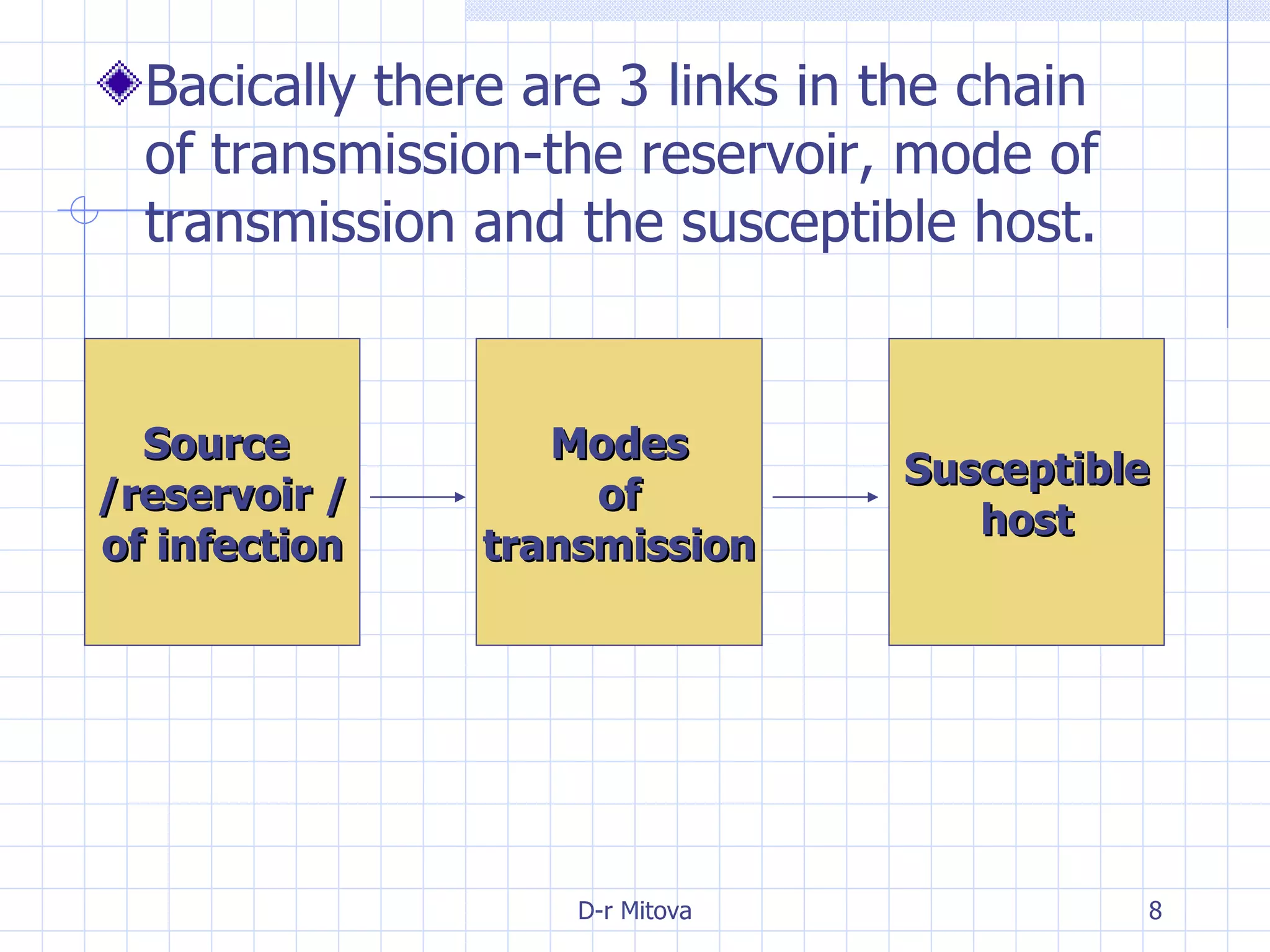
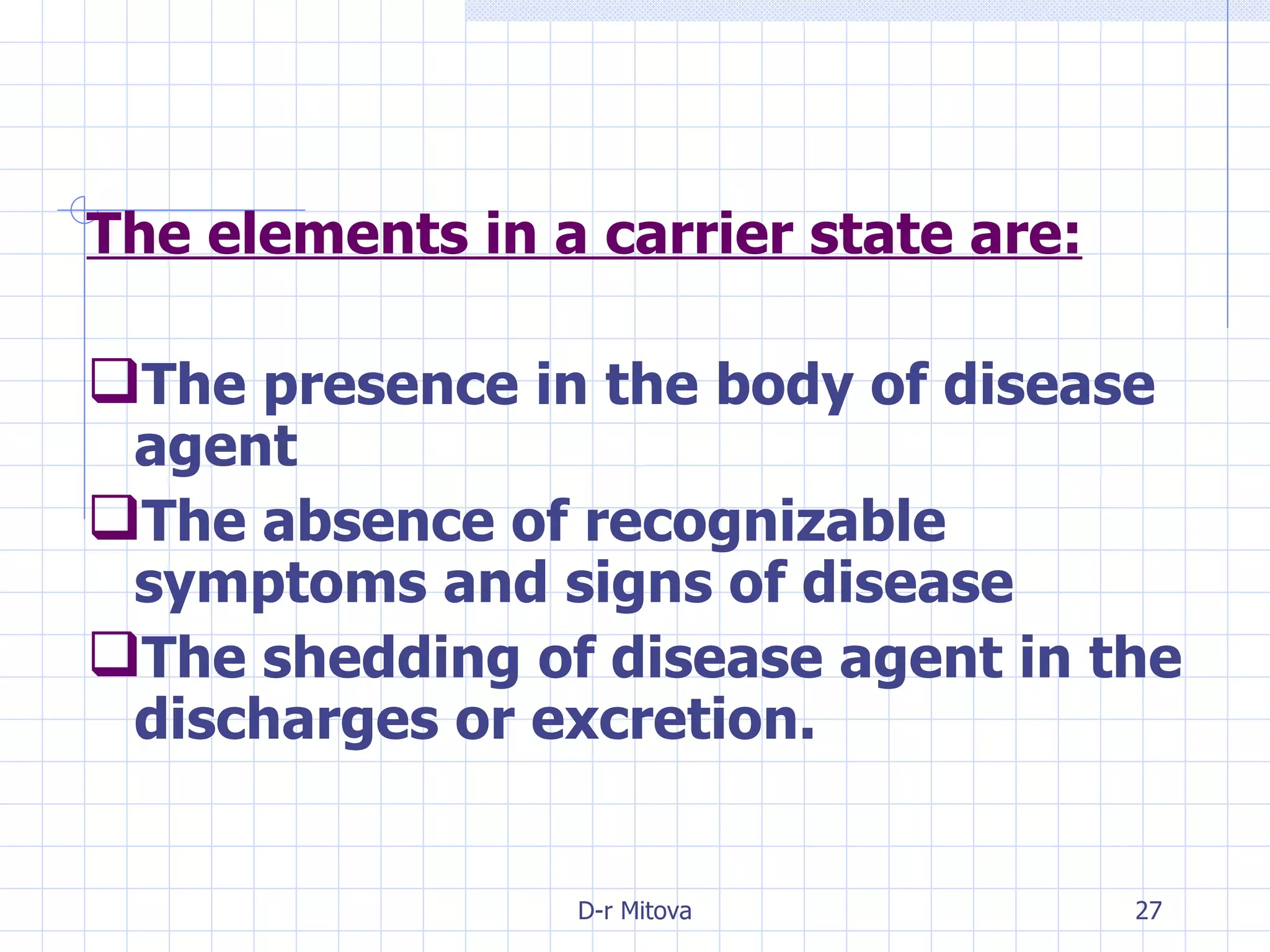
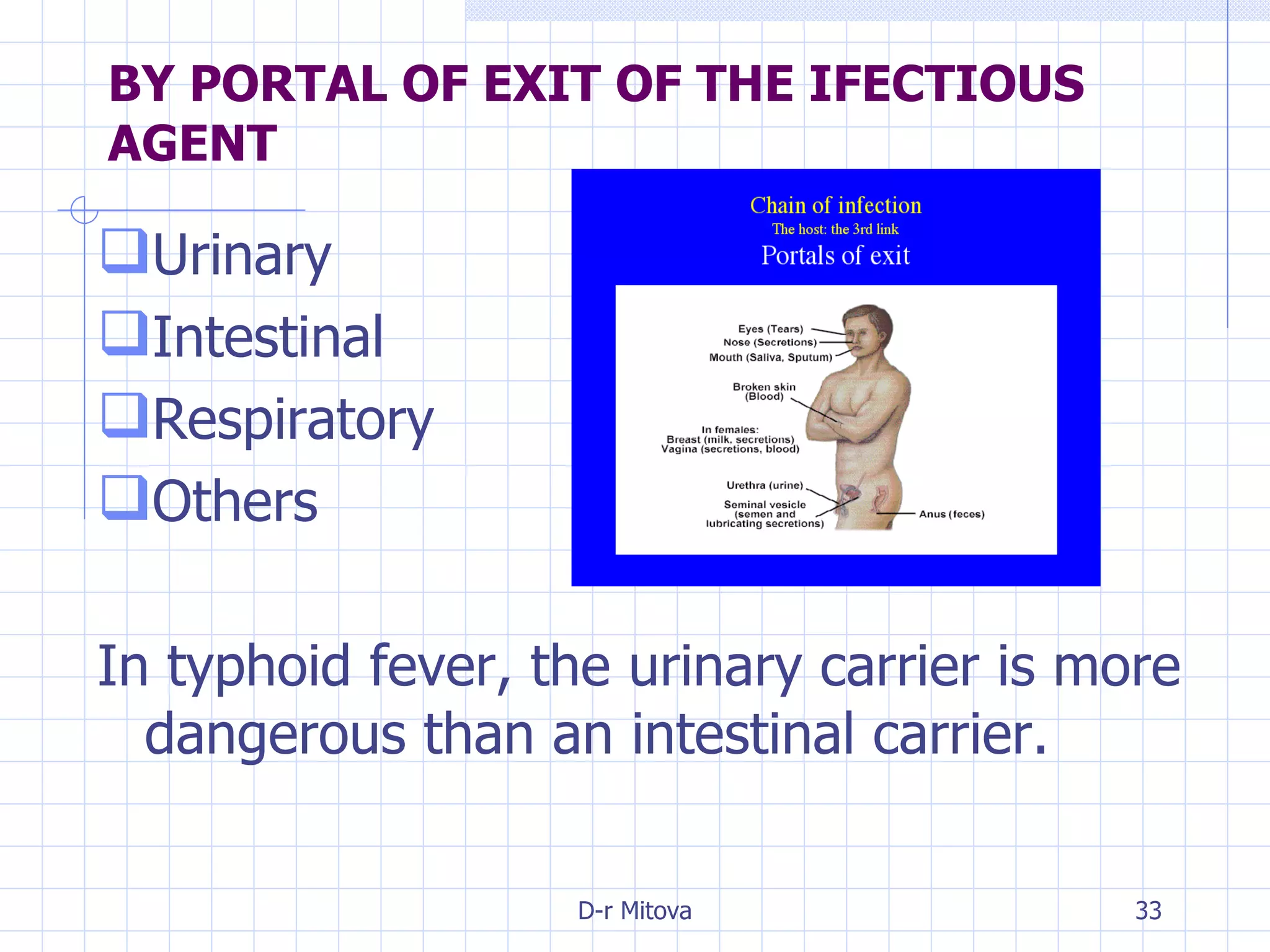
