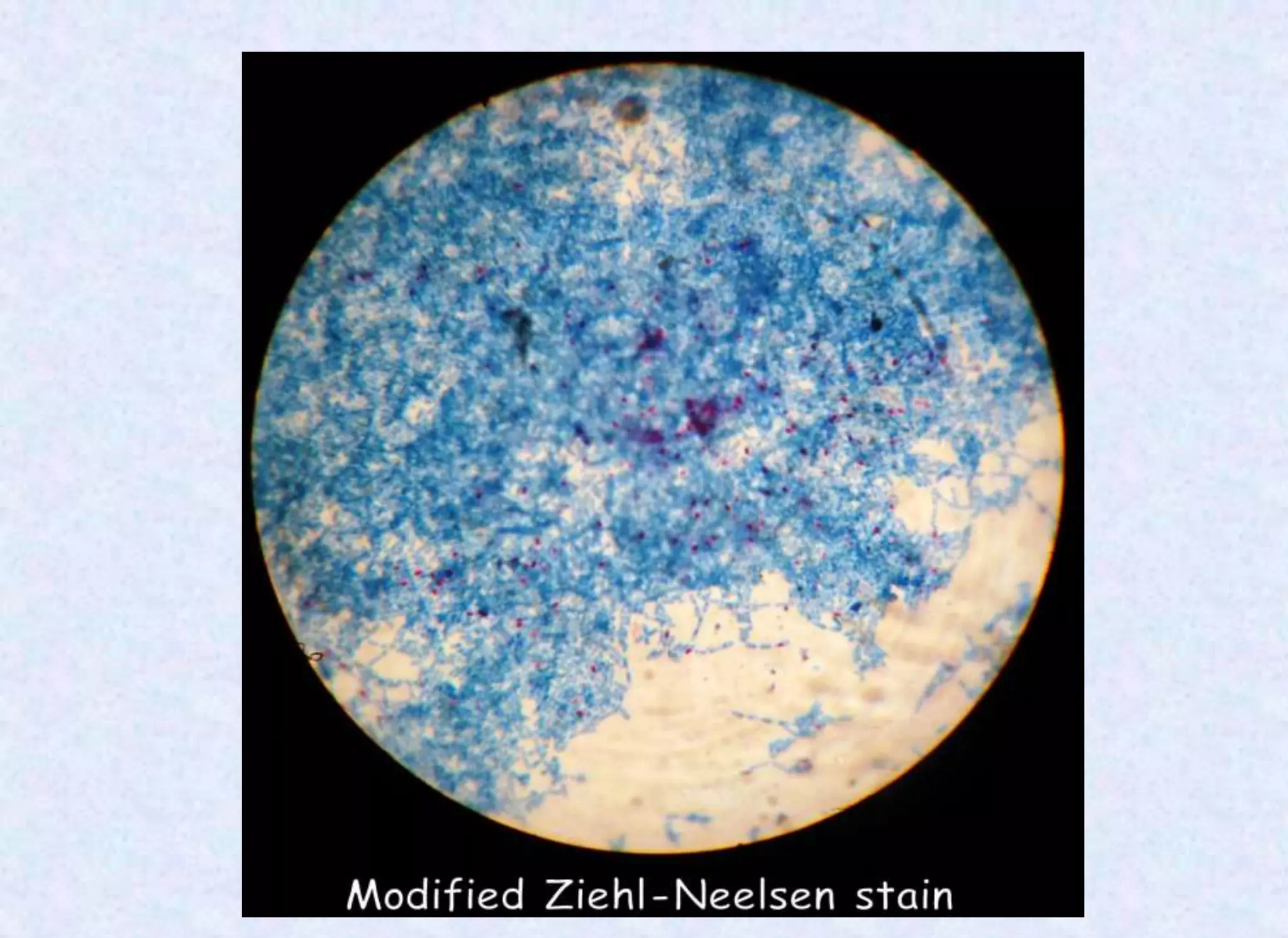
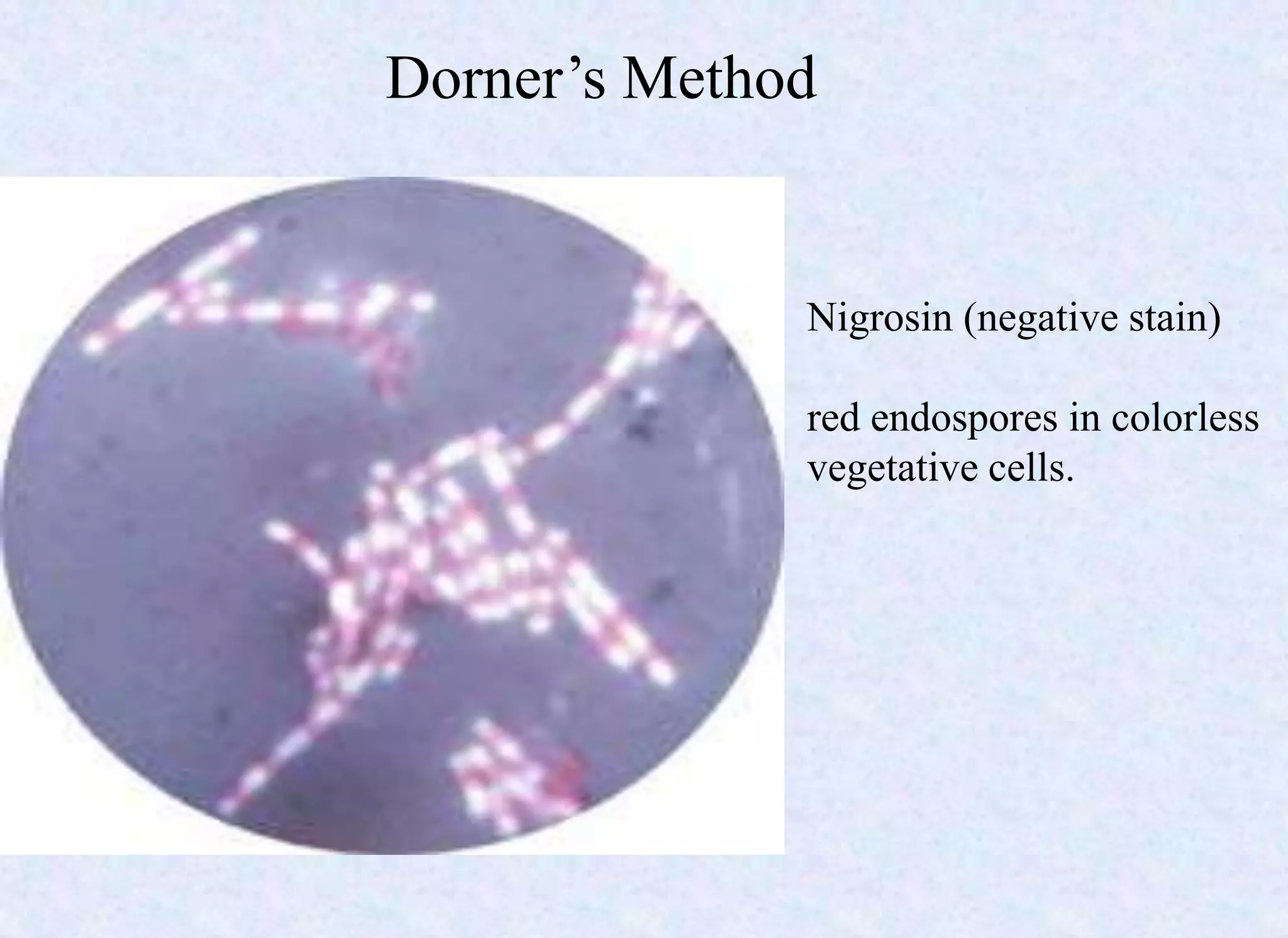
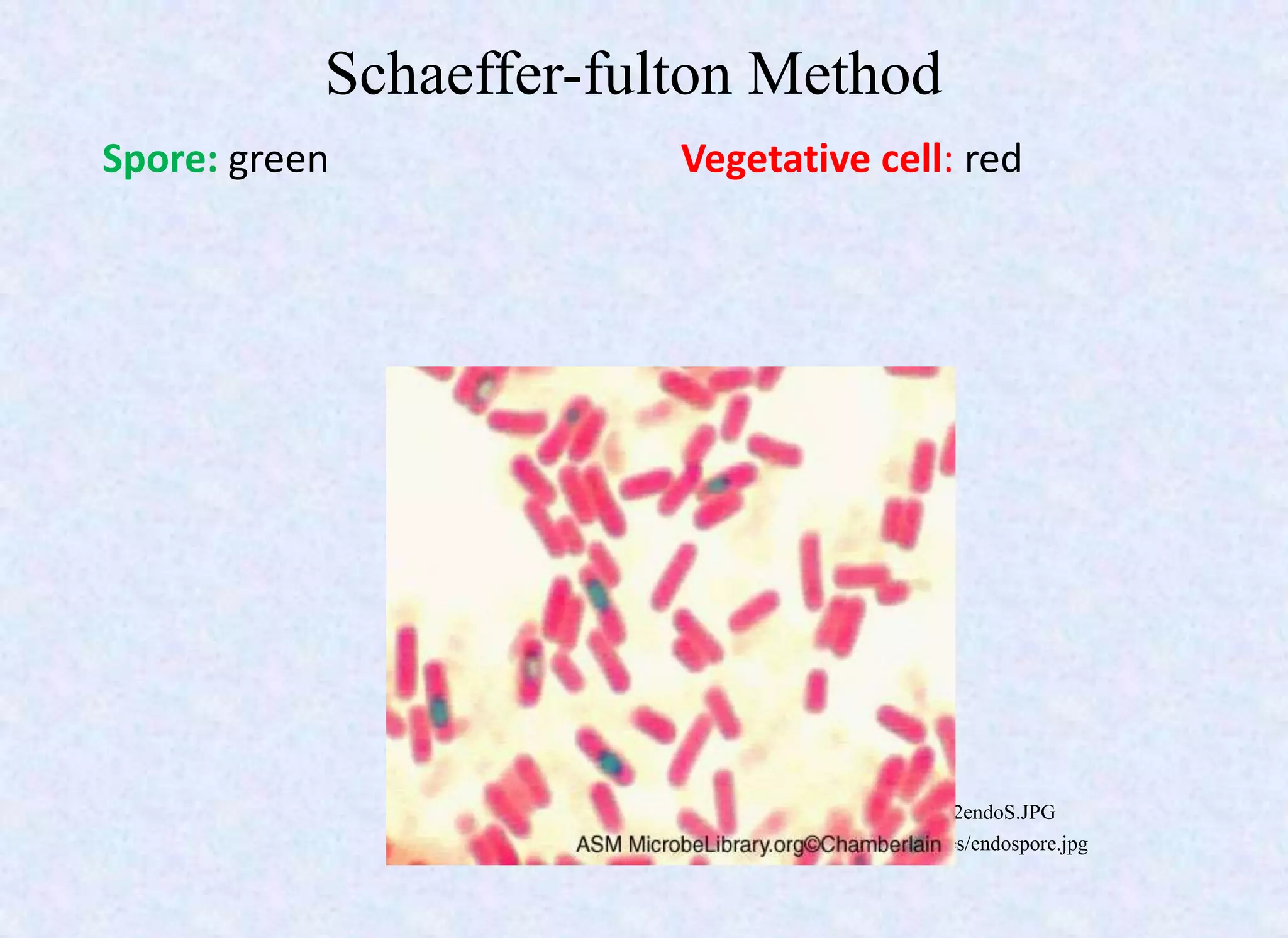
This document provides an overview of bacterial spores, including their definition, structure, important spore-forming