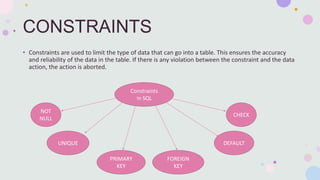
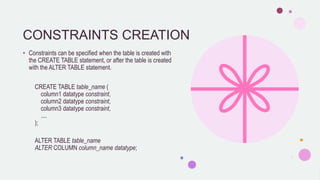
SQL constraints such as NOT NULL, UNIQUE, PRIMARY KEY, FOREIGN KEY, CHECK, and DEFAULT are used to enforce data integrity in tables by limiting the type of data that can be inserted. Constraints can be specified during table creation or altered afterwards, and they ensure that the data adheres to predefined rules, preventing actions that would violate these rules. Each type of constraint serves a specific purpose, like ensuring uniqueness or defining relationships between tables.