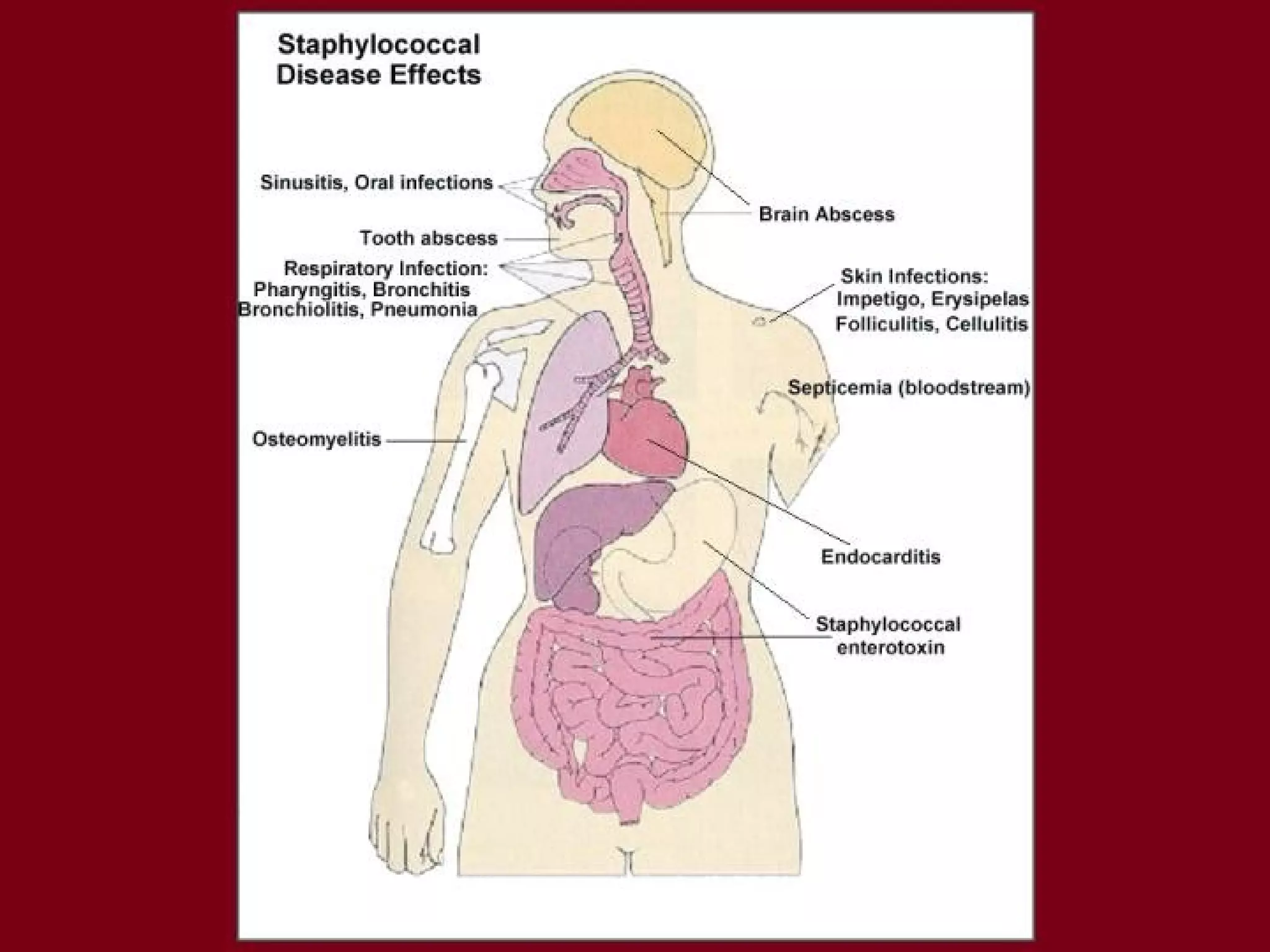
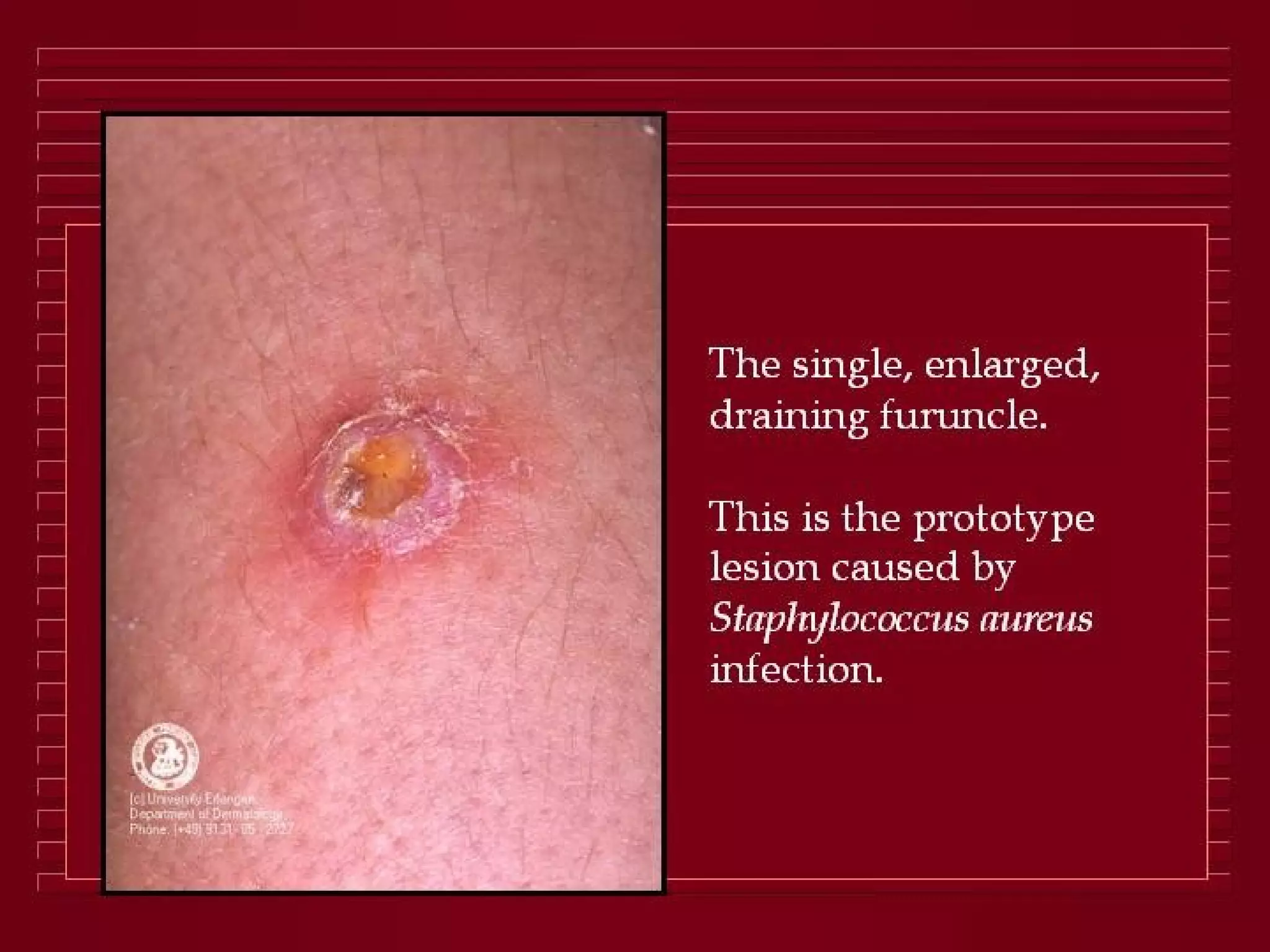
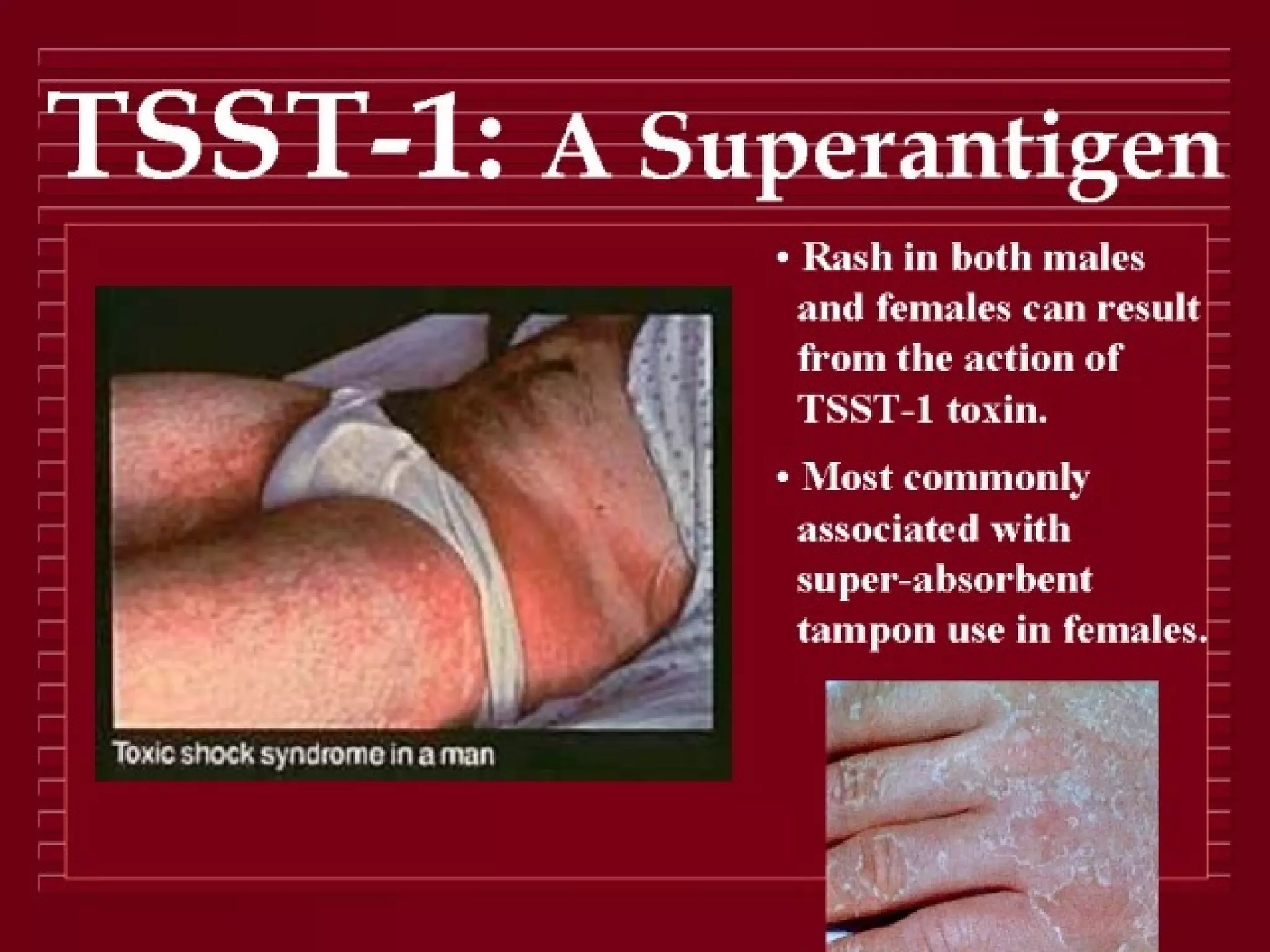
