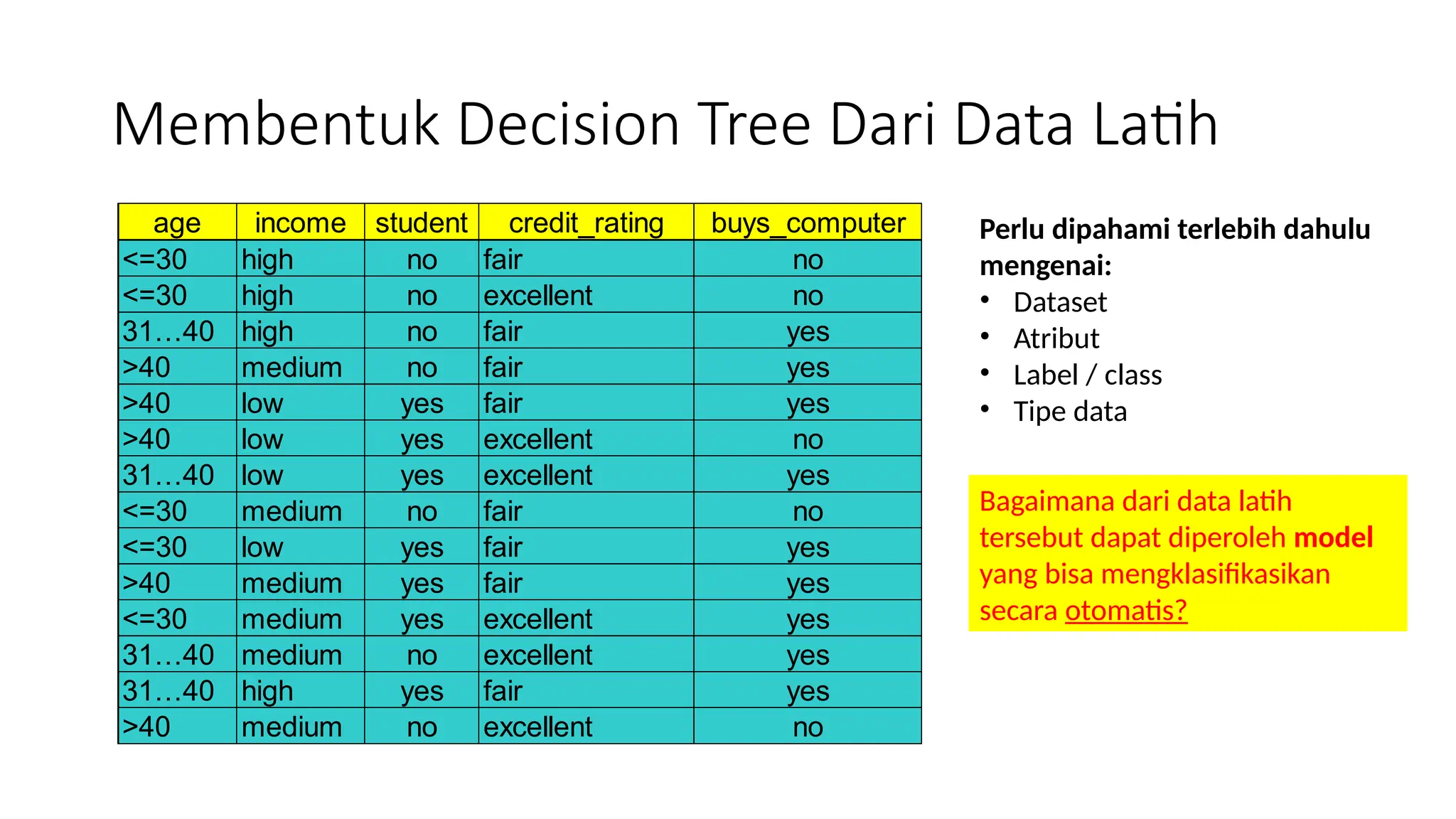
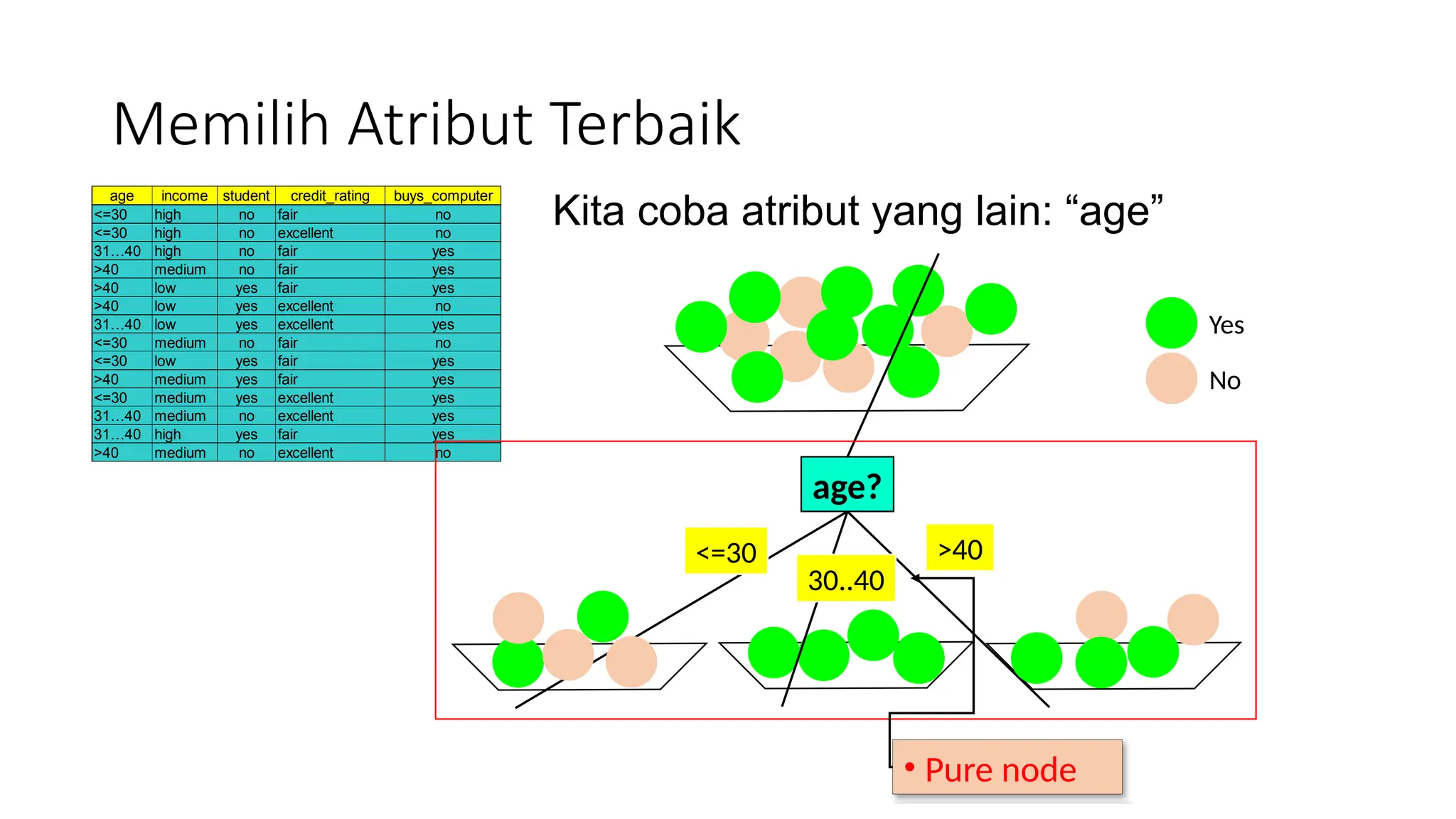
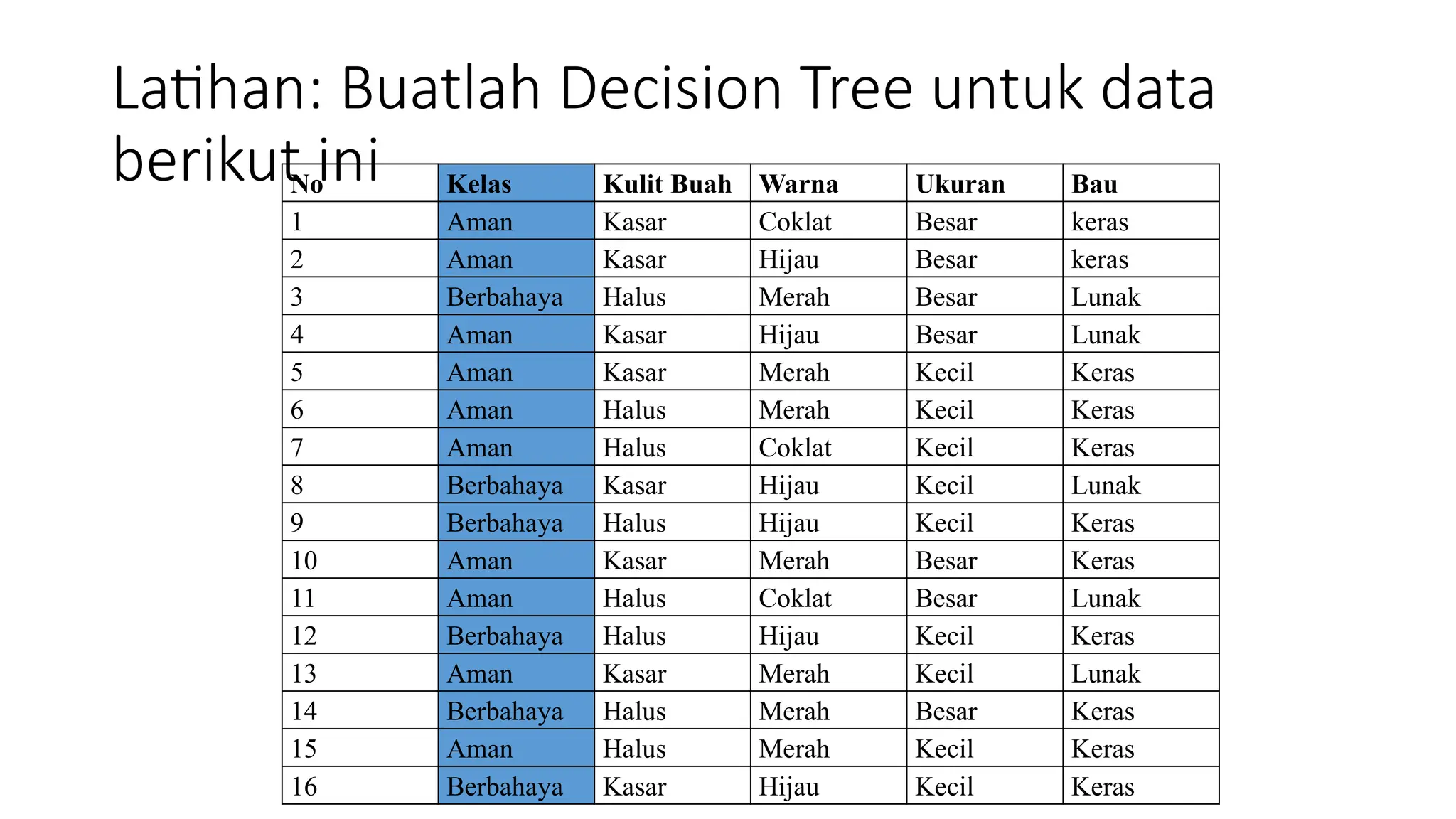
Dokumen ini menjelaskan konsep pembelajaran tersupervisi dengan fokus pada algoritma decision tree, termasuk perbedaan antara supervised dan unsupervised learning. Materi mencakup cara membangun decision tree dari dataset, pemilihan atribut terbaik, serta perhitungan entropy dan information gain. Selain itu, document ini juga membahas kapan sebaiknya menggunakan decision tree dalam analisis data.