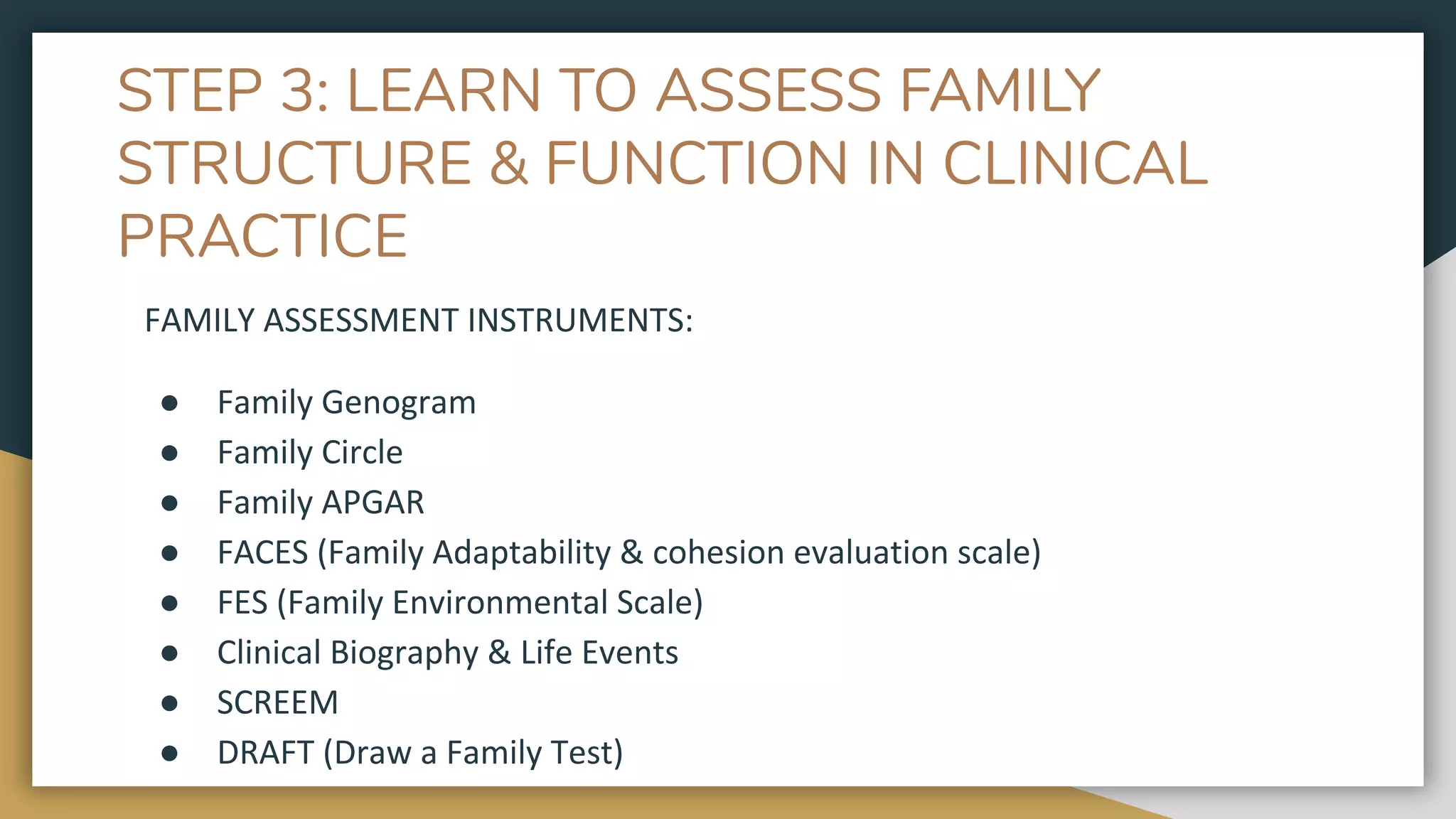
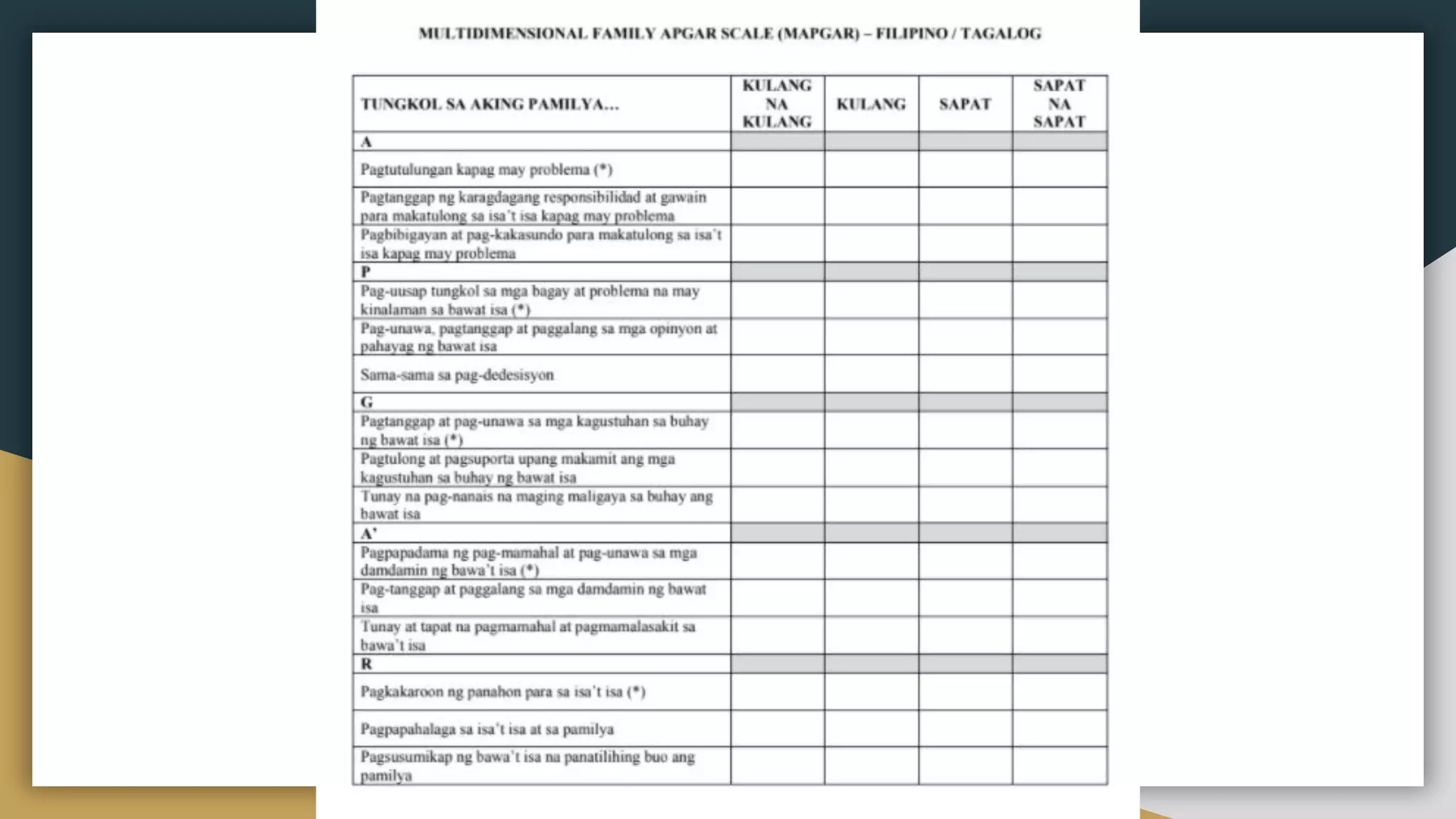
The document discusses tools that can be used in family assessment by family physicians. It describes several tools including the family genogram, family APGAR questionnaire, and draw-a-family test. The family genogram provides a graphic representation of a family's structure and medical history. It is used to understand family relationships and potential health issues. The family APGAR questionnaire evaluates a patient's satisfaction with key areas of family functioning. It is used to screen for family dysfunction. Understanding a family's structure and dynamics is important for family physicians to provide comprehensive patient care.