bacteria, sporulation process, properties, resistance, germination, and uses. Key points include:
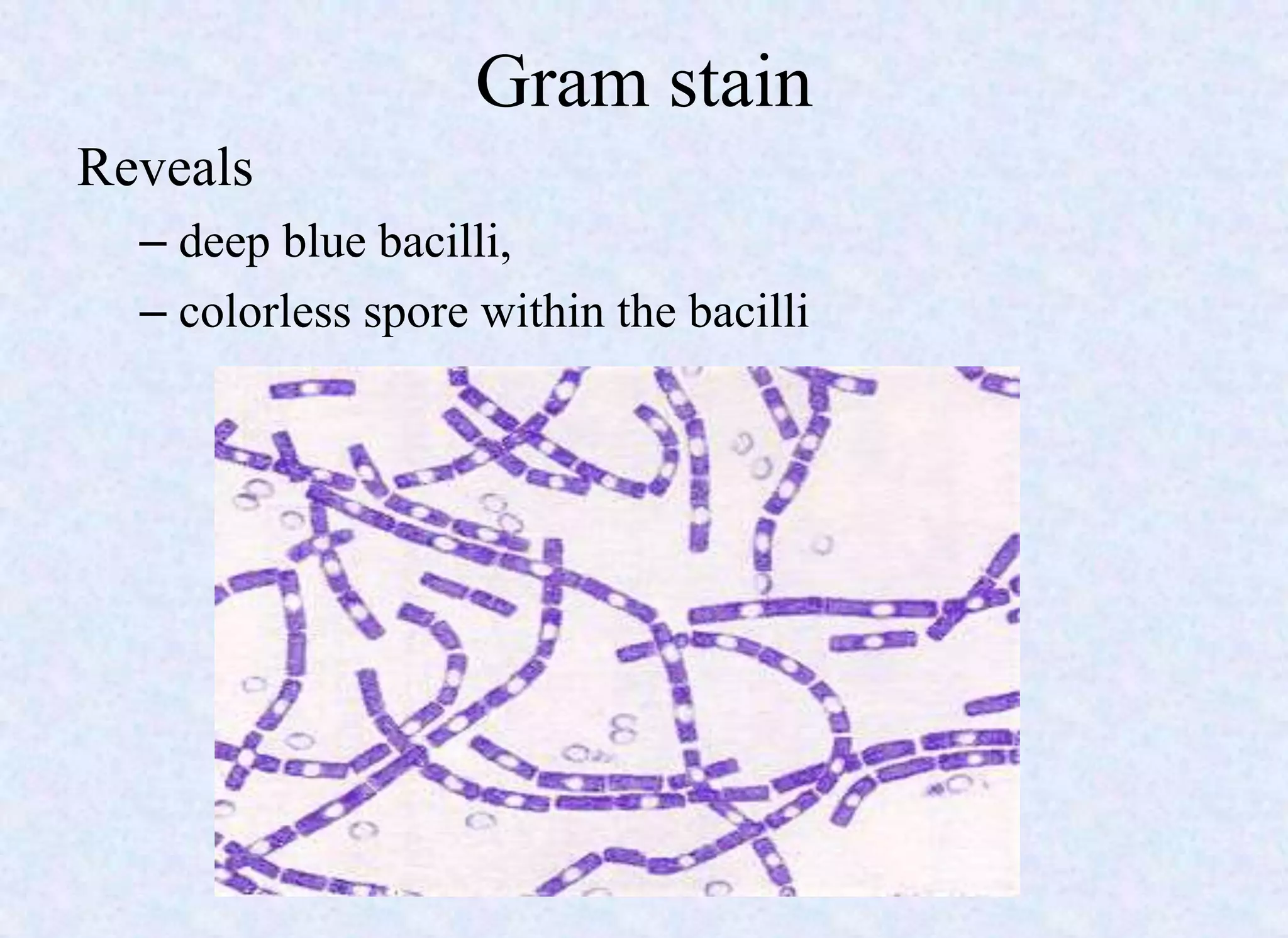
- Bacterial spores are dormant, highly resistant forms of bacteria that form in response to starvation or stress.
