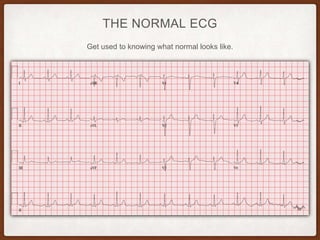
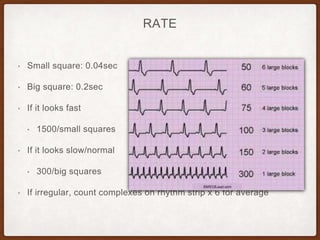
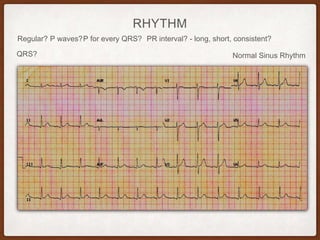
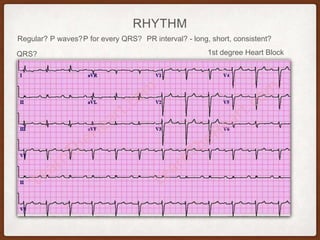
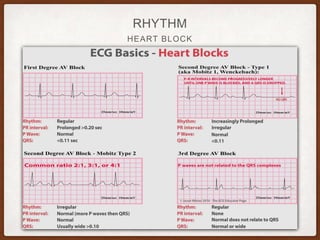
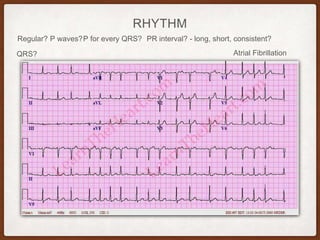
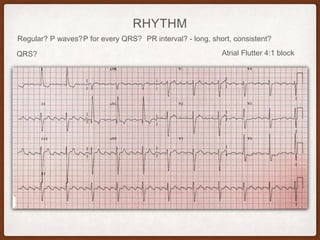
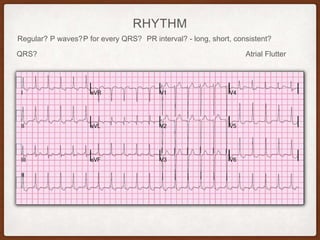
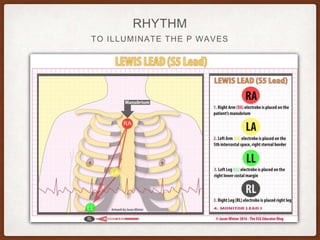
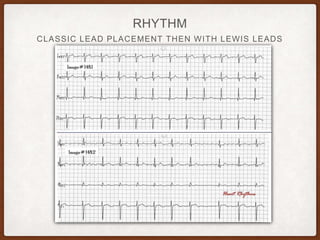
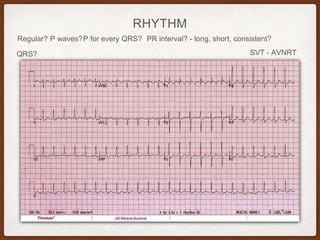
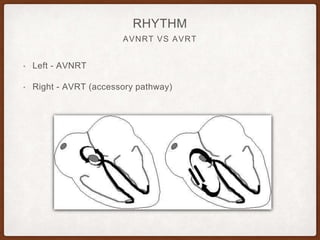
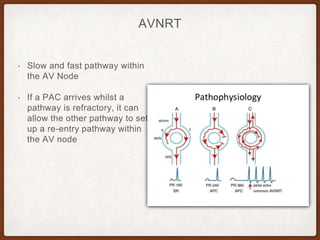
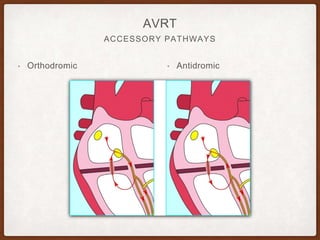
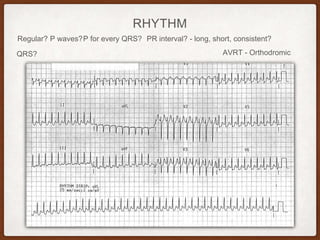
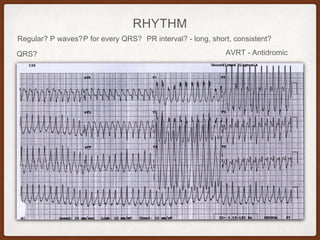
