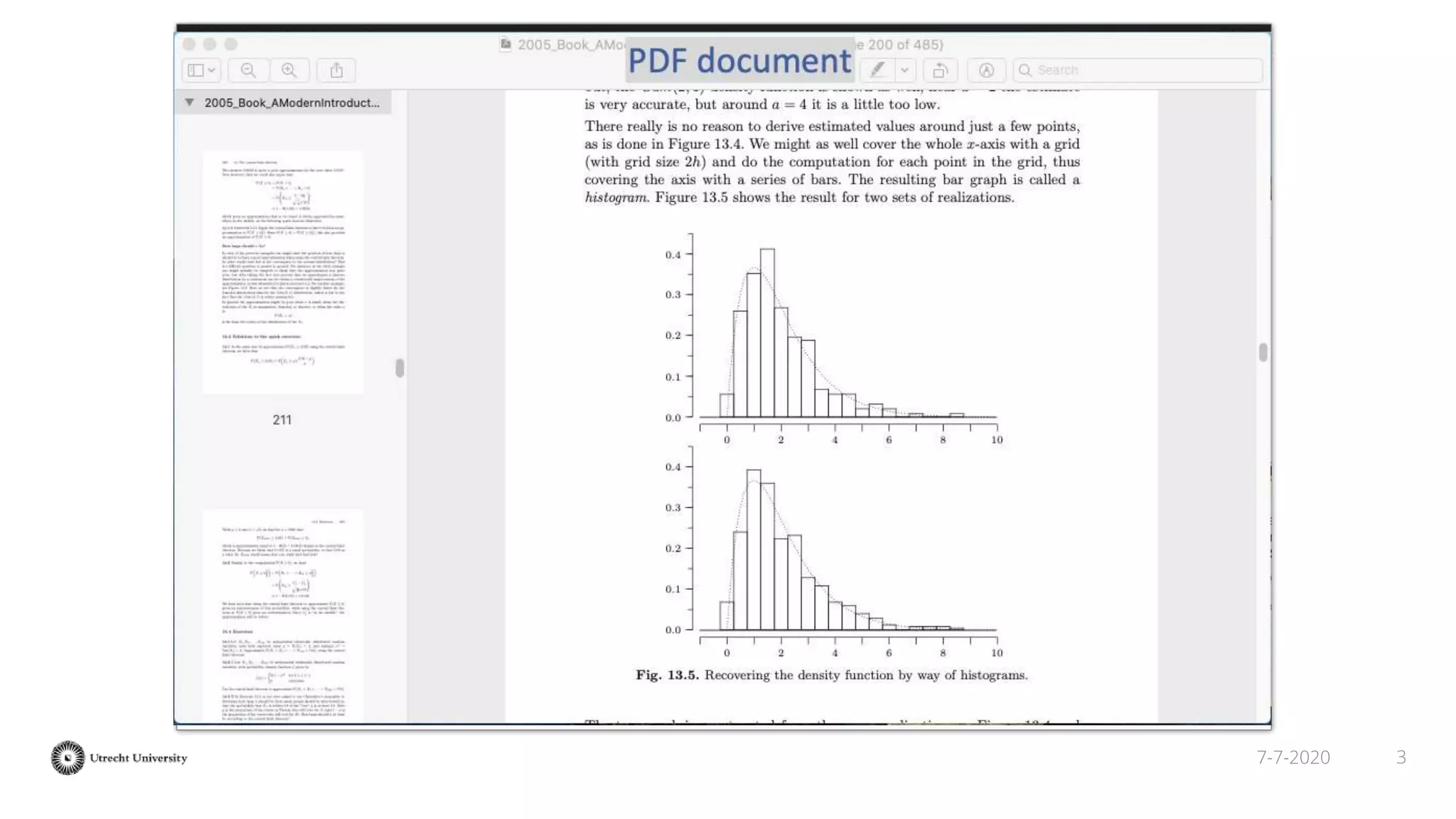
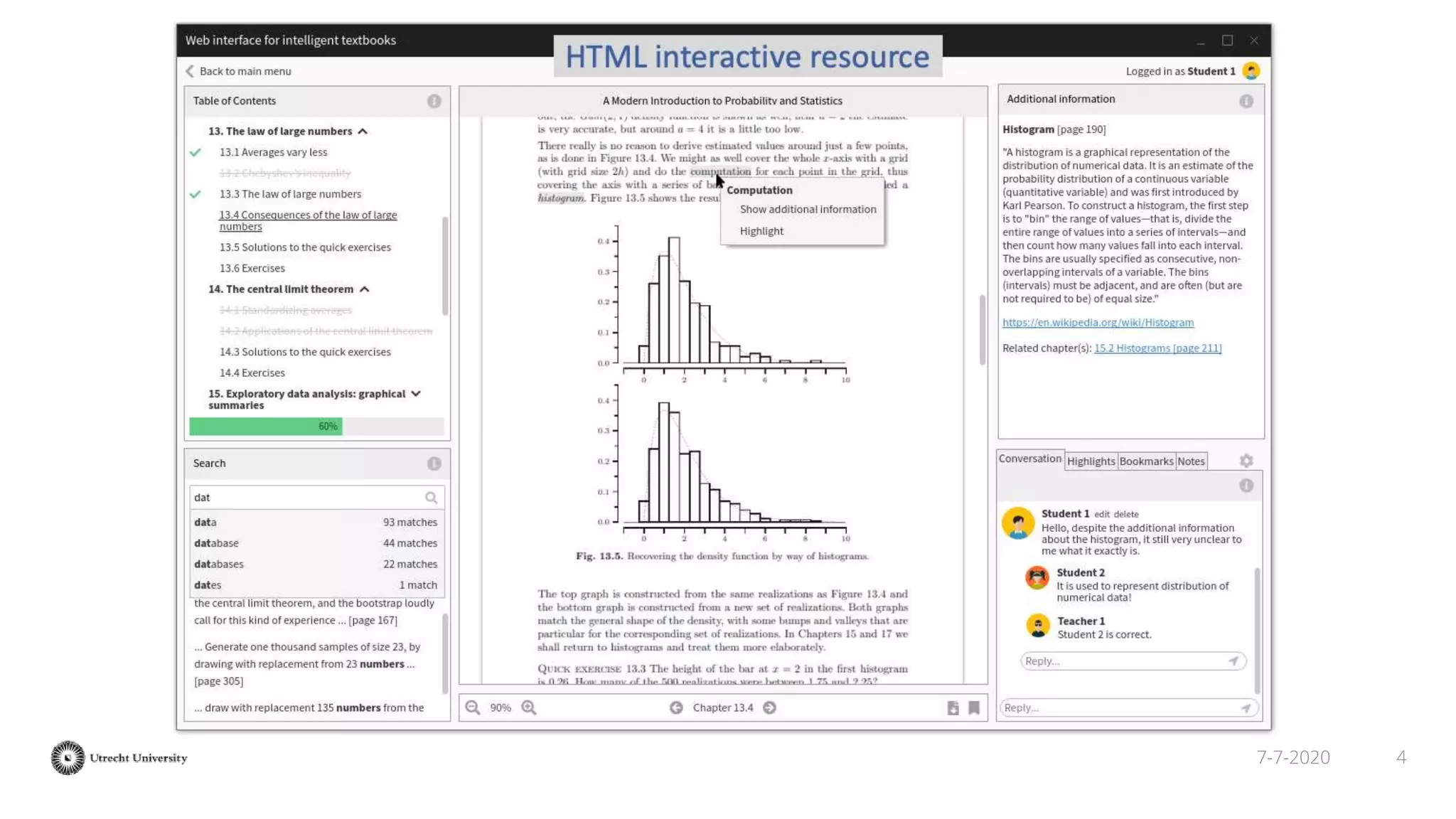
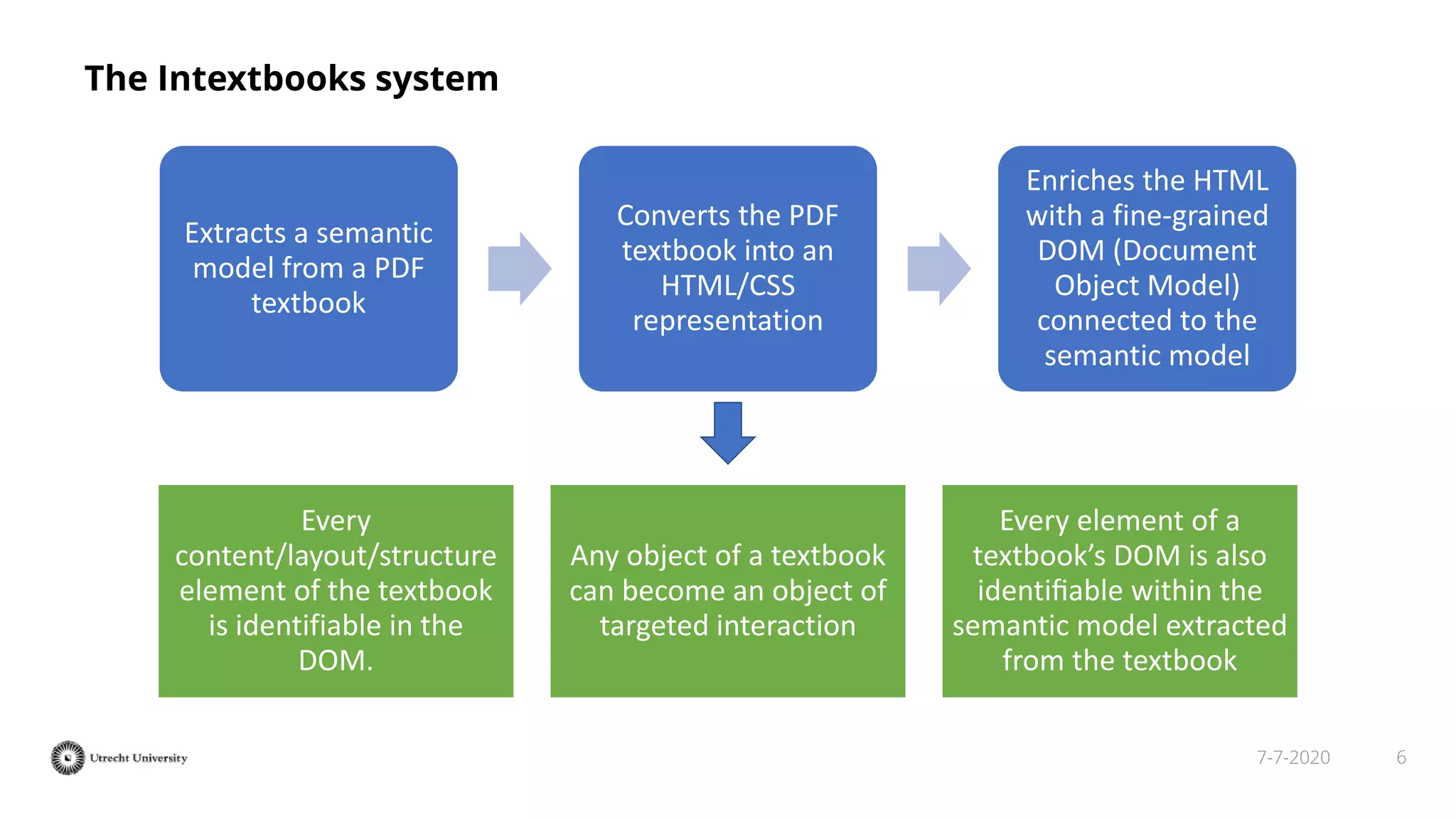
