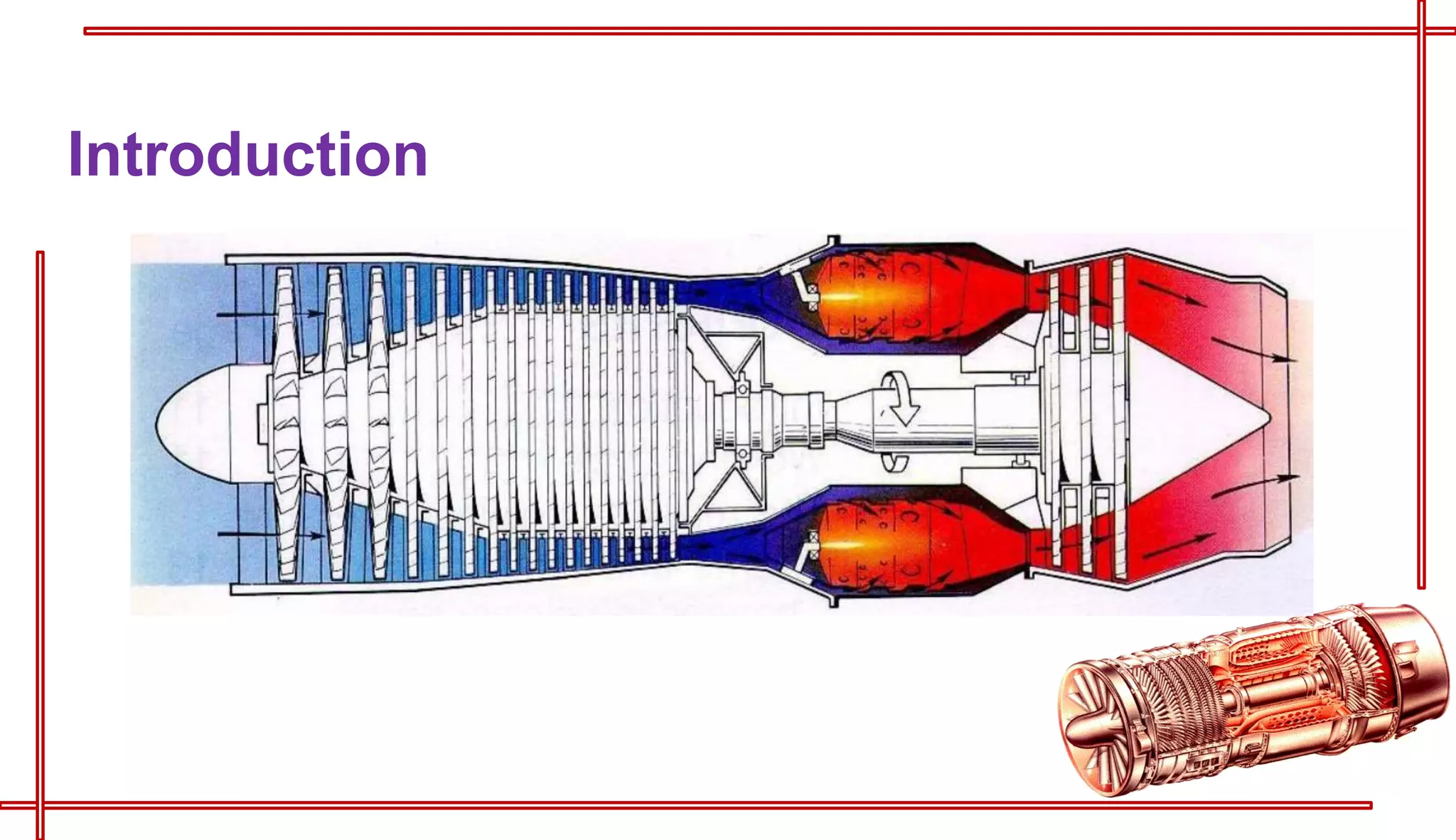
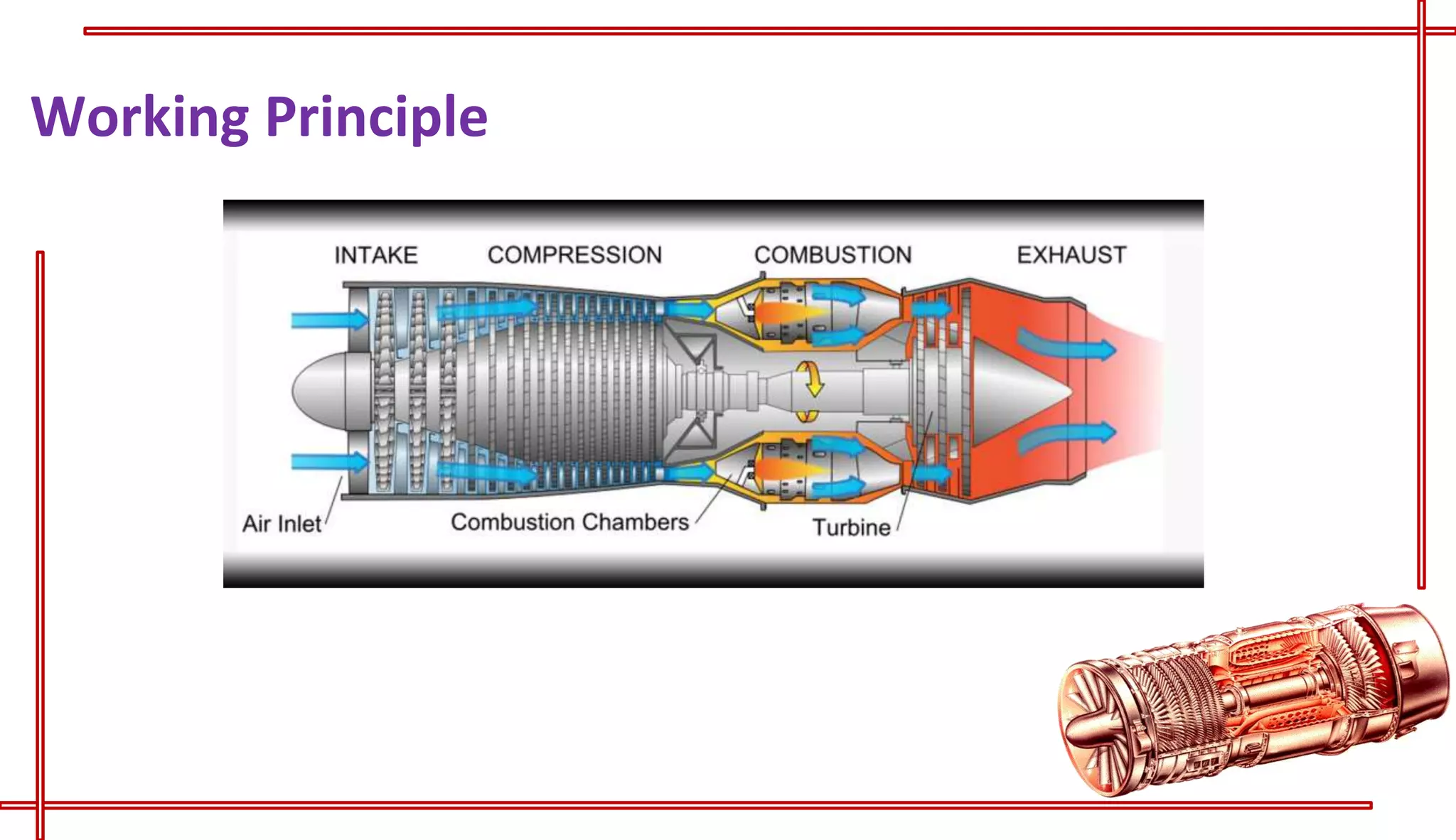

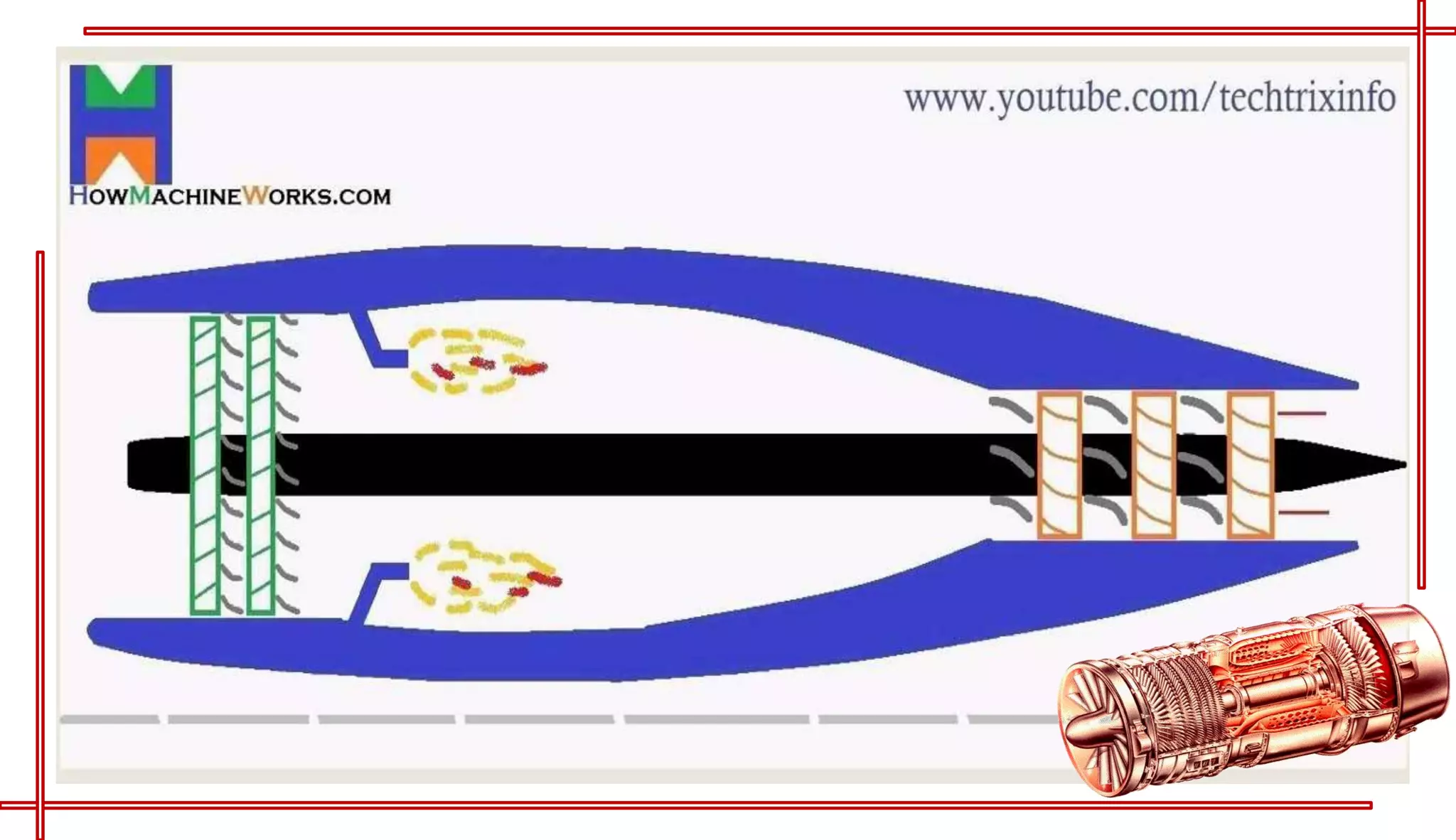
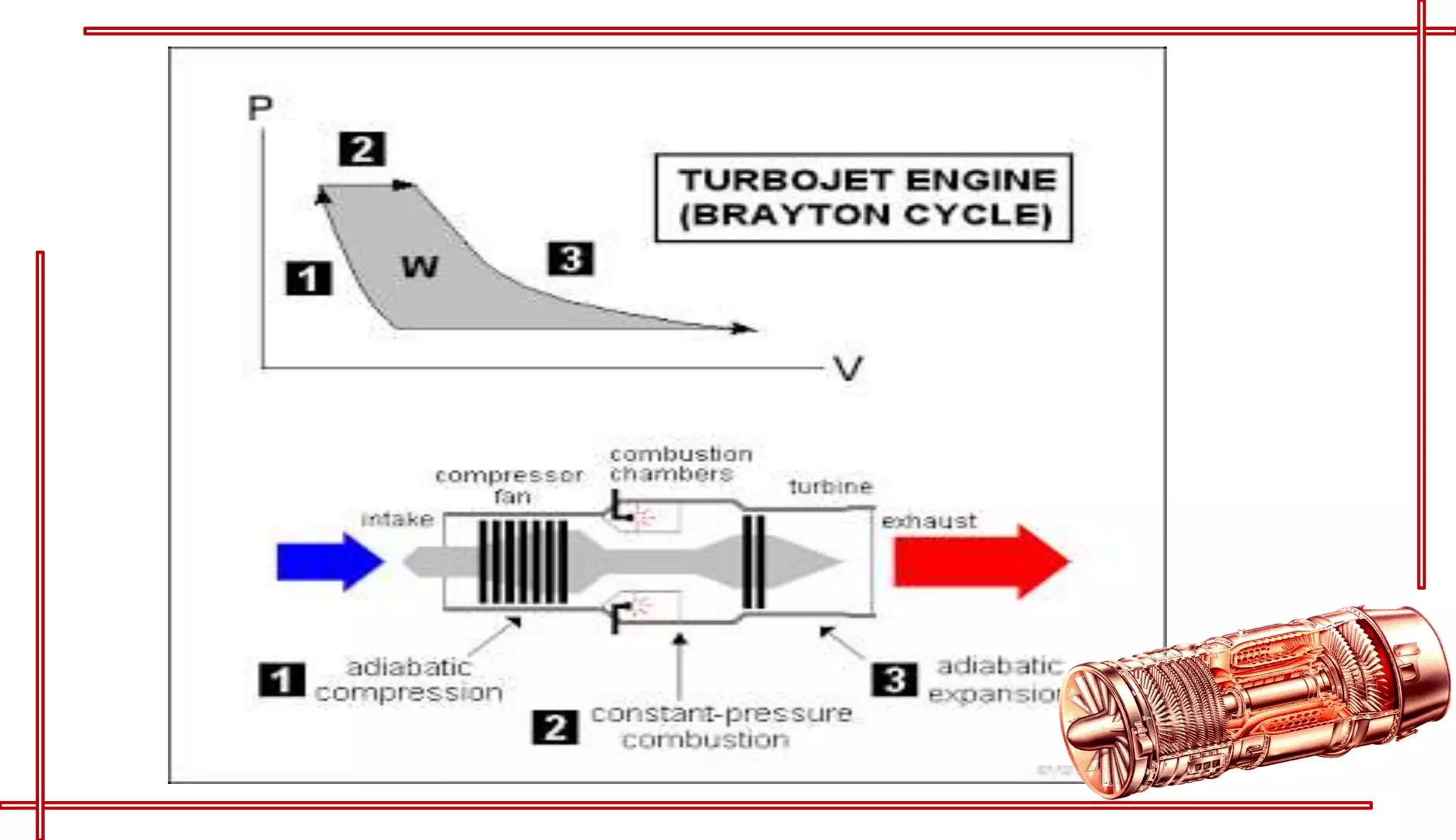
