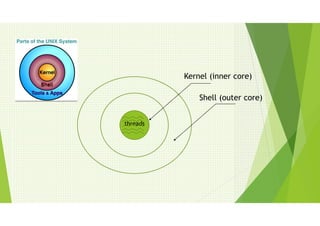
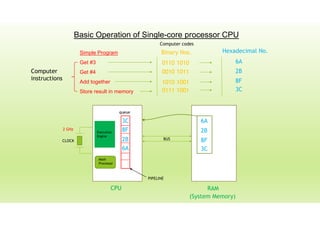
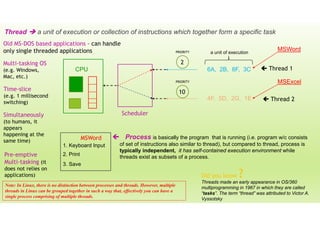
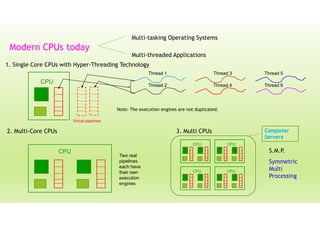
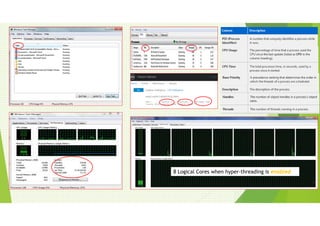
This document provides an outline for a presentation on threads. It discusses single-threaded and multi-threaded approaches, with single-threaded having a single execution path per process and multi-threaded allowing multiple threads within a process. It also covers characteristics of threads like processes and threads differences, thread execution states, synchronization, and types of threads. The presentation aims to explain threads and their advantages in modern multi-core CPUs and multi-tasking operating systems.