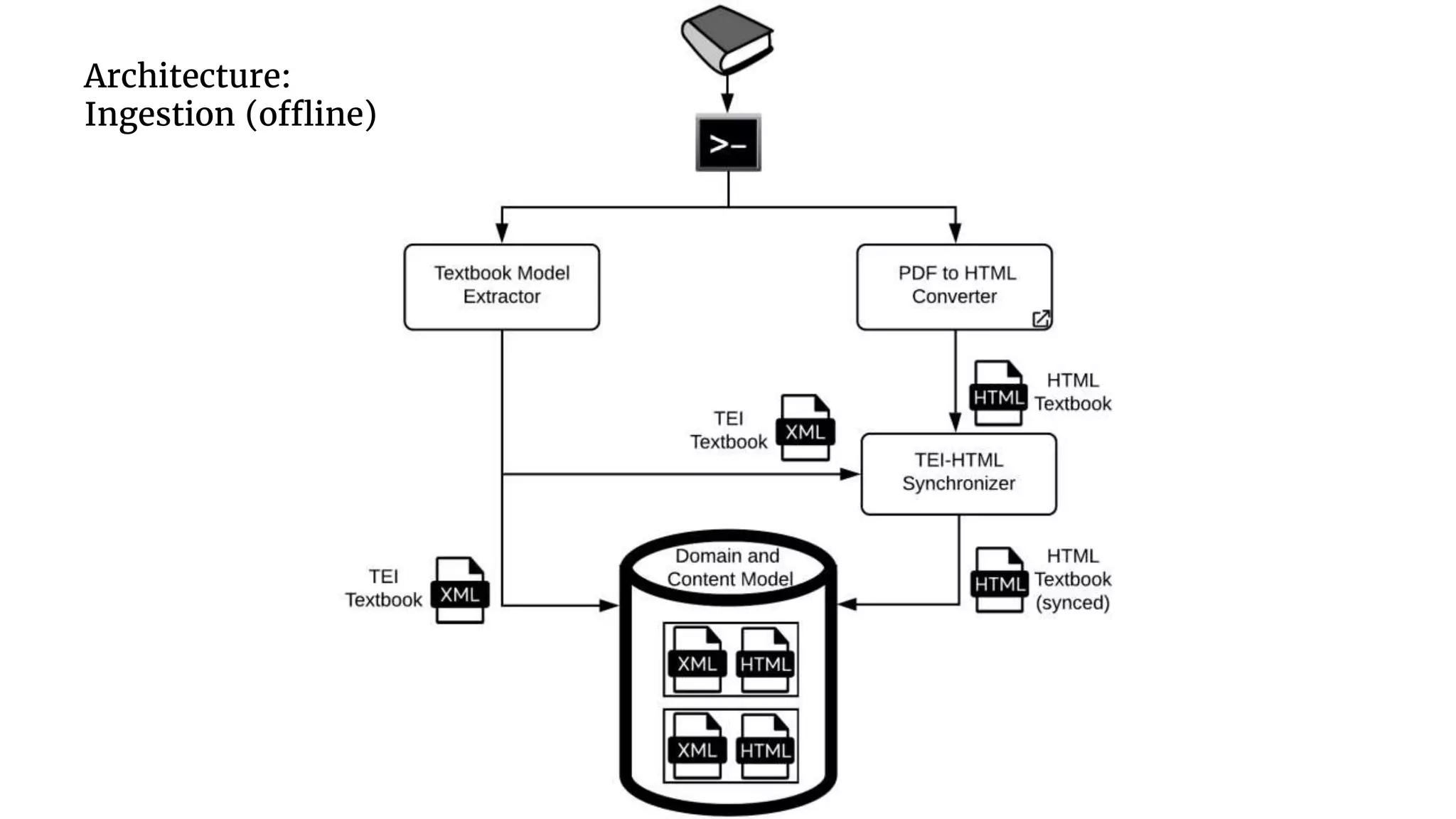
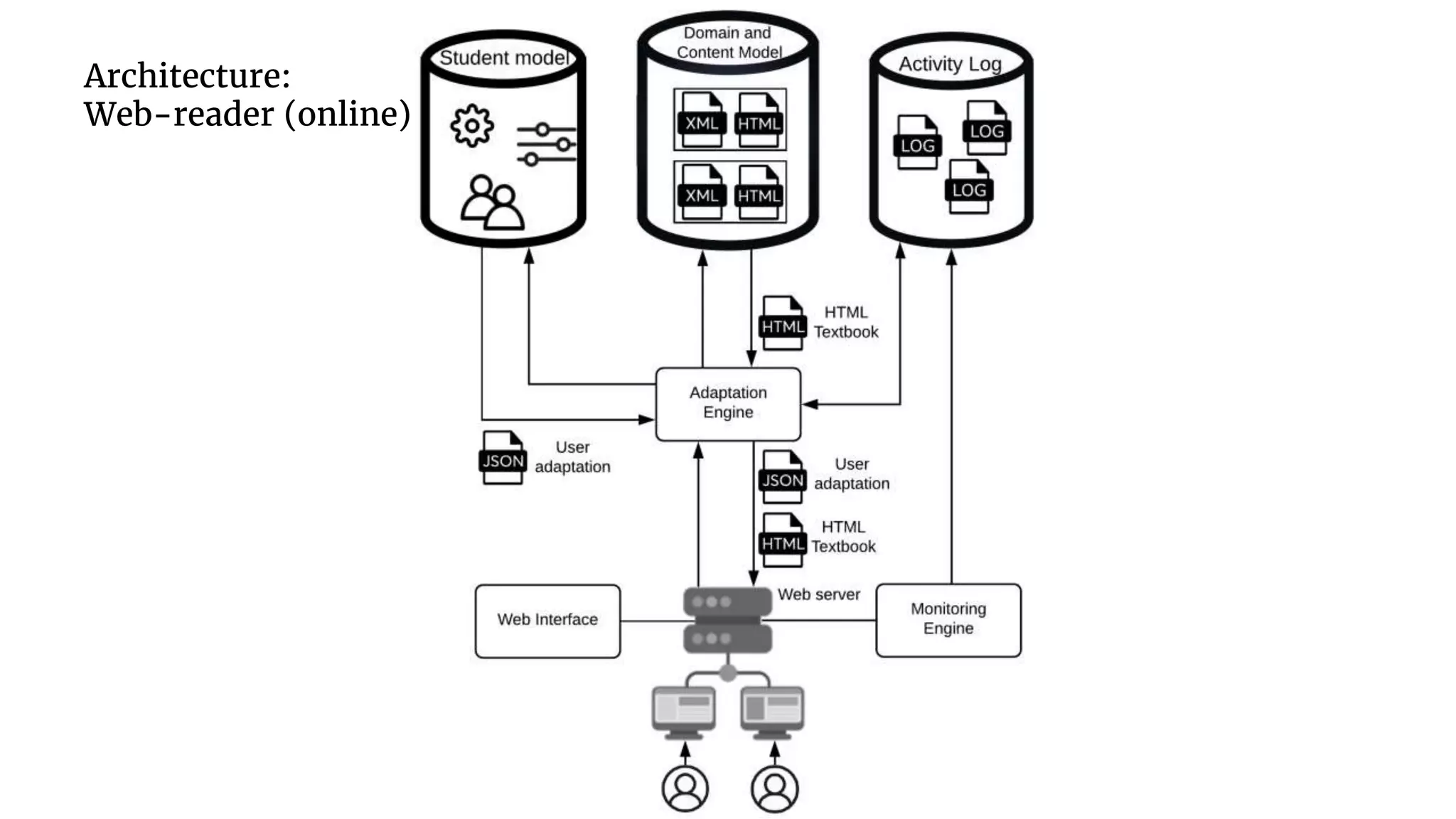
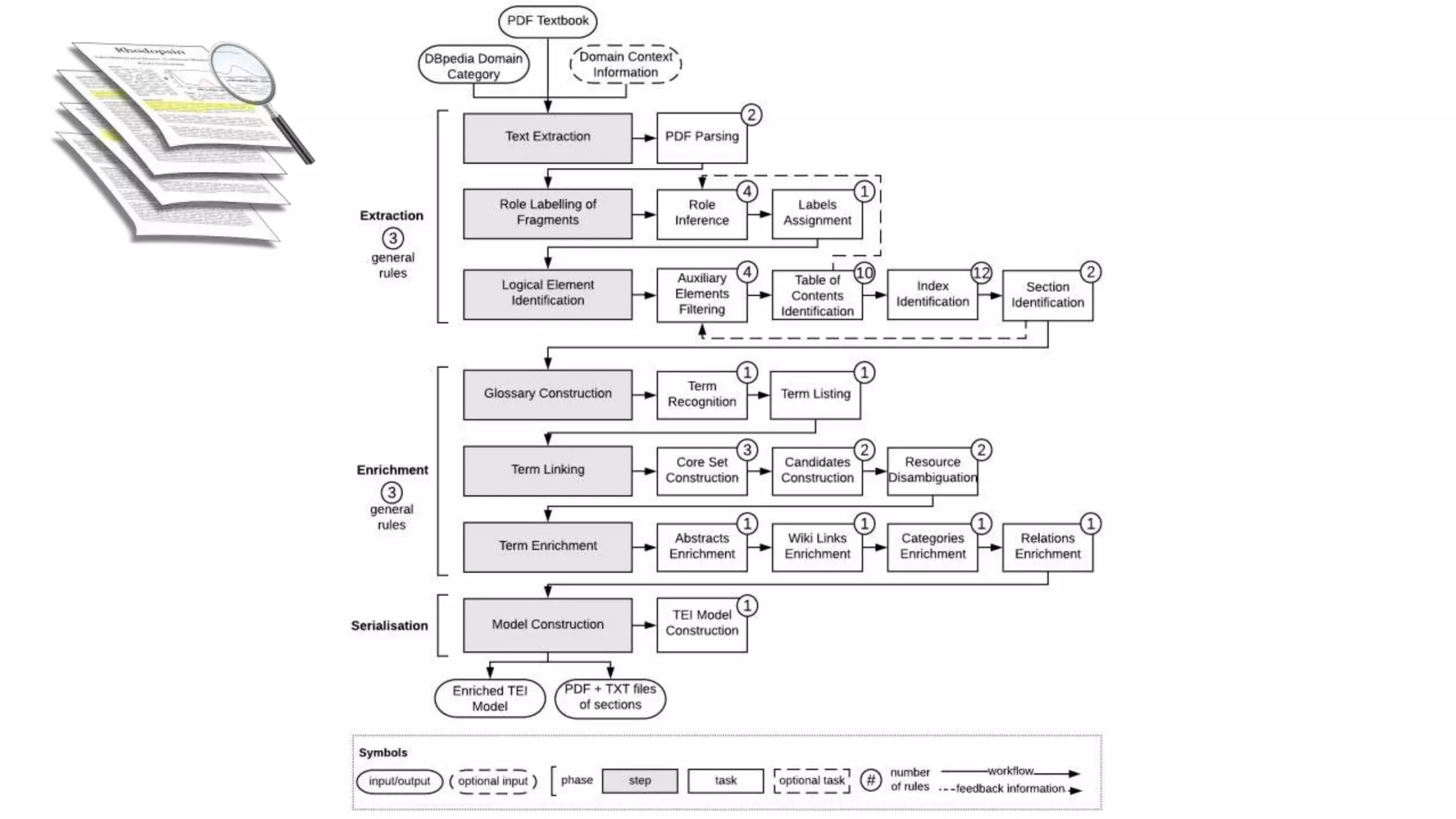
