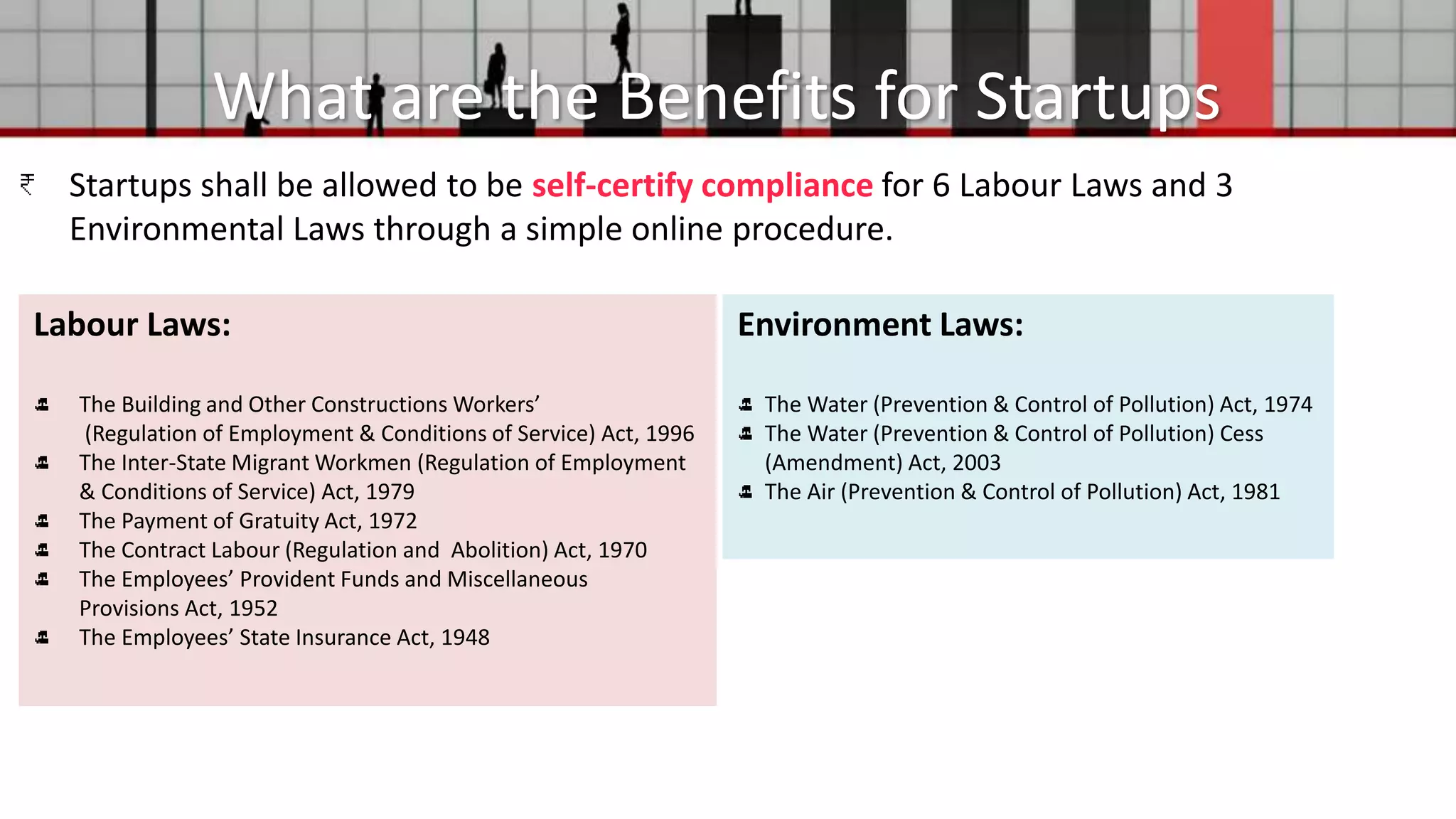
This document provides information about startups in India. It defines a startup as a company less than 10 years old with an annual turnover not exceeding 100 crore rupees. The Department for Promotion of Industry and Internal Trade (DPIIT) oversees startup policy. Startups can self-certify compliance for 6 labor laws and 3 environmental laws through a simple online process. They also receive benefits like income tax exemptions, ease of selling to the government marketplace, fast-tracked patent applications, a 90-day window for winding up, and easier access to funds. The document was compiled by Harry Chadha from the MSME office based on information from the Startup India website.