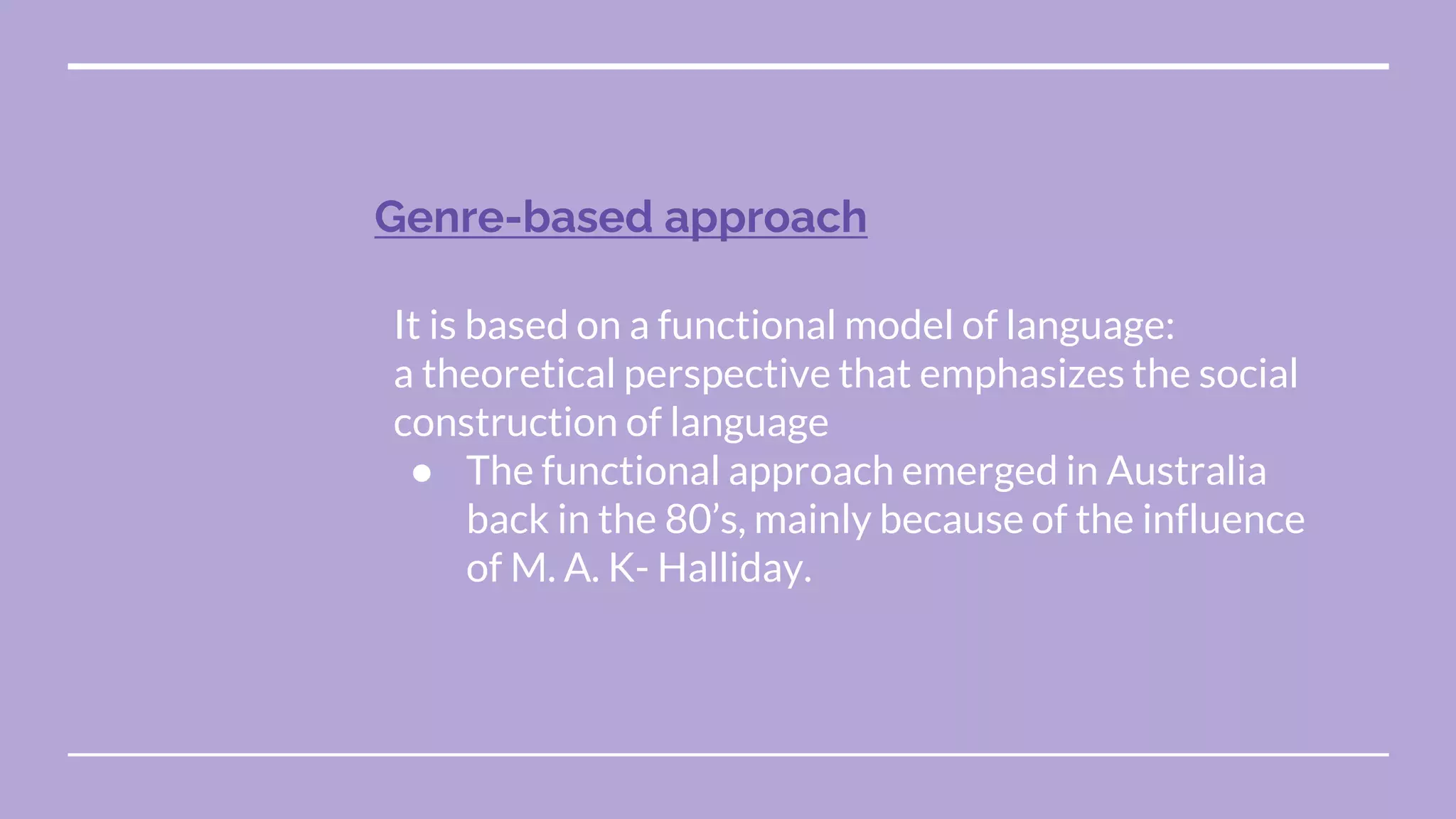
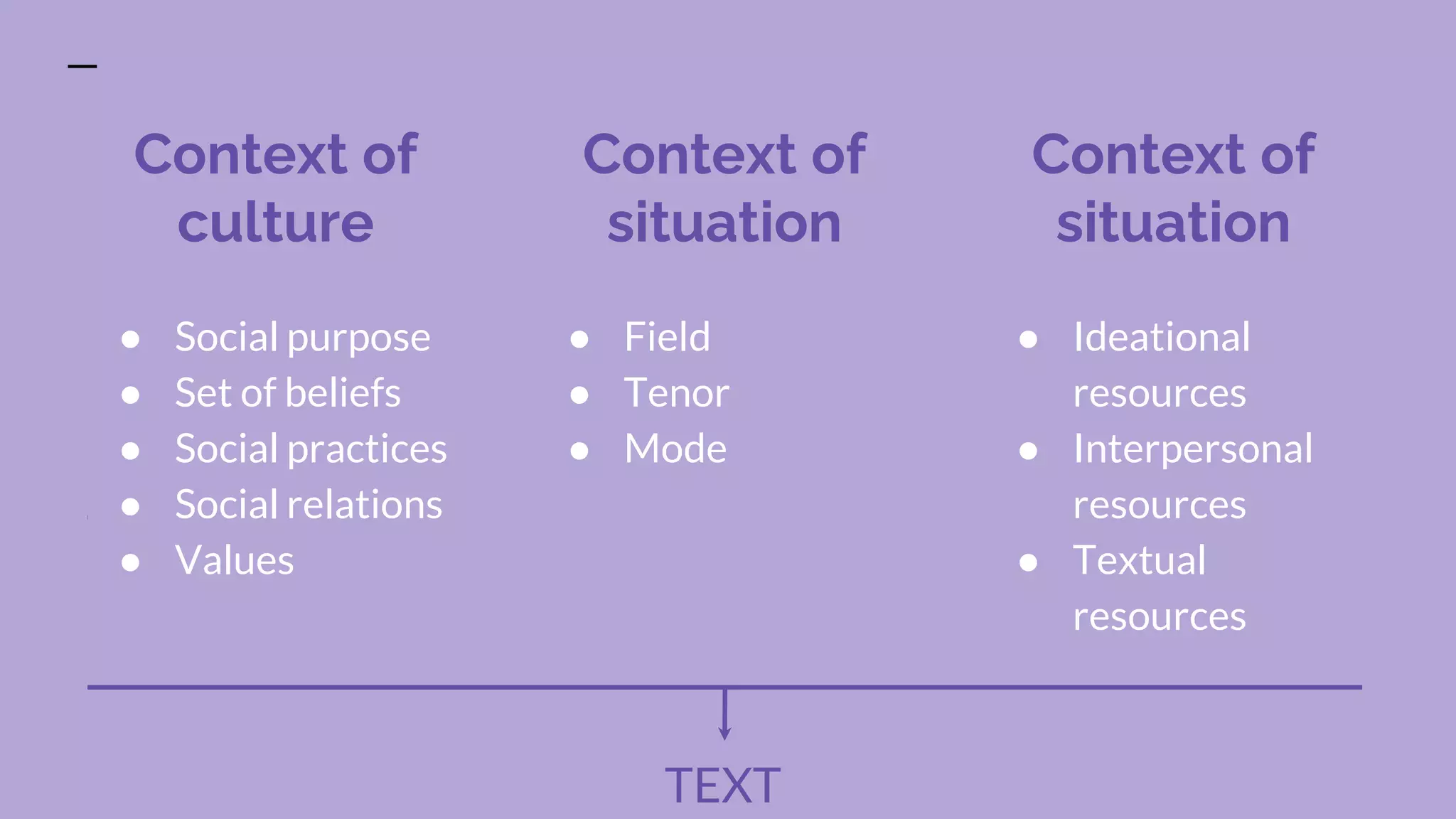
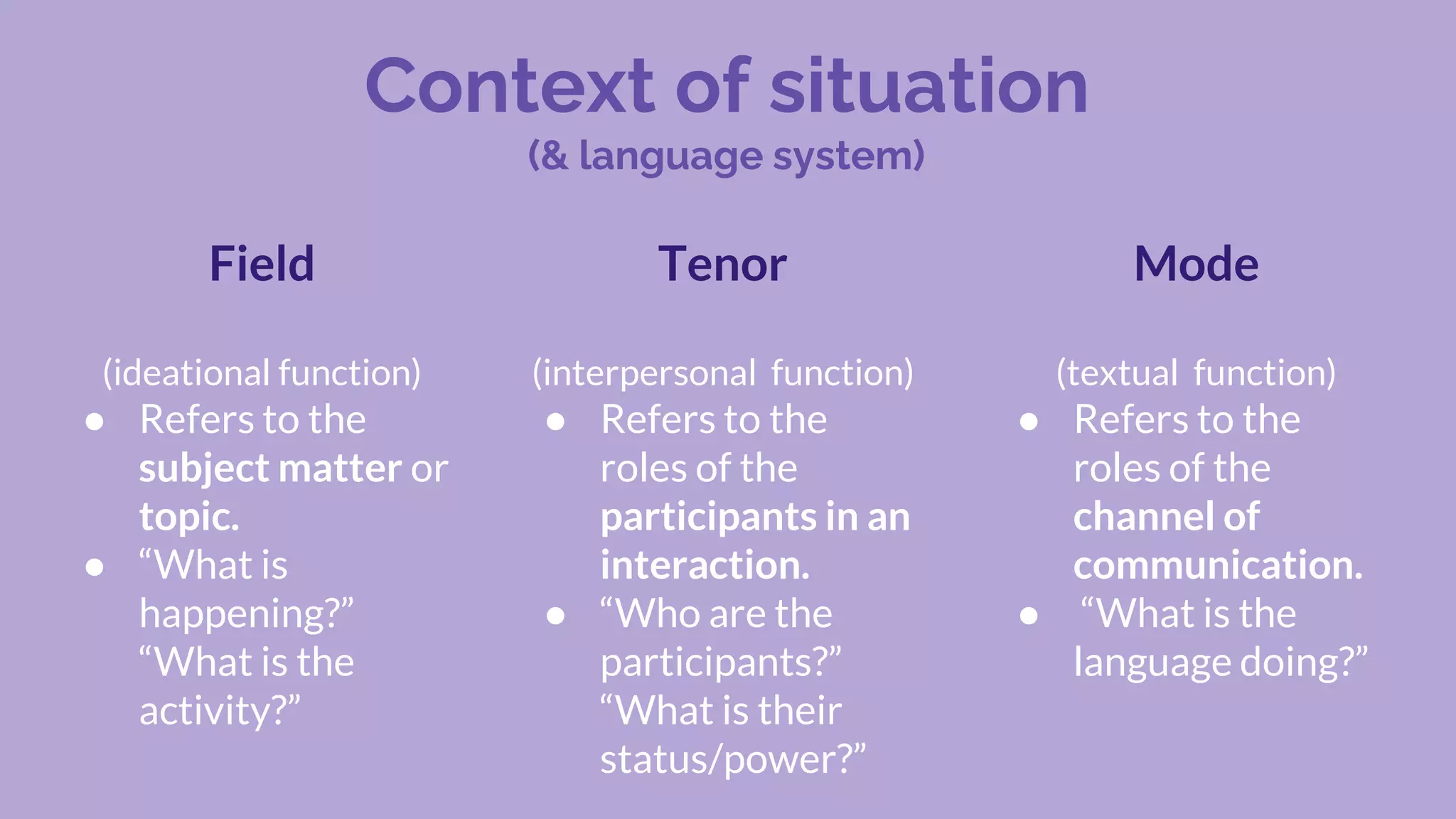
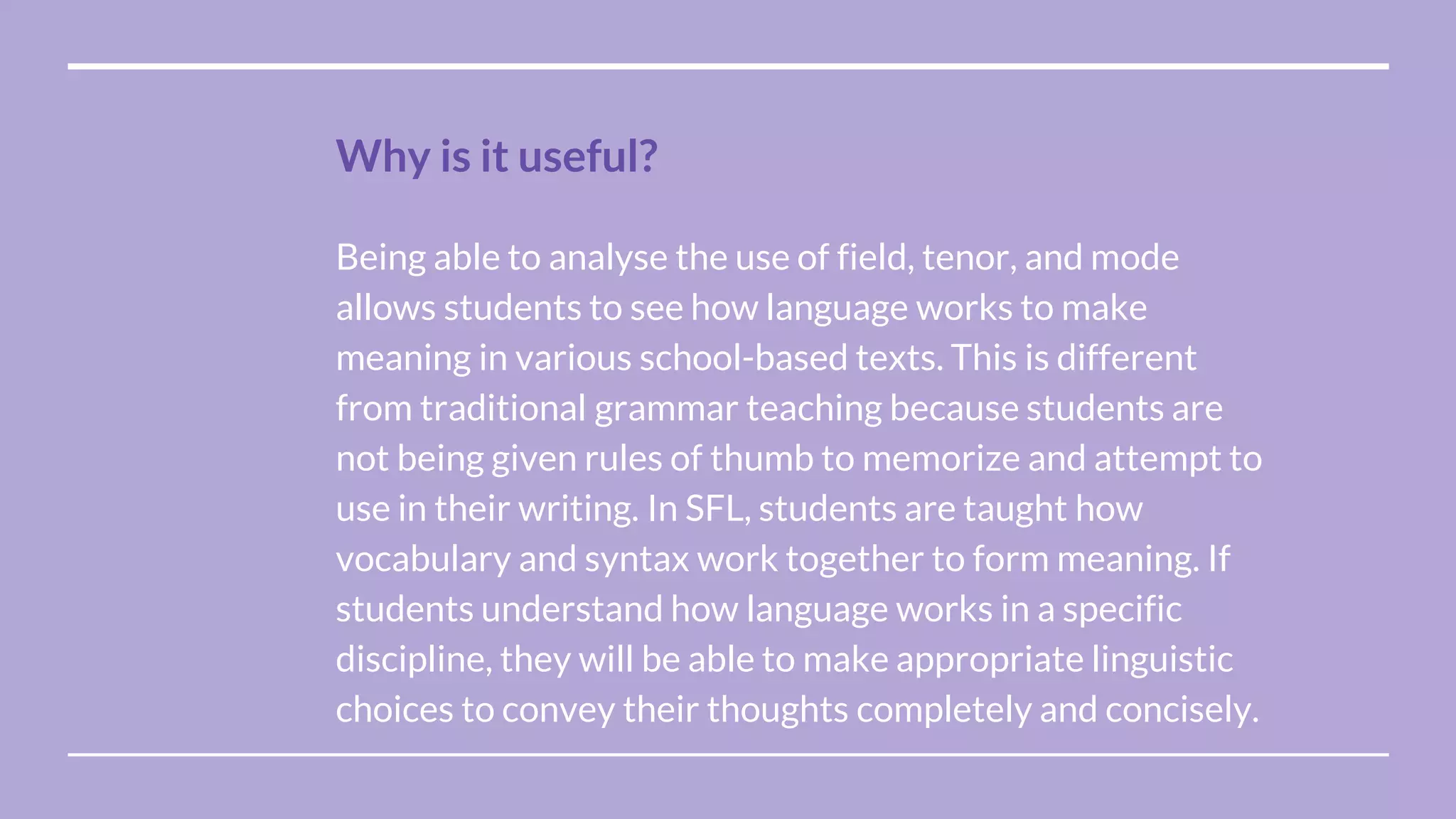