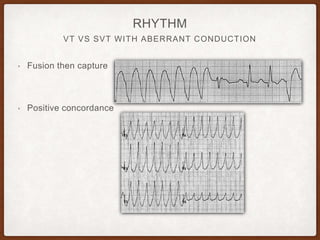
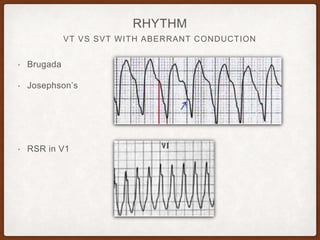
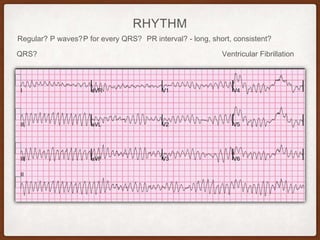
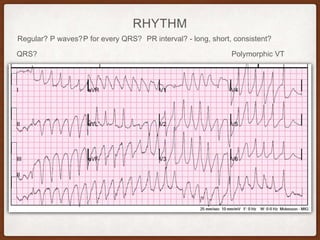
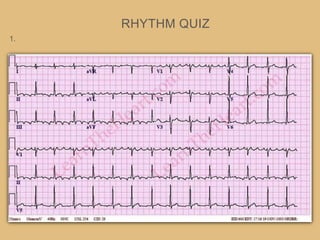
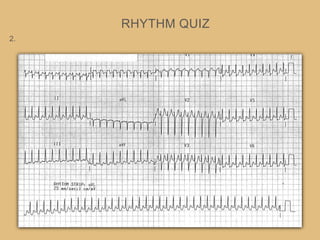
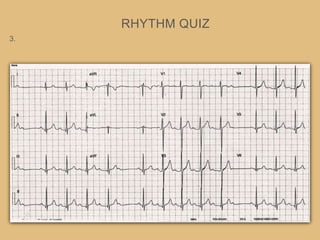
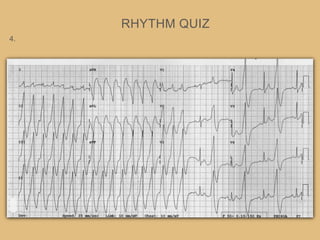
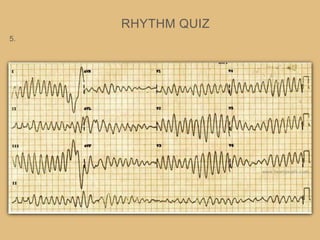
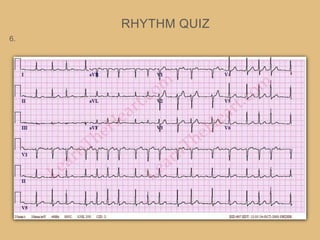
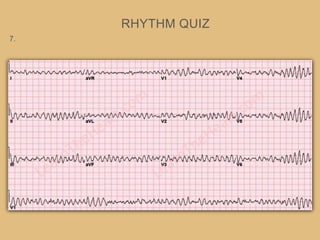
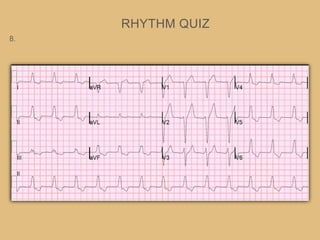
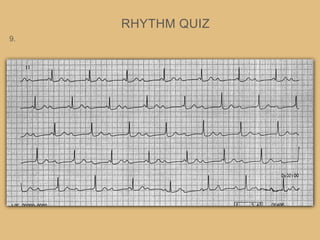
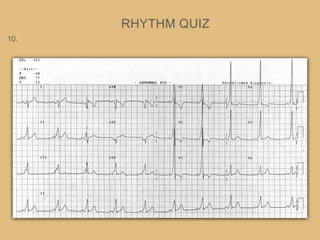
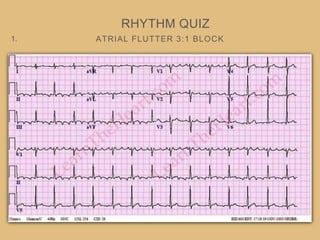
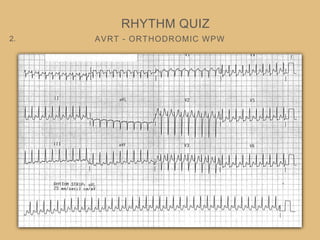
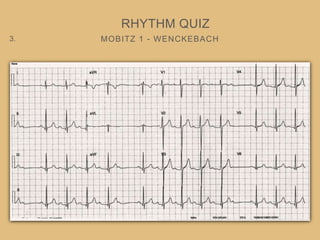
