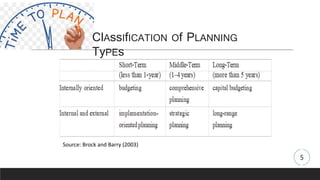
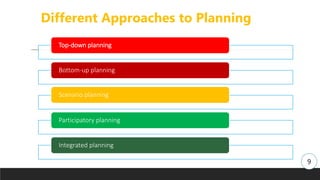
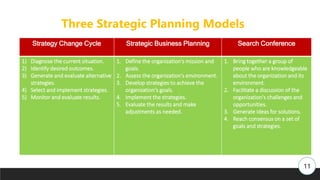
The document discusses strategic management and planning, outlining the importance of aligning an organization with its environment through disciplined efforts in defining missions, assessing strengths and weaknesses, and developing strategies. It highlights various approaches and levels of planning, as well as the necessity of budgeting in the strategic planning process. Additionally, it describes a systematic cycle for strategic implementation, monitoring, and evaluation.