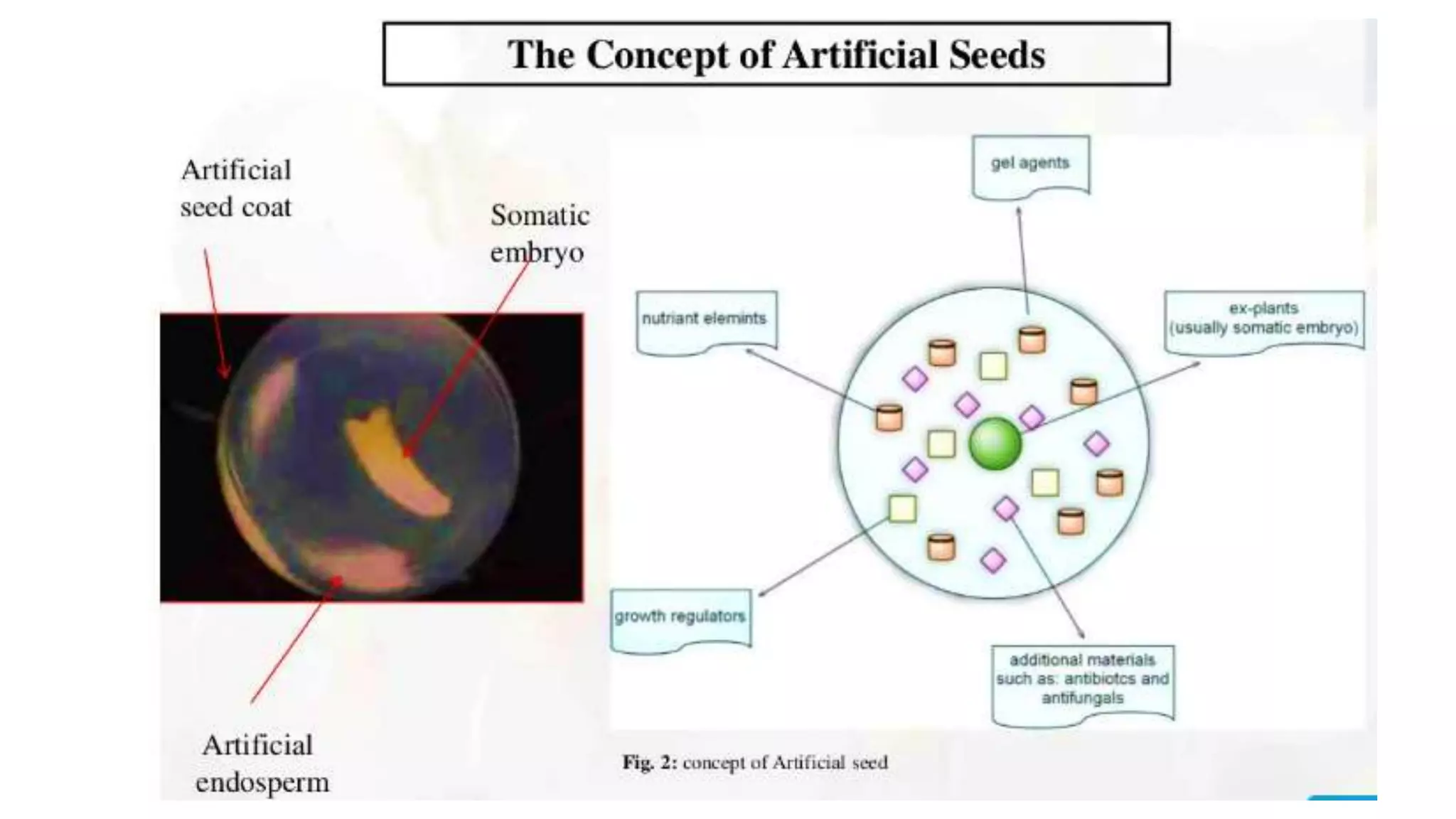
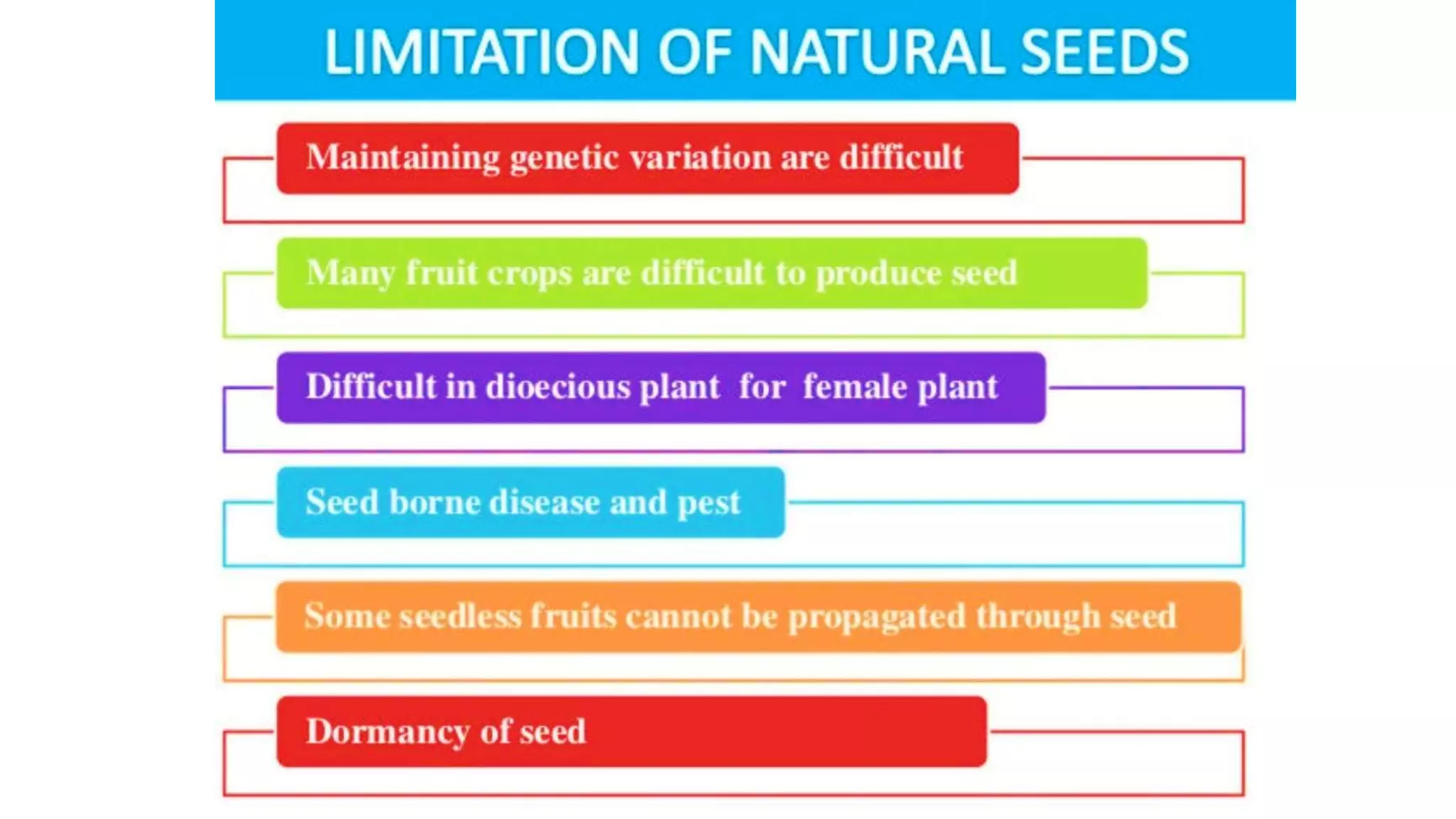
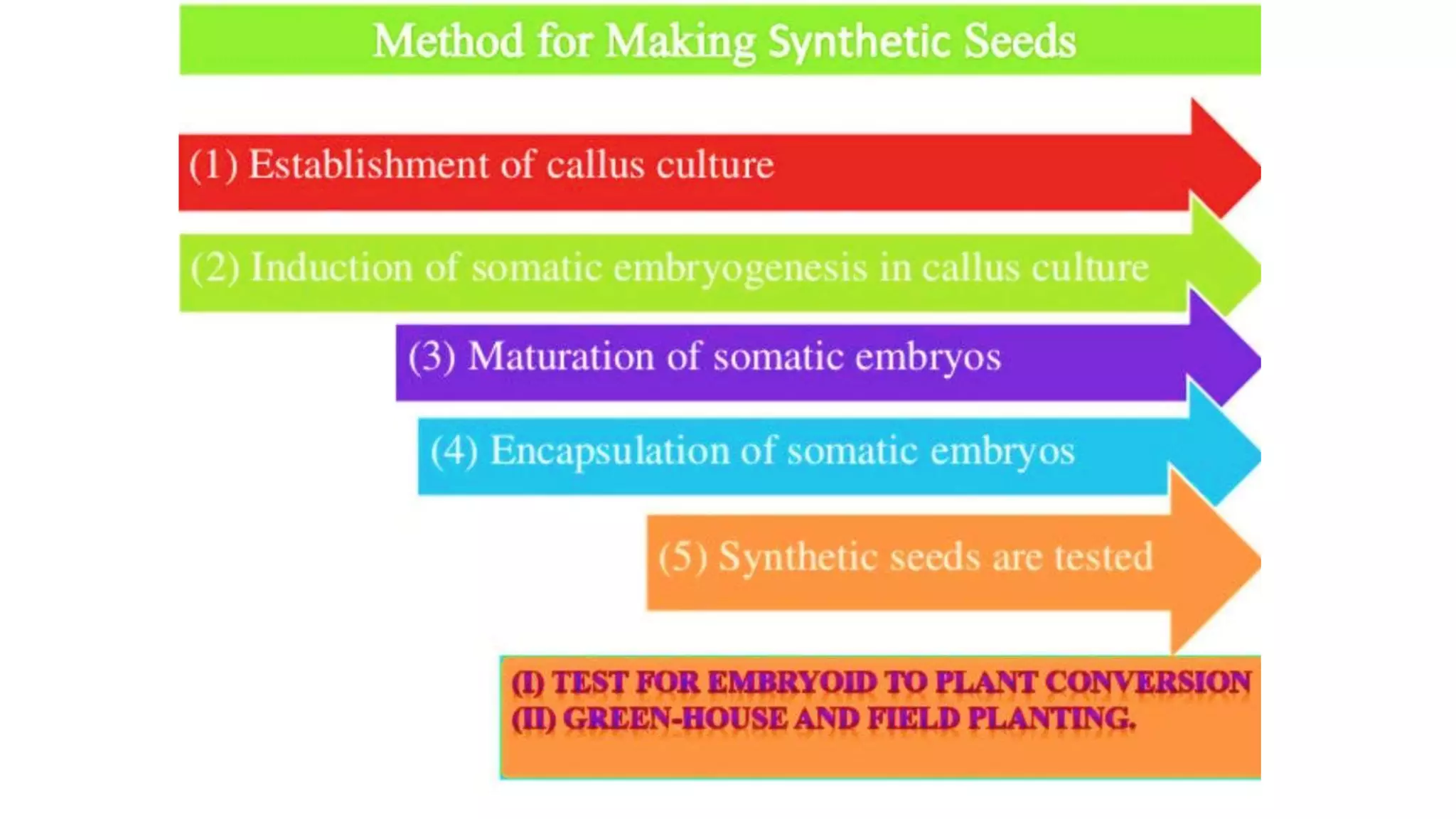