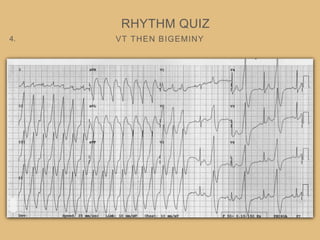
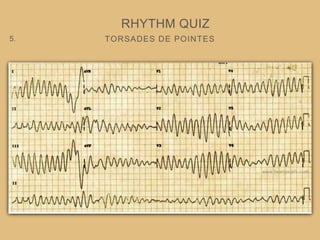
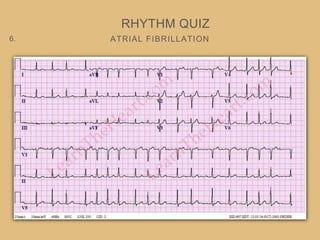
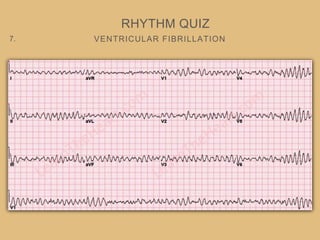
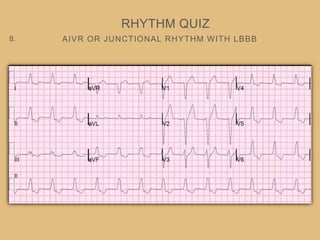
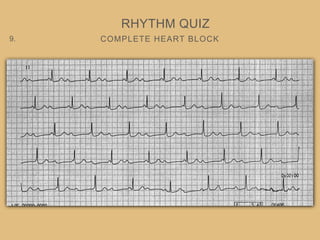
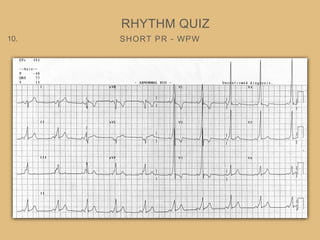
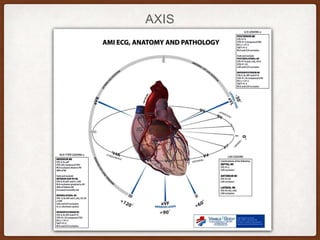
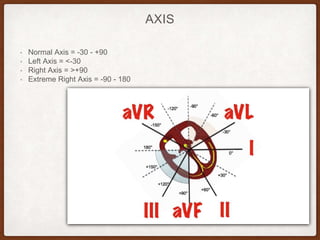
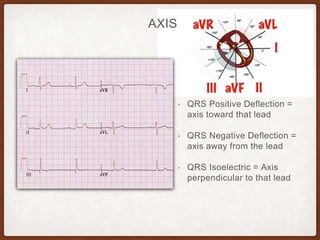
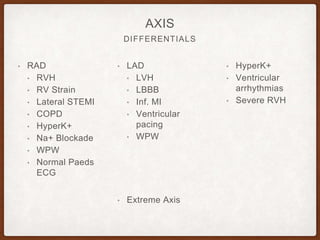
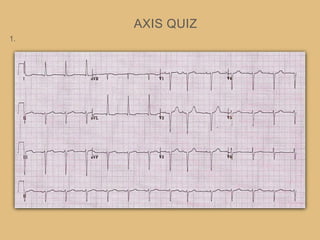
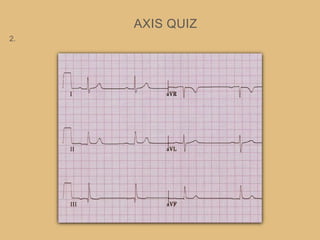
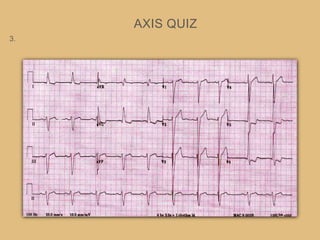
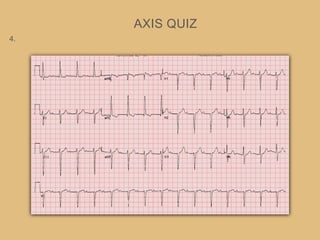
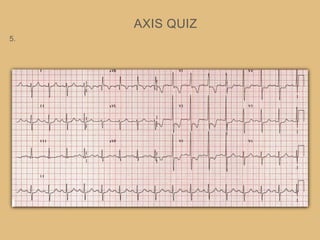