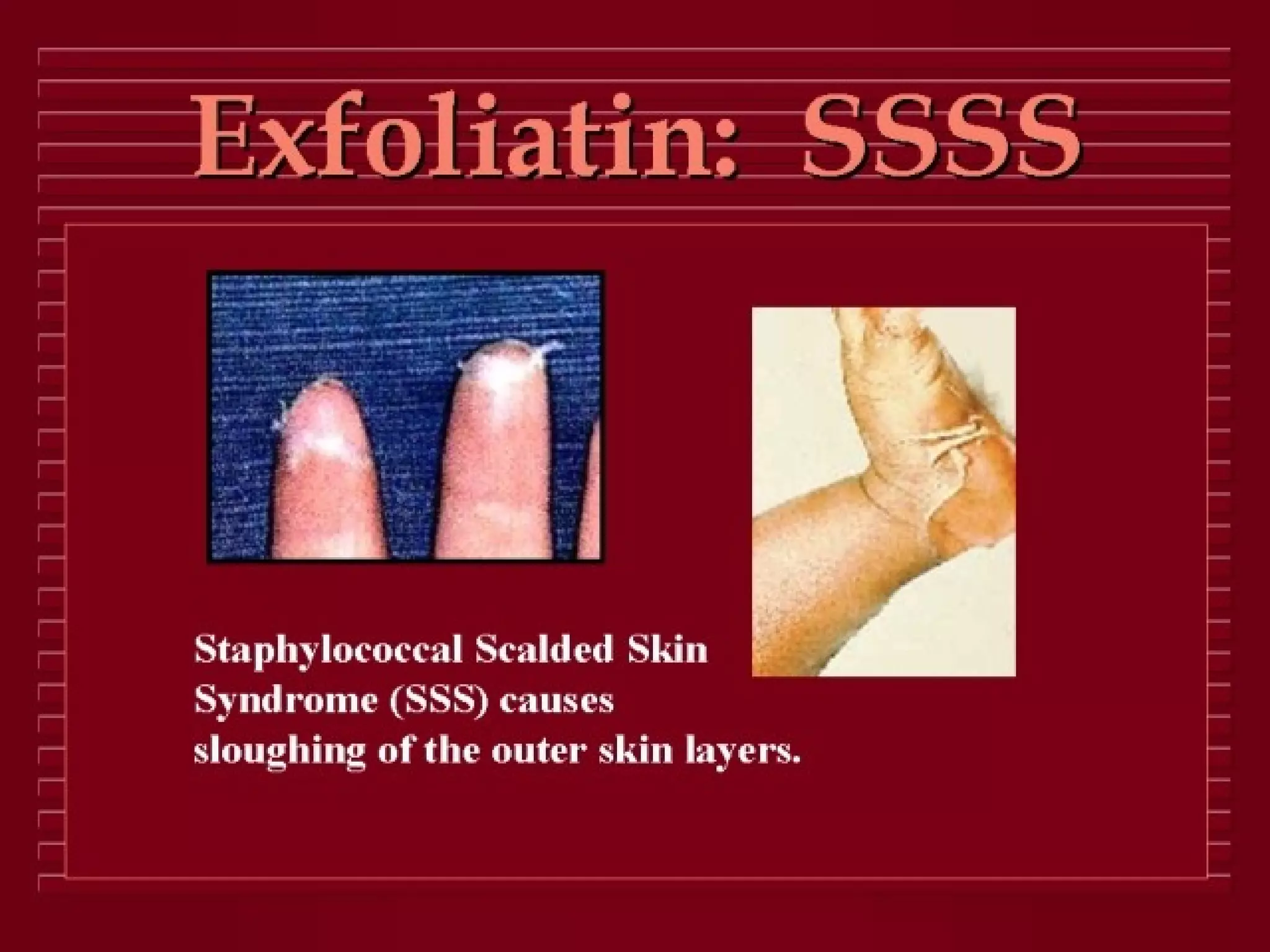
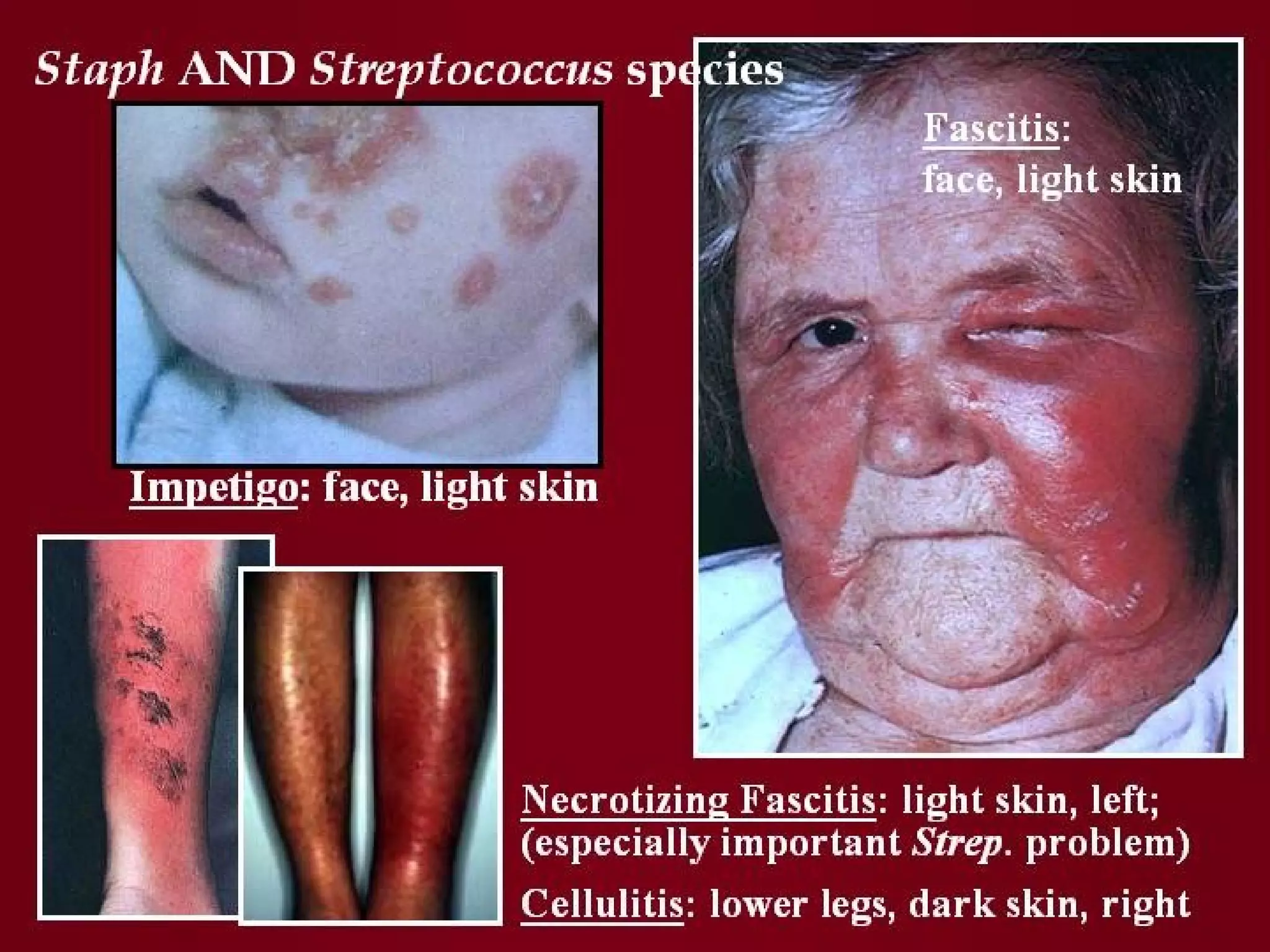
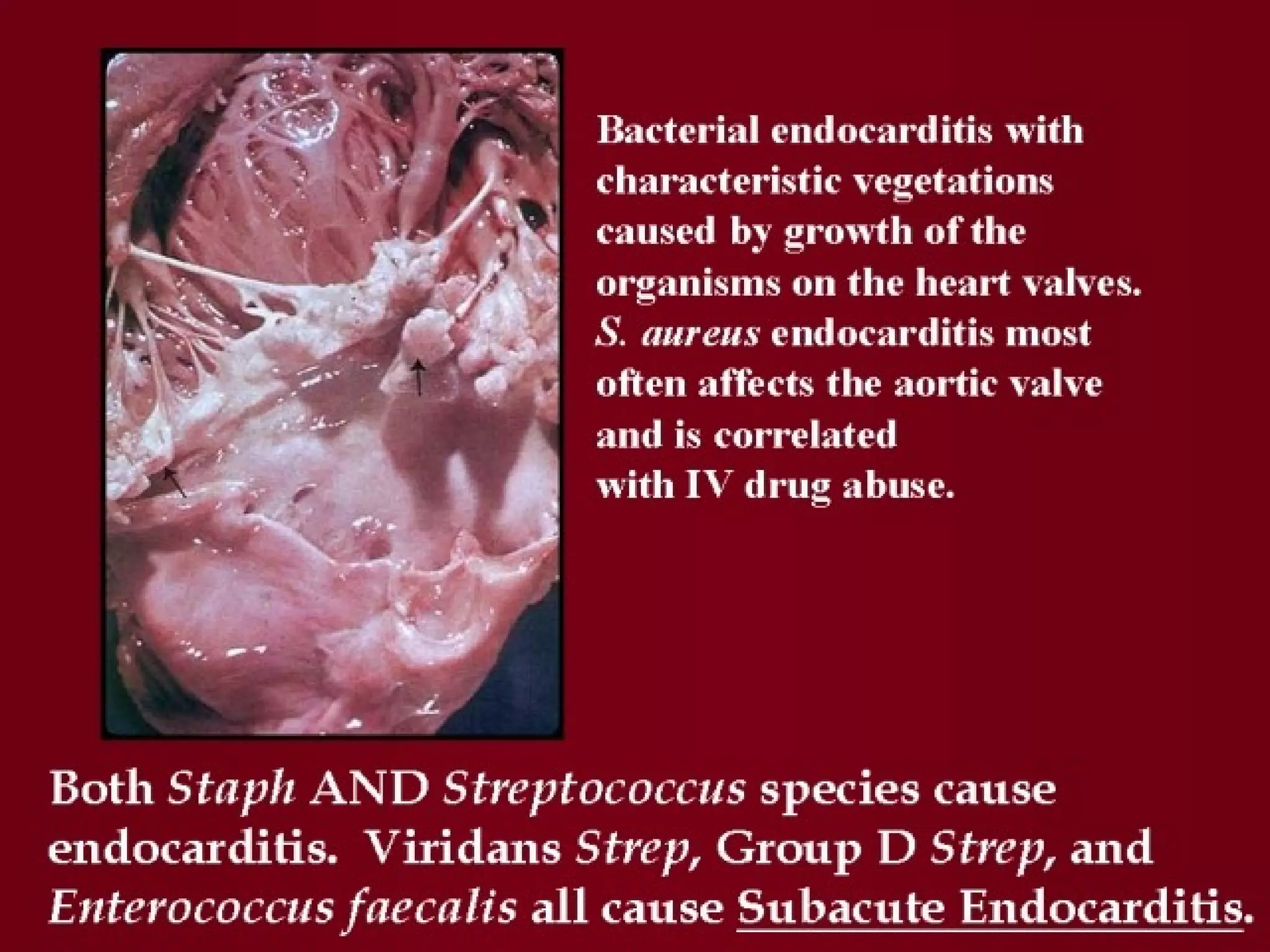