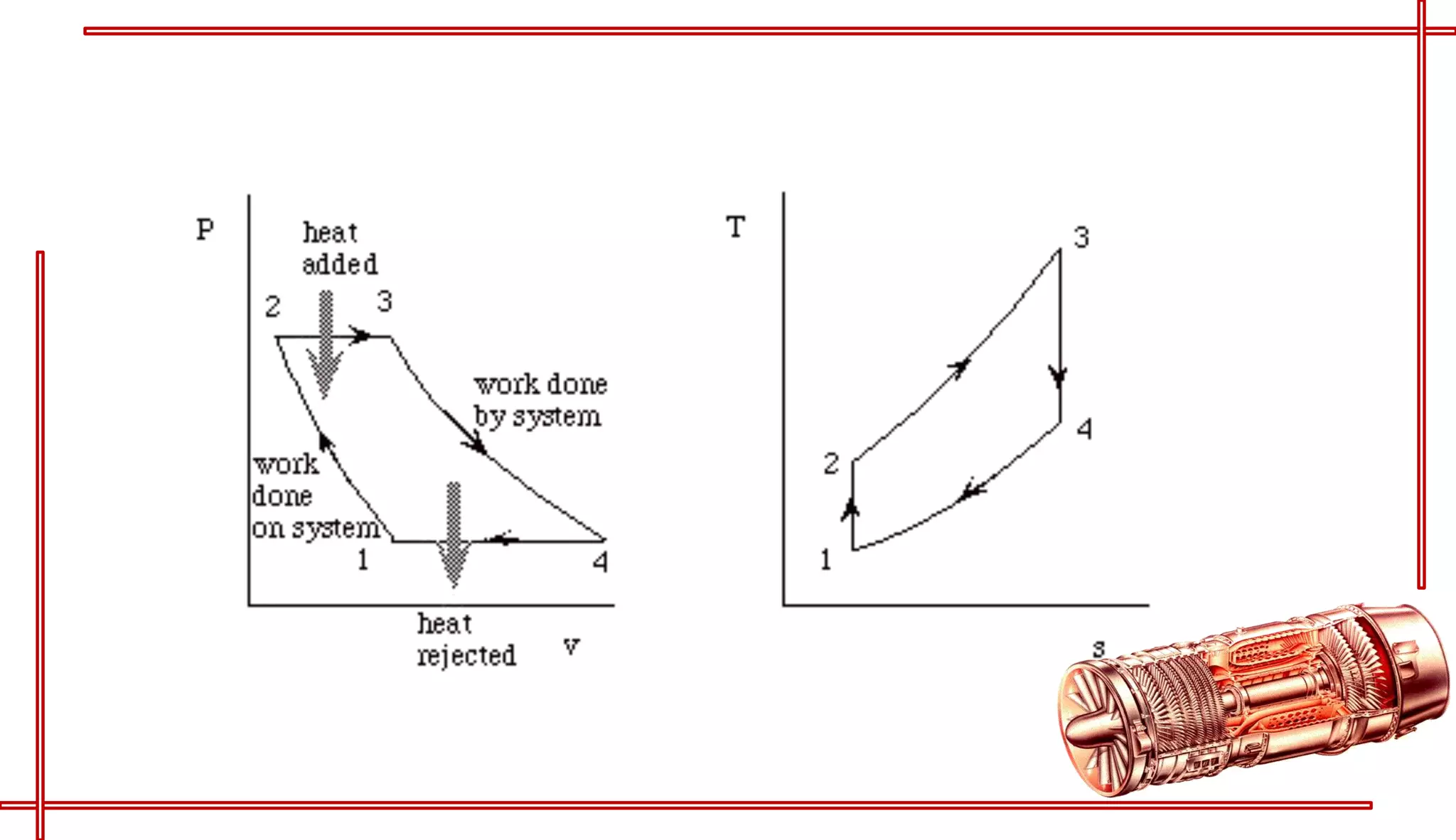
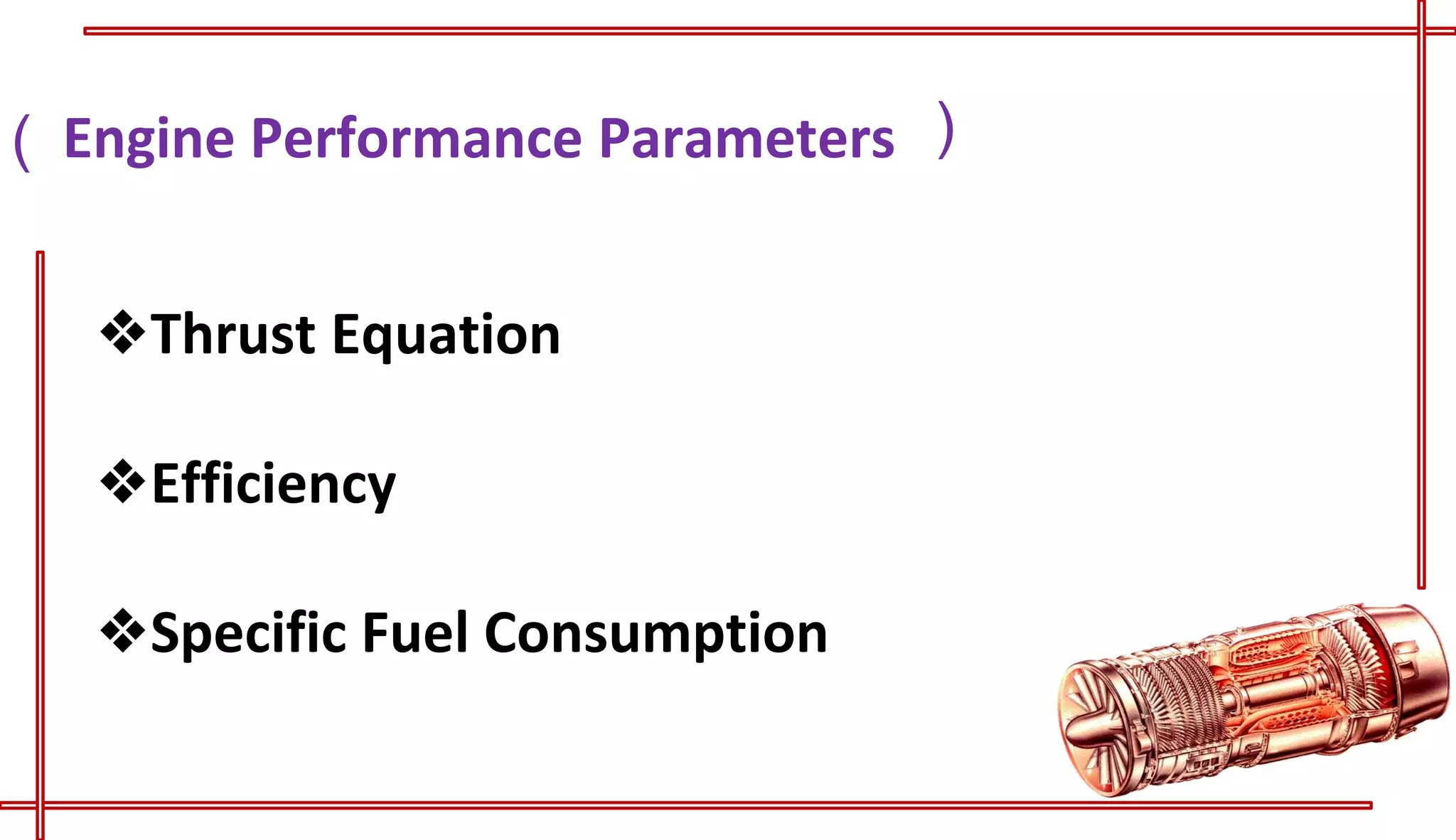
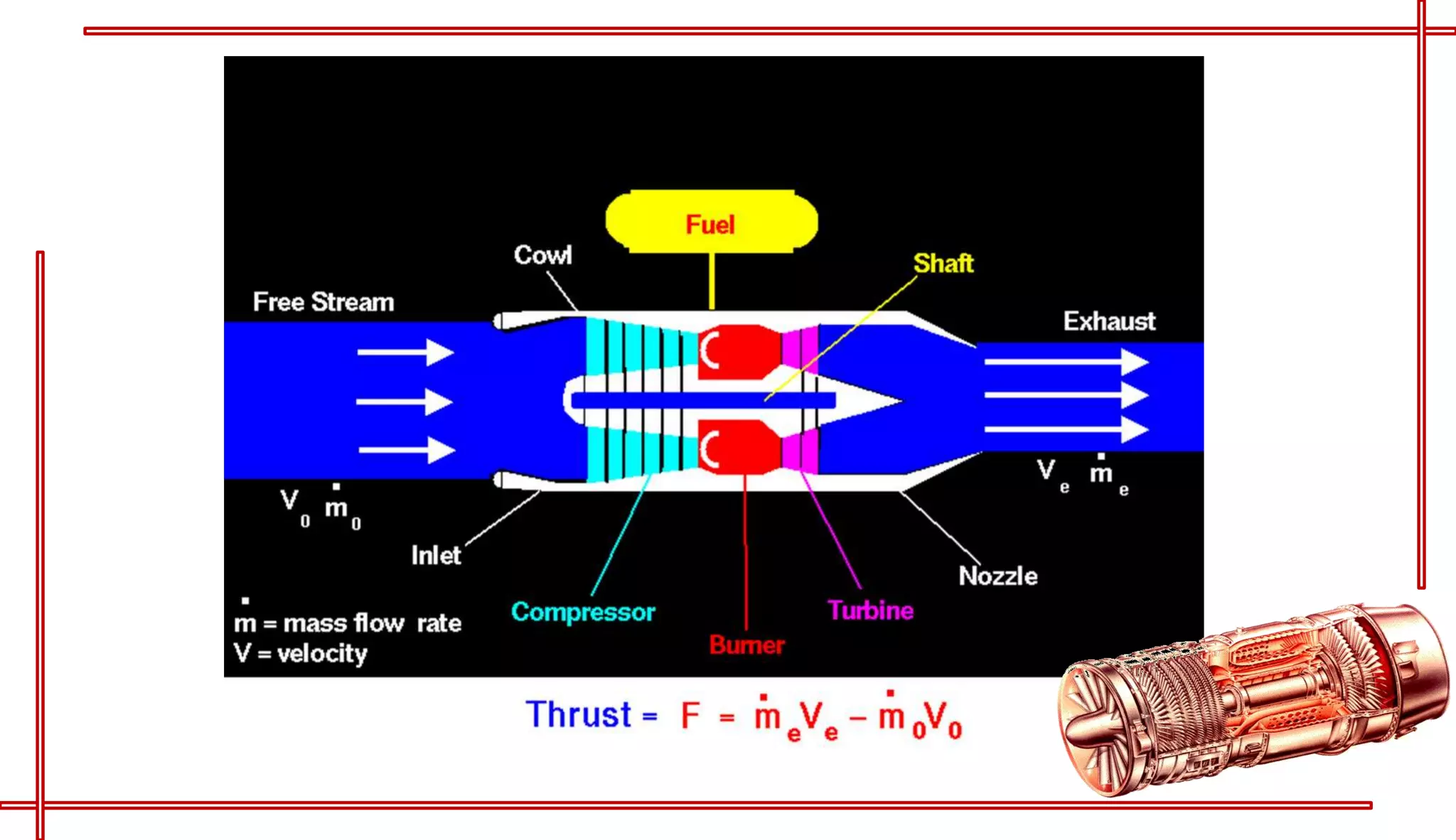
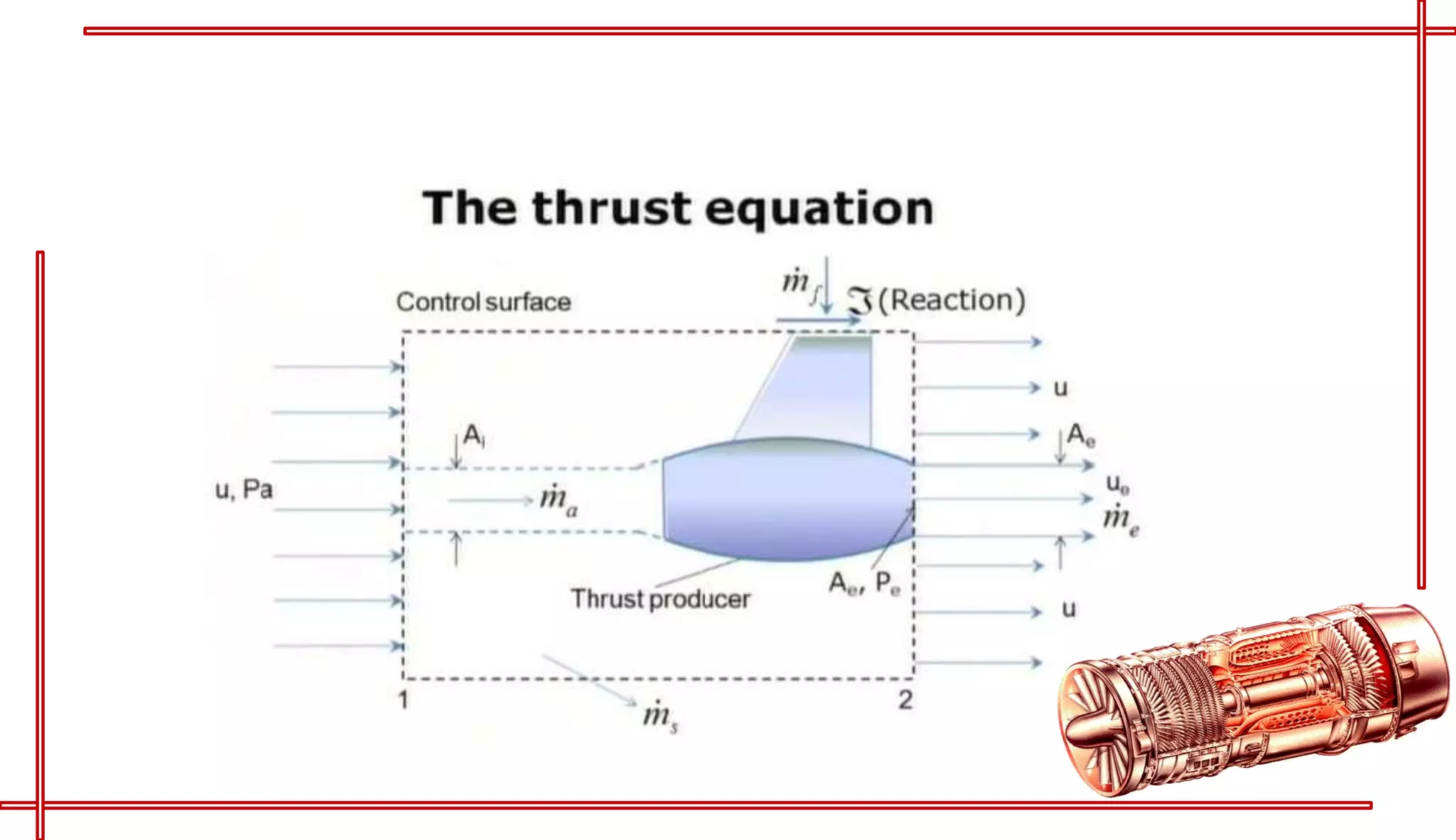