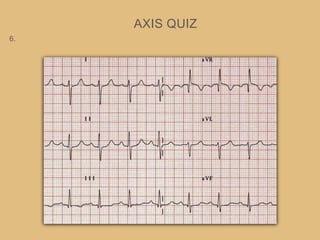
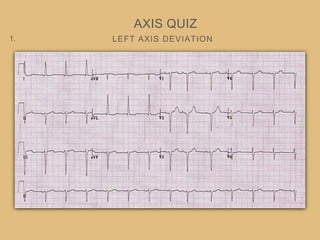
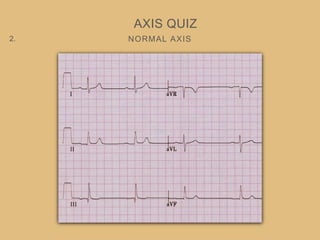
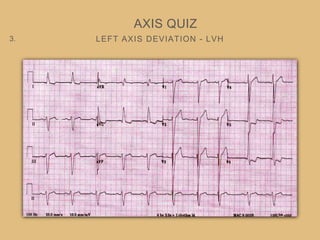
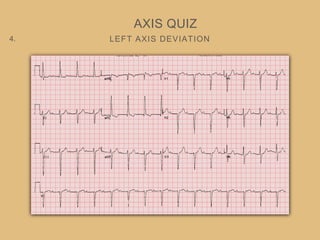
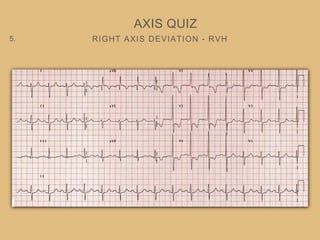
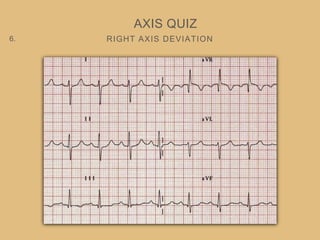
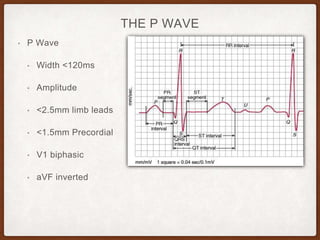
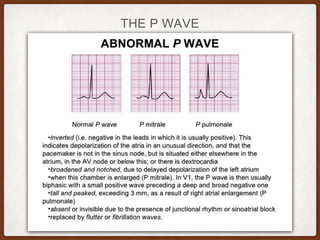
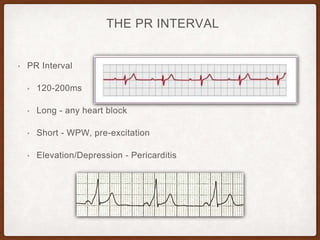
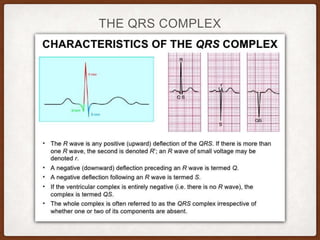
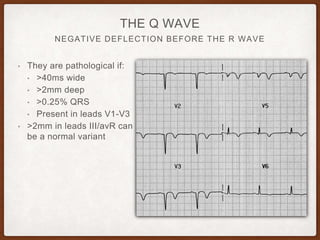
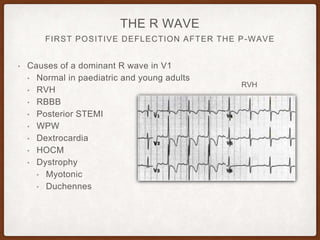
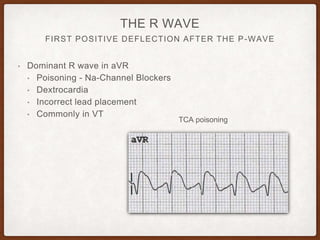
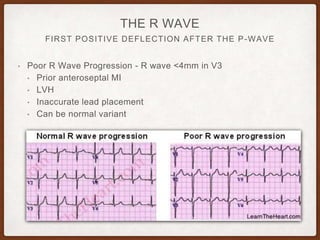
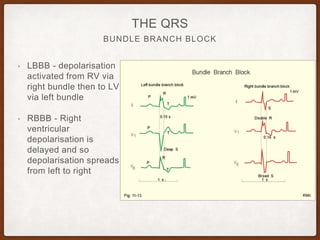
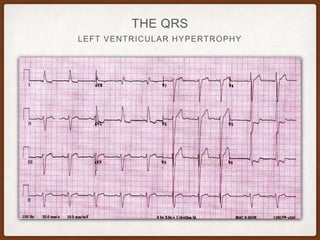