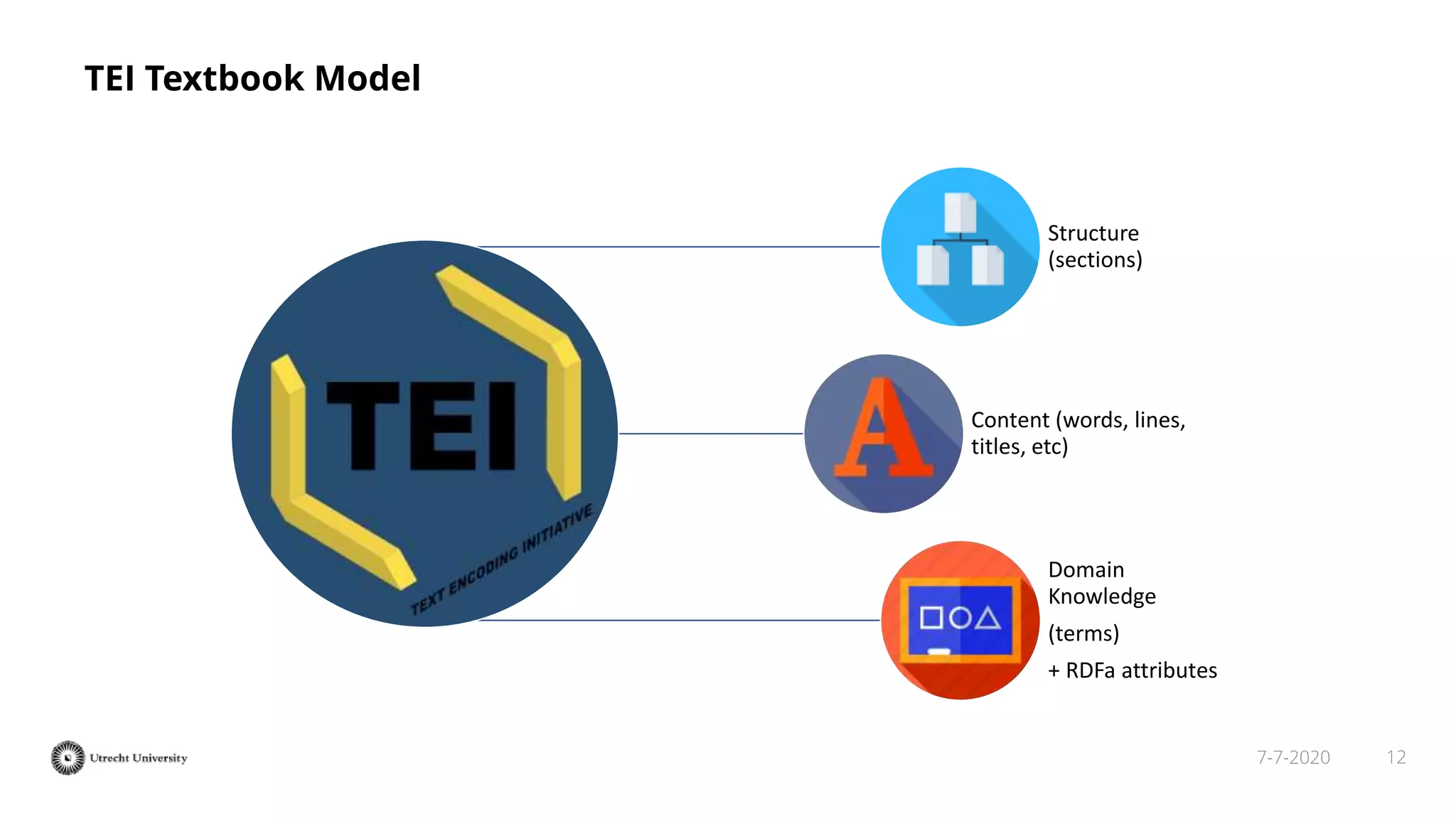
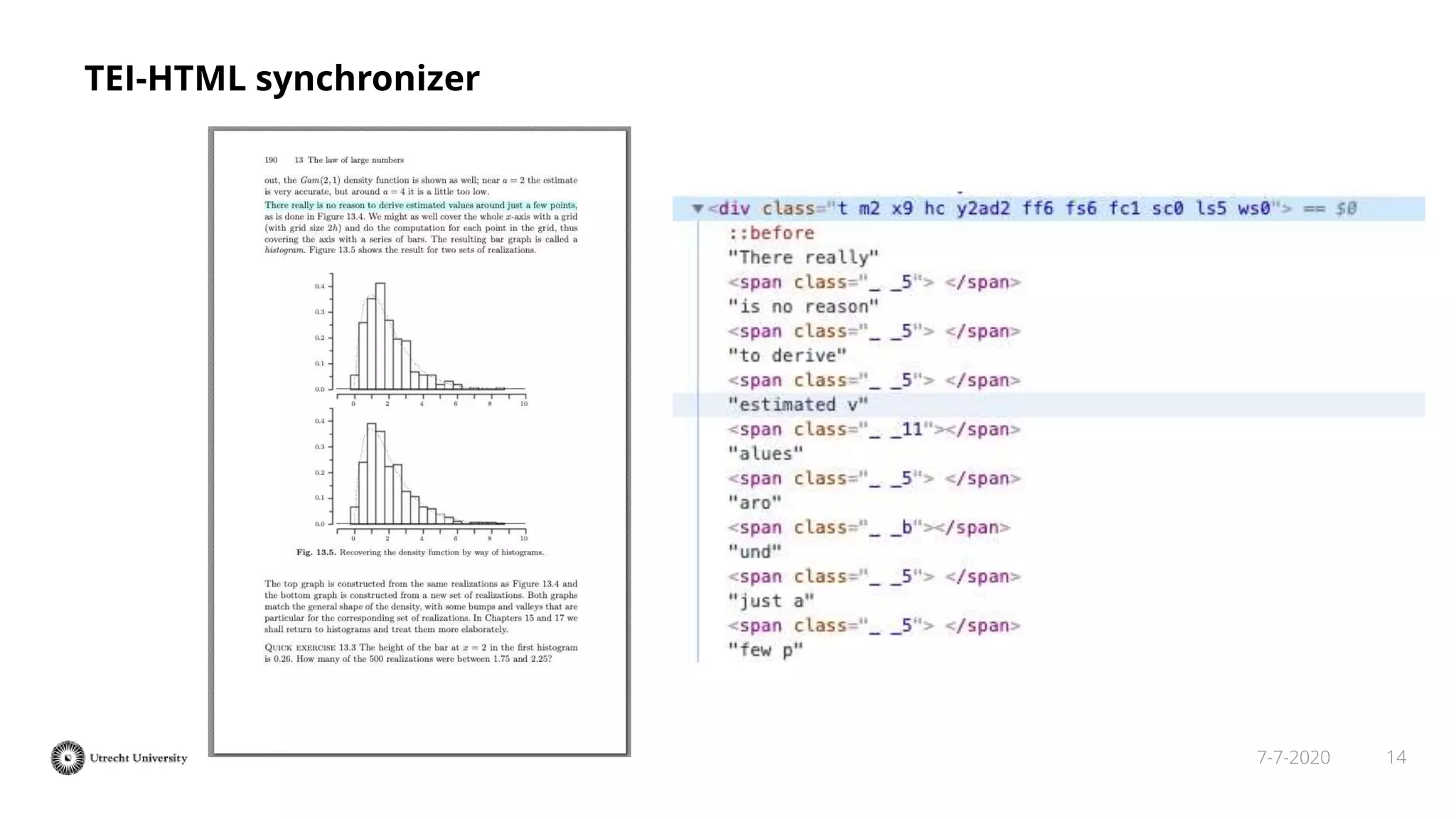
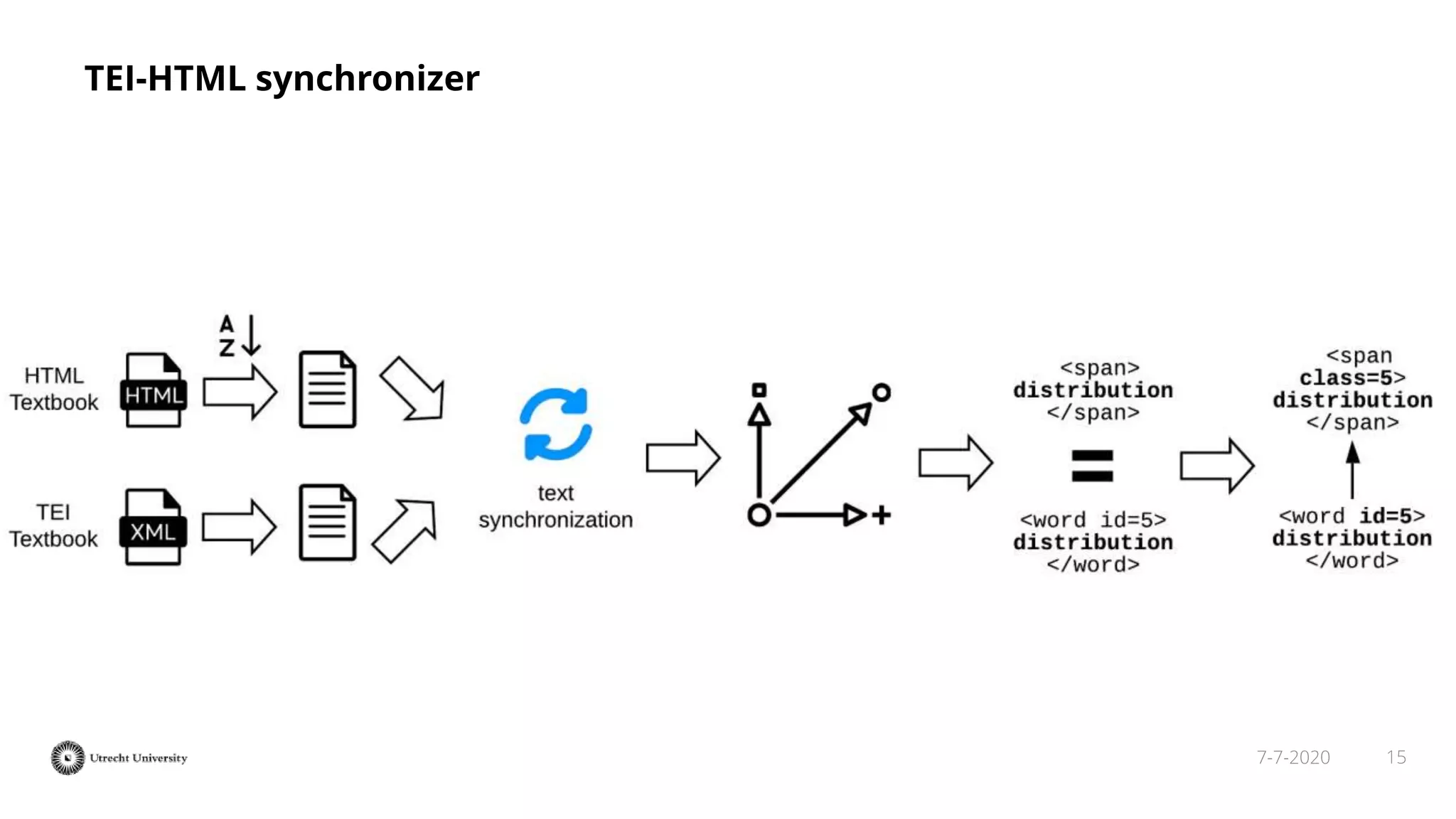
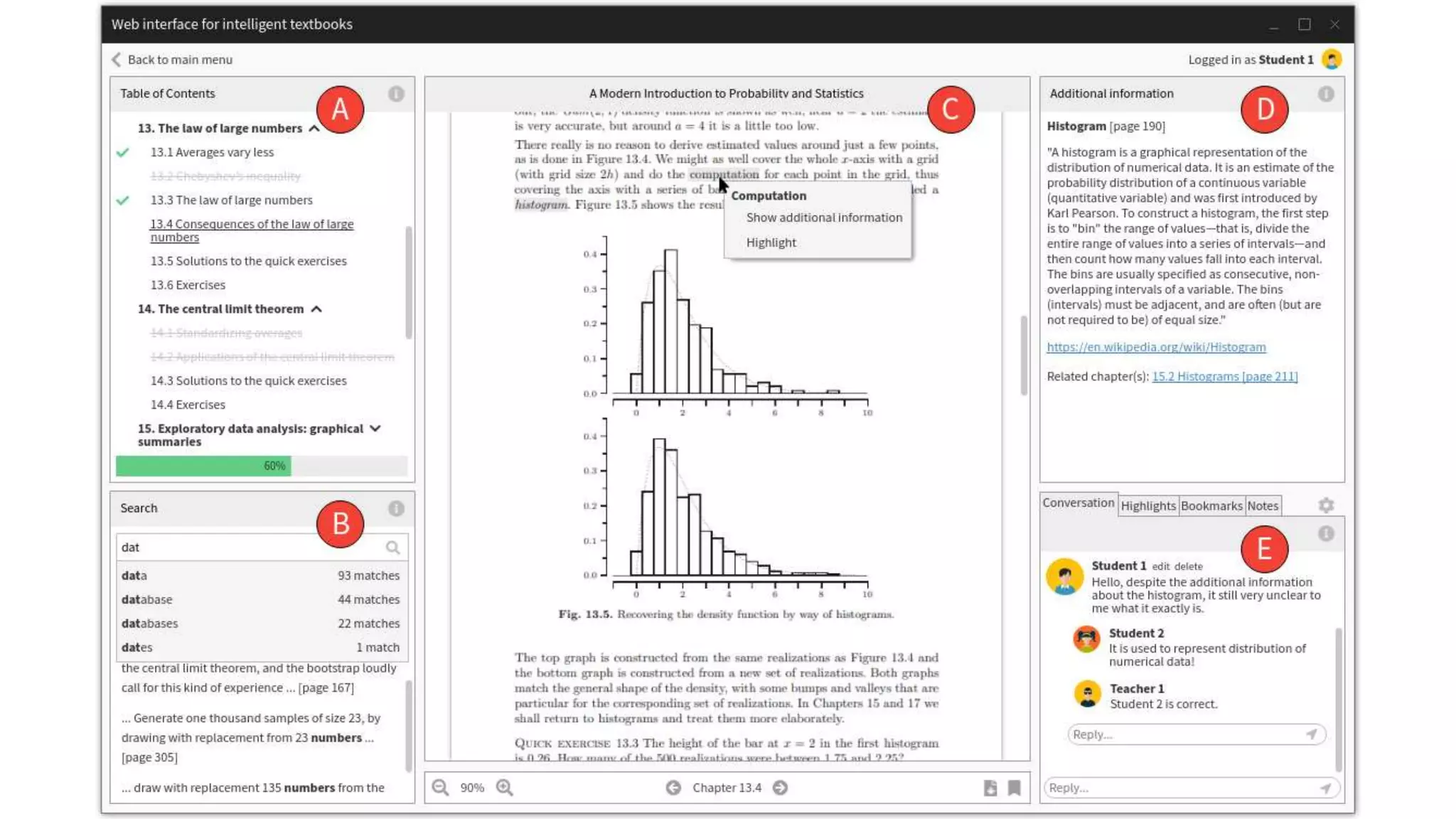