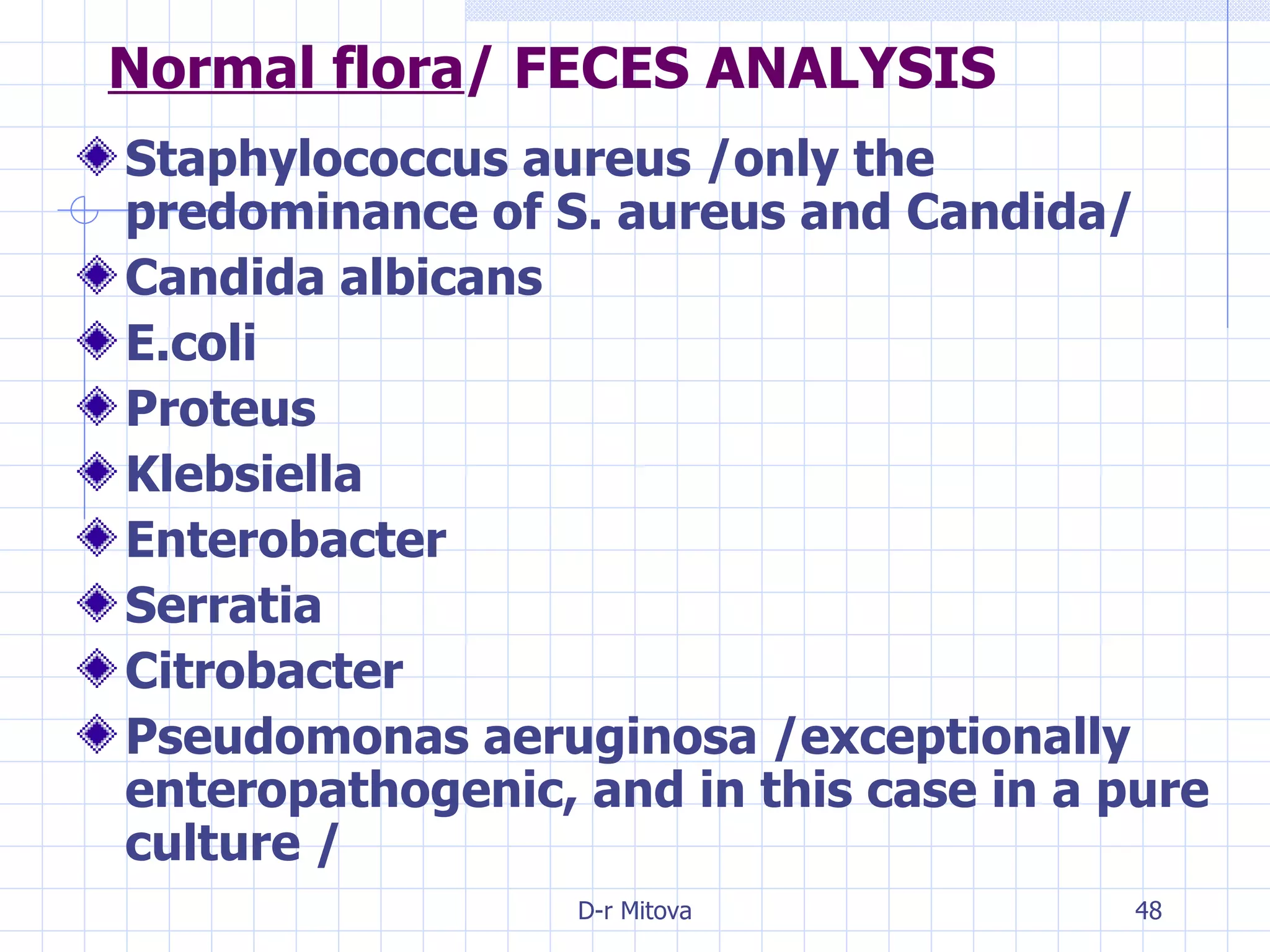
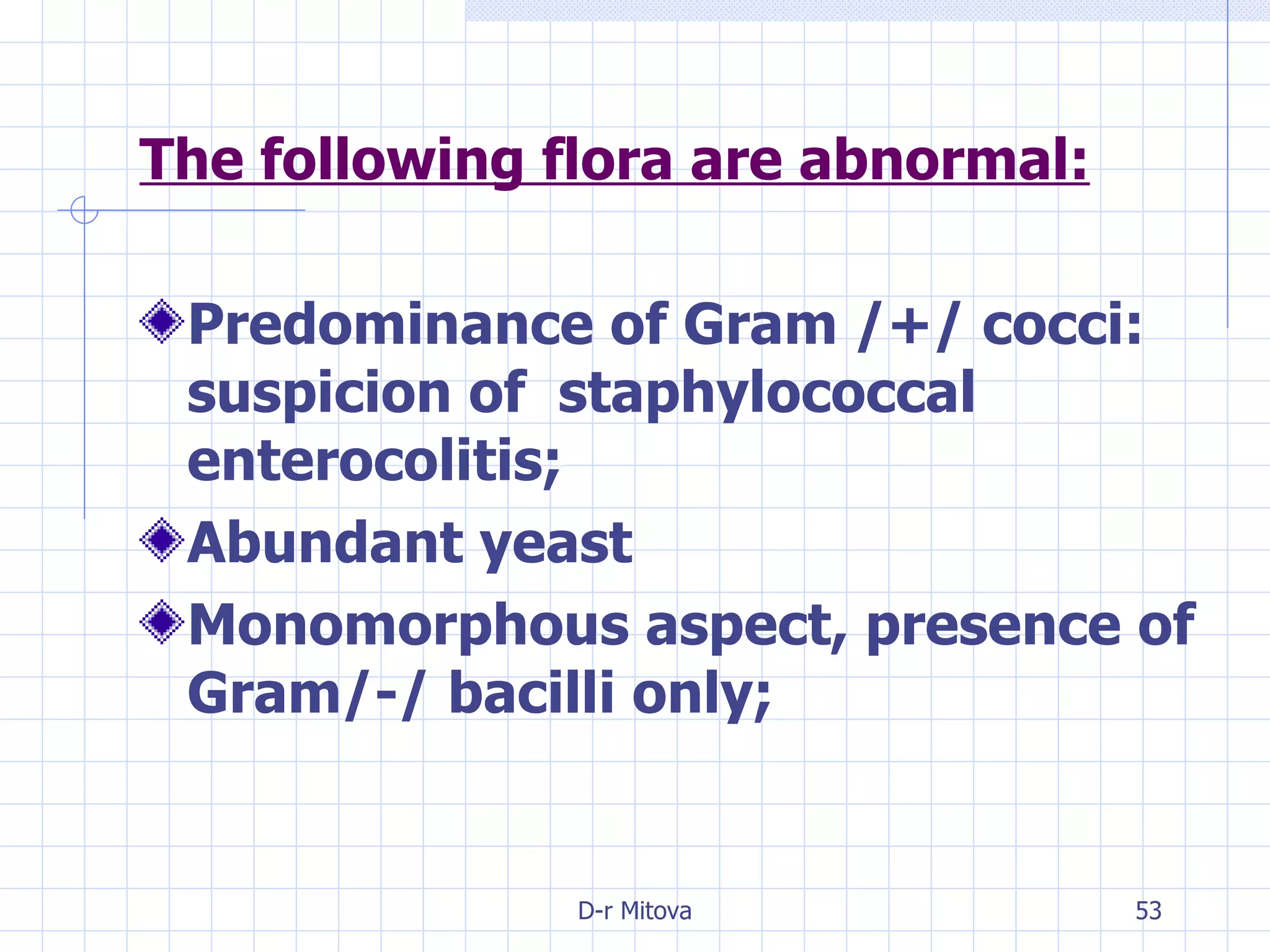
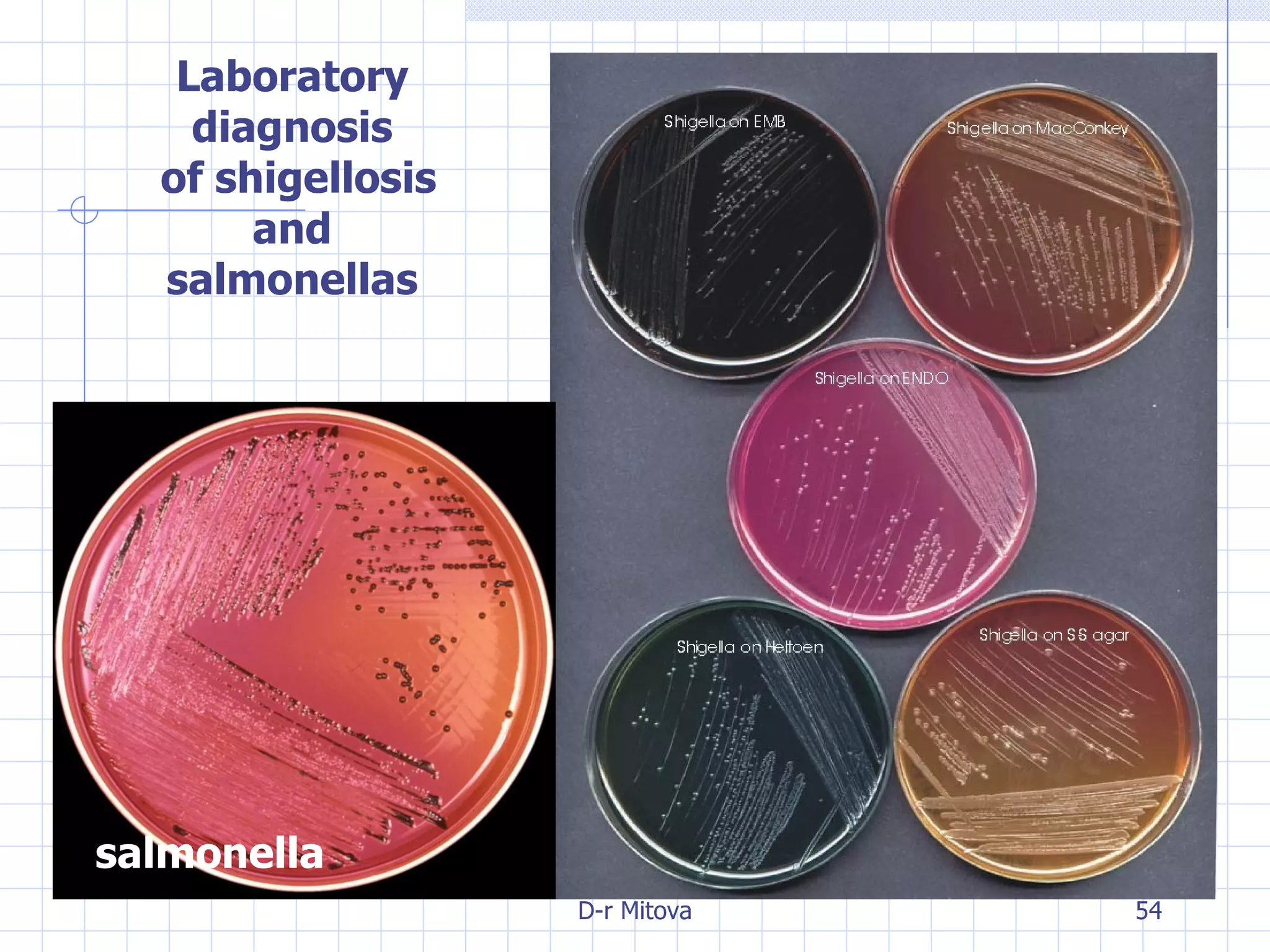