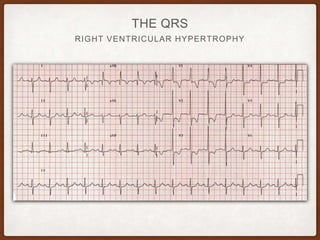
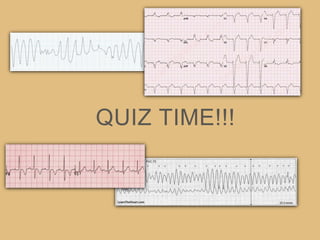
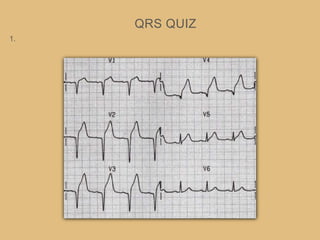
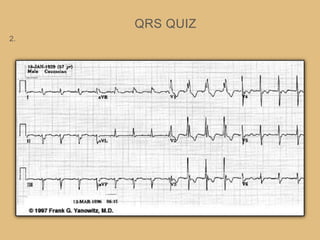
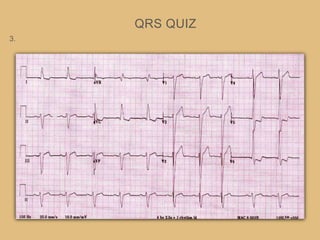
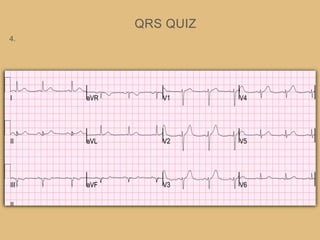
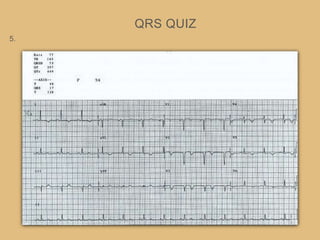
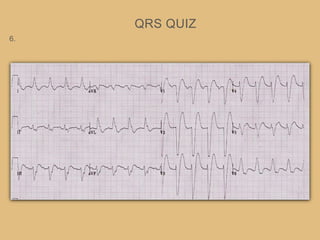
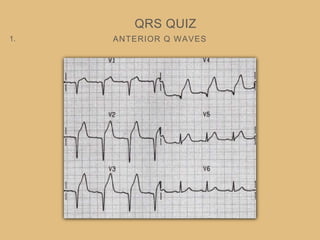
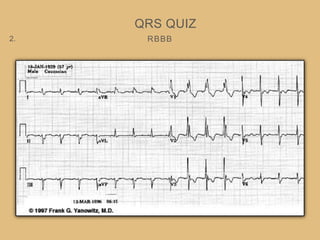
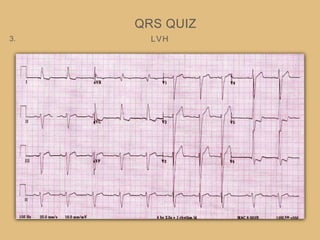
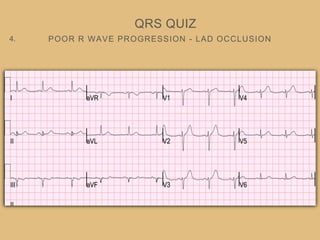
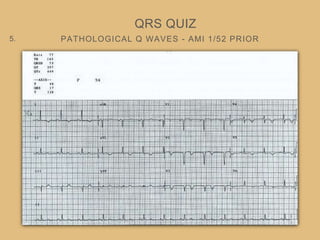
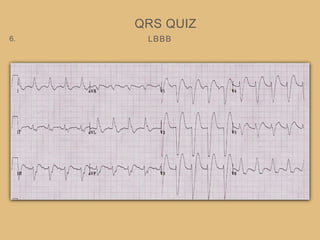
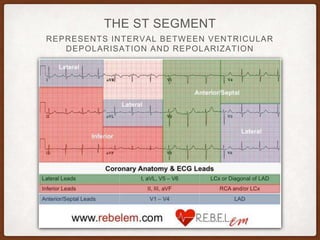
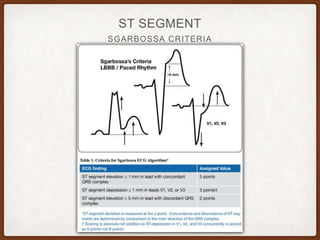
