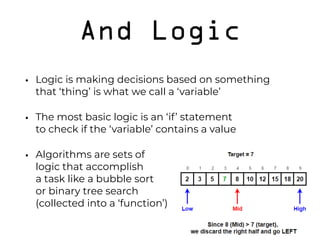
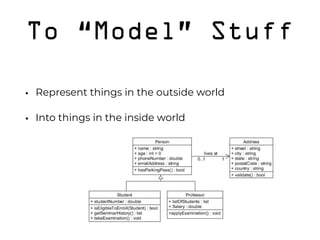
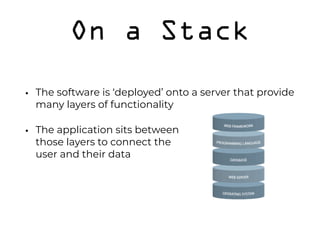
The document discusses the role of developers as creative problem solvers who use various programming concepts and tools to build applications, websites, and IoT devices. It emphasizes the importance of treating developers as creative workers and explains key programming principles such as objects, inheritance, composition, APIs, and frameworks. Additionally, it highlights the significance of user experience in software development and the necessity of code testing and proper repository management.


![Creative Problem
Solvers
• Inventive
• Adaptive
• Curios
• Thoughtful
• Passionate
• Abstract
'Treat your developers like creative
workers – or watch them leave'
Jeff Lawson, Twilio CEO
“[Software engineering] is perhaps the
most creative field imaginable. It’s just
your thoughts and a screen waiting to be
filled with code. In that screen you can
create anything.”
Nick Malik, CEO
Vanguard Enterprise Architects](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/devsworld-191022124417/85/The-Developers-World-3-320.jpg)