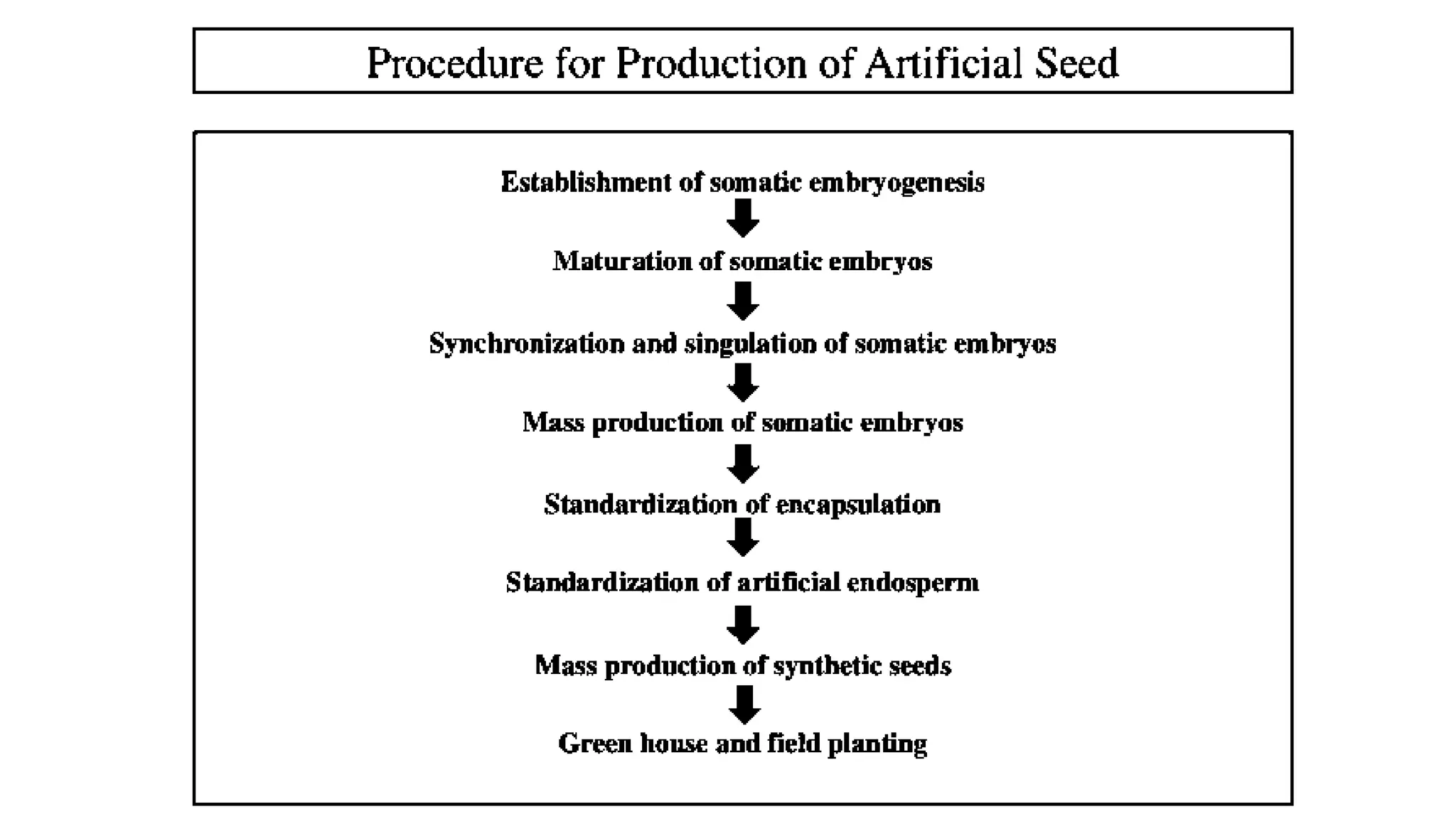
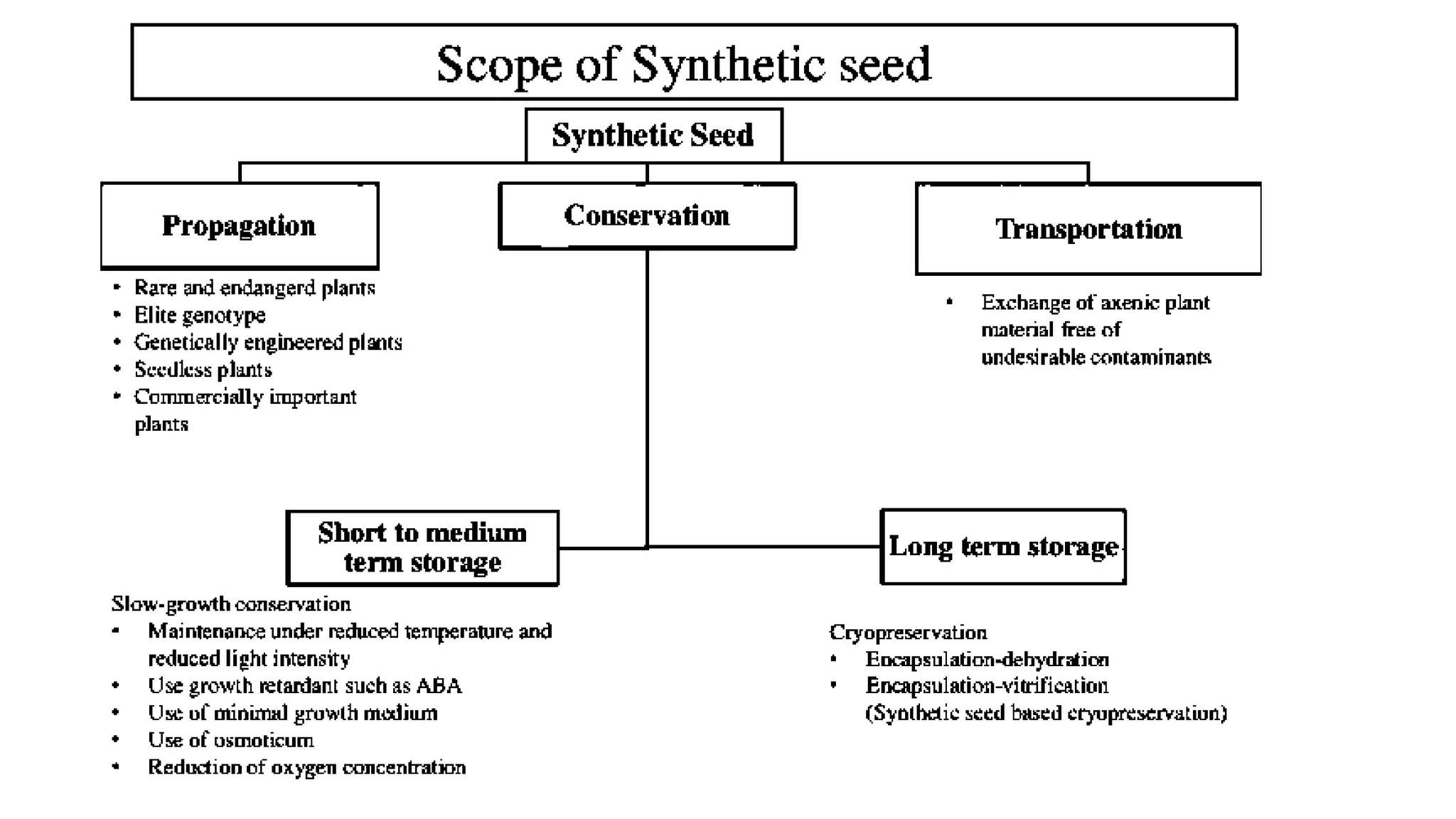
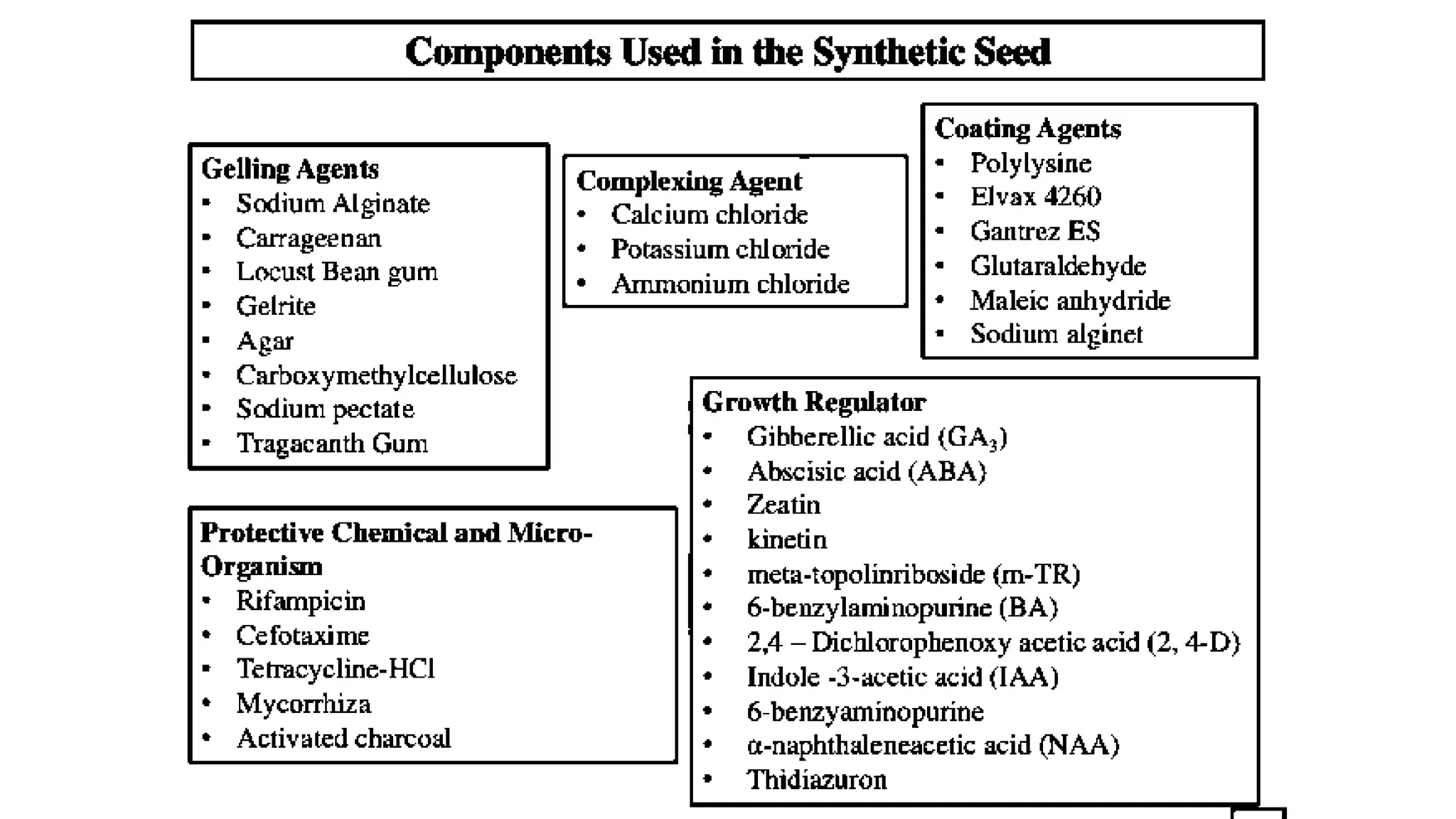