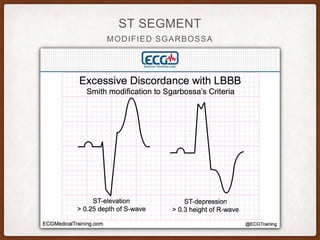
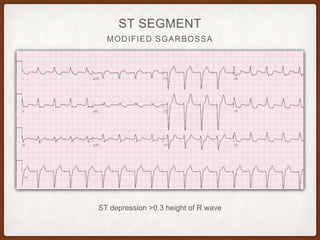
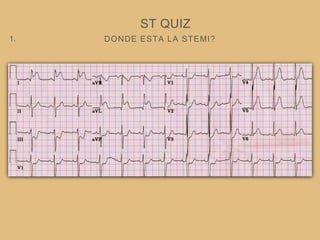
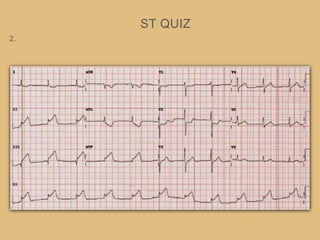
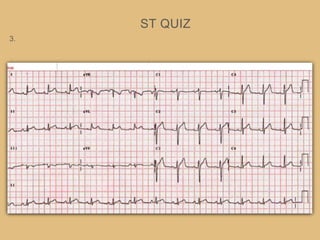
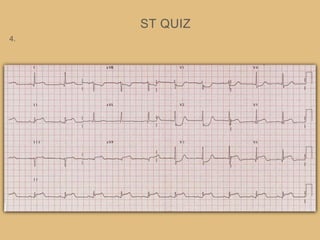
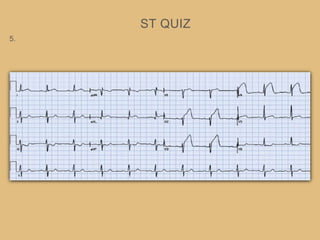
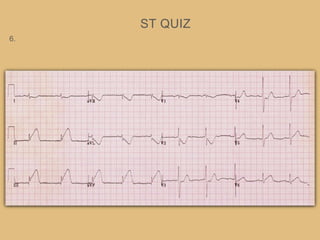
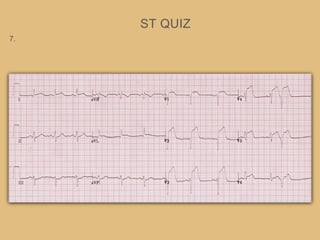
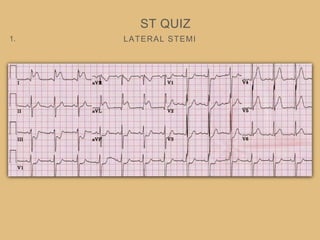
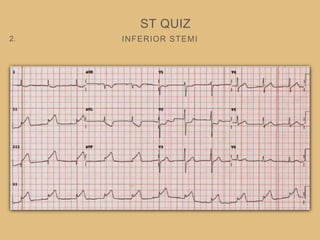
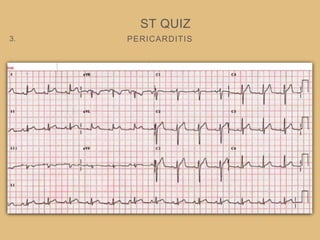
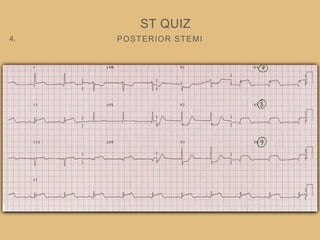
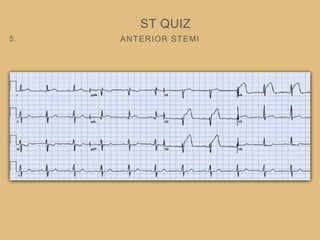
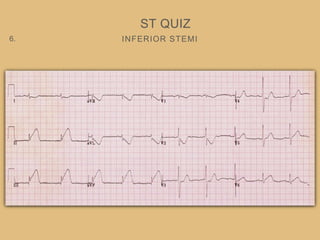
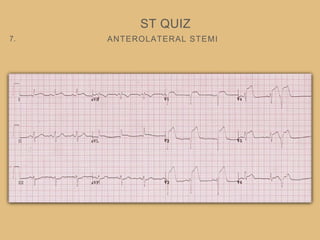
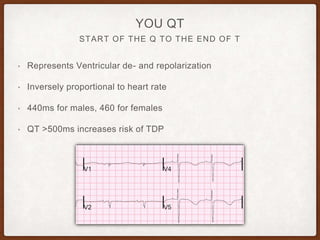
