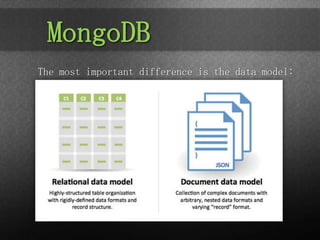
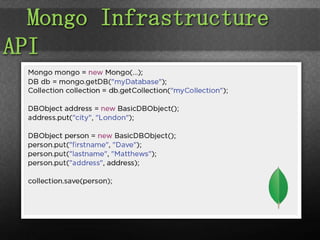
The document provides an overview of Spring Data, focusing on its integration with NoSQL and relational databases such as MongoDB, emphasizing its flexible data model and ease of scalability. It discusses components like JPA for object/relational mapping, repository abstractions, and the use of templates for simplified data access. Finally, it highlights the Spring Data mission statement and the importance of a consistent programming model while retaining specific features of different data stores.