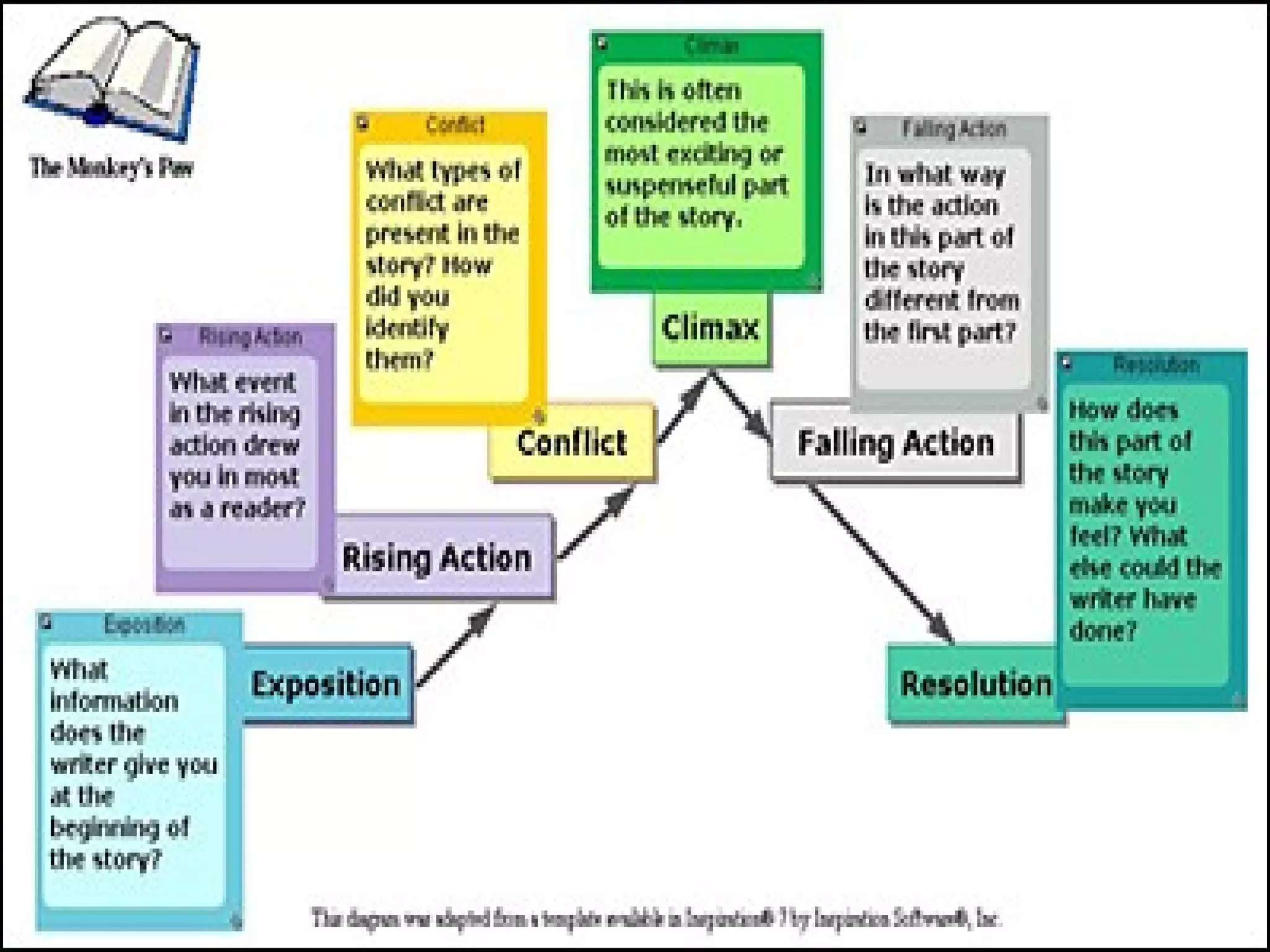
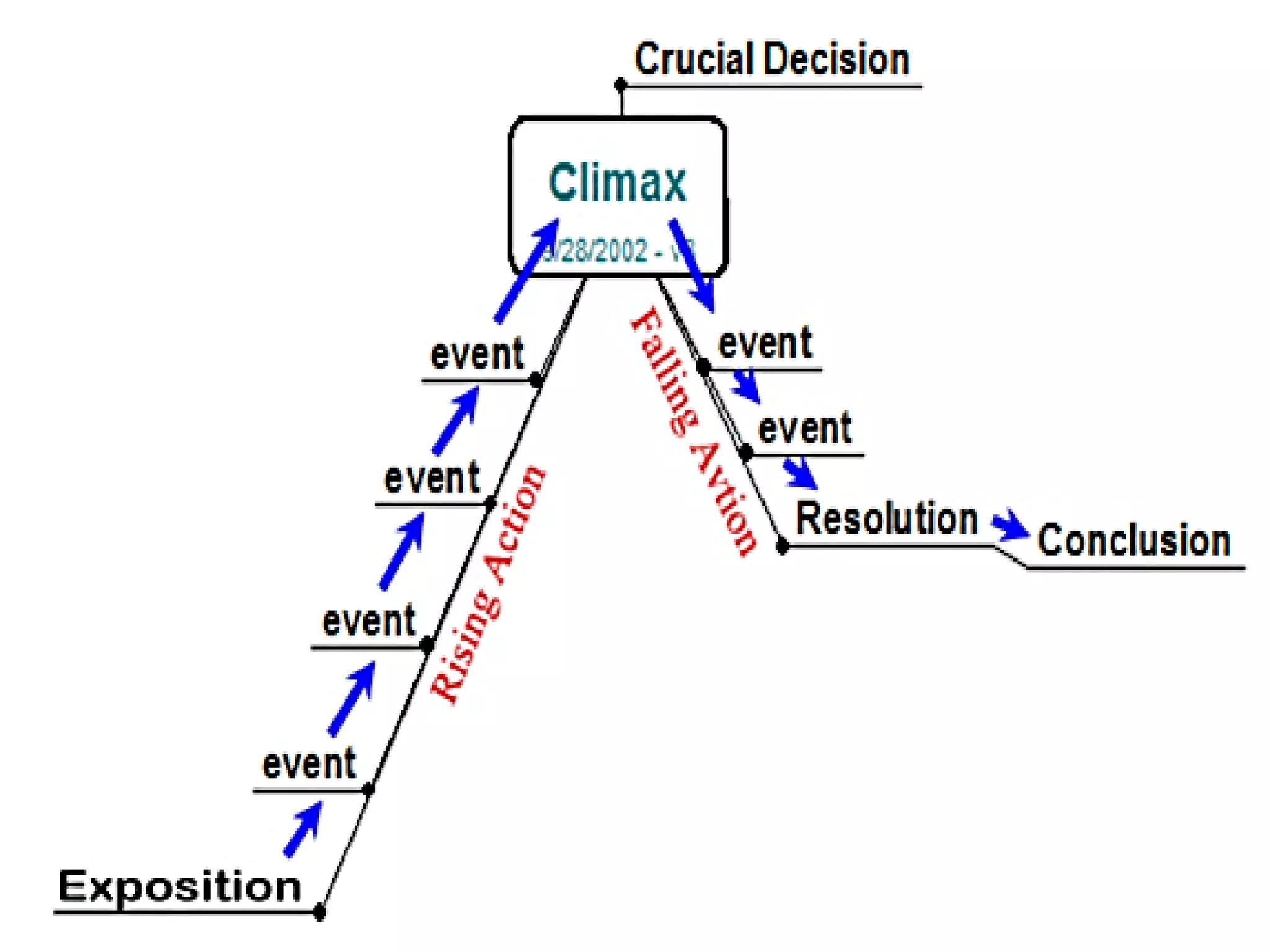
The document outlines the fundamental elements of storytelling, including setting, characters, plot, theme, exposition, conflict, climax, and resolution. It differentiates between various types of characters, such as heroes, villains, and stock characters, and explains how these elements contribute to the overall narrative. Understanding these components helps readers and writers appreciate and construct engaging stories.