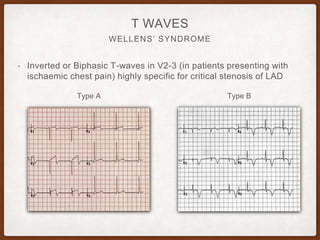
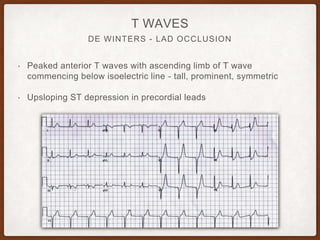
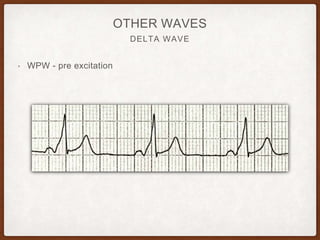
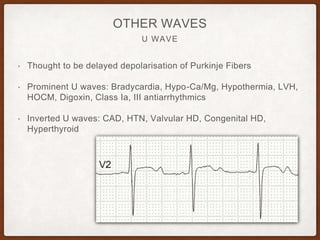
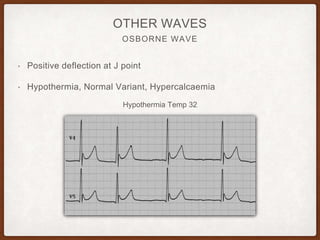
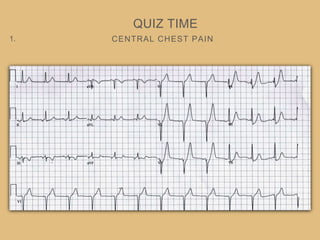
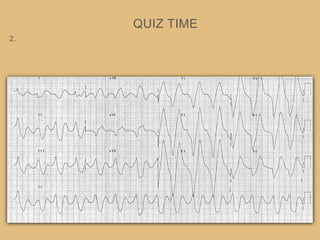
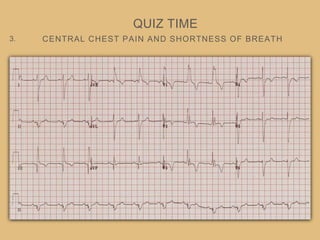
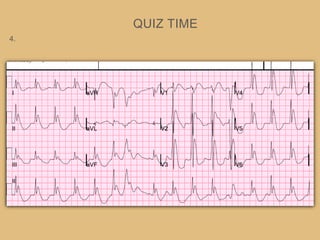
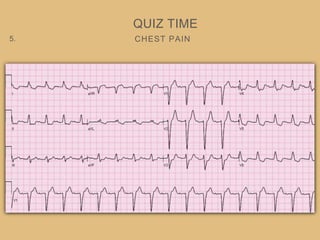
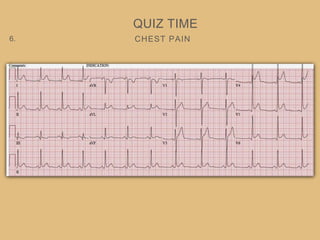
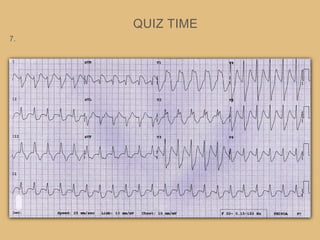
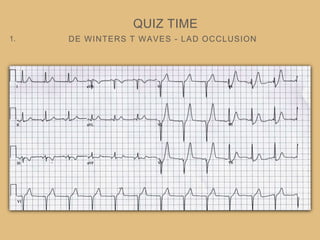
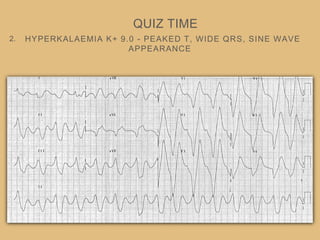
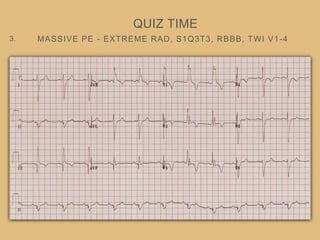
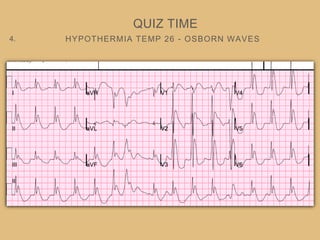