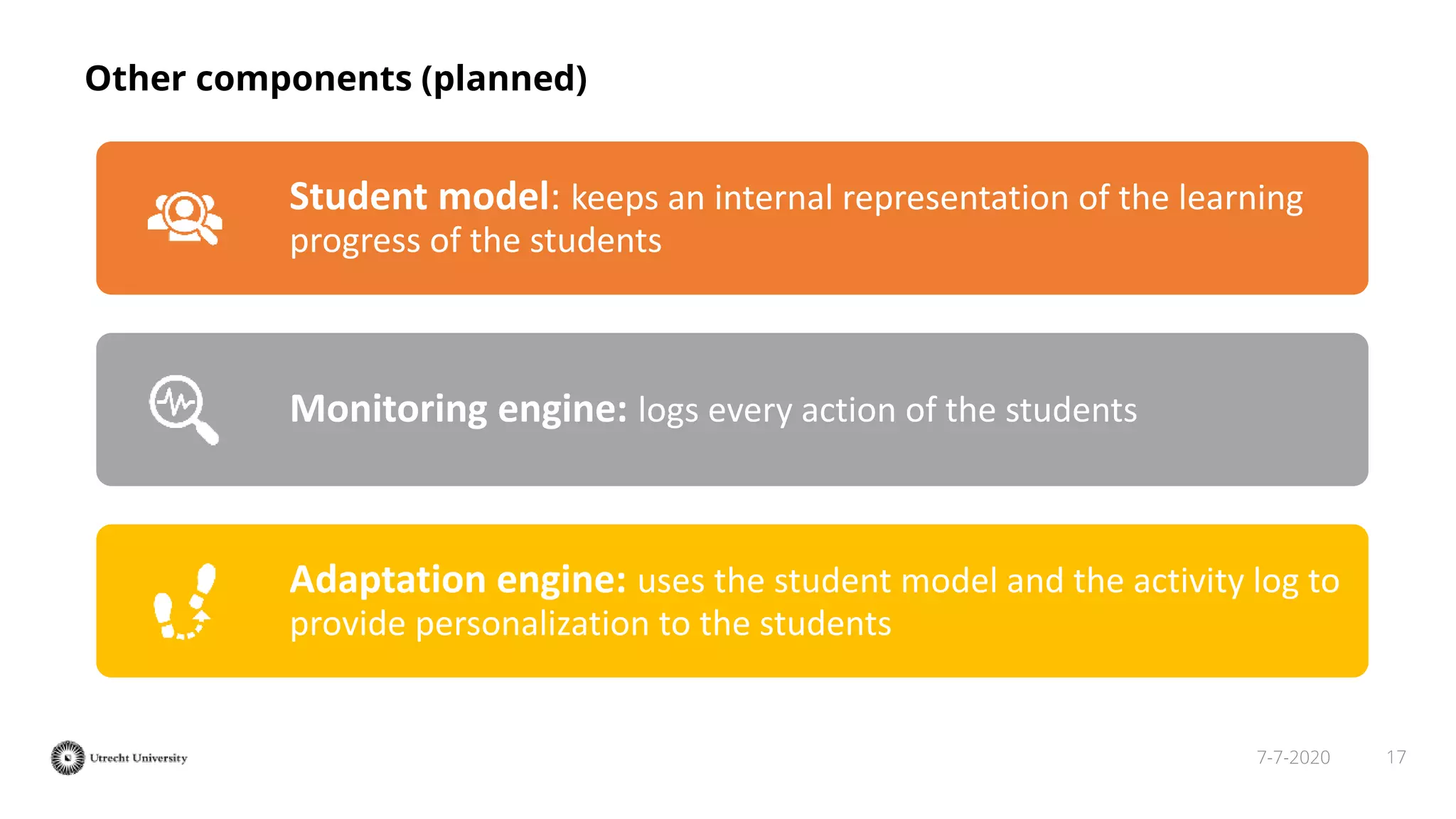
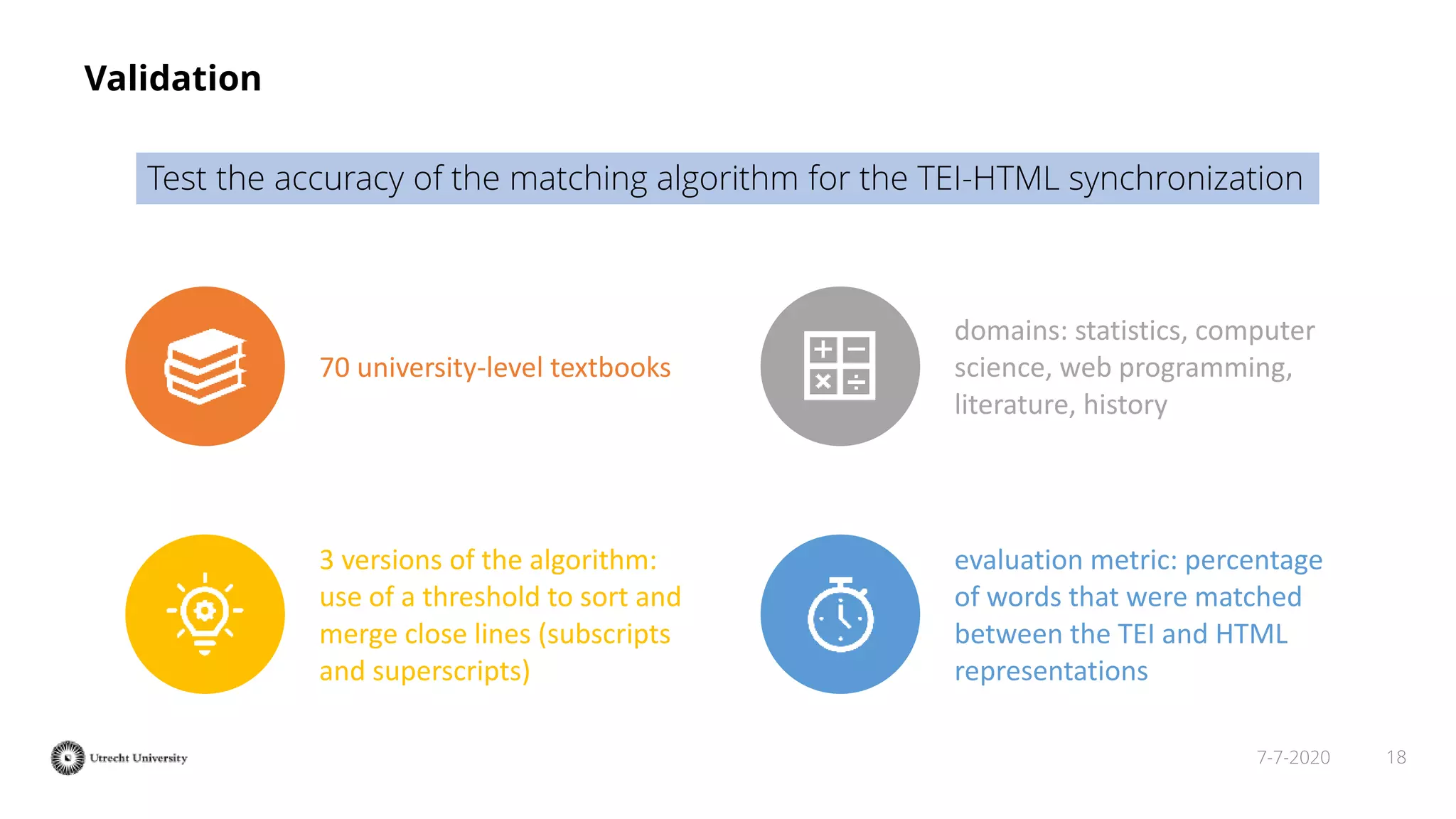
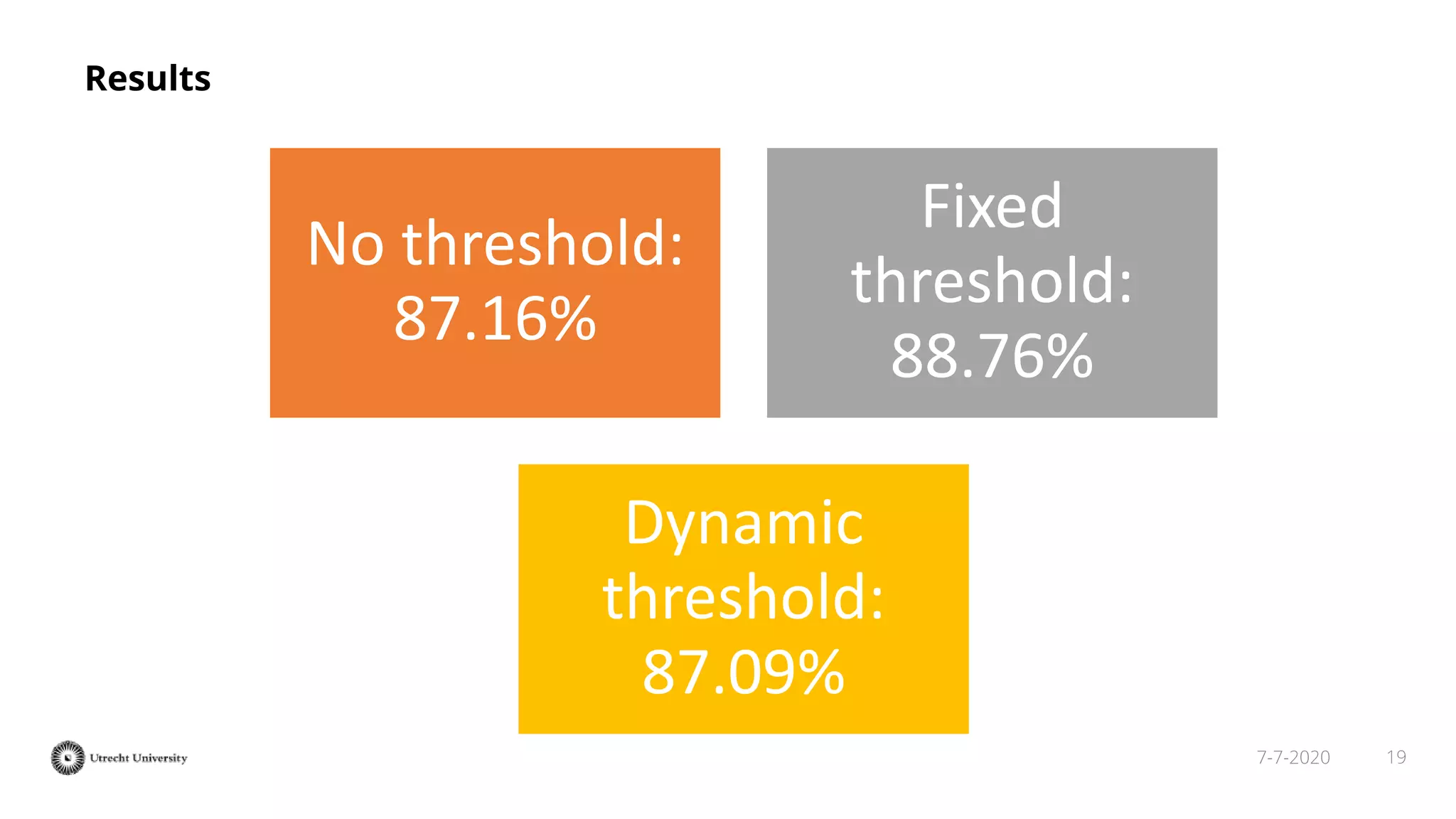
The document discusses the transformation of PDF textbooks into interactive online educational resources using the InTextbooks system, which creates semantically rich HTML representations from PDFs. It details the architecture, the matching algorithms used, and the accuracy of the synchronization between TEI and HTML formats, achieving roughly 88% matching accuracy. Future work includes improving the system's components and evaluating its effectiveness with real students across various academic domains.