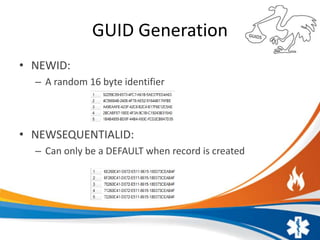
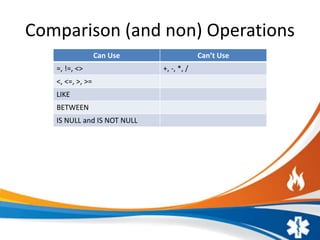
The document presents an overview of Global Unique Identifiers (GUIDs), detailing their generation, advantages, and disadvantages. GUIDs have a unique 16-byte size, can be generated offline, and are beneficial for identifying data from multiple sources; however, they lead to larger data sizes, slower performance on joins/updates, and increased index fragmentation. The presentation includes demos and resources for further exploration of GUIDs.