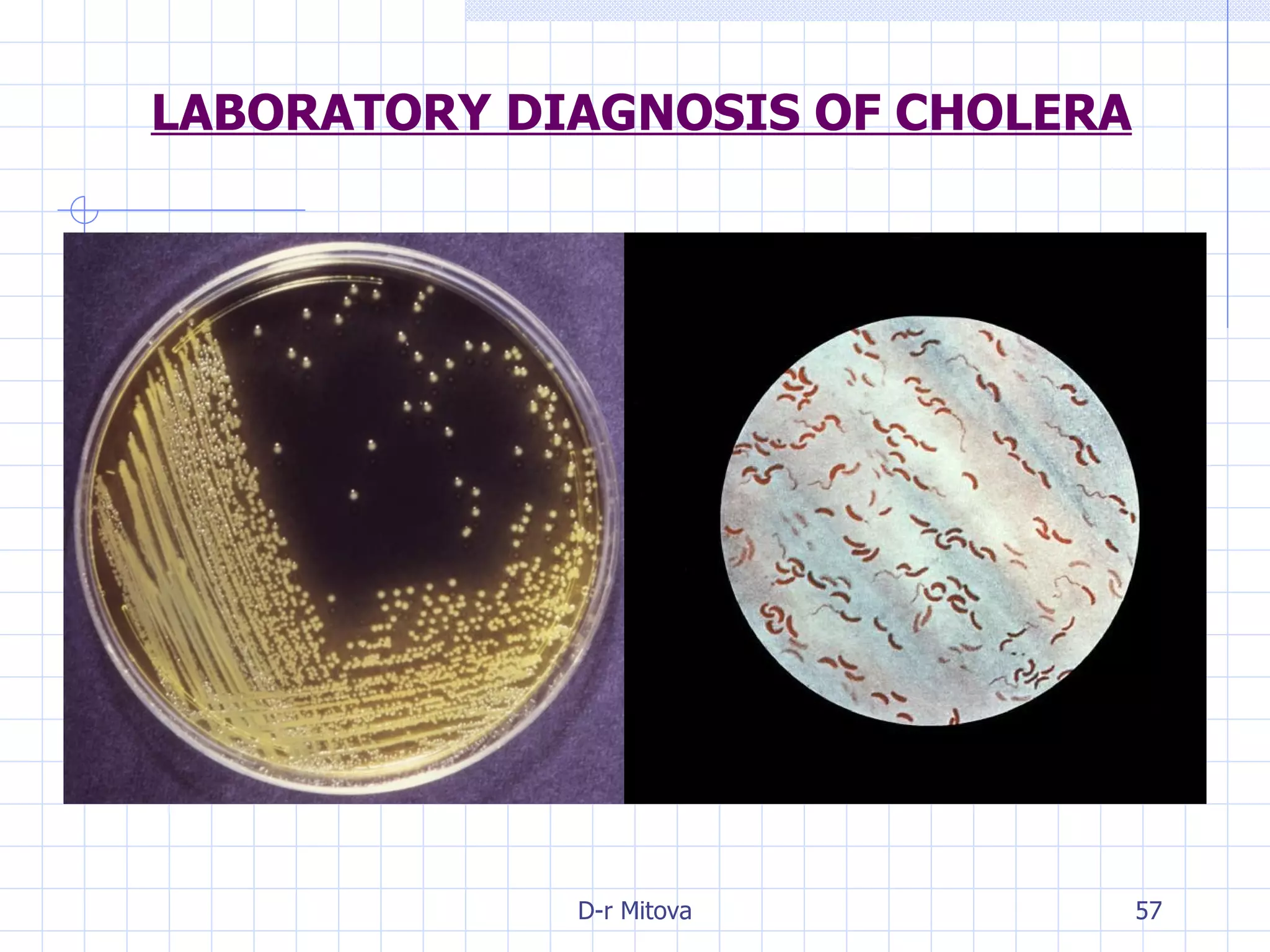
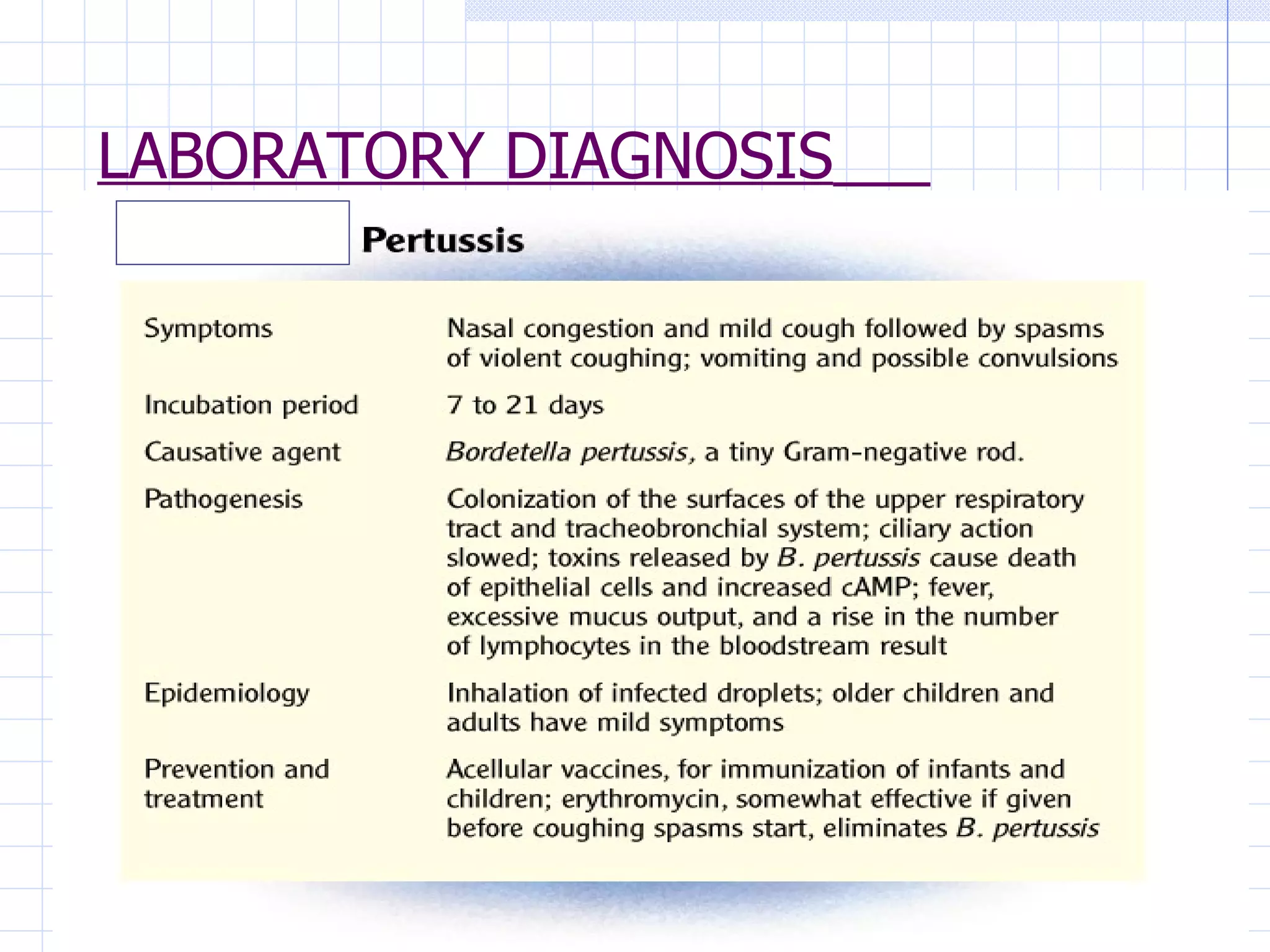
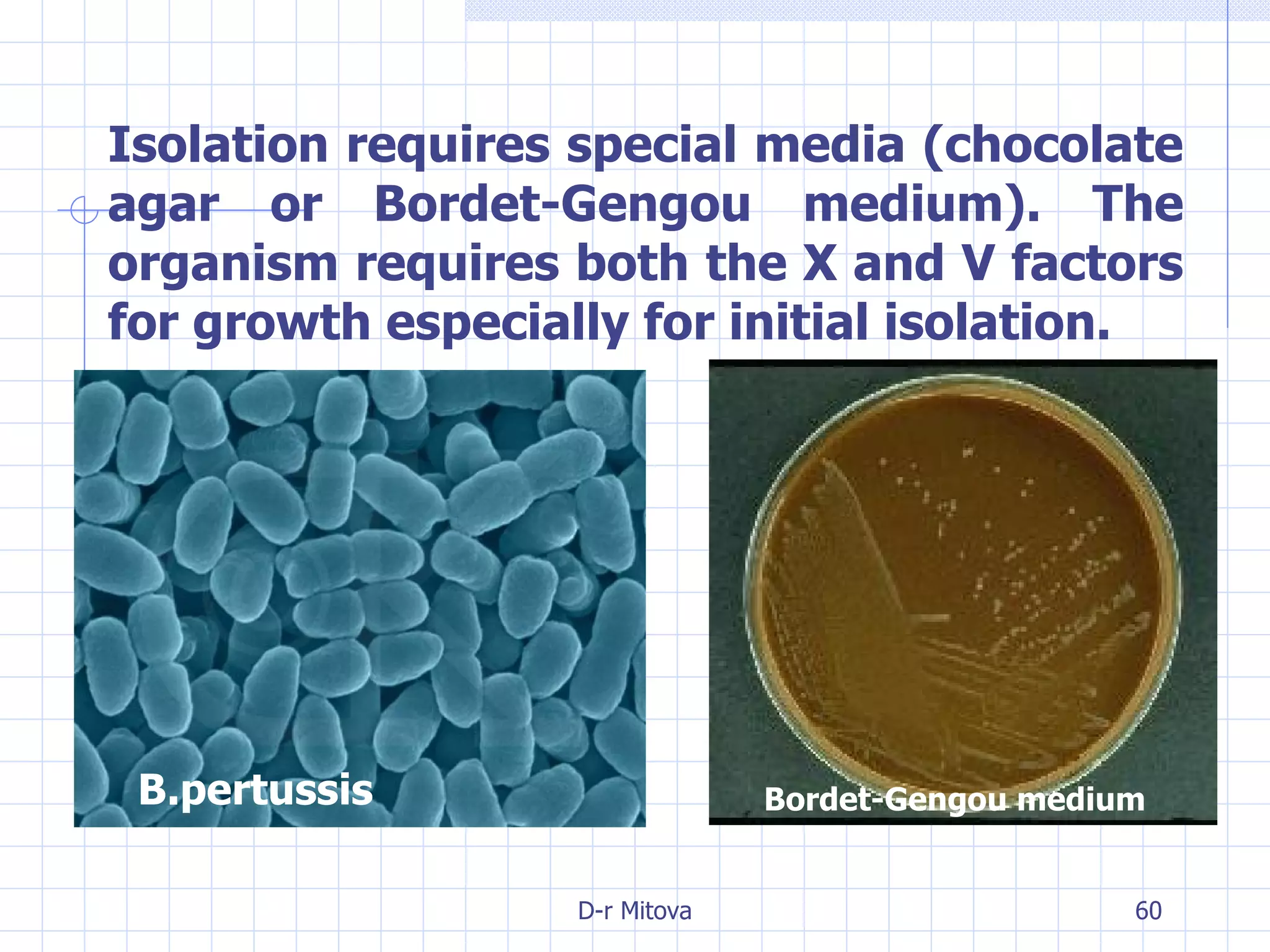
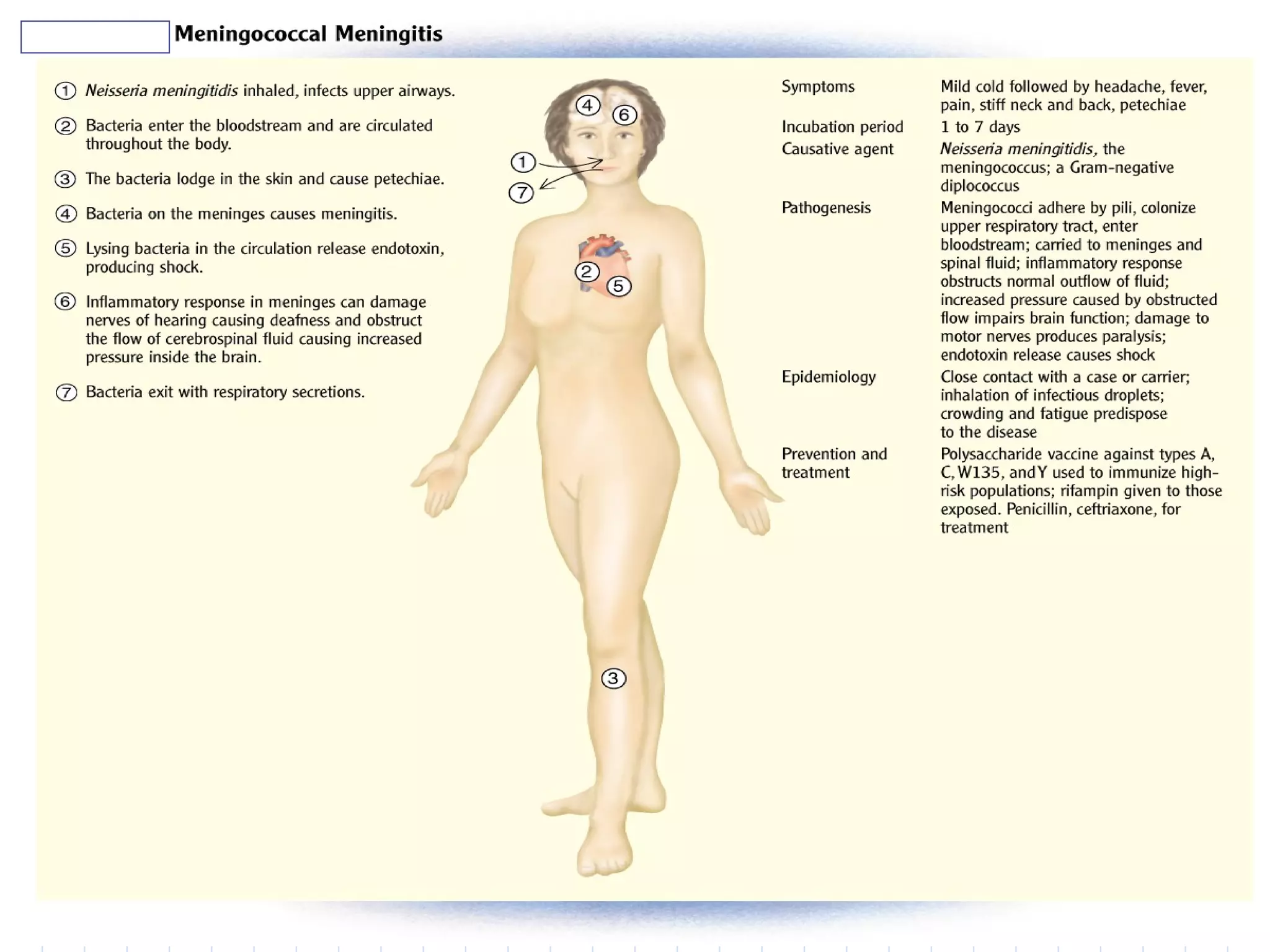
