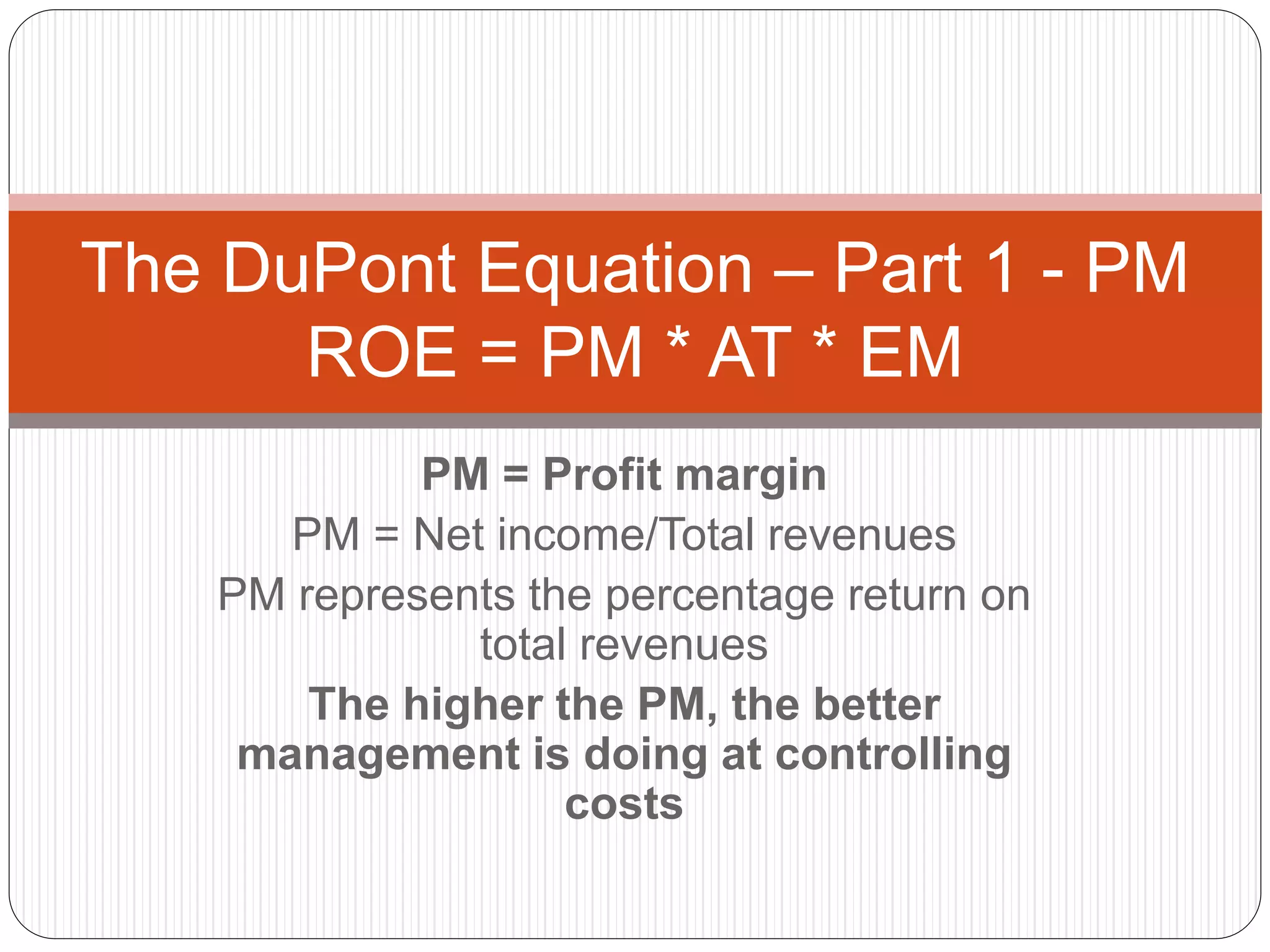
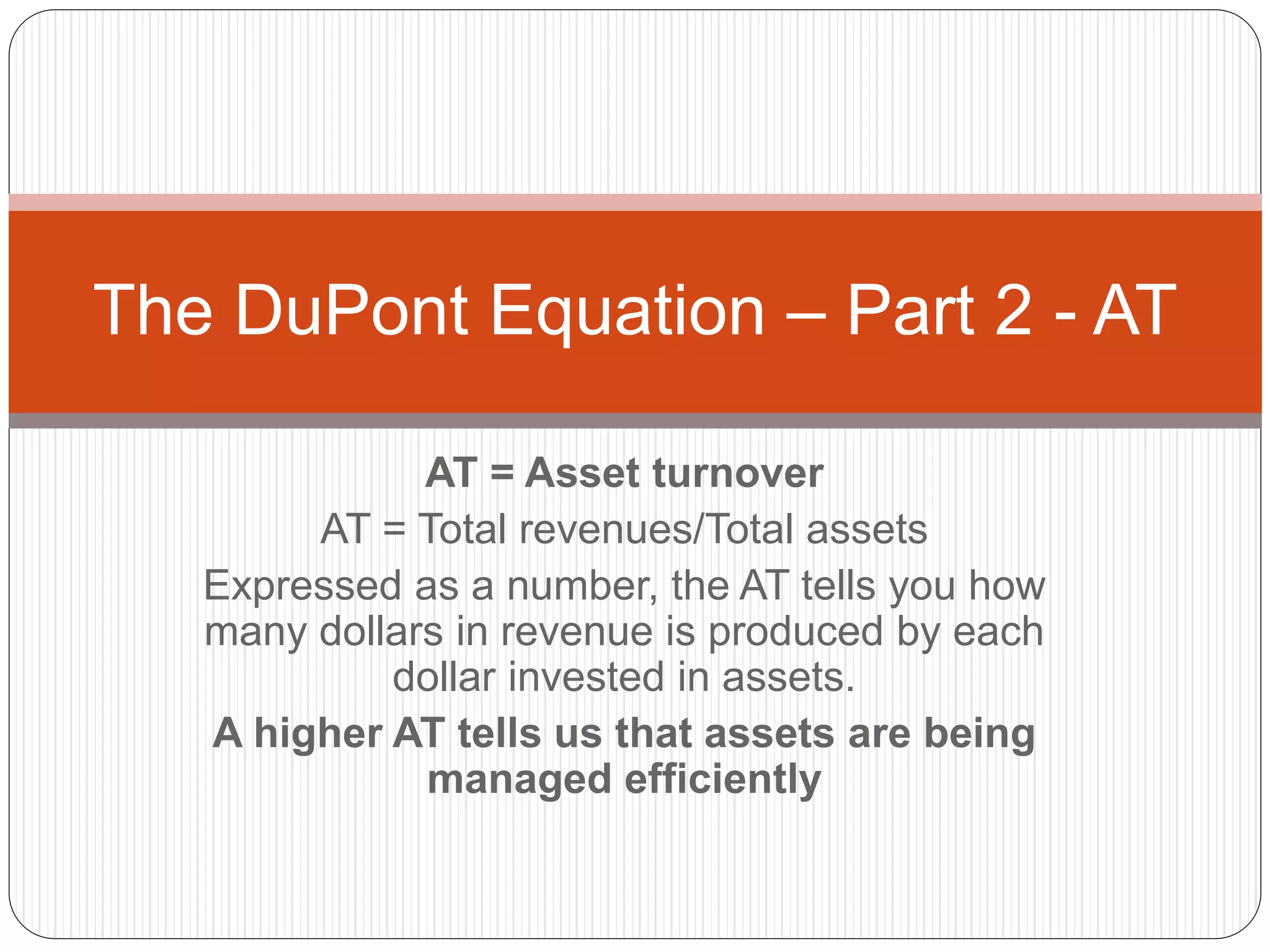
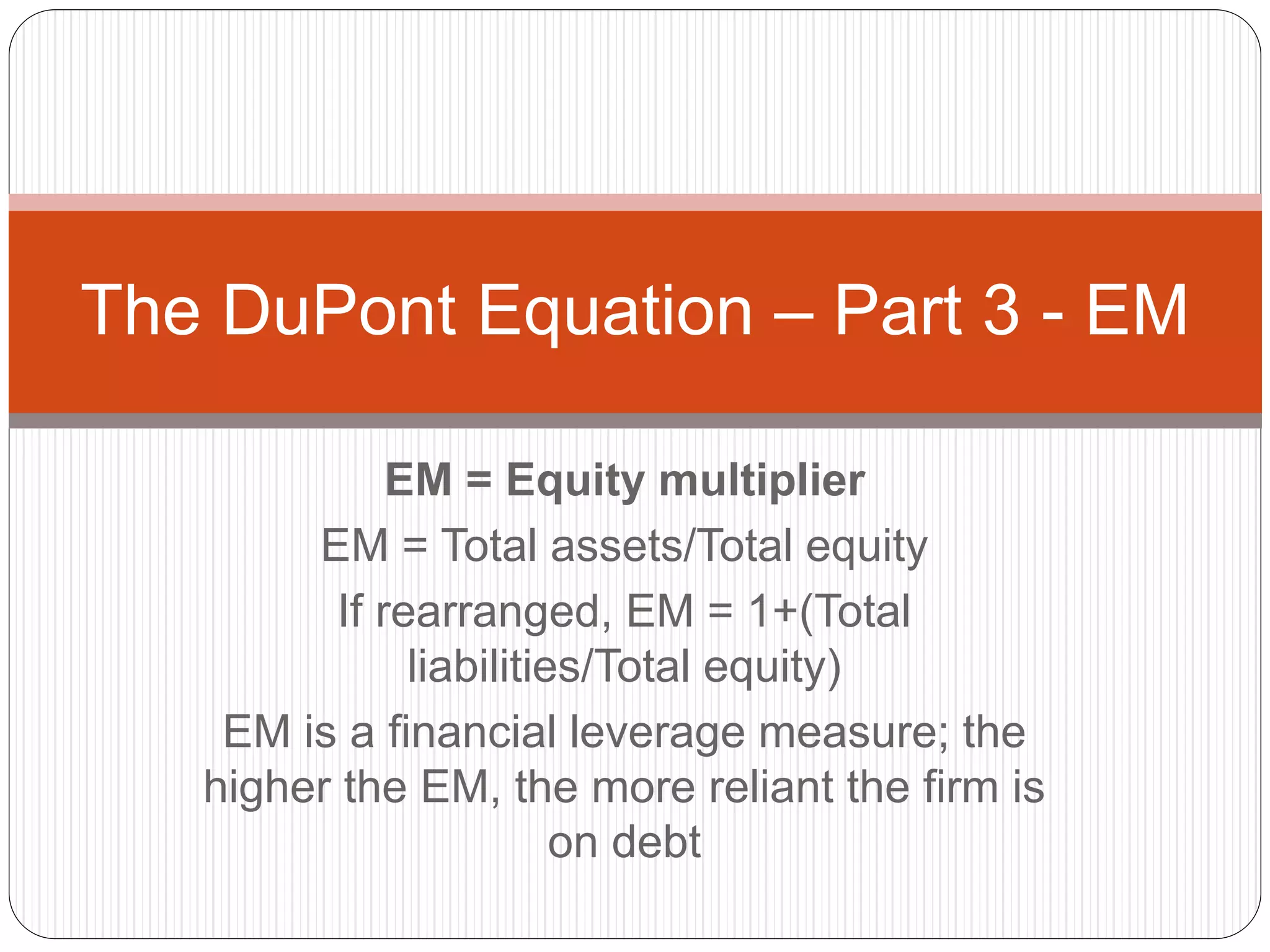
The DuPont equation breaks down return on equity (ROE) into three components: profit margin (PM), asset turnover (AT), and equity multiplier (EM). PM measures the percentage of revenues converted to net income, AT measures how efficiently assets generate revenue, and EM measures financial leverage through the use of debt. Together, analyzing these three factors provides insight into a company's profitability, asset efficiency, and financial stability.