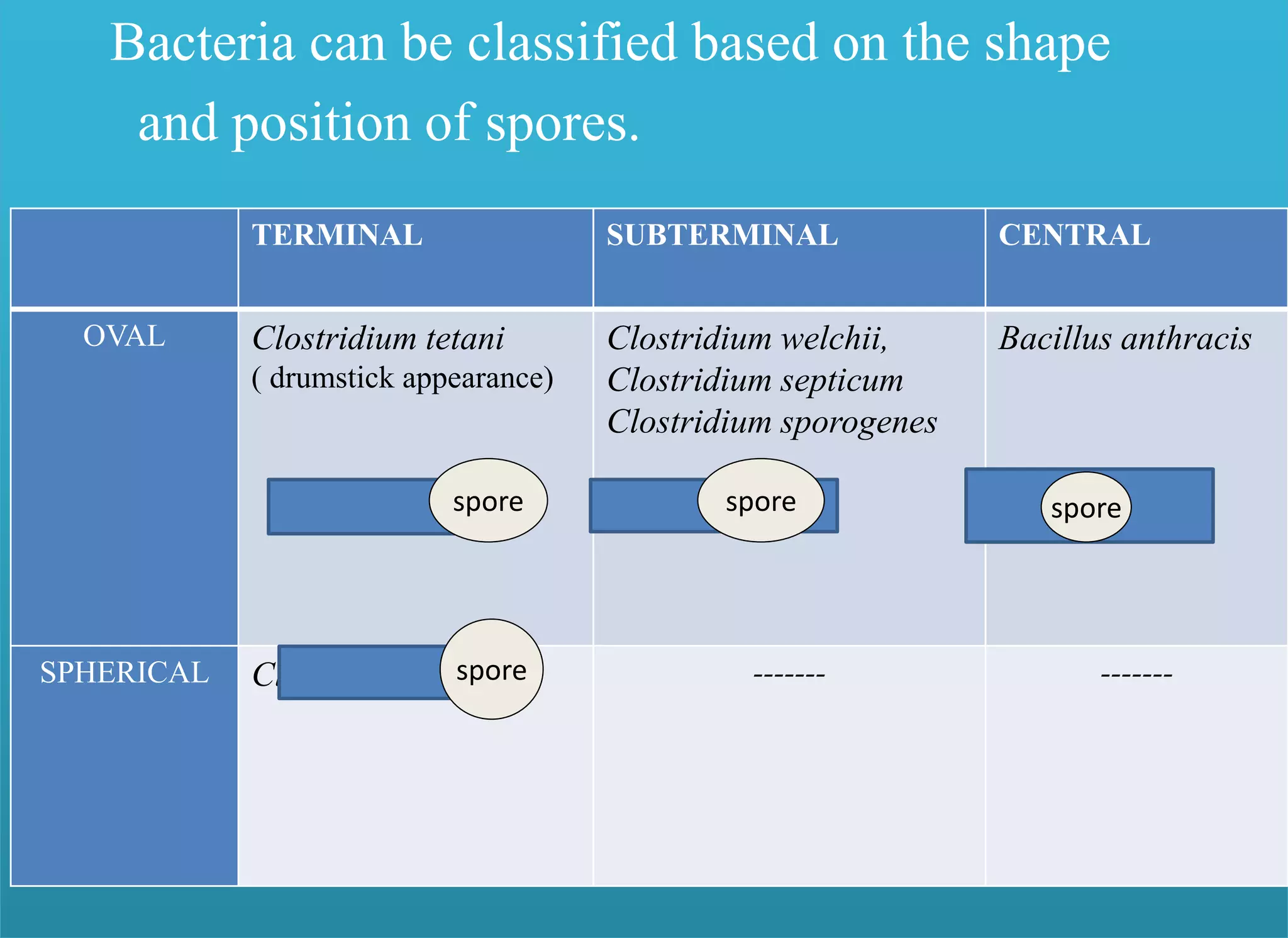
- Important spore-forming genera include Bacillus and Clostridium, which include pathogenic species.