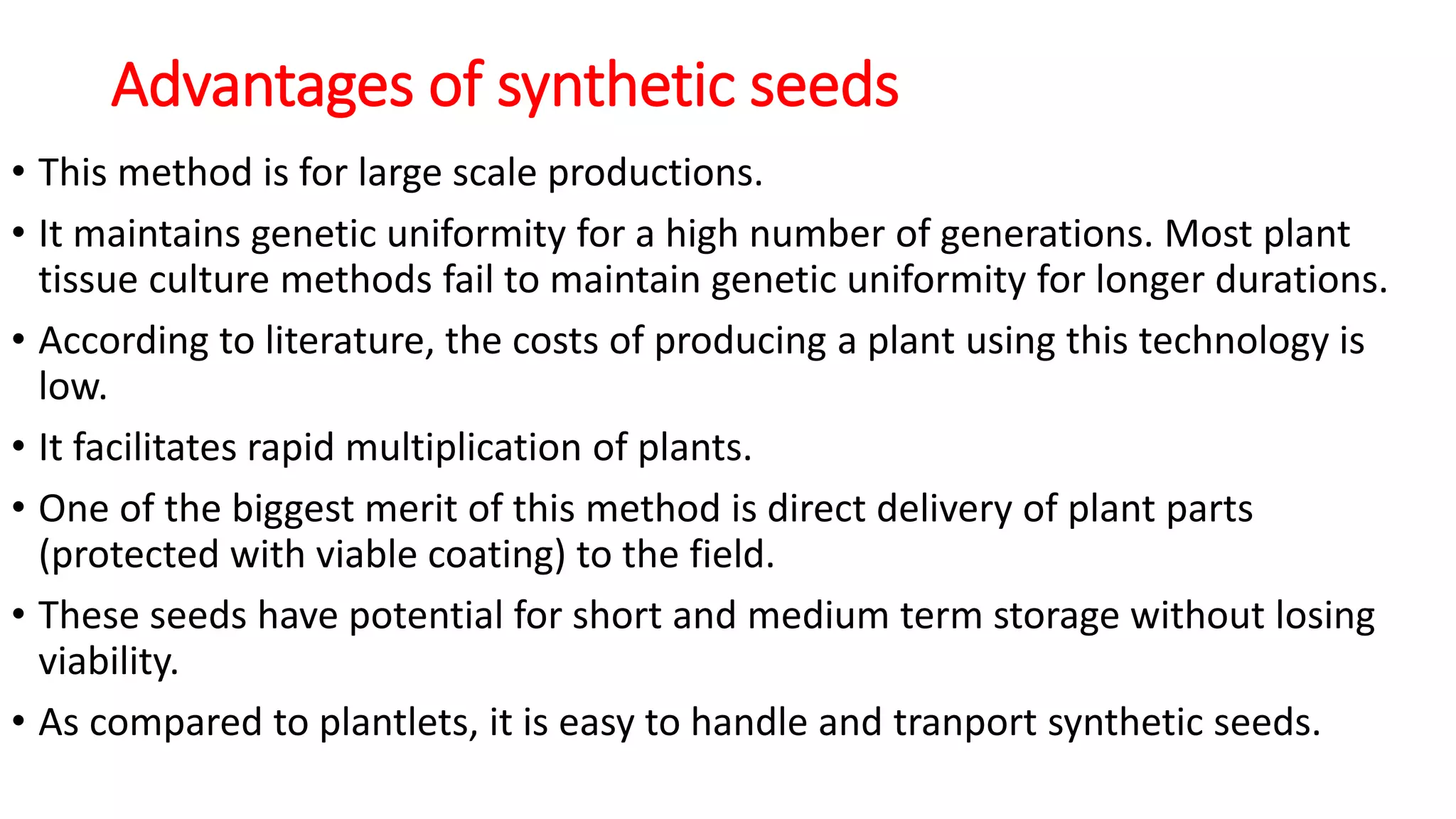
Production of synthetic seed involves encapsulating somatic embryos, shoot buds, or cell aggregates using tissue culture techniques. This allows for the large-scale, low-cost propagation of plants while maintaining genetic uniformity. Synthetic seeds can be stored longer than traditional seeds and planted directly in fields without the need for transplanting. While synthetic seeds have advantages over traditional micropropagation methods, their production and germination rates can still be limited for some plant species.