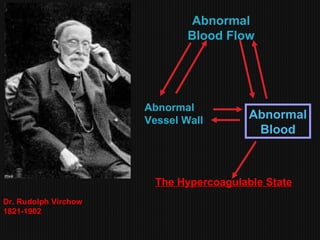
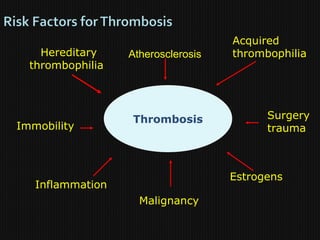
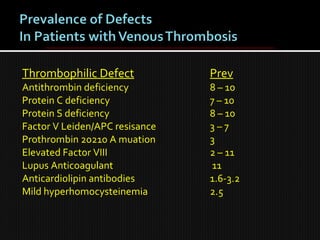
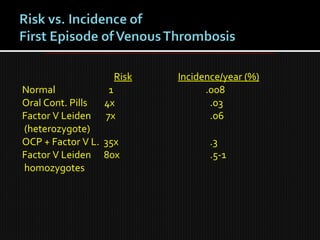
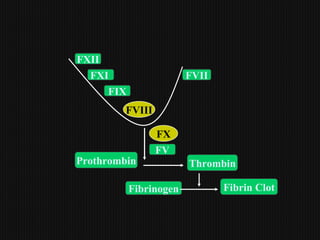
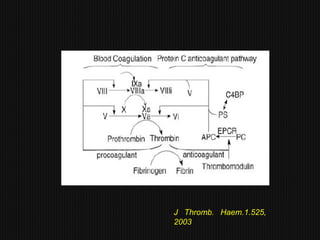
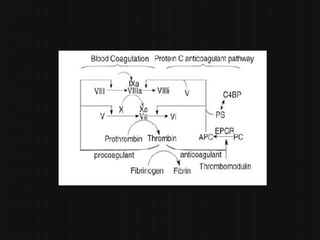
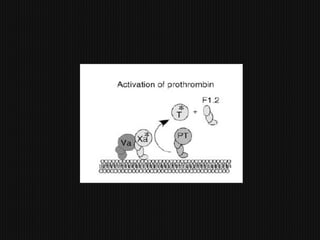
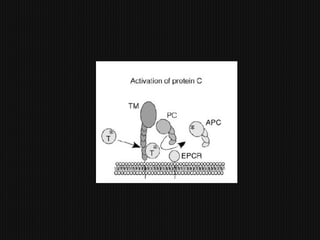
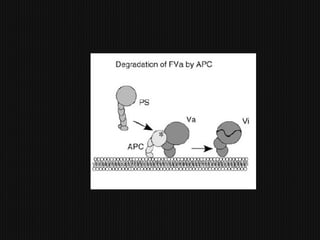
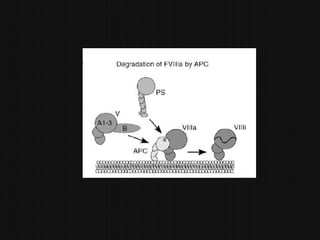
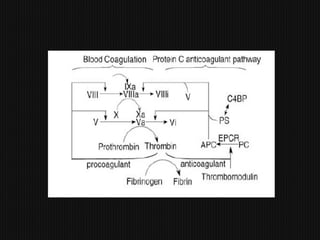
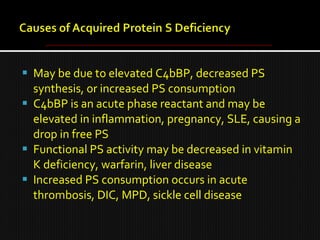
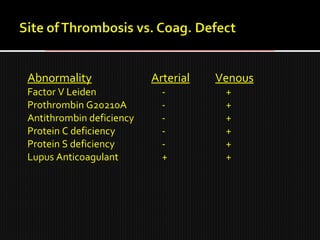
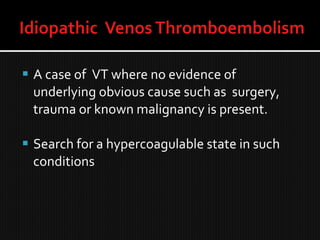
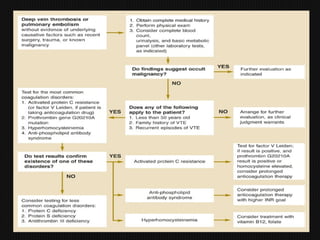
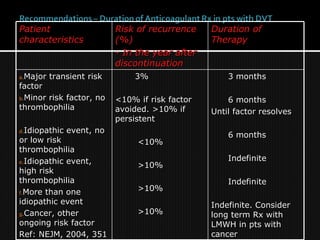
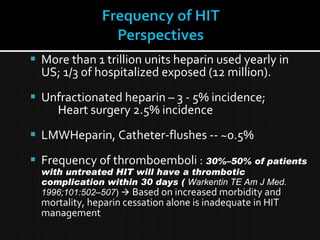
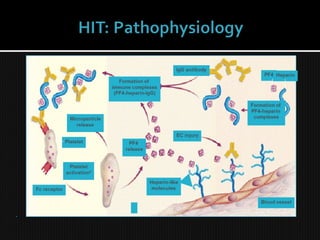
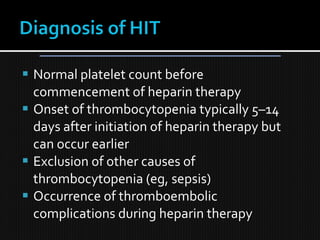
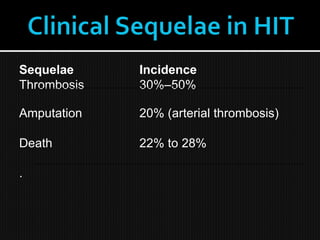
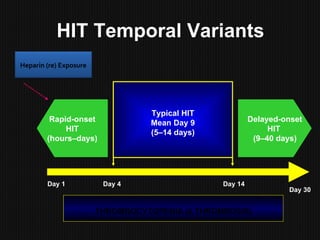
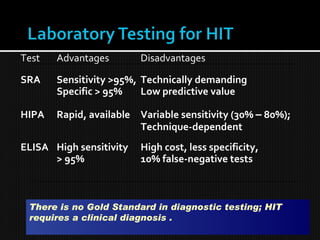
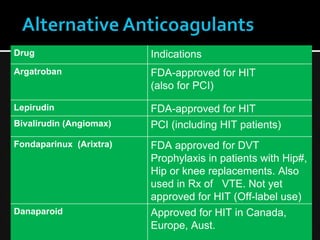
This document discusses thrombophilia and hypercoagulability. It defines thrombophilia as a propensity to develop blood clots due to an abnormality in coagulation. Thrombophilia can be hereditary or acquired. Common causes include inherited defects like Factor V Leiden mutation or acquired conditions like cancer, estrogen use, immobilization, or surgery. Testing for inherited thrombophilias includes screening for deficiencies in antithrombin, protein C, and protein S, as well as mutations in Factor V and prothrombin genes. Management depends on risk level, with indefinite anticoagulation for highest risk individuals.