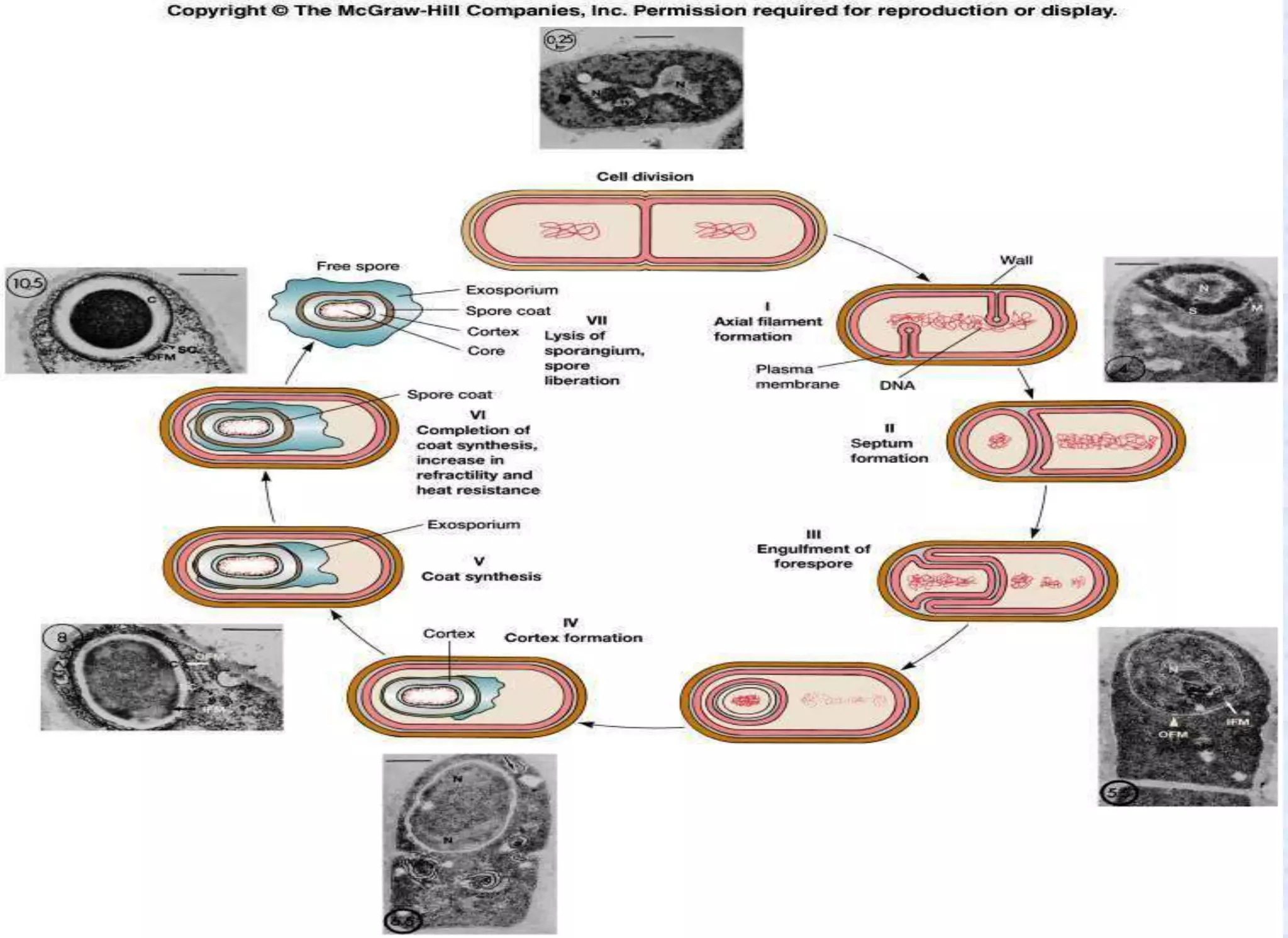
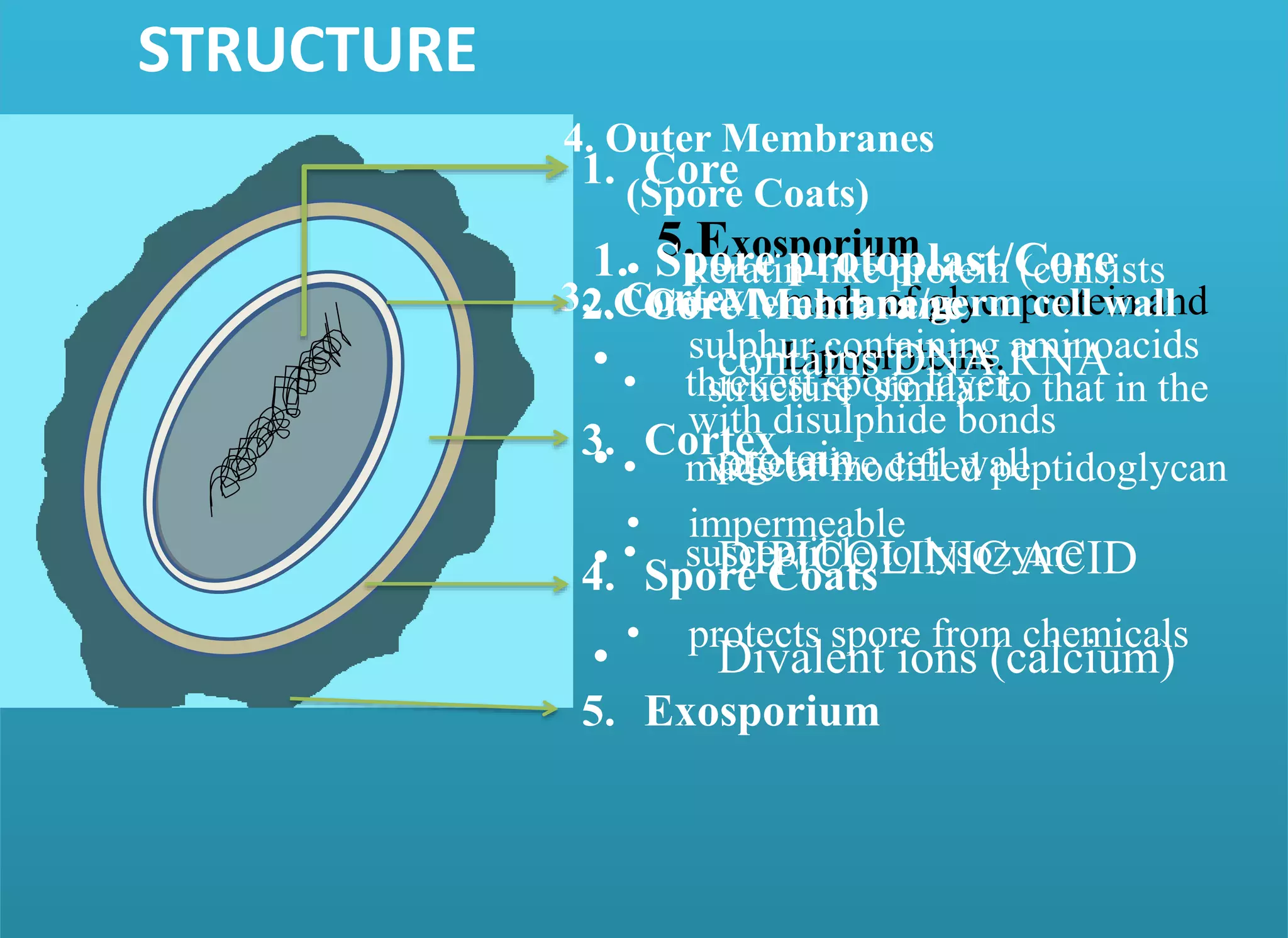
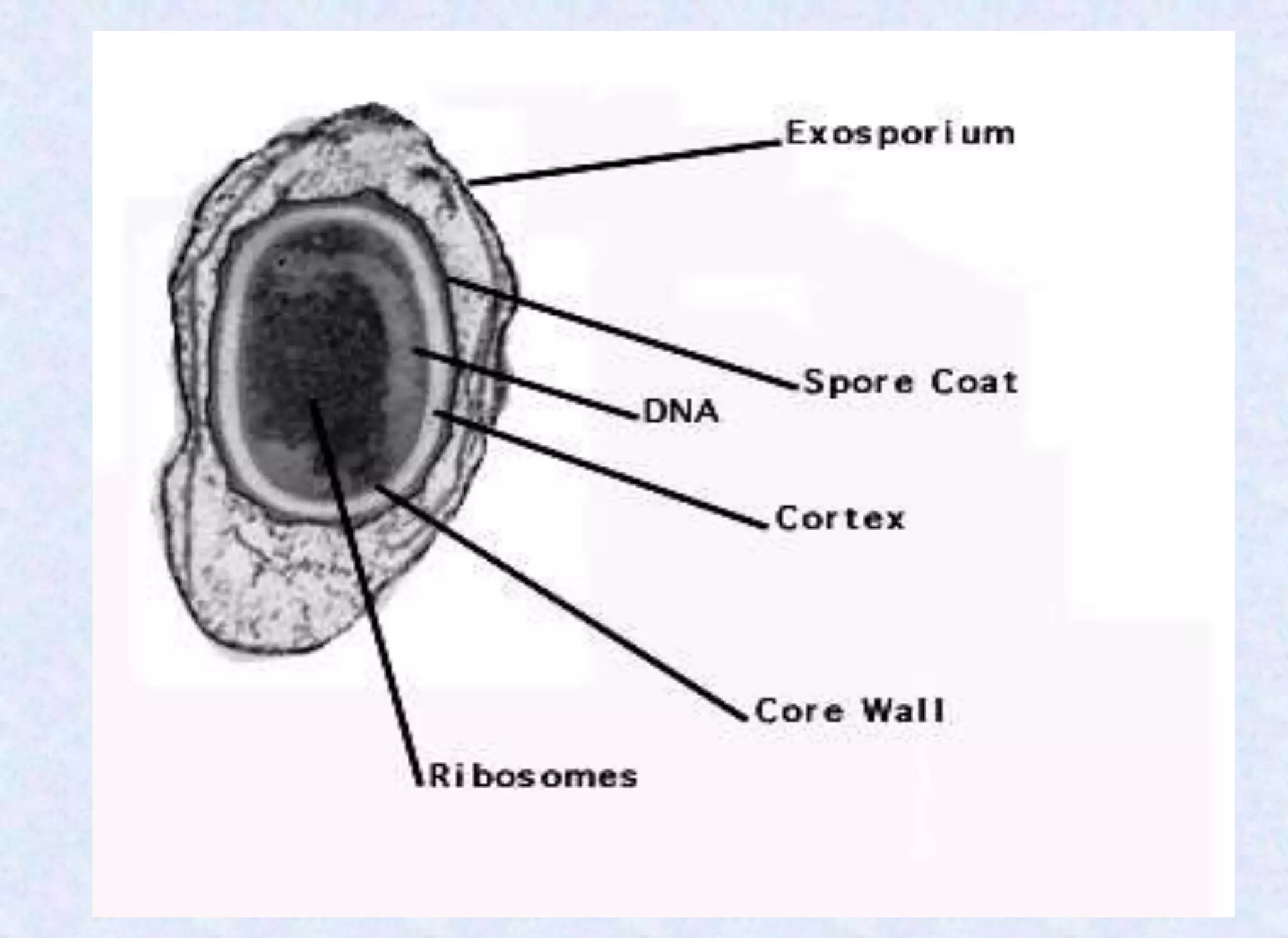