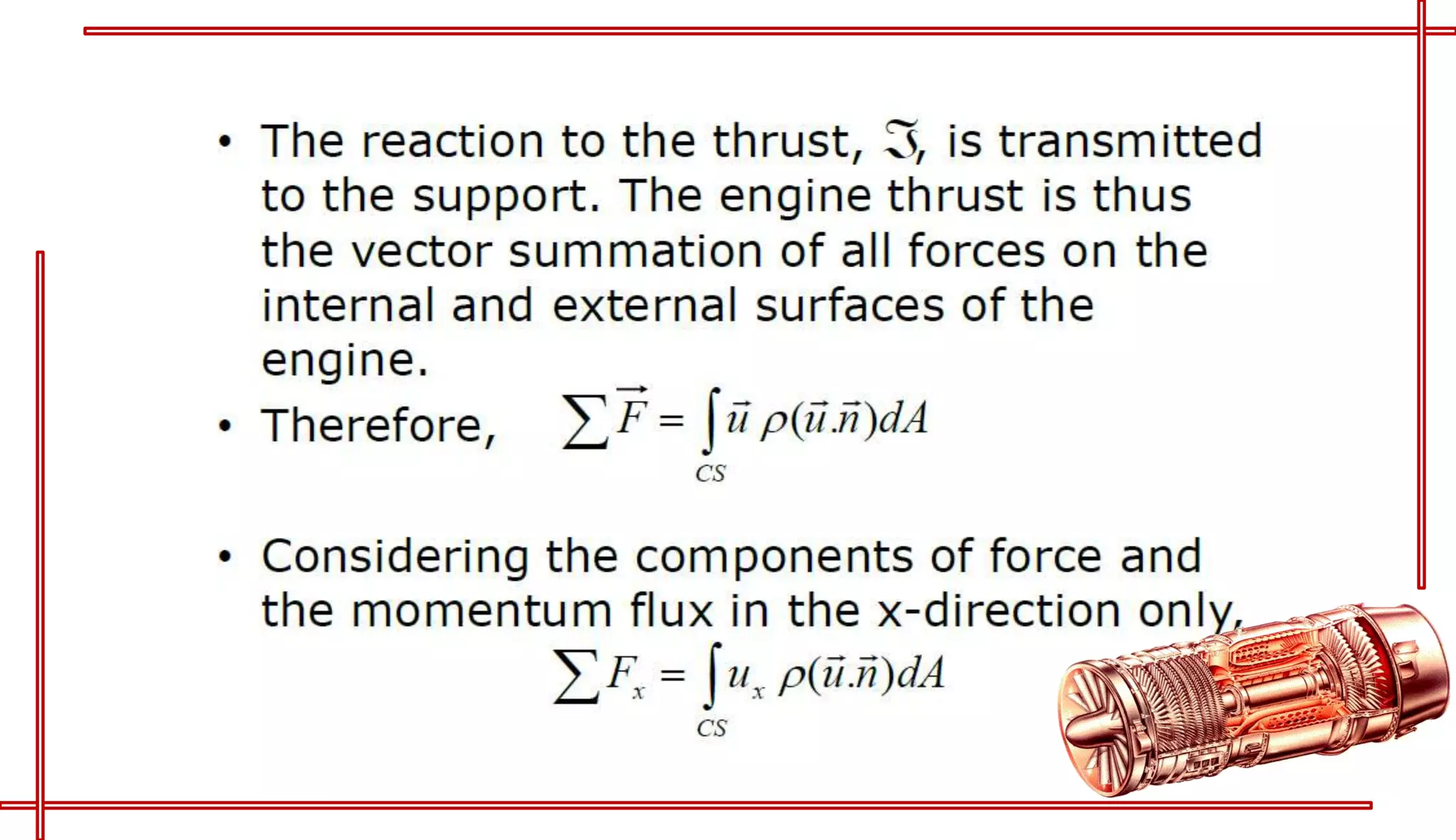

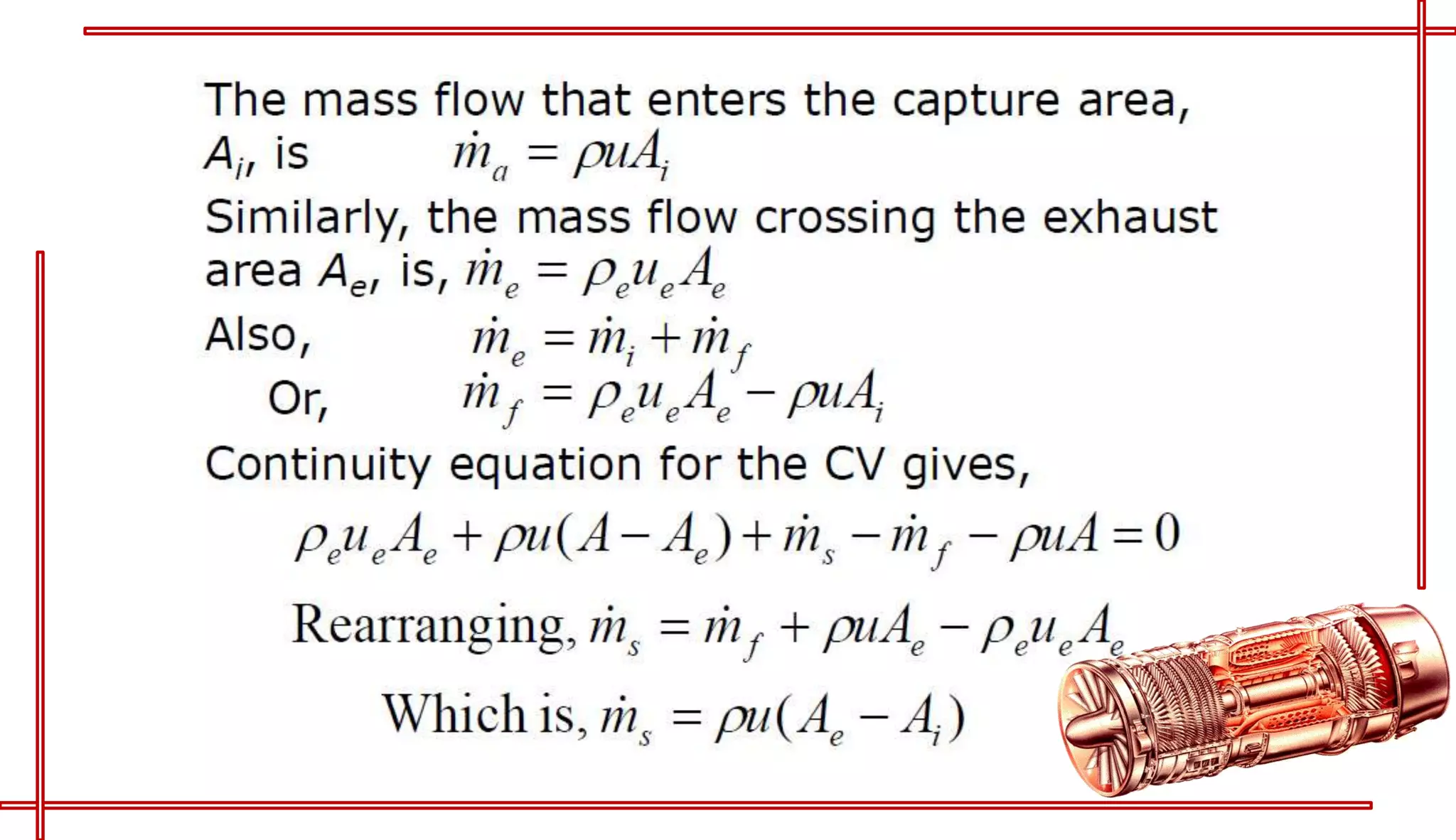
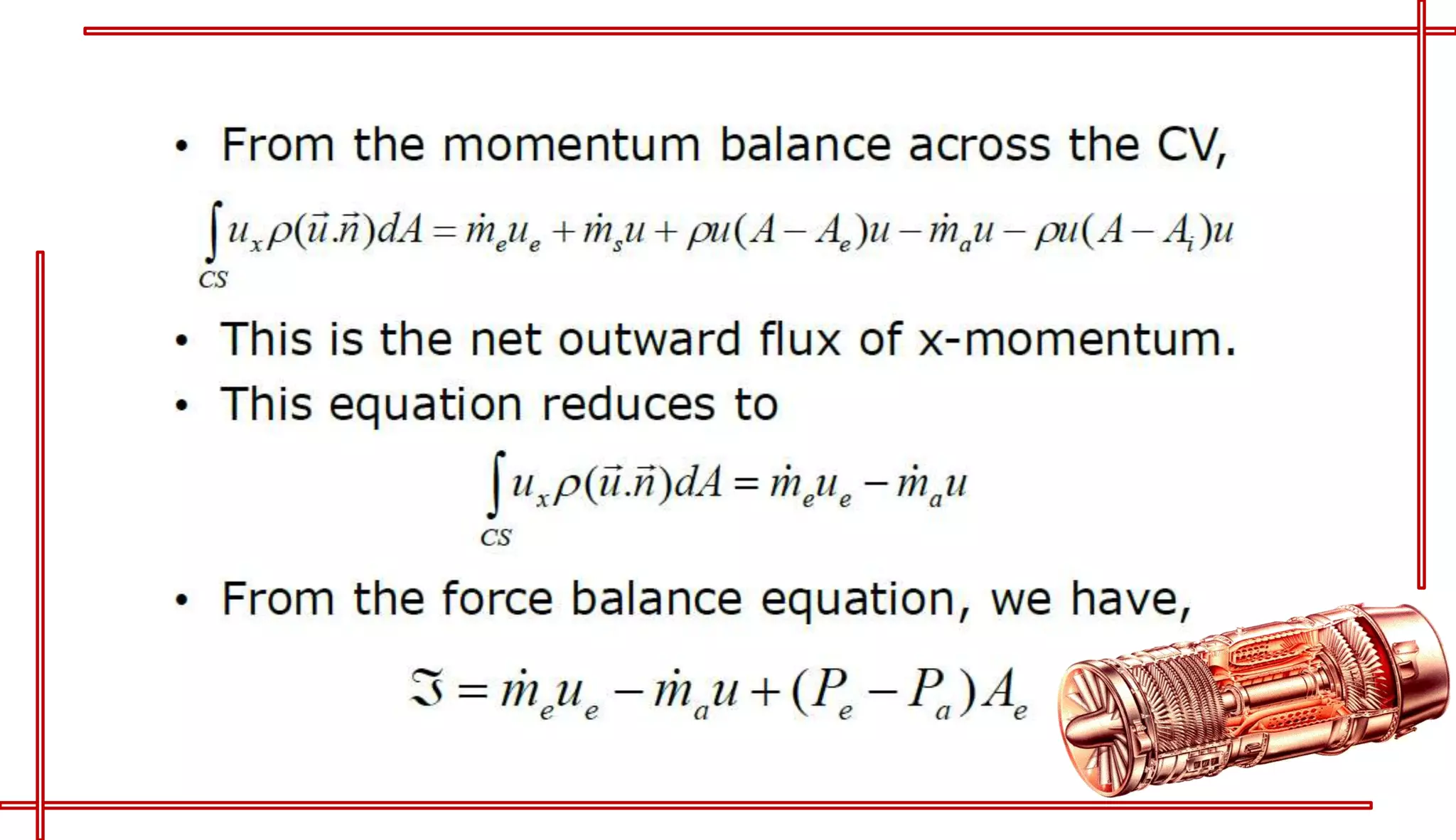
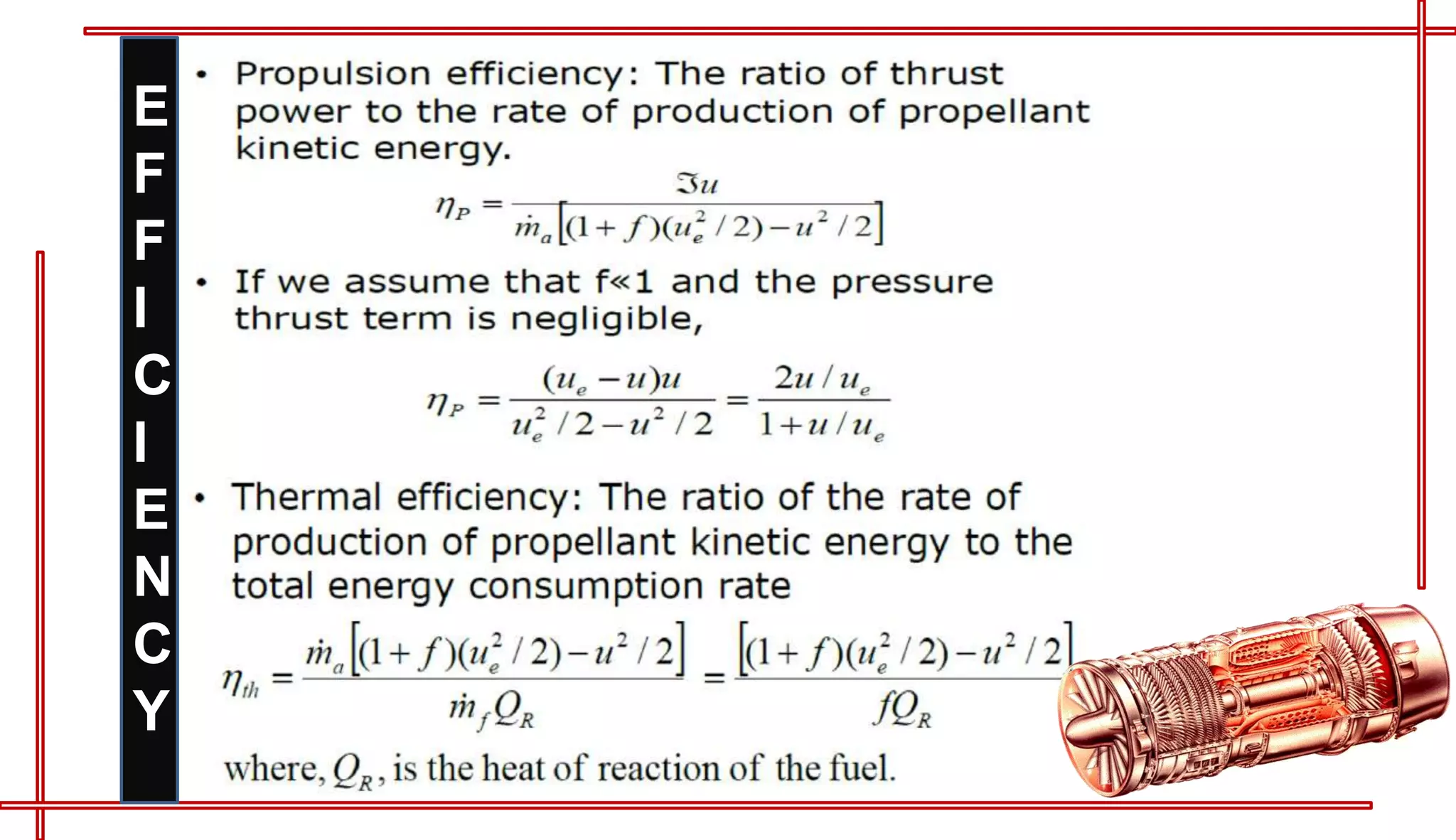