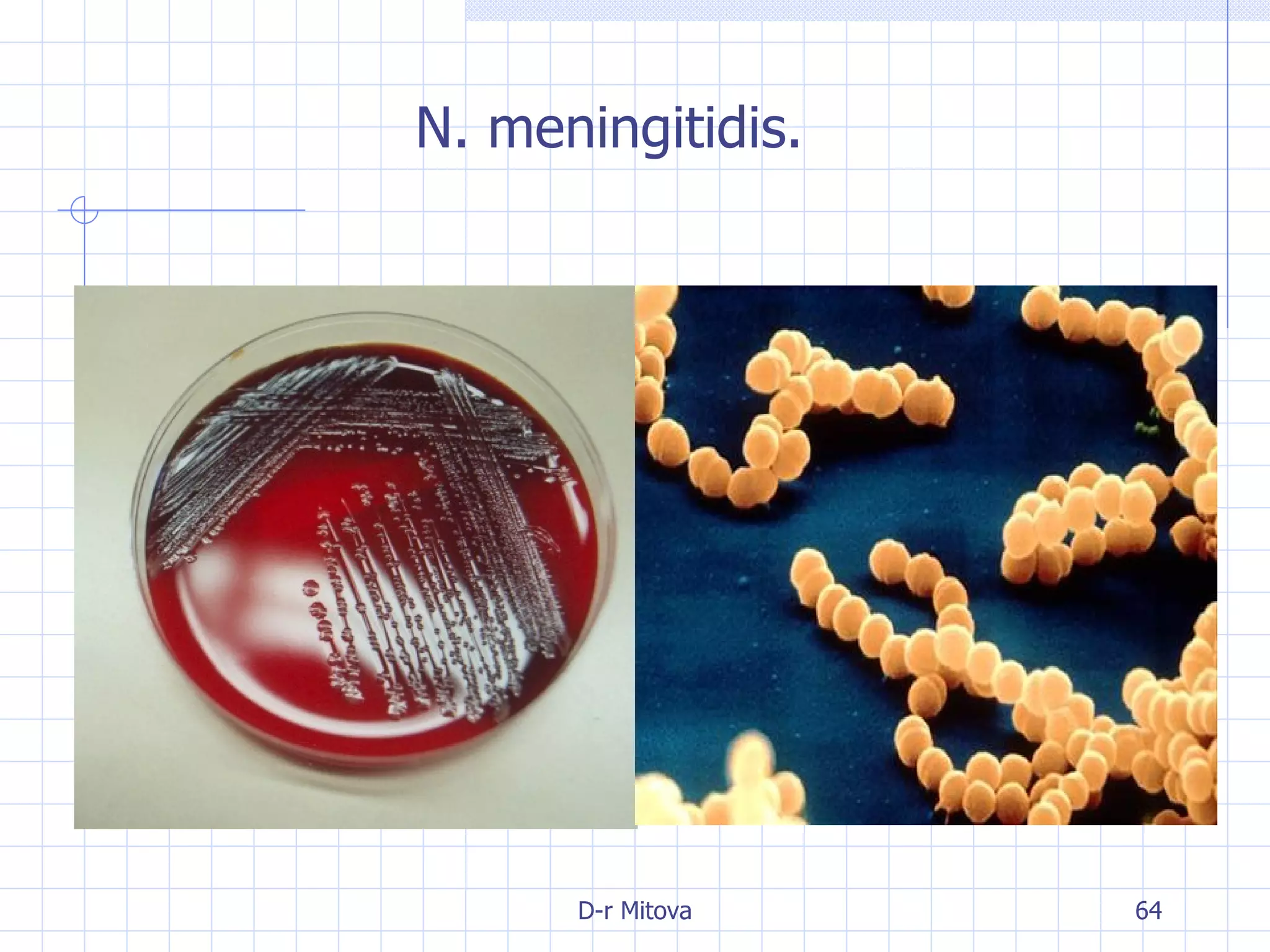
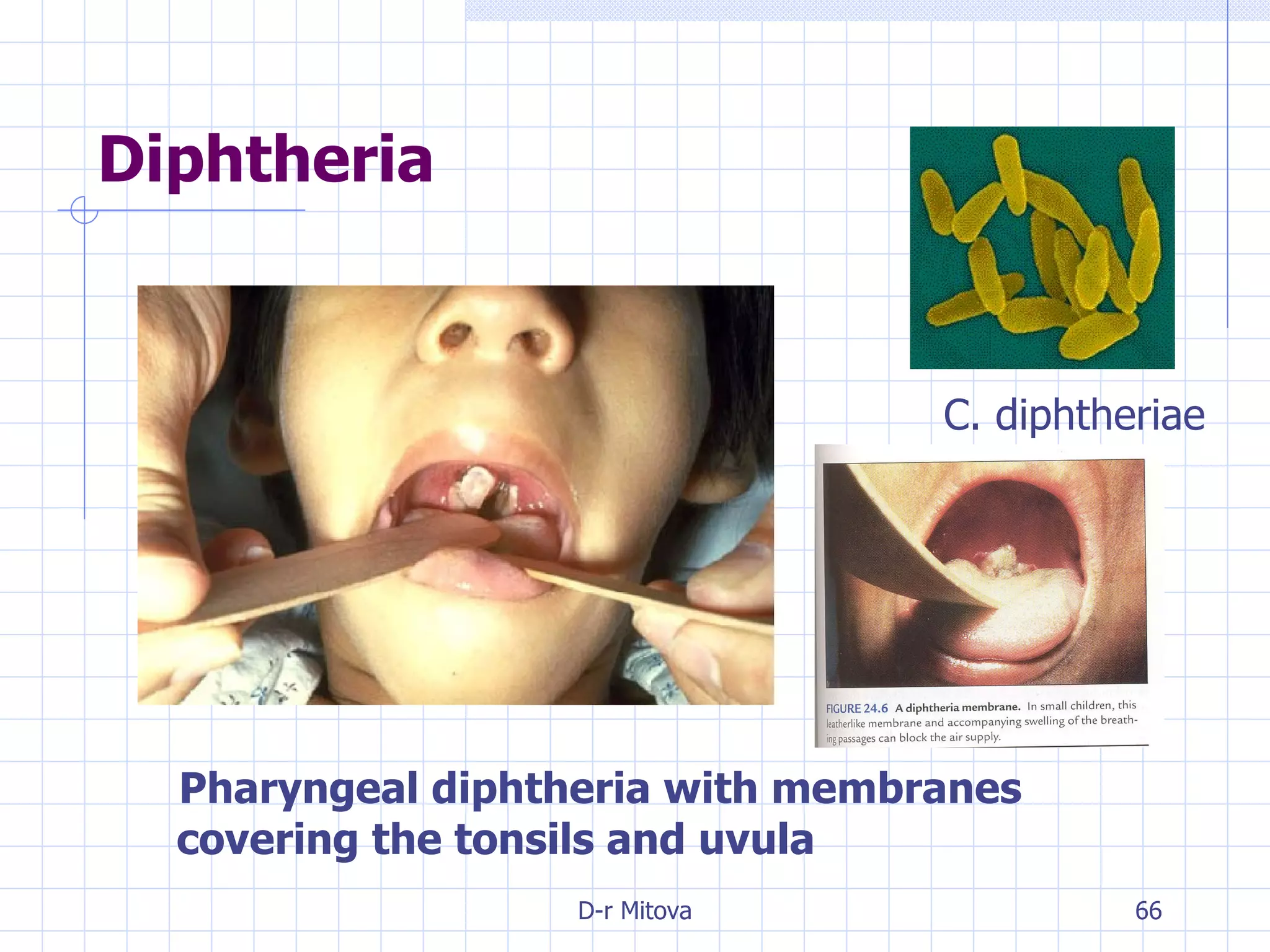
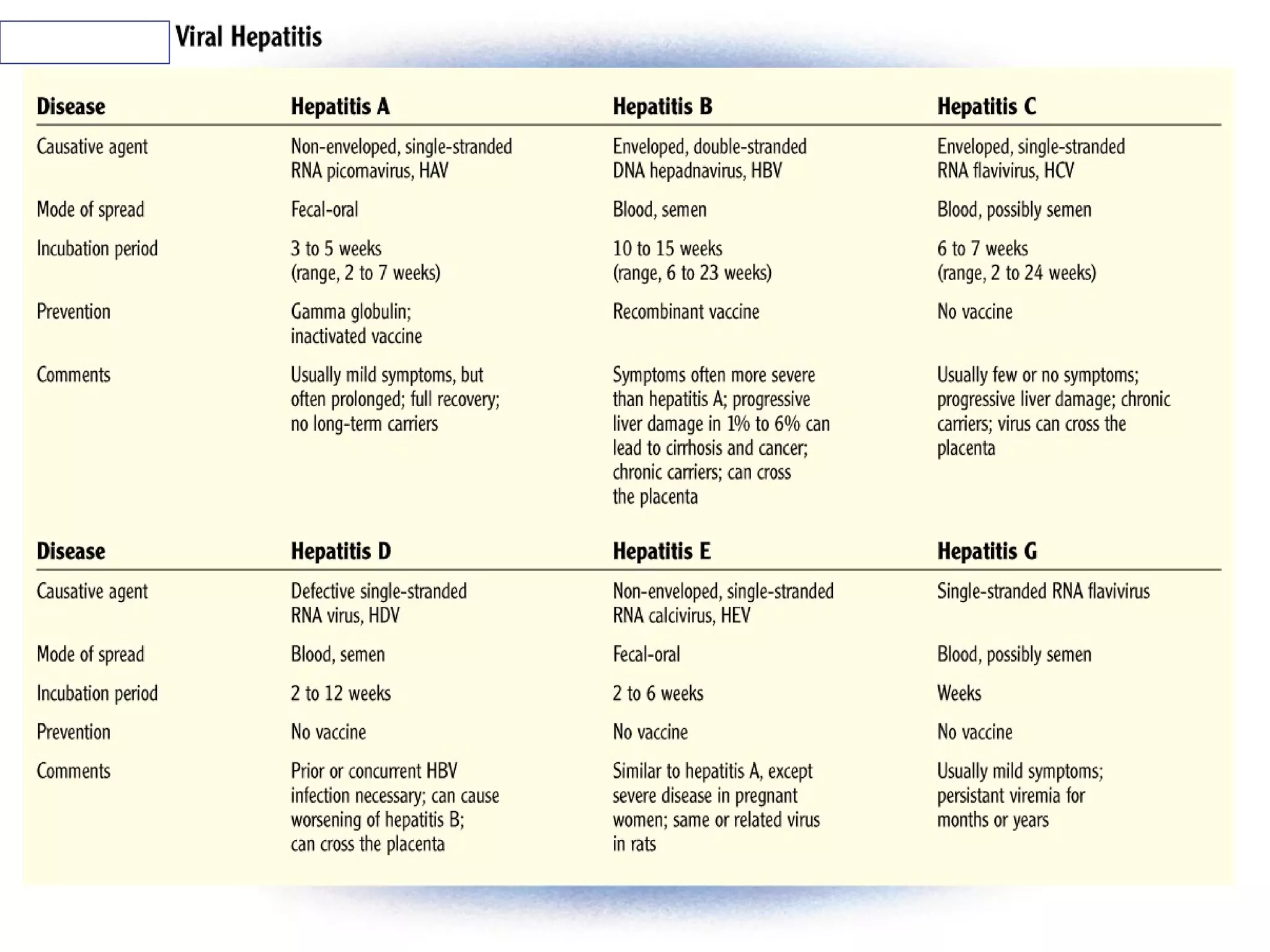
