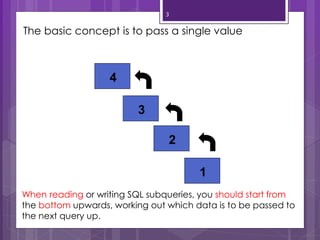
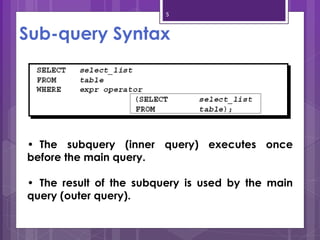
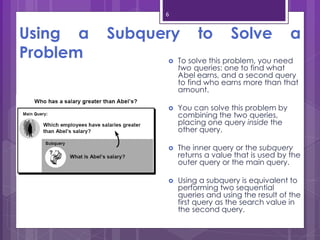
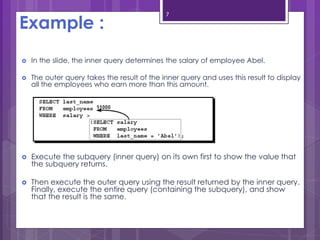
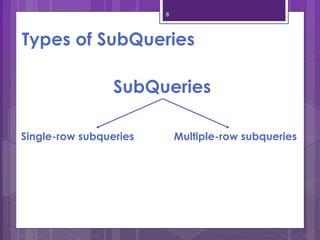
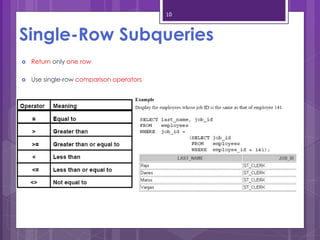
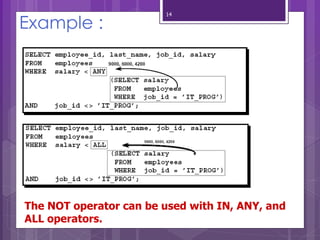
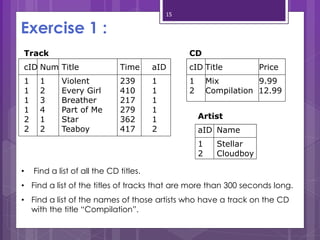
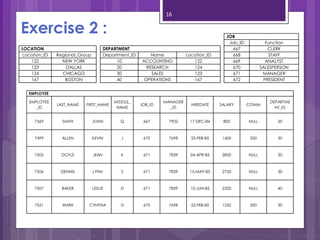
A subquery is a SELECT statement embedded within another SQL statement. It allows queries to retrieve data from multiple tables or queries. There are two types of subqueries: single-row and multiple-row. Single-row subqueries return only one row of data and use single-row comparison operators like =. Multiple-row subqueries return more than one row of data and use operators like IN, ANY, ALL that can handle multiple values. Subqueries are useful for solving problems that require performing multiple related queries by nesting one query within another.