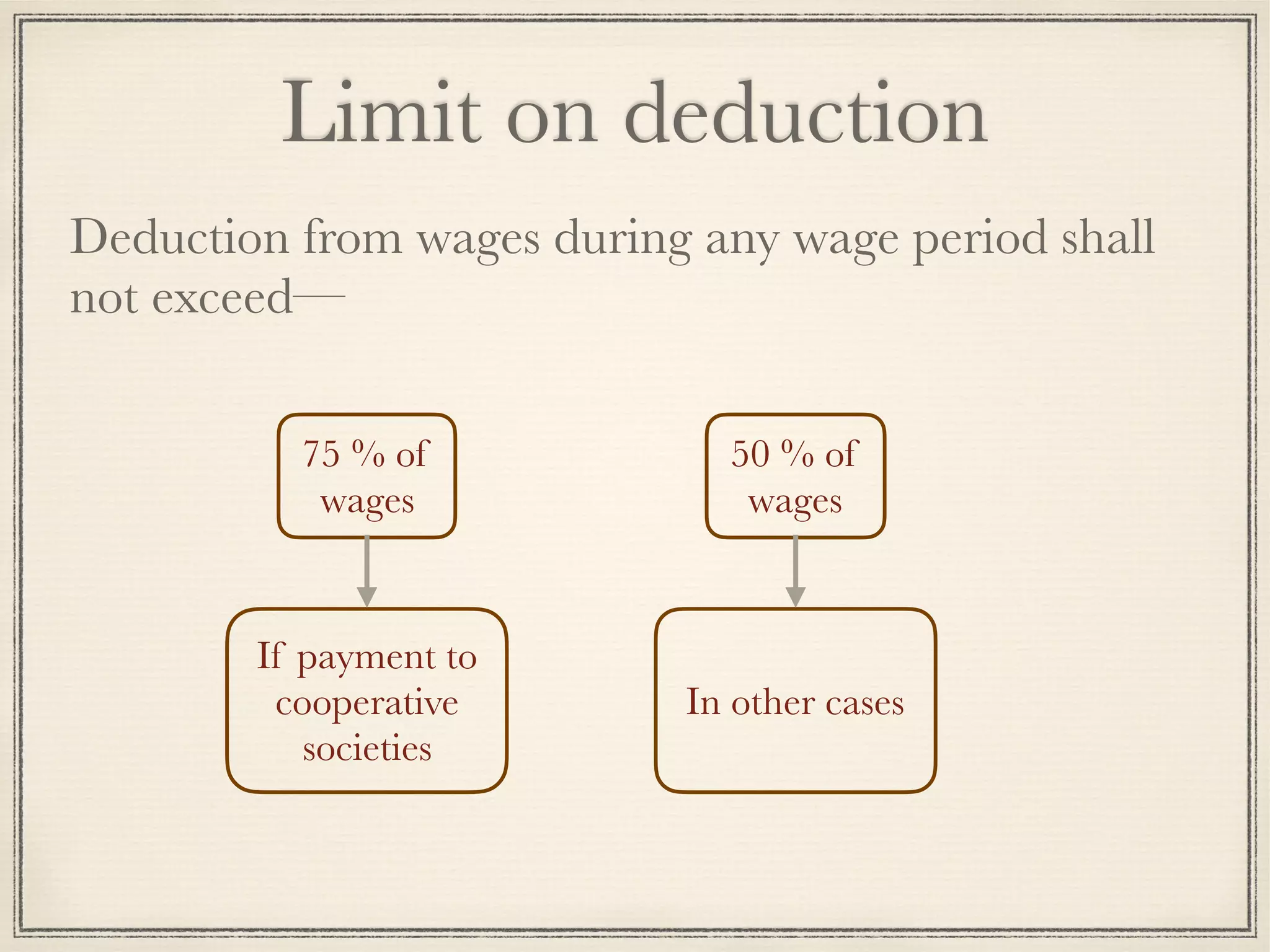
The Payment of Wages Act, 1936 regulates payment of wages to certain classes of employees in industries. Its objectives are to ensure wages are paid within prescribed time periods and without unjustified deductions. It applies to factories, railways, and other establishments specified in the Act employing workers earning up to Rs. 18,000 per month. Wages must be paid within 7-10 days of the end of the wage period, which cannot exceed one month. Only limited deductions are permitted from wages.