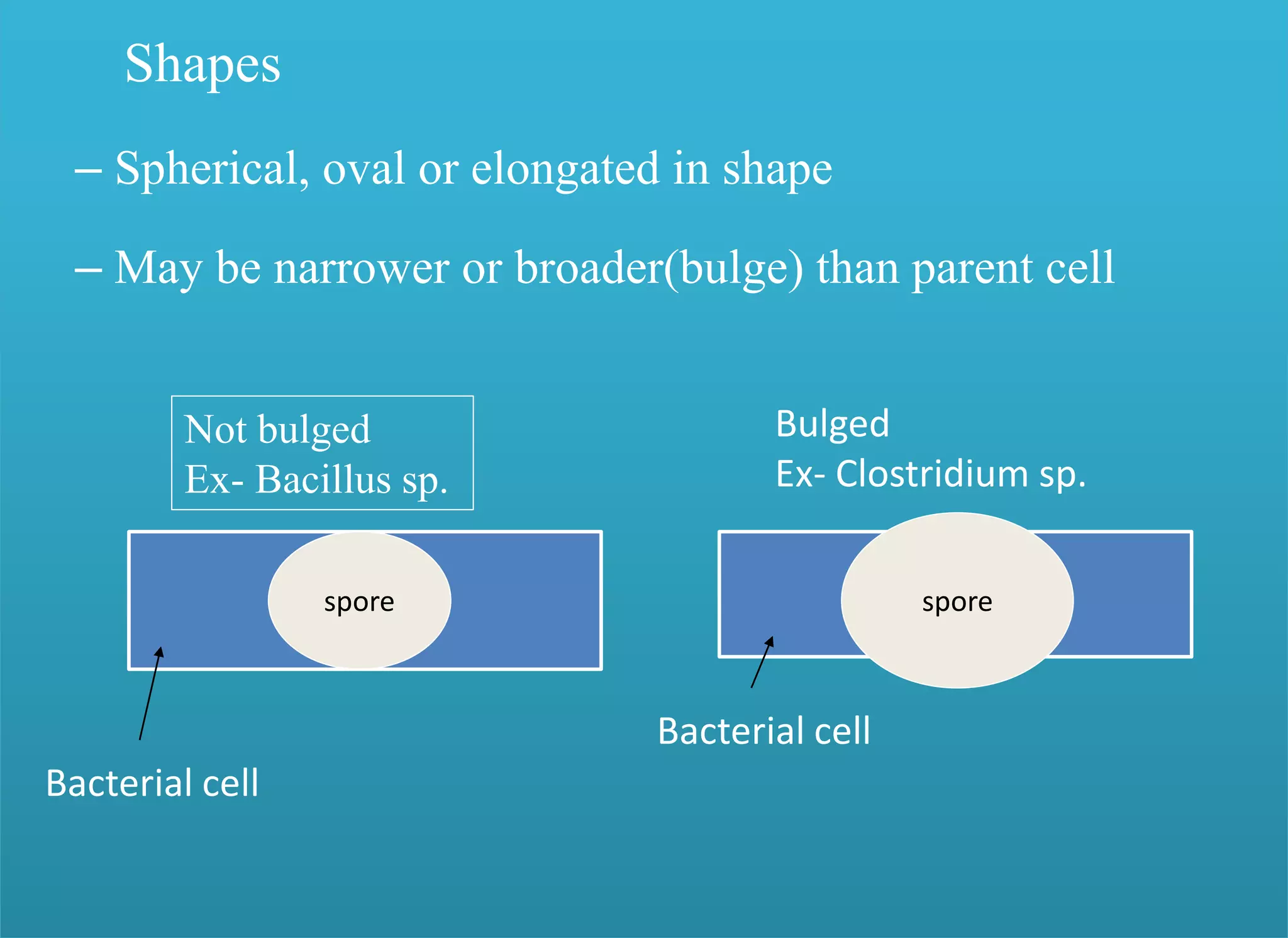
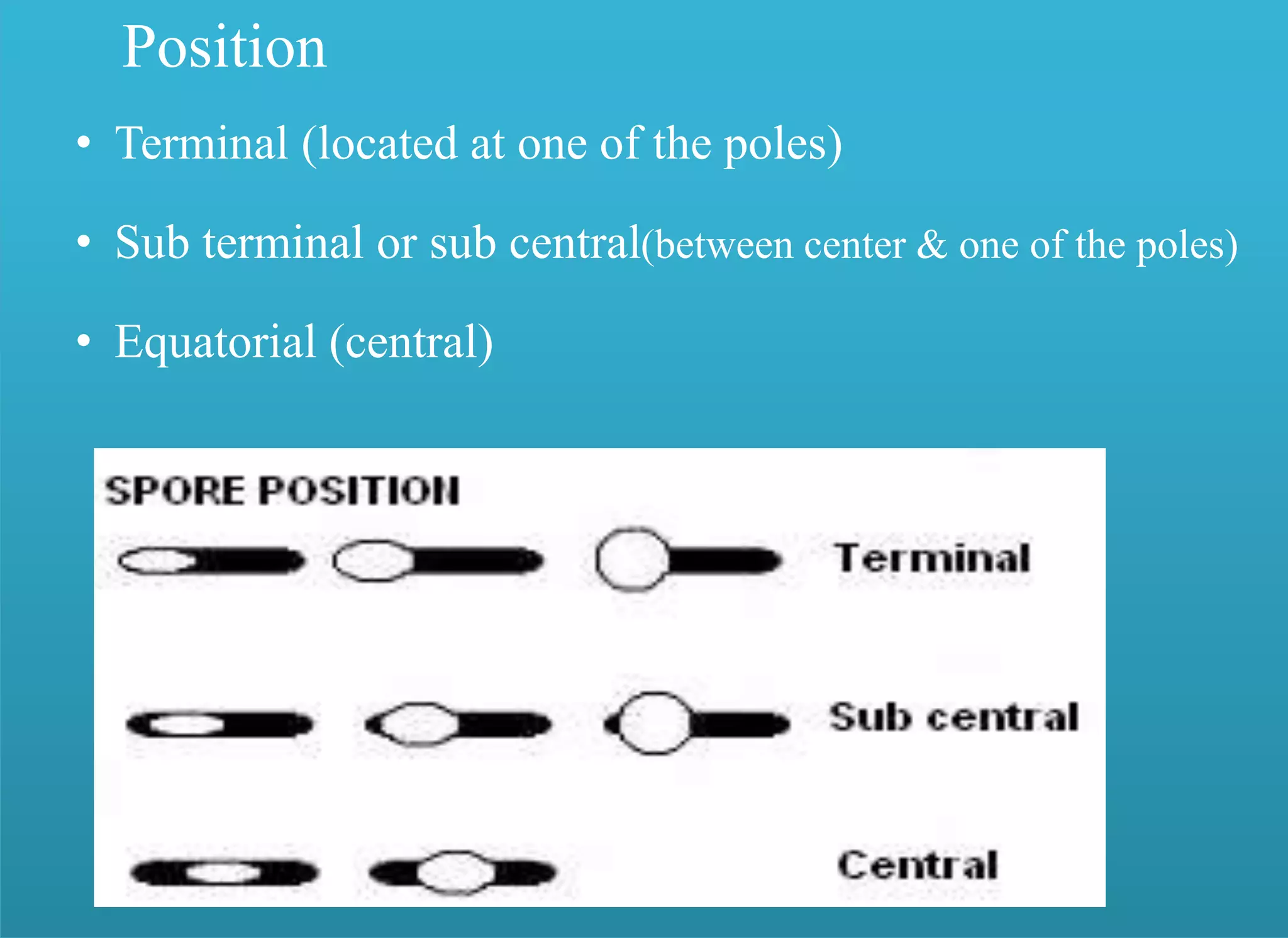
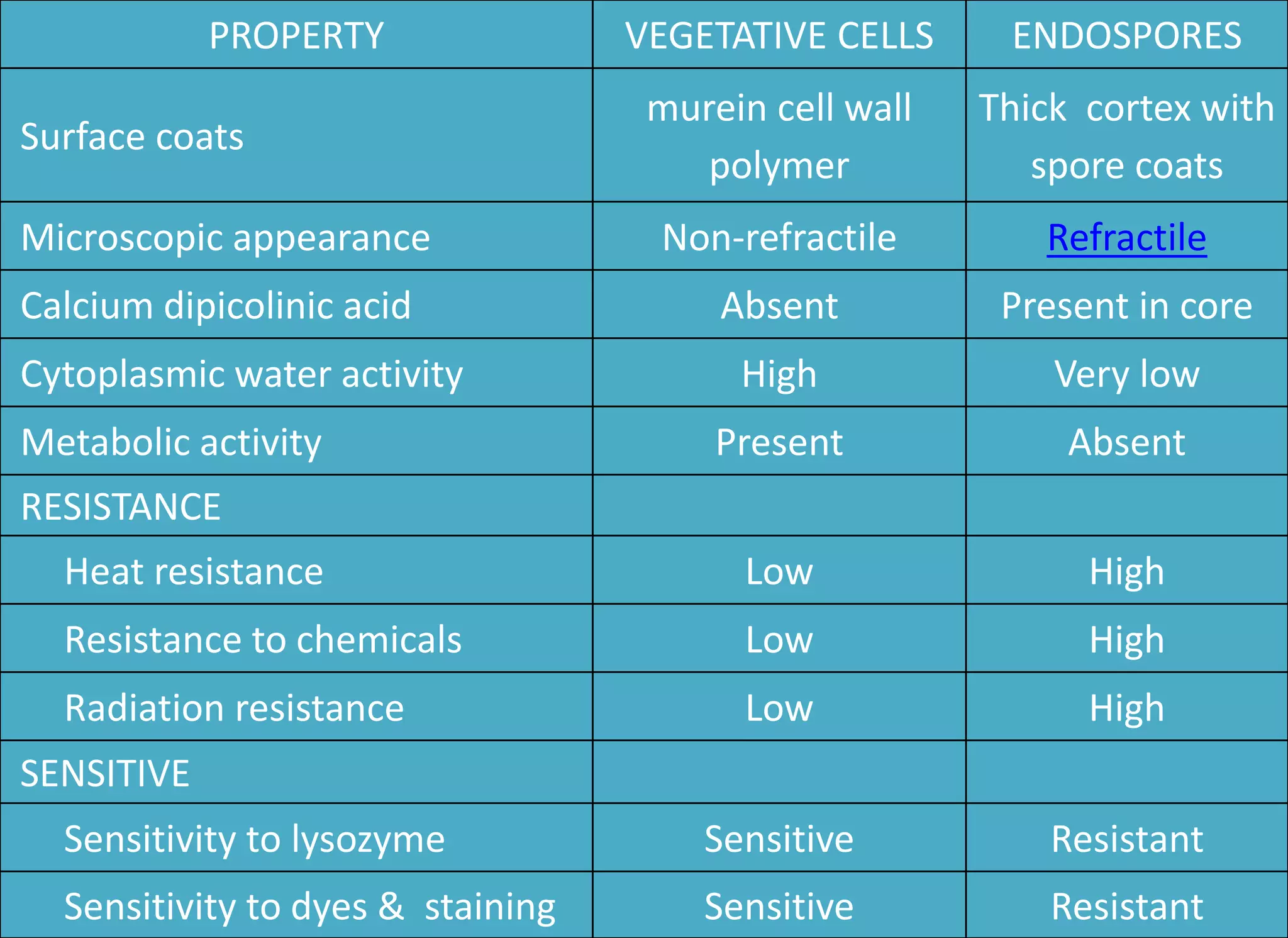