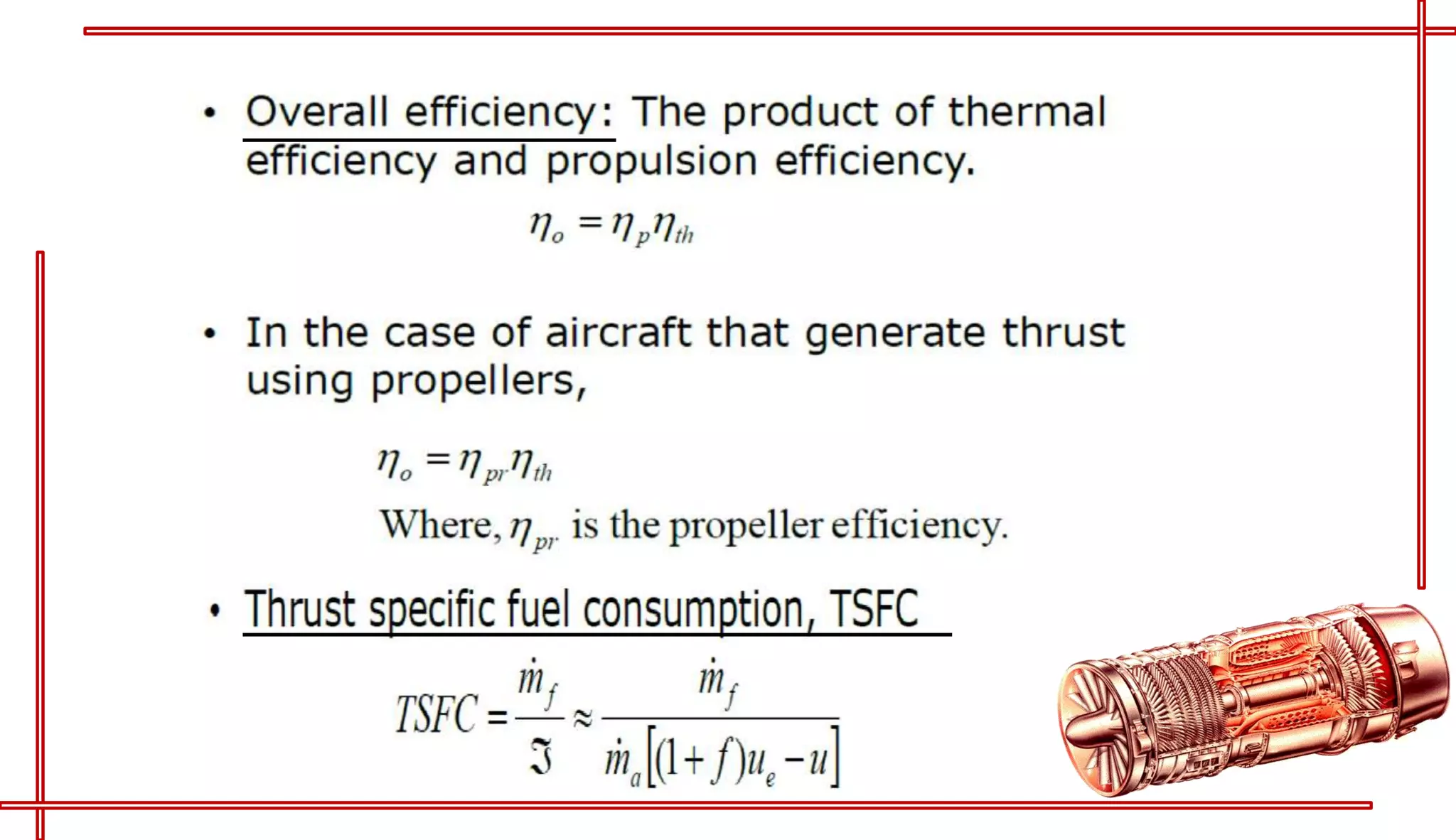


This document provides an introduction to turbo jet engines, including their working principle and performance parameters. It explains that turbo jets work by compressing air in a rotating compressor, mixing it with fuel and igniting it to produce hot combustion gases, which expand through a turbine to extract power and drive the compressor. The high-velocity exhaust gases exiting the turbine nozzle produce thrust based on Newton's third law of motion. Key engine performance metrics are described as thrust, efficiency, and specific fuel consumption. Advantages of turbo jets include high power-to-weight ratio and compact size, while disadvantages are higher cost and slower response compared to reciprocating engines.




















