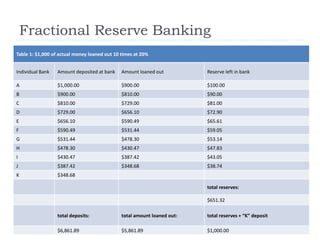
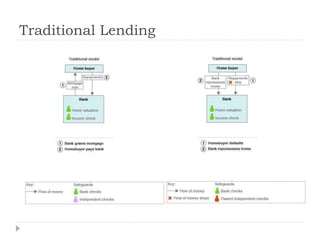
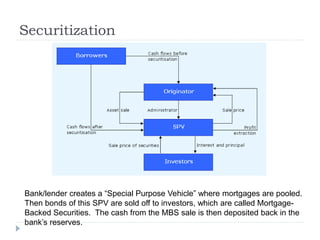
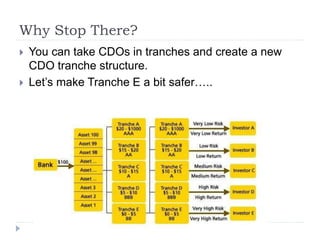
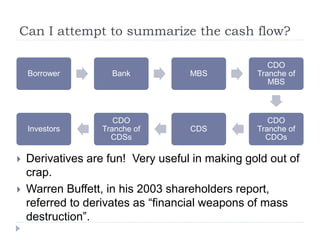
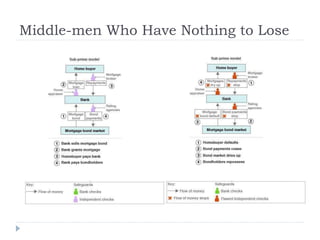
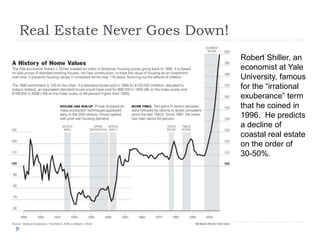
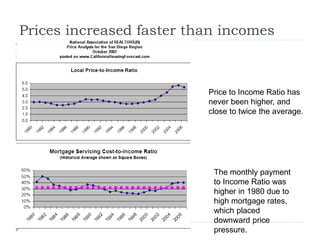
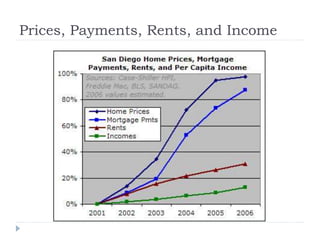
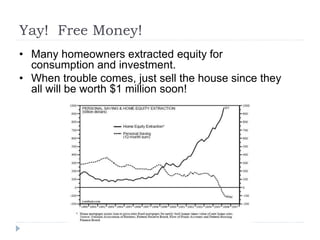
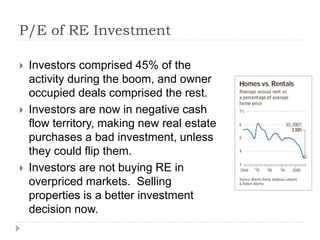
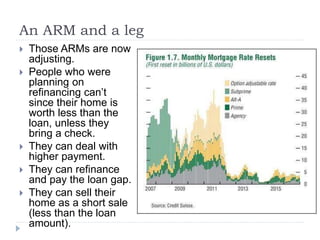
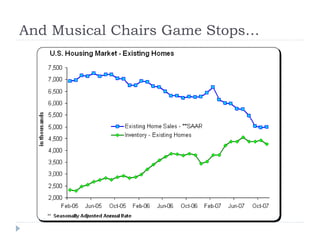
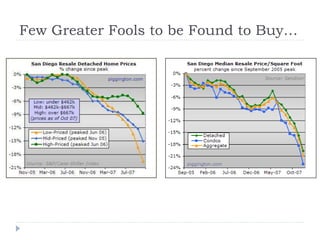
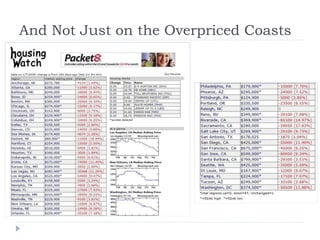
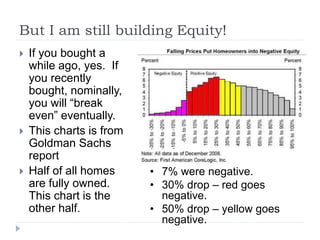
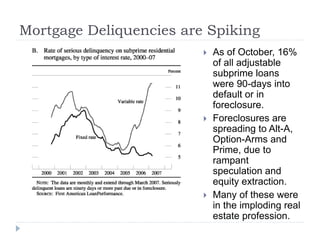
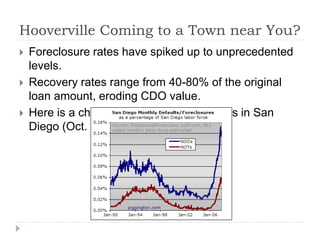
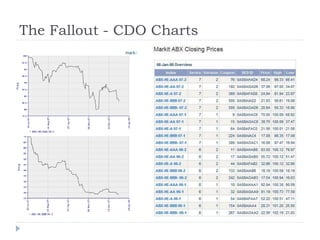
The document discusses the credit crunch of 2008, highlighting how the sudden reduction in credit availability was influenced by increased risk perception and monetary conditions. It explains the mechanisms of fractional reserve banking, traditional lending, securitization, and the creation of collateralized debt obligations (CDOs), which ultimately led to significant financial instability. The fallout included skyrocketing mortgage delinquencies, foreclosures, and the severe impact on the values of CDOs, as well as the role of government-backed entities in attempting to stabilize the mortgage market.