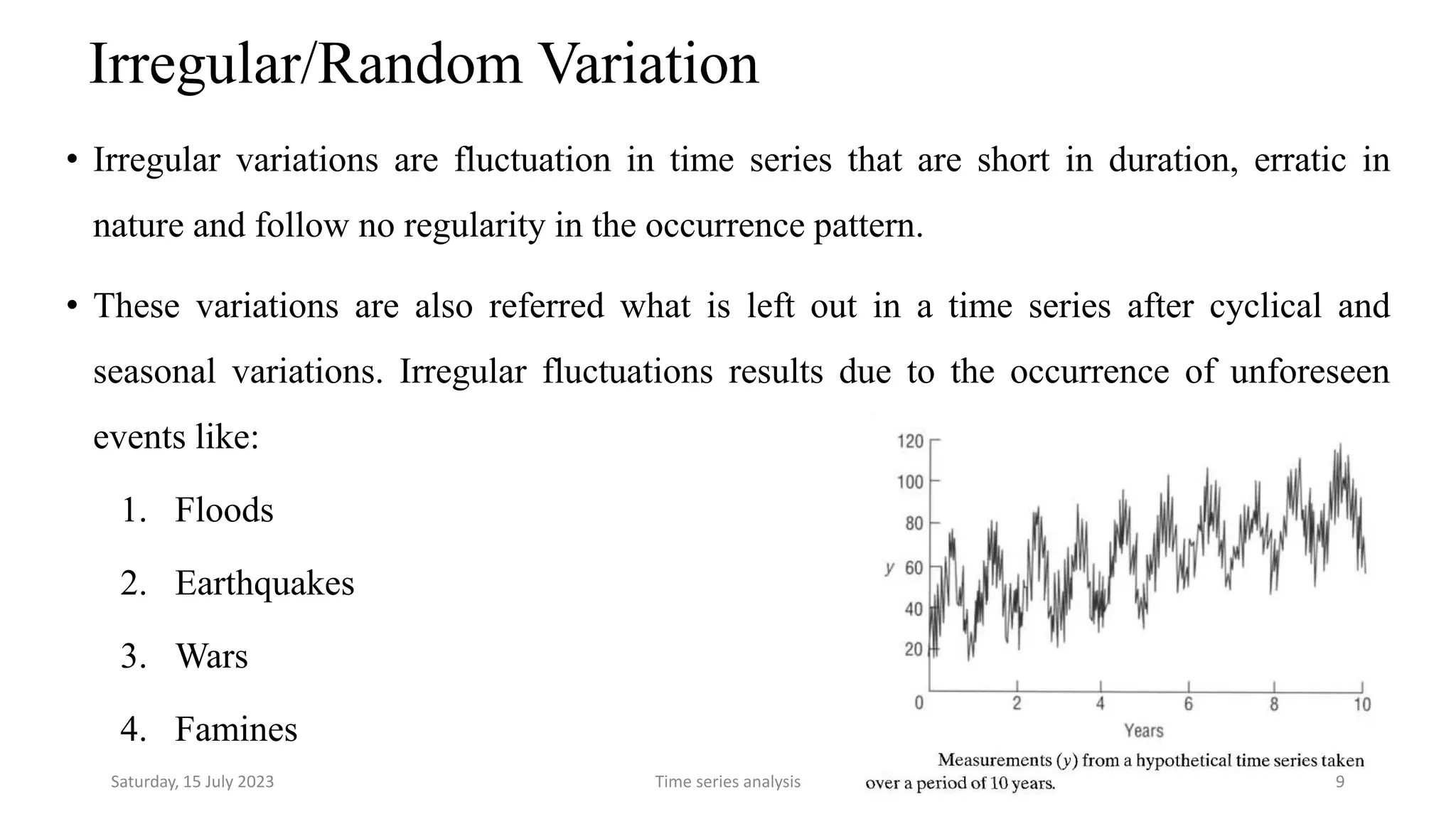
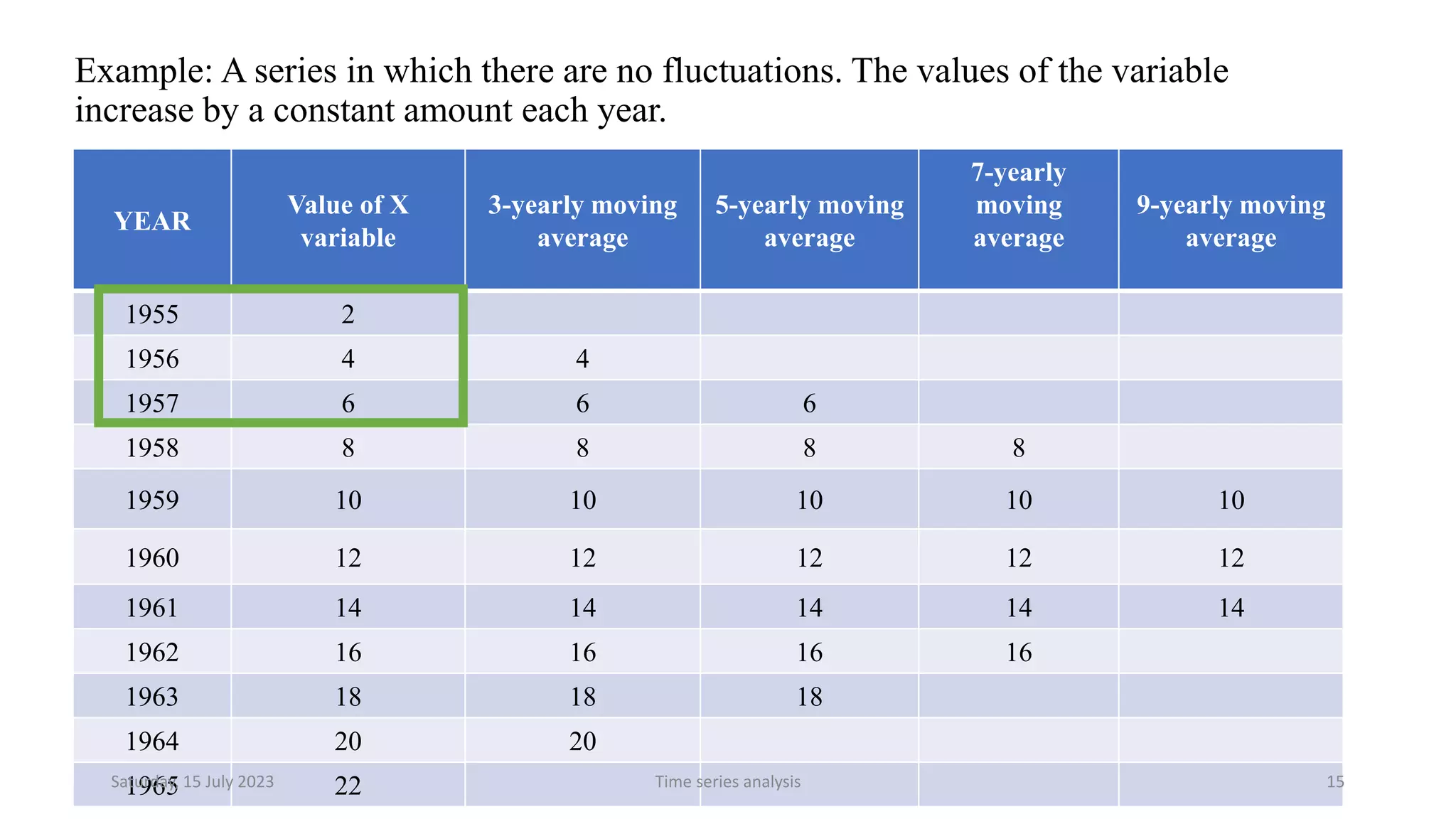
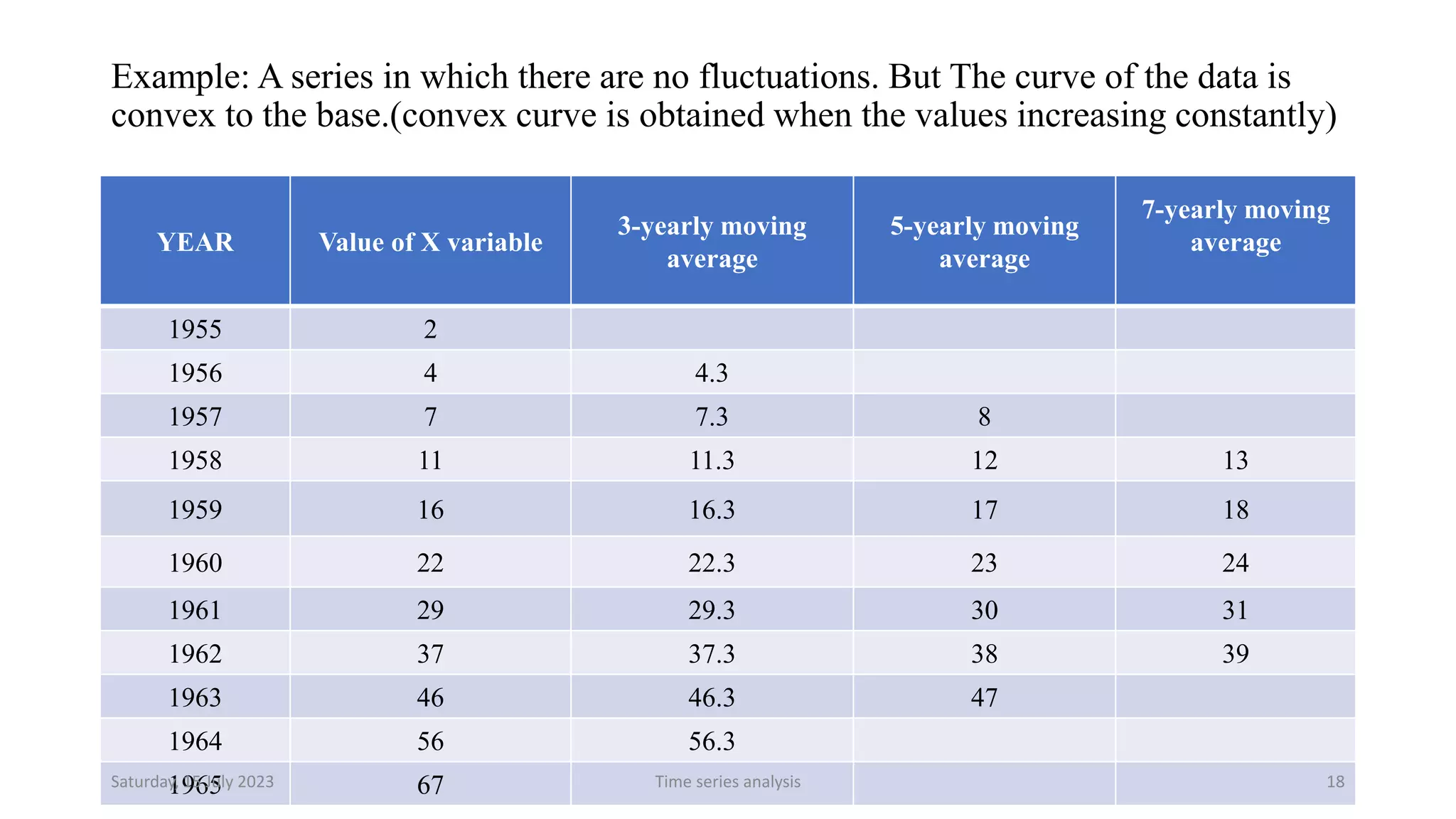