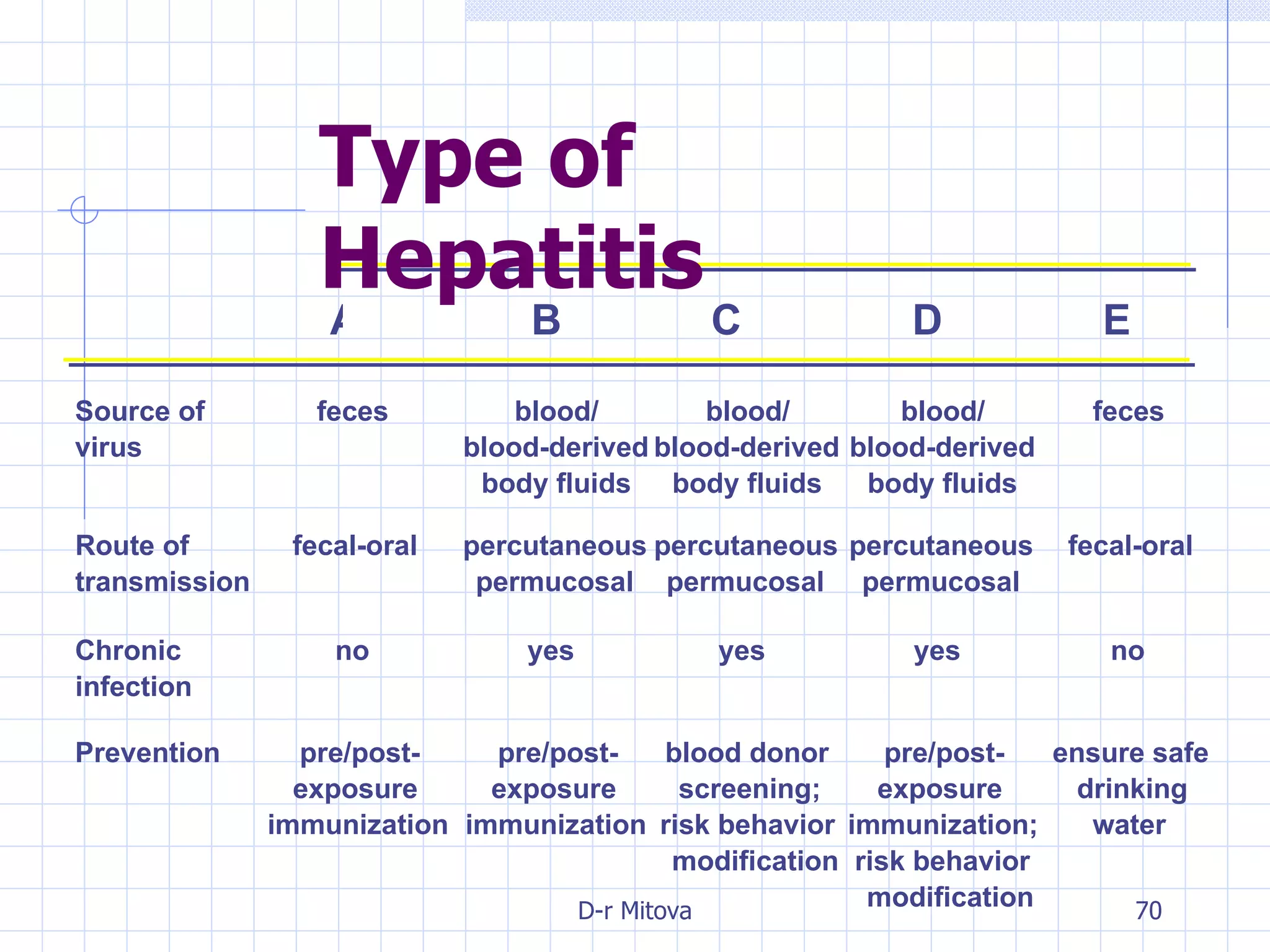
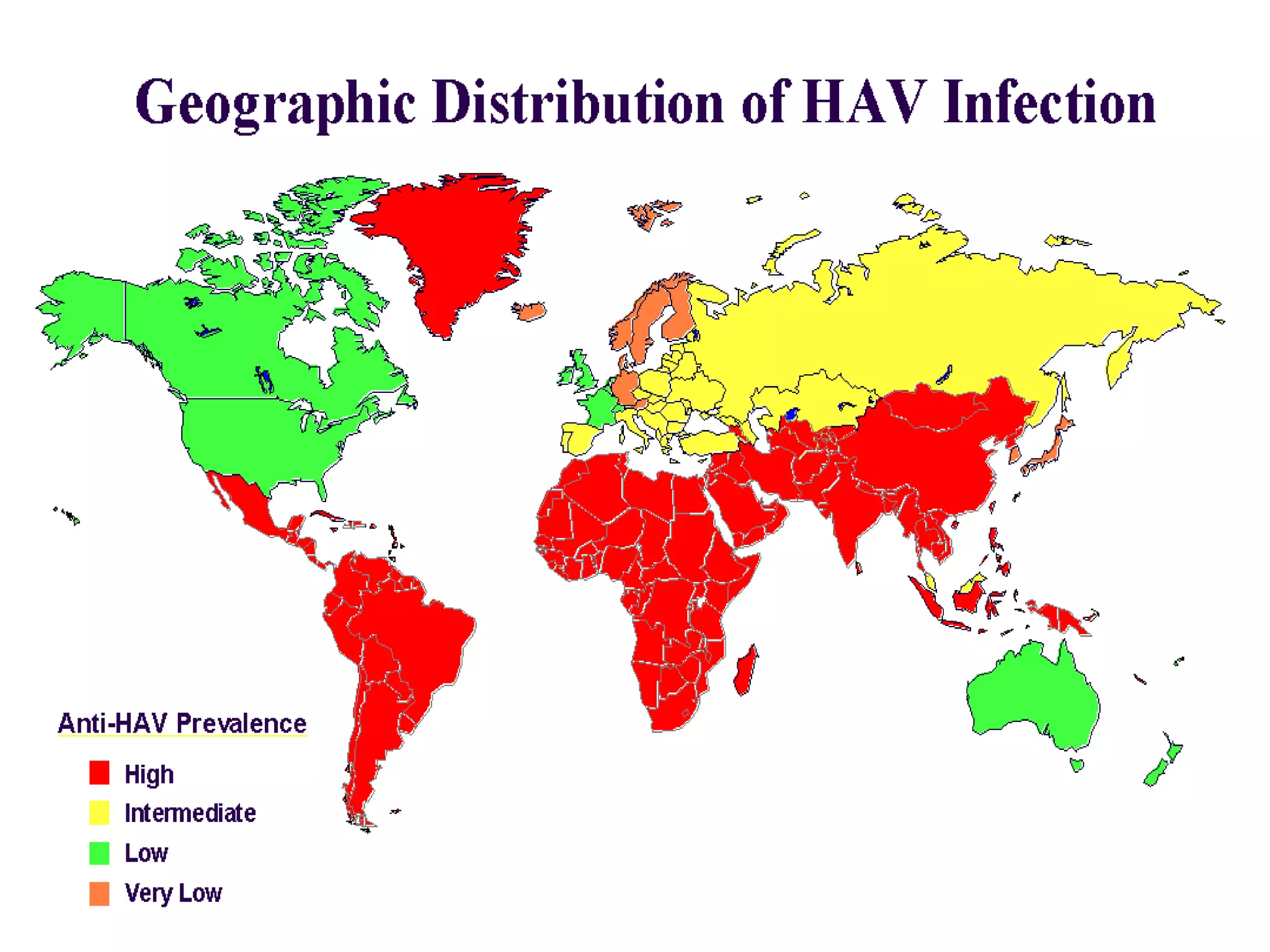
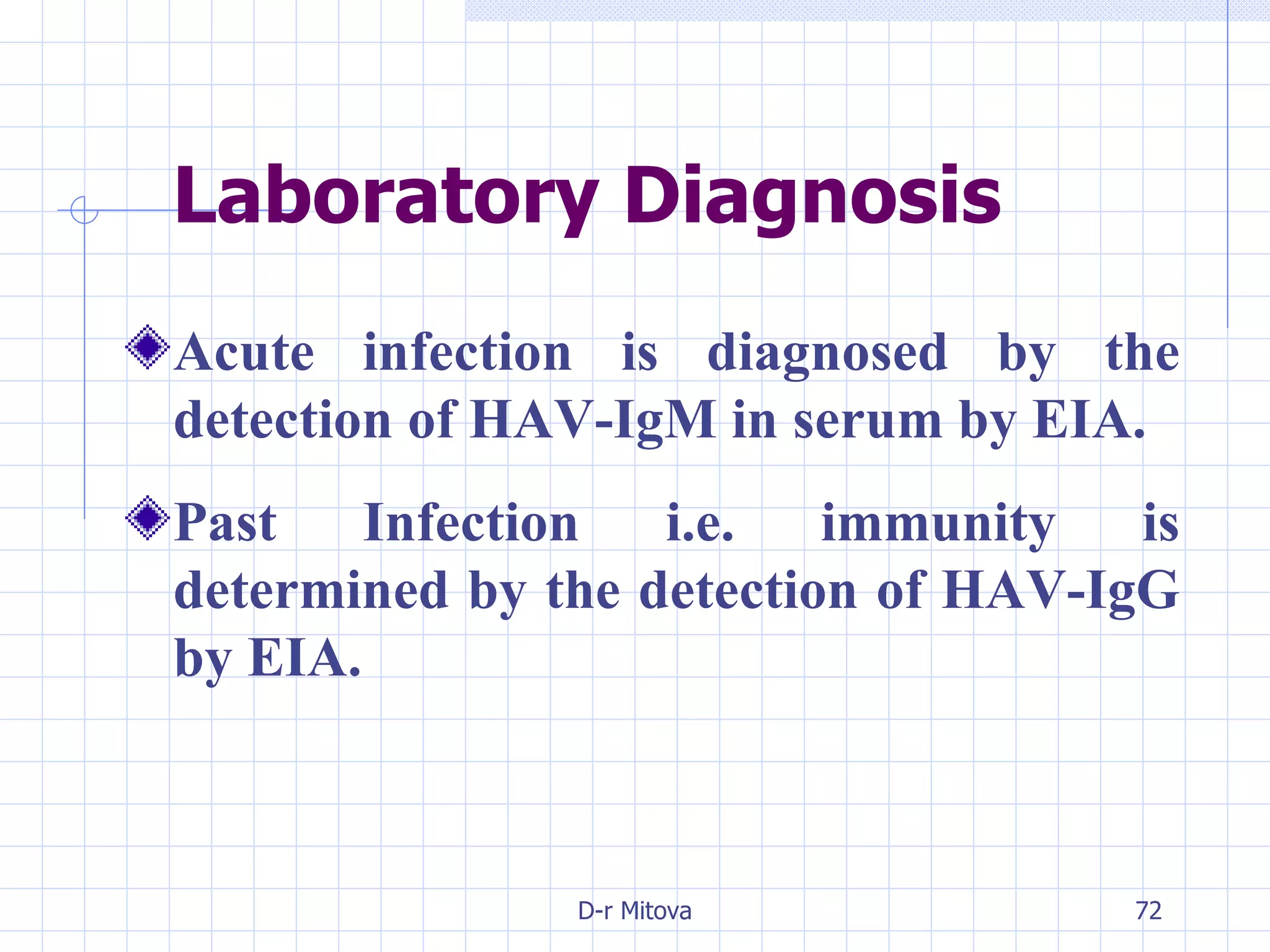
