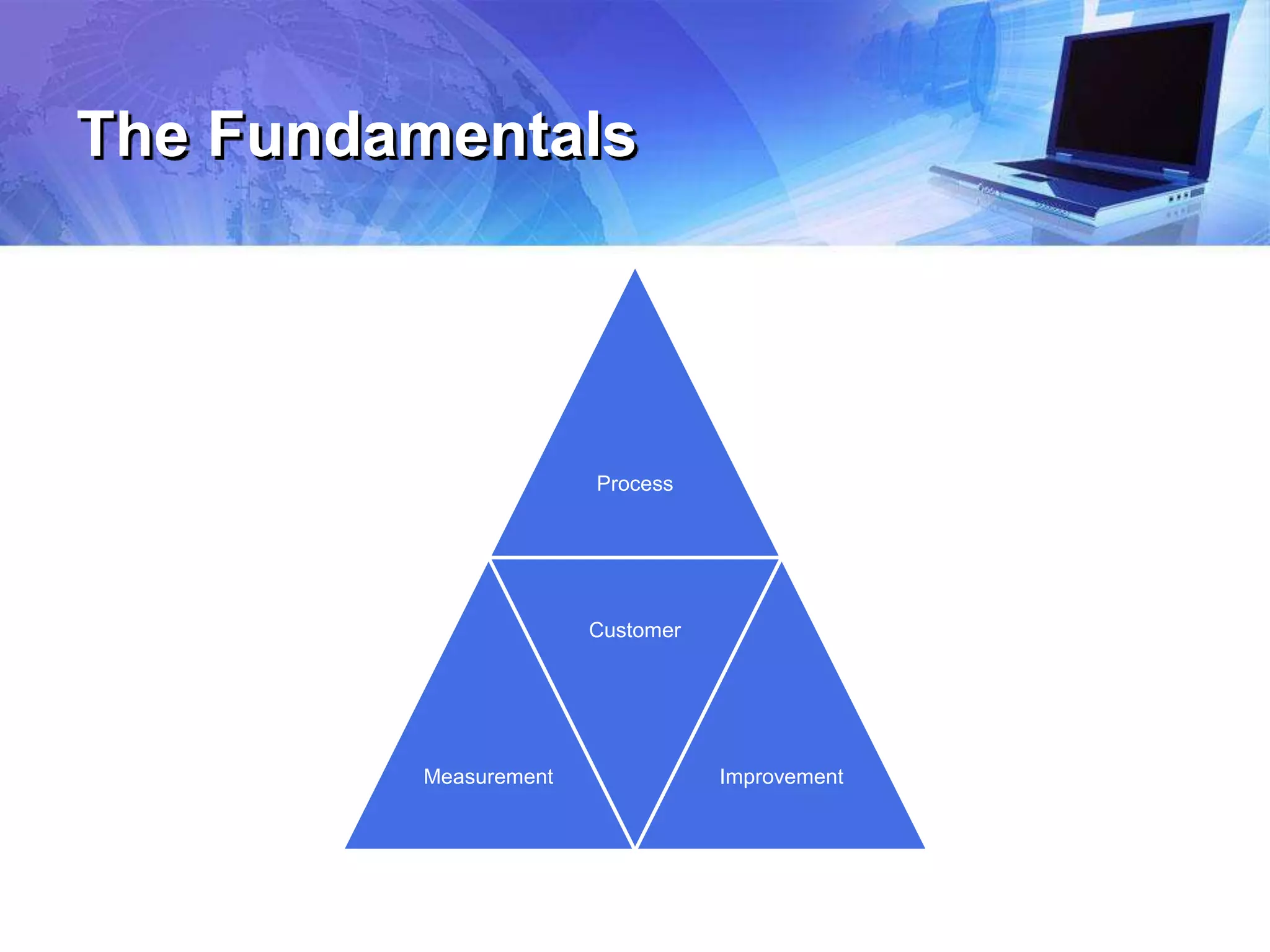
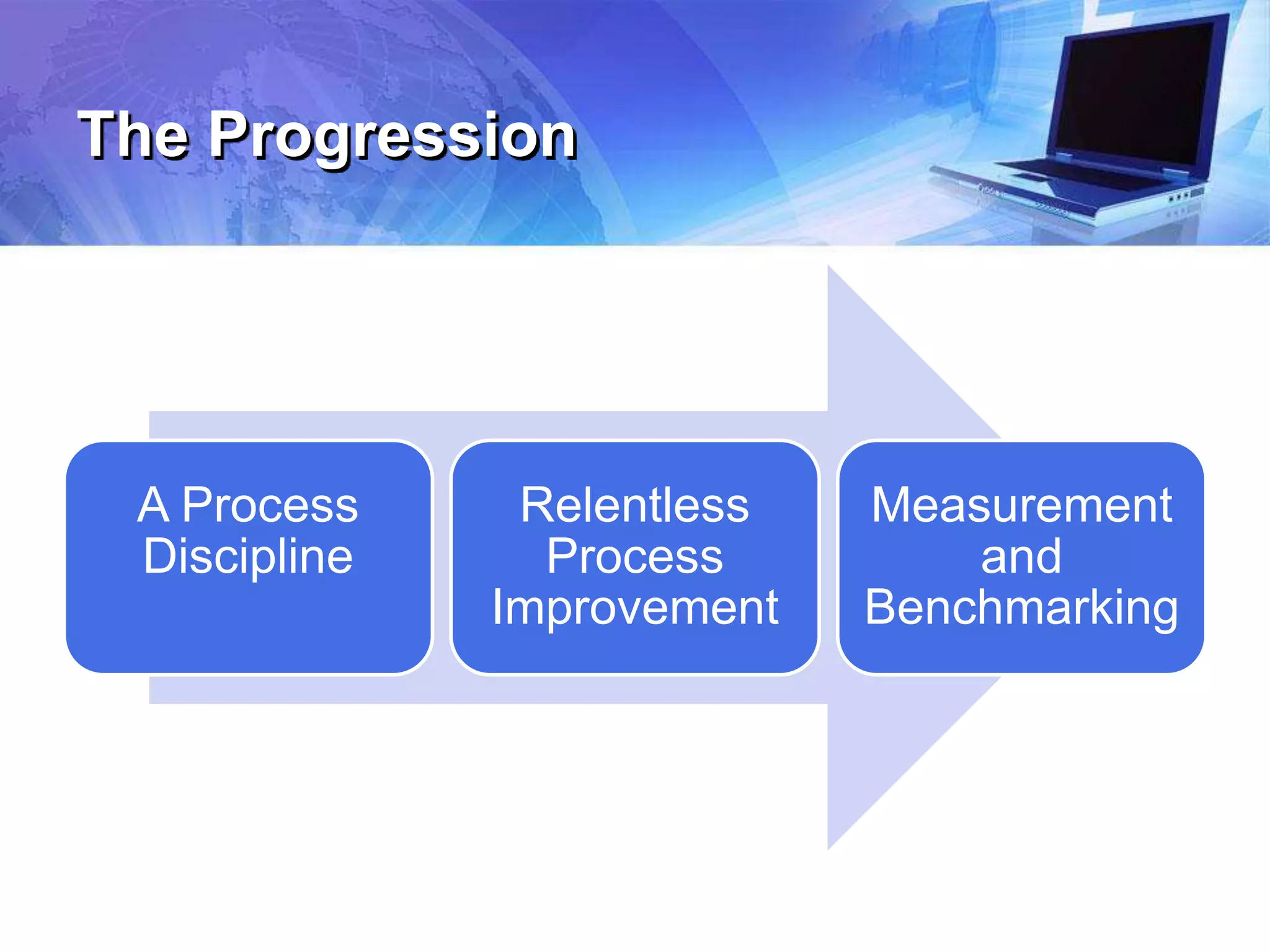
The document outlines a presentation on enhancing K-12 leadership in technology operations at Memphis Public Schools, focusing on the journey of Brevard Public Schools towards improved technology integration and customer service. It highlights the importance of effective process management, the six key questions for assessing operations, and the necessity of strong leadership in overcoming challenges related to technology use in education. The session aims to equip participants with the tools and knowledge to transform processes, improve efficiency, and create a culture of excellence in technology operations.