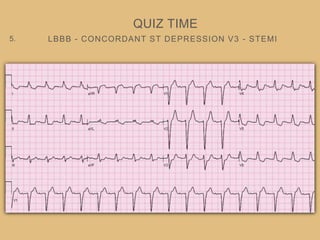
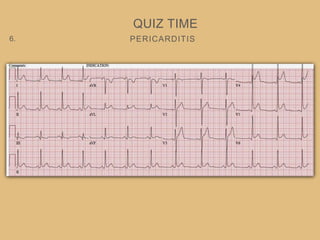
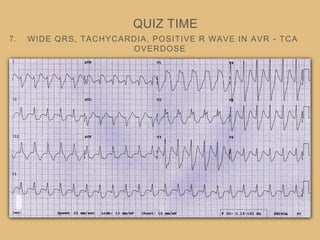
This document provides an overview of systematically analyzing an ECG. It discusses the normal components of an ECG including rate, rhythm, axis, P wave, PR interval, QRS complex, QT interval, ST segment, T wave, and other waves. It then examines each component in more detail, providing examples of normal and abnormal findings. Key aspects that could indicate conditions like myocardial infarction, arrhythmias, conduction abnormalities, and structural heart disease are emphasized. The document concludes with sample ECG rhythm and segment interpretation questions.