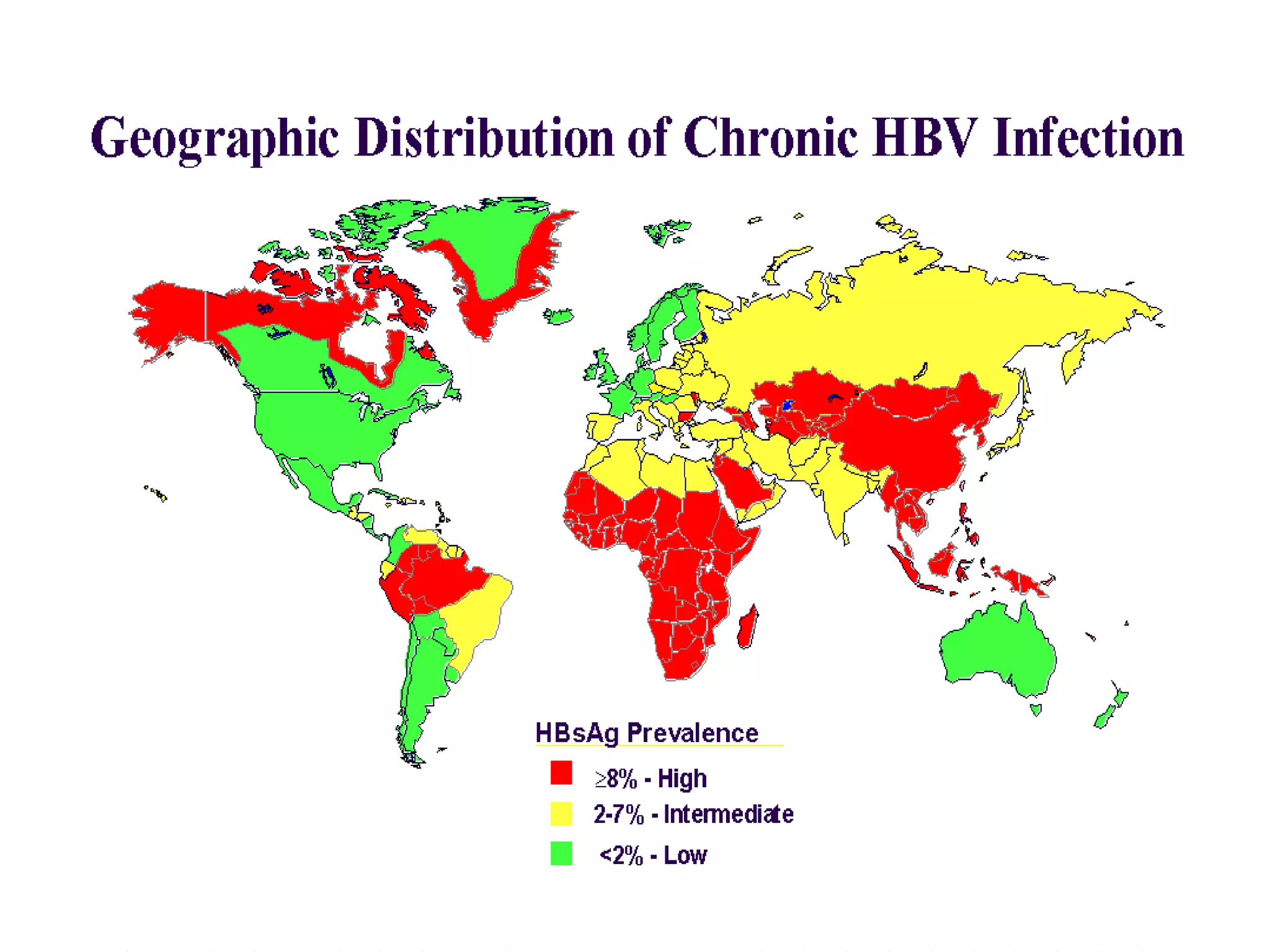
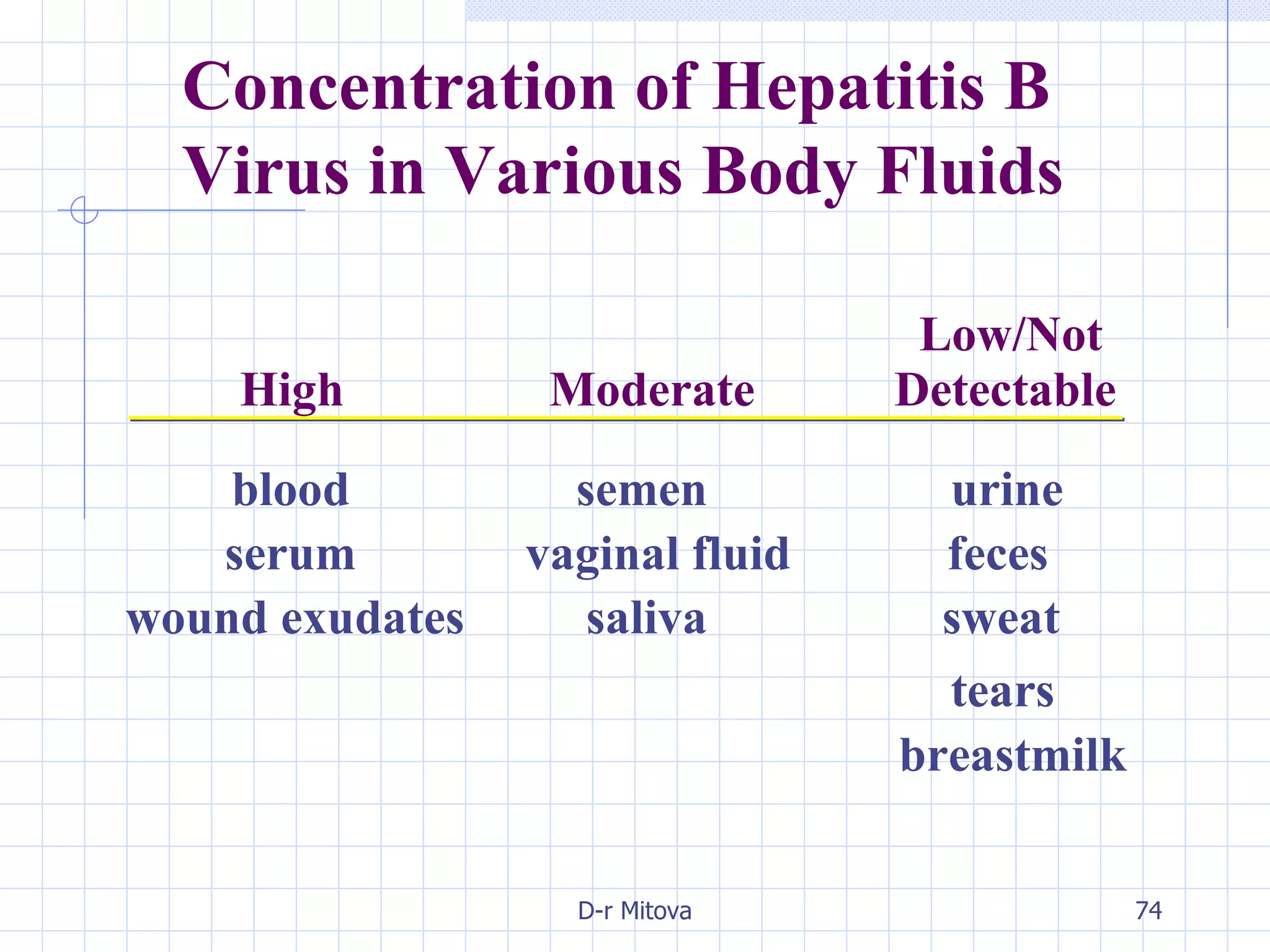
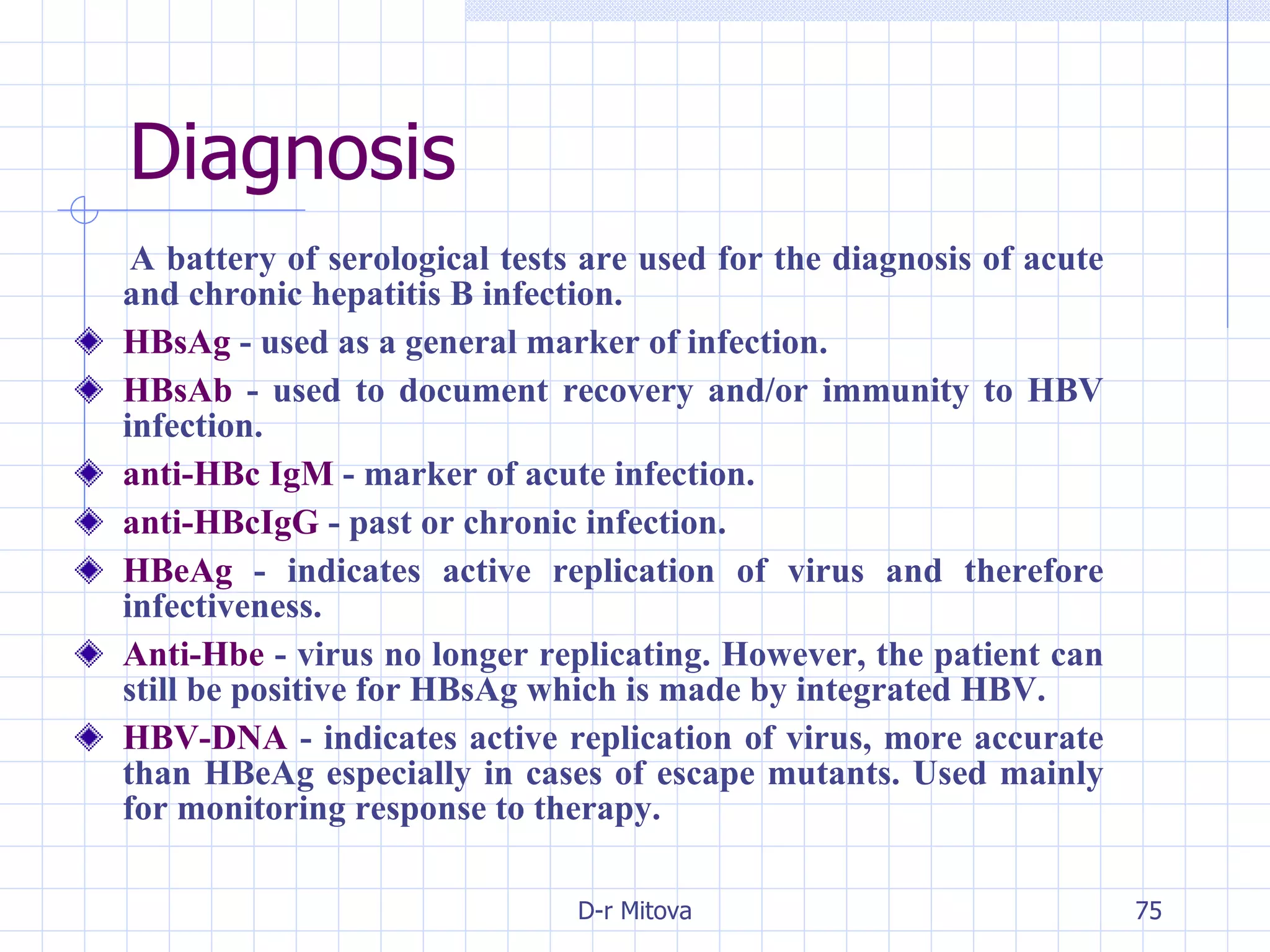
