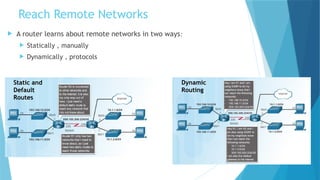
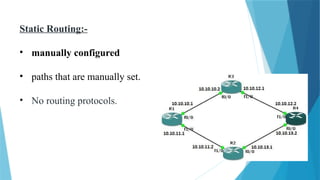
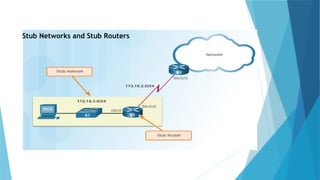
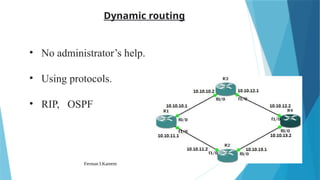
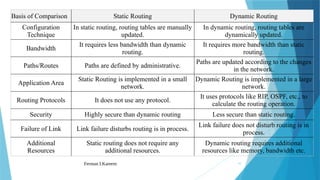
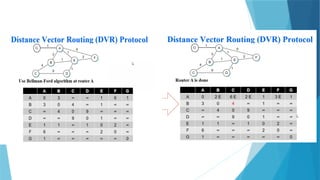
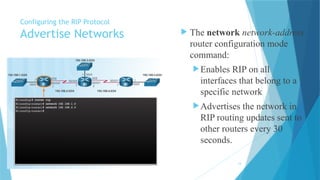
joidv osdjfs opsjdof sopjdf sodjf sdfojsd fosjdf sdfoijsdf sdfoijsdf sfdisjfdoijsdf dojfoisjfdisjdfisjfdisjoidv osdjfs opsjdof sopjdf sodjf sdfojsd fosjdf sdfoijsdf sdfoijsdf sfdisjfdoijsdf dojfoisjfdisjdfisjfdisjoidv osdjfs opsjdof sopjdf sodjf sdfojsd fosjdf sdfoijsdf sdfoijsdf sfdisjfdoijsdf dojfoisjfdisjdfisjfdisjoidv osdjfs opsjdof sopjdf sodjf sdfojsd fosjdf sdfoijsdf sdfoijsdf sfdisjfdoijsdf dojfoisjfdisjdfisjfdisjoidv osdjfs opsjdof sopjdf sodjf sdfojsd fosjdf sdfoijsdf sdfoijsdf sfdisjfdoijsdf dojfoisjfdisjdfisjfdisjoidv osdjfs opsjdof sopjdf sodjf sdfojsd fosjdf sdfoijsdf sdfoijsdf sfdisjfdoijsdf dojfoisjfdisjdfisjfdisjoidv osdjfs opsjdof sopjdf sodjf sdfojsd fosjdf sdfoijsdf sdfoijsdf sfdisjfdoijsdf dojfoisjfdisjdfisjfdisjoidv osdjfs opsjdof sopjdf sodjf sdfojsd fosjdf sdfoijsdf sdfoijsdf sfdisjfdoijsdf dojfoisjfdisjdfisjfdisjoidv osdjfs opsjdof sopjdf sodjf sdfojsd fosjdf sdfoijsdf sdfoijsdf sfdisjfdoijsdf dojfoisjfdisjdfisjfdisjoidv osdjfs opsjdof sopjdf sodjf sdfojsd fosjdf sdfoijsdf sdfoijsdf sfdisjfdoijsdf dojfoisjfdisjdfisjfdisjoidv osdjfs opsjdof sopjdf sodjf sdfojsd fosjdf sdfoijsdf sdfoijsdf sfdisjfdoijsdf dojfoisjfdisjdfisjfdisjoidv osdjfs opsjdof sopjdf sodjf sdfojsd fosjdf sdfoijsdf sdfoijsdf sfdisjfdoijsdf dojfoisjfdisjdfisjfdisjoidv osdjfs opsjdof sopjdf sodjf sdfojsd fosjdf sdfoijsdf sdfoijsdf sfdisjfdoijsdf dojfoisjfdisjdfisjfdisjoidv osdjfs opsjdof sopjdf sodjf sdfojsd fosjdf sdfoijsdf sdfoijsdf sfdisjfdoijsdf dojfoisjfdisjdfisjfdisjoidv osdjfs opsjdof sopjdf sodjf sdfojsd fosjdf sdfoijsdf sdfoijsdf sfdisjfdoijsdf dojfoisjfdisjdfisjfdisjoidv osdjfs opsjdof sopjdf sodjf sdfojsd fosjdf sdfoijsdf sdfoijsdf sfdisjfdoijsdf dojfoisjfdisjdfisjfdisjoidv osdjfs opsjdof sopjdf sodjf sdfojsd fosjdf sdfoijsdf sdfoijsdf sfdisjfdoijsdf dojfoisjfdisjdfisjfdisjoidv osdjfs opsjdof sopjdf sodjf sdfojsd fosjdf sdfoijsdf sdfoijsdf sfdisjfdoijsdf dojfoisjfdisjdfisjfdisjoidv osdjfs opsjdof sopjdf sodjf sdfojsd fosjdf sdfoijsdf sdfoijsdf sfdisjfdoijsdf dojfoisjfdisjdfisjfdisjoidv osdjfs opsjdof sopjdf sodjf sdfojsd fosjdf sdfoijsdf sdfoijsdf sfdisjfdoijsdf dojfoisjfdisjdfisjfdisjoidv osdjfs opsjdof sopjdf sodjf sdfojsd fosjdf sdfoijsdf sdfoijsdf sfdisjfdoijsdf dojfoisjfdisjdfisjfdisjoidv osdjfs opsjdof sopjdf sodjf sdfojsd fosjdf sdfoijsdf sdfoijsdf sfdisjfdoijsdf dojfoisjfdisjdfisjfdisjoidv osdjfs opsjdof sopjdf sodjf sdfojsd fosjdf sdfoijsdf sdfoijsdf sfdisjfdoijsdf dojfoisjfdisjdfisjfdisjoidv osdjfs opsjdof sopjdf sodjf sdfojsd fosjdf sdfoijsdf sdfoijsdf sfdisjfdoijsdf dojfoisjfdisjdfisjfdisjoidv osdjfs opsjdof sopjdf sodjf sdfojsd fosjdf sdfoijsdf sdfoijsdf sfdisjfdoijsdf dojfoisjfdisjdfisjfdisjoidv osdjfs opsjdof sopjdf sodjf sdfojsd fosjdf sdfoijsdf sdfoijsdf sfdisjfdoijsdf dojfoisjfdisjdfisjfdisjoidv osdjfs opsjdof sopjdf sodjf sdfojsd fosjdf sdfoijsdf sdfoijsdf sfdisjfdoijsdf dojfoisjfdisjdfisjfdisjoidv osdjfs opsjdof sopjdf sodjf sdfojsd fosjdf sdfoijsdf sdfoijsdf sfdisjfdoijsdf dojfoisjfdisjdfisjfdisjoidv osdjfs opsjdof sopjdf sodj