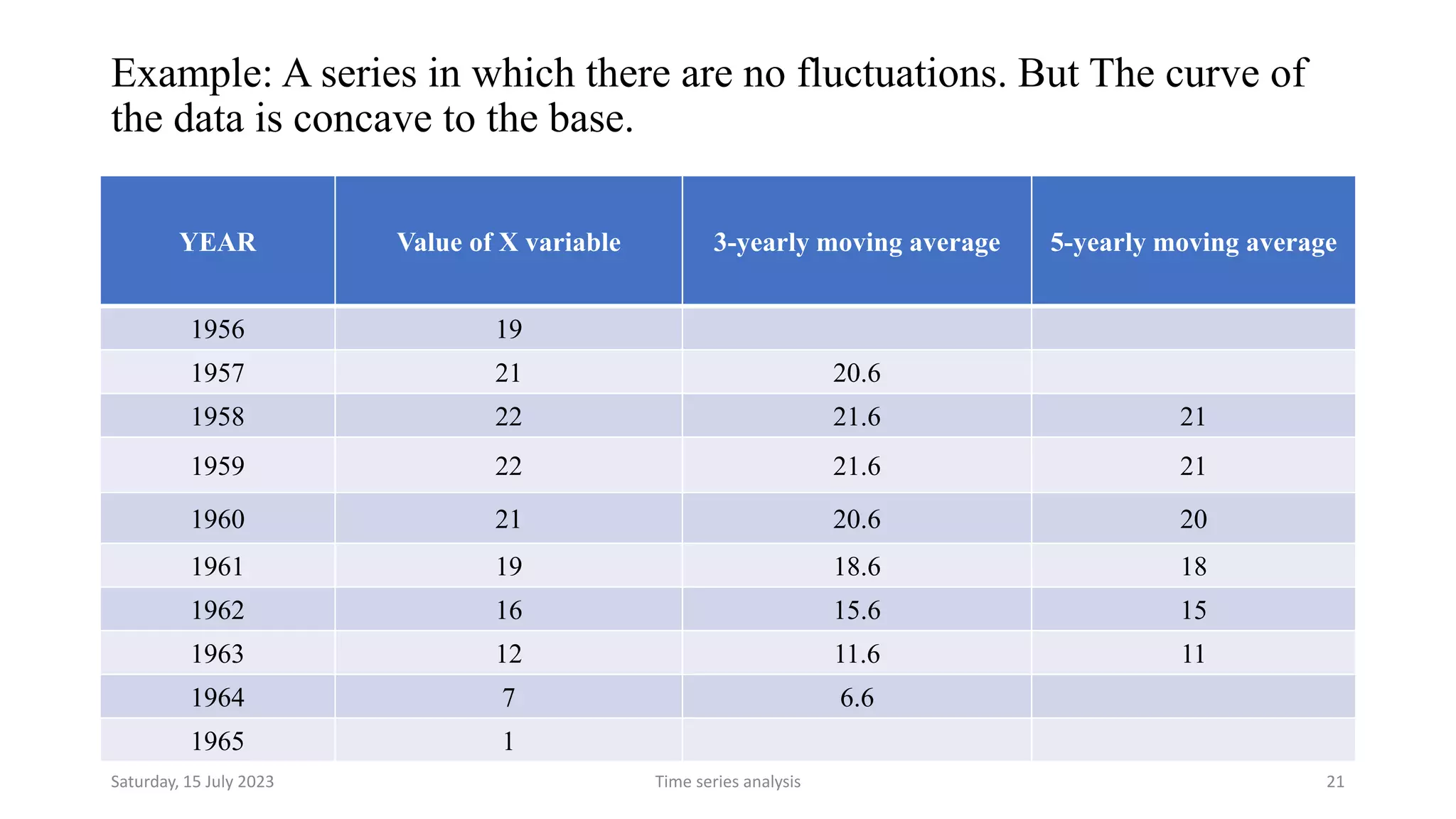
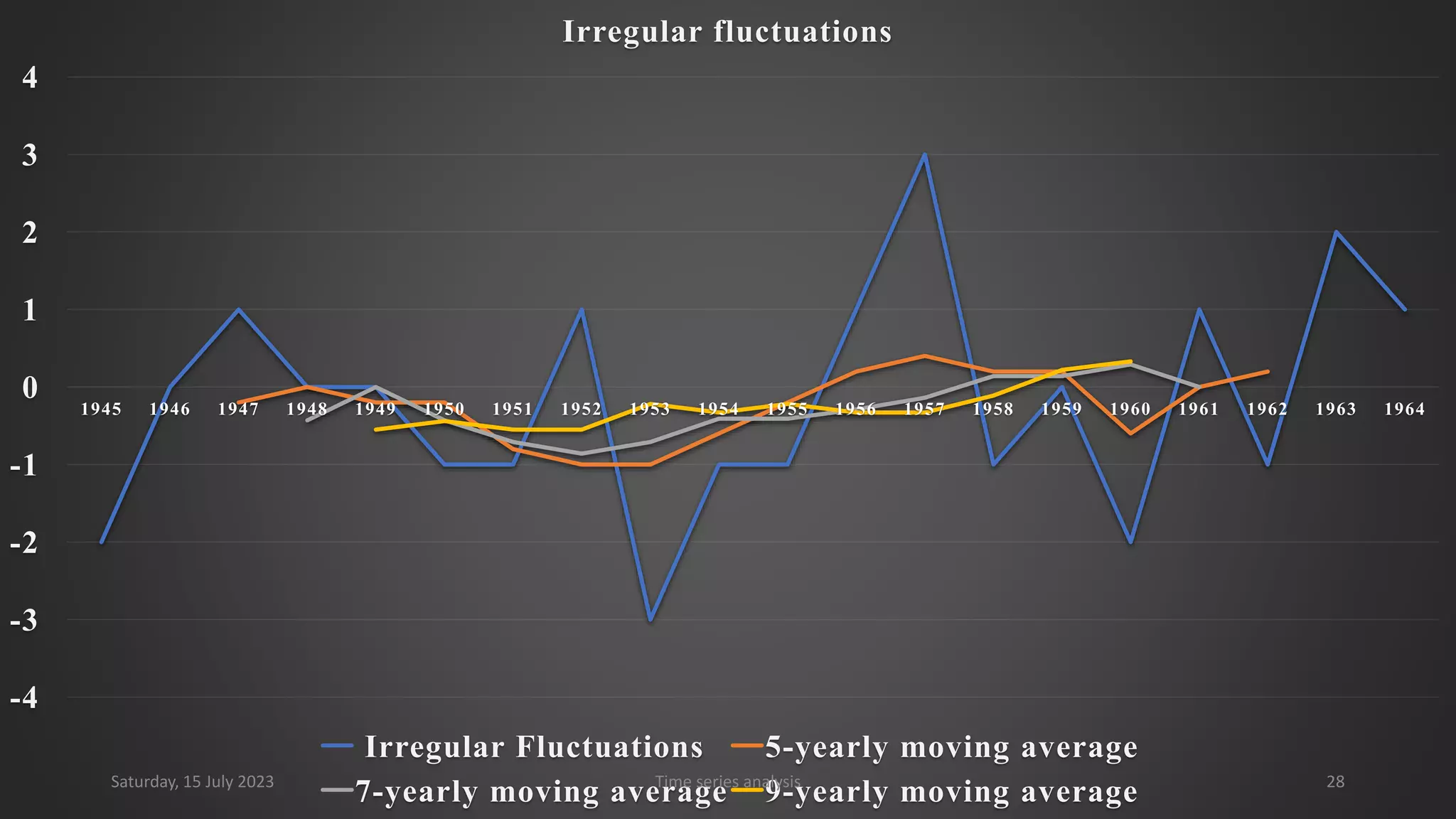
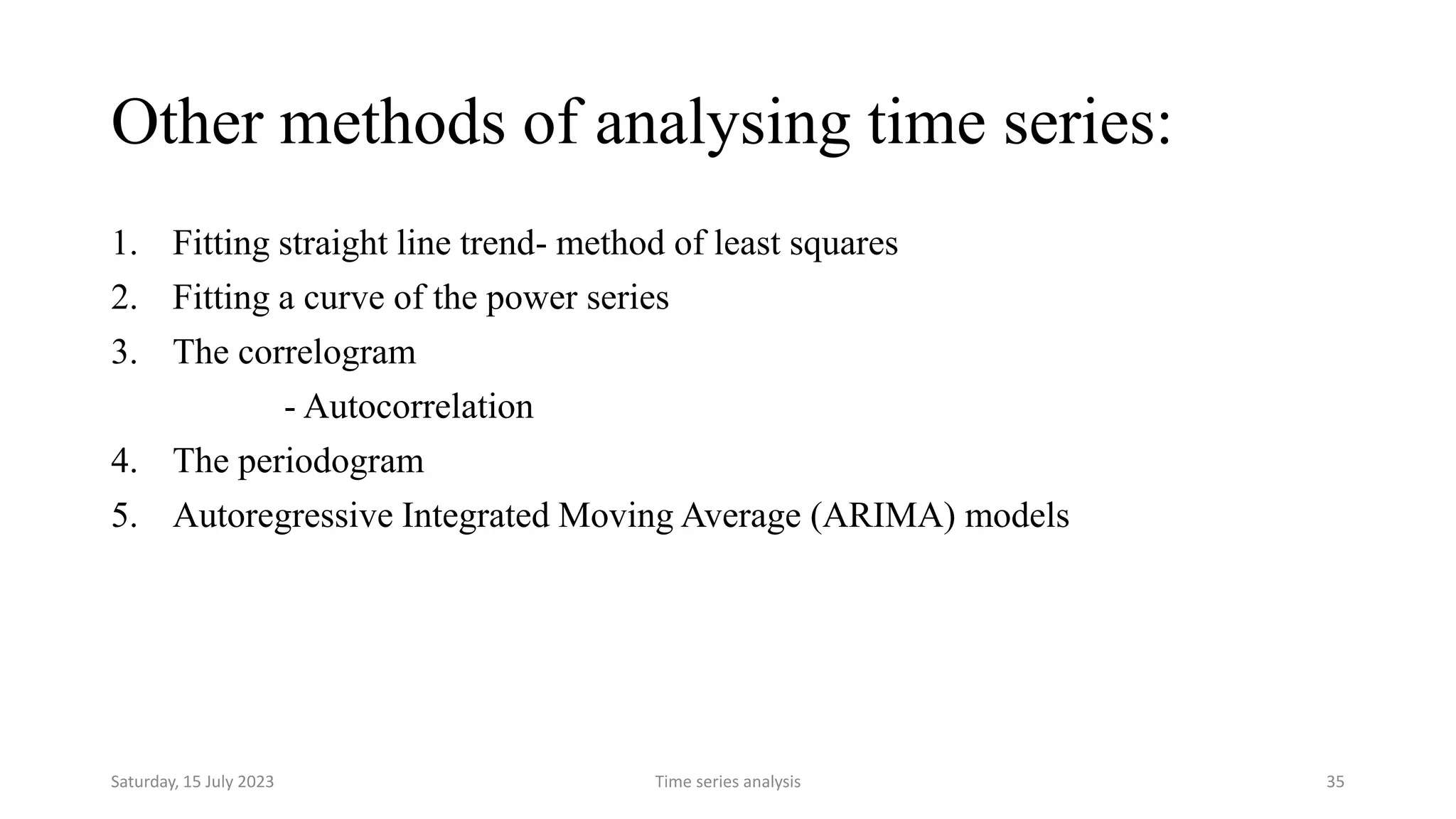
Time series analysis is a statistical methodology used to analyze longitudinal data measured over multiple time points. It can help understand the underlying process driving changes over time or evaluate the effects of interventions. Key components of time series include trends, seasonal variations, cyclical variations, and random variations. Moving average methods are commonly used to calculate trends and reduce other fluctuations in the data. Curve fitting by mathematical equations can also be used when the pattern of changes follows a known function.