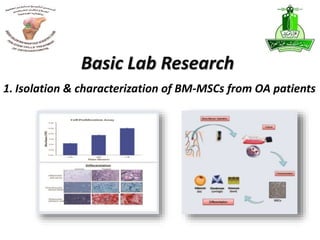
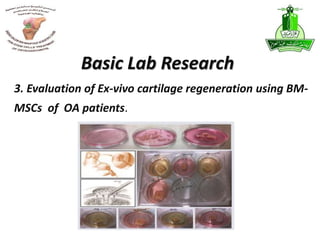
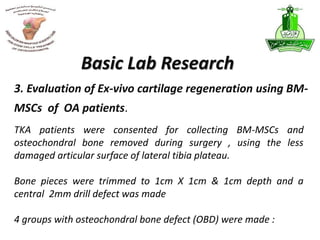
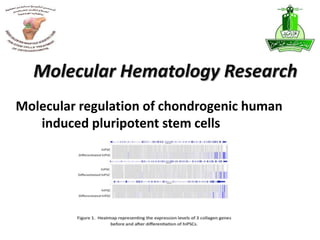
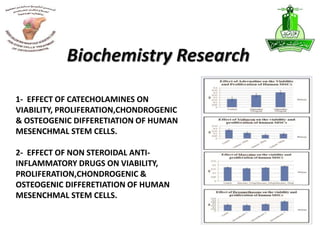
This document summarizes stem cell research projects conducted by Dr. Mohammad Abbas at King Abdulaziz University. It outlines 5 research groups: 1) Isolation and characterization of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells from osteoarthritis patients, 2) Effect of heat shock on bone marrow MSCs from OA patients, 3) Evaluation of ex-vivo cartilage regeneration using MSCs from OA patients, 4) Impact of MSCs impregnated with cartilage paste on repairing cartilage defects in rabbits, and 5) Impact of a hyaluronic acid scaffold impregnated with MSCs and cartilage paste on surgically induced arthritis in rabbits. Additional research includes studies on the effects of catecholamines and NSAIDs