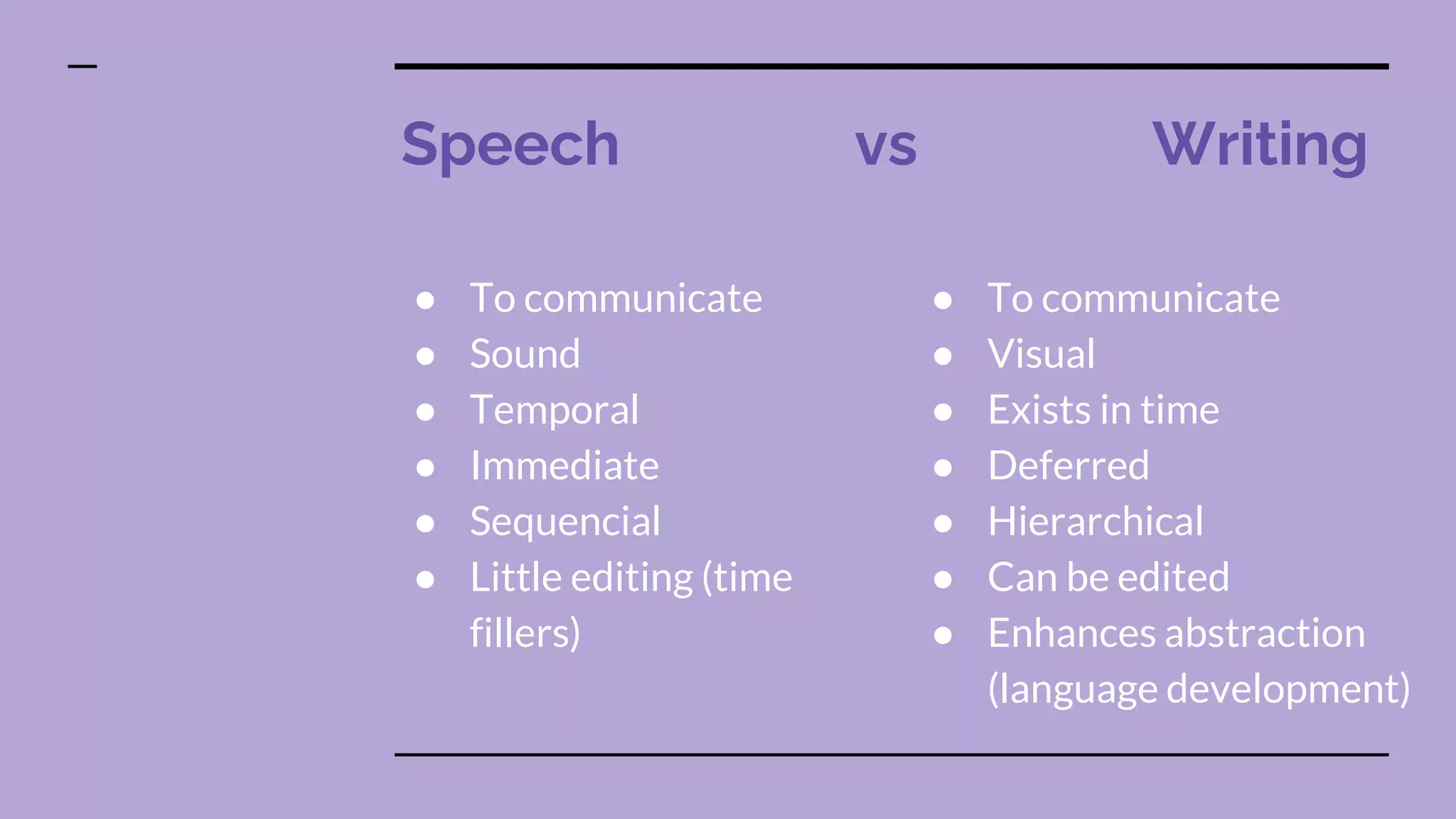
Systemic functional linguistics is a theory that views language as a social semiotic system used to make meaning in social contexts. It analyzes language through three metafunctions - ideational, interpersonal, and textual. Language is also analyzed at the level of discourse and genres. Key concepts include genre, register, text, context, and grammar. The functional approach emphasizes the social construction of language and emerged in Australia in the 1980s due to M.A.K. Halliday's influence. Context, including field, tenor, and mode, plays an important role in meaning-making. The genre, text, and grammar approach provides students the ability to effectively use writing codes and genres.