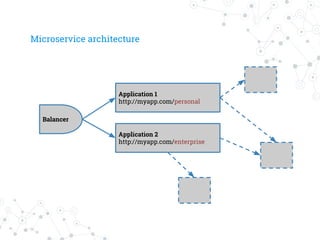
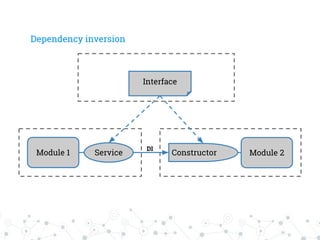
The document discusses managing dependencies in large projects, emphasizing the 'divide and conquer' strategy to prevent monolithic structures. It highlights tools like Composer for PHP dependency management and concepts like static and dynamic dependencies, suggesting interfaces to minimize direct dependencies between modules. Additionally, it touches on microservices architecture, advocating for the use of APIs and service discovery tools like Consul for effective configuration management.























![Example: Laravel
<?php
namespace MyCompanySms;
use IlluminateSupportServiceProvider;
class SmsServiceProvider extends ServiceProvider
{
public function register()
{
$this->app['sms.sender'] = $this->app->share(function($app) {
$gateway = $app['config']['mycompany/sms::gateway'];
return new Sender($gateway);
});
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2-palamarchuk-151017121159-lva1-app6892/85/slide-31-320.jpg)
![Example: Laravel (2)
<?php
namespace MyCompanyContact;
use IlluminateSupportServiceProvider;
class ContactsServiceProvider extends ServiceProvider
{
public function register()
{
$this->app['contacts'] = $this->app->share(function($app) {
$senderId = $app['config']['mycompany/contact::sms_sender_id'];
$file = $app['config']['mycompany/contact::file'];
return new Manager($app[$senderId], $file);
});
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2-palamarchuk-151017121159-lva1-app6892/85/slide-32-320.jpg)