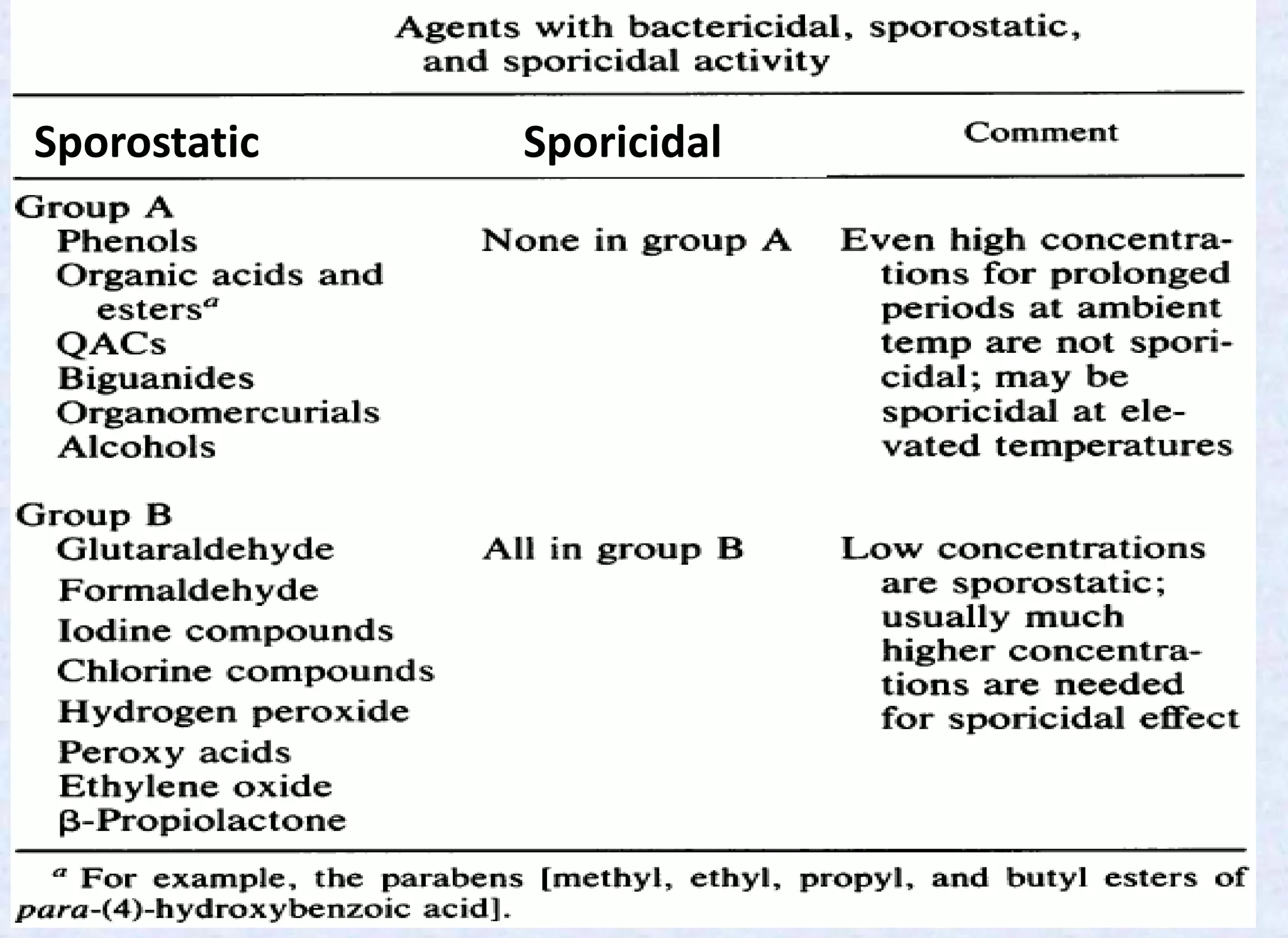
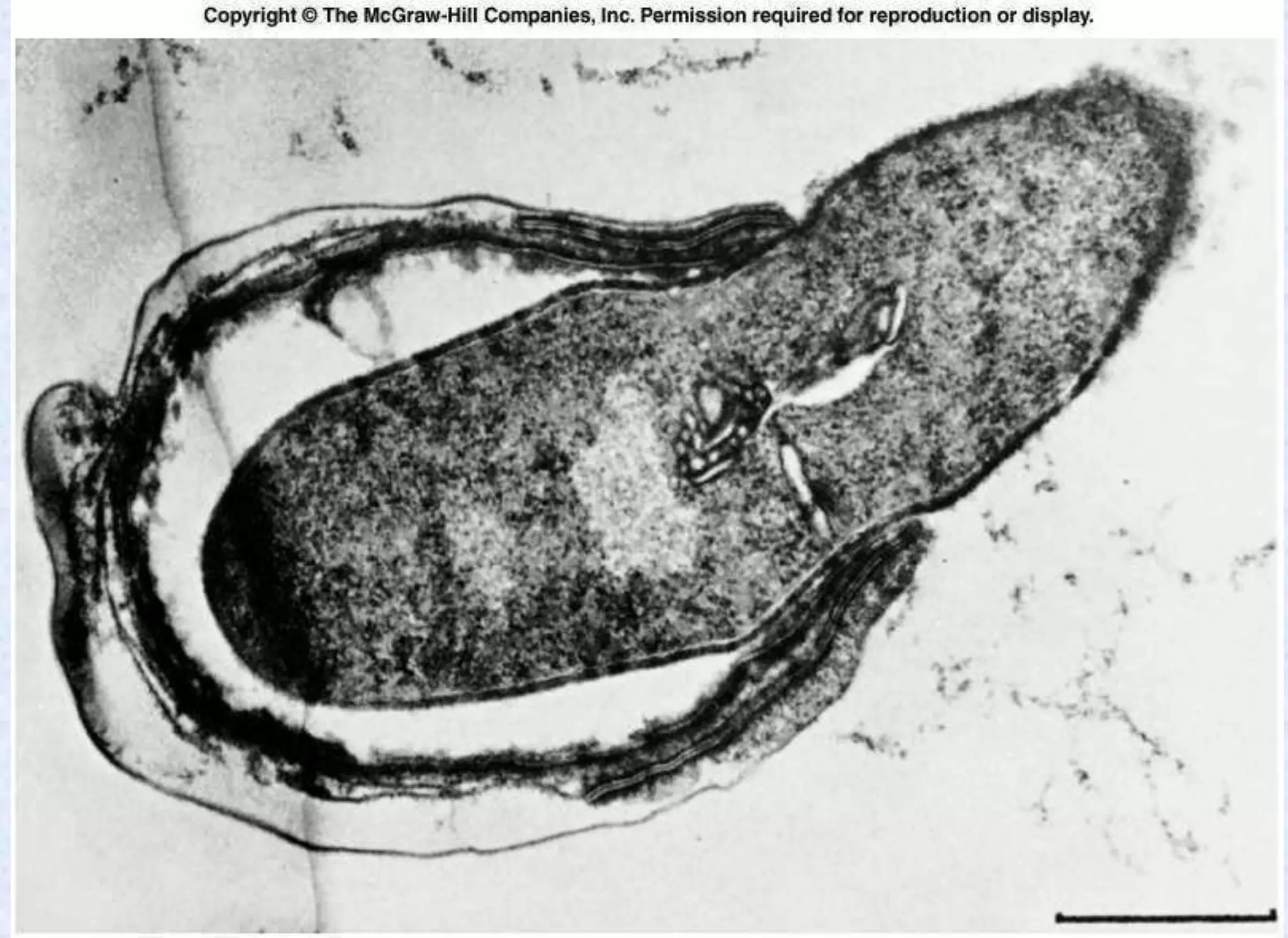
- Spores have a protective multilayer structure and properties like low water content that make them highly resistant to heat, chemicals, radiation, and desiccation.
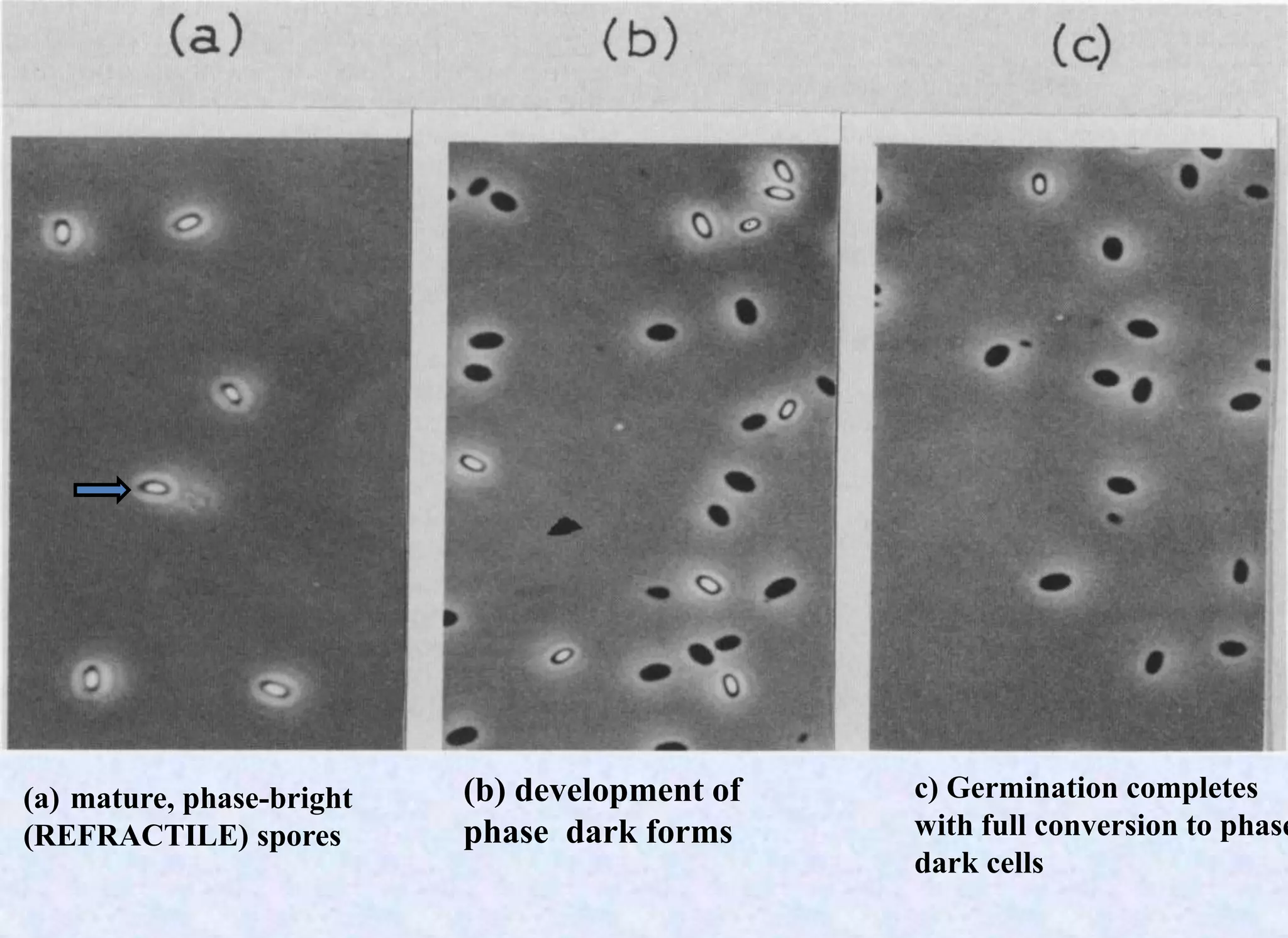
- Spores can germinate into active vegetative cells in response to certain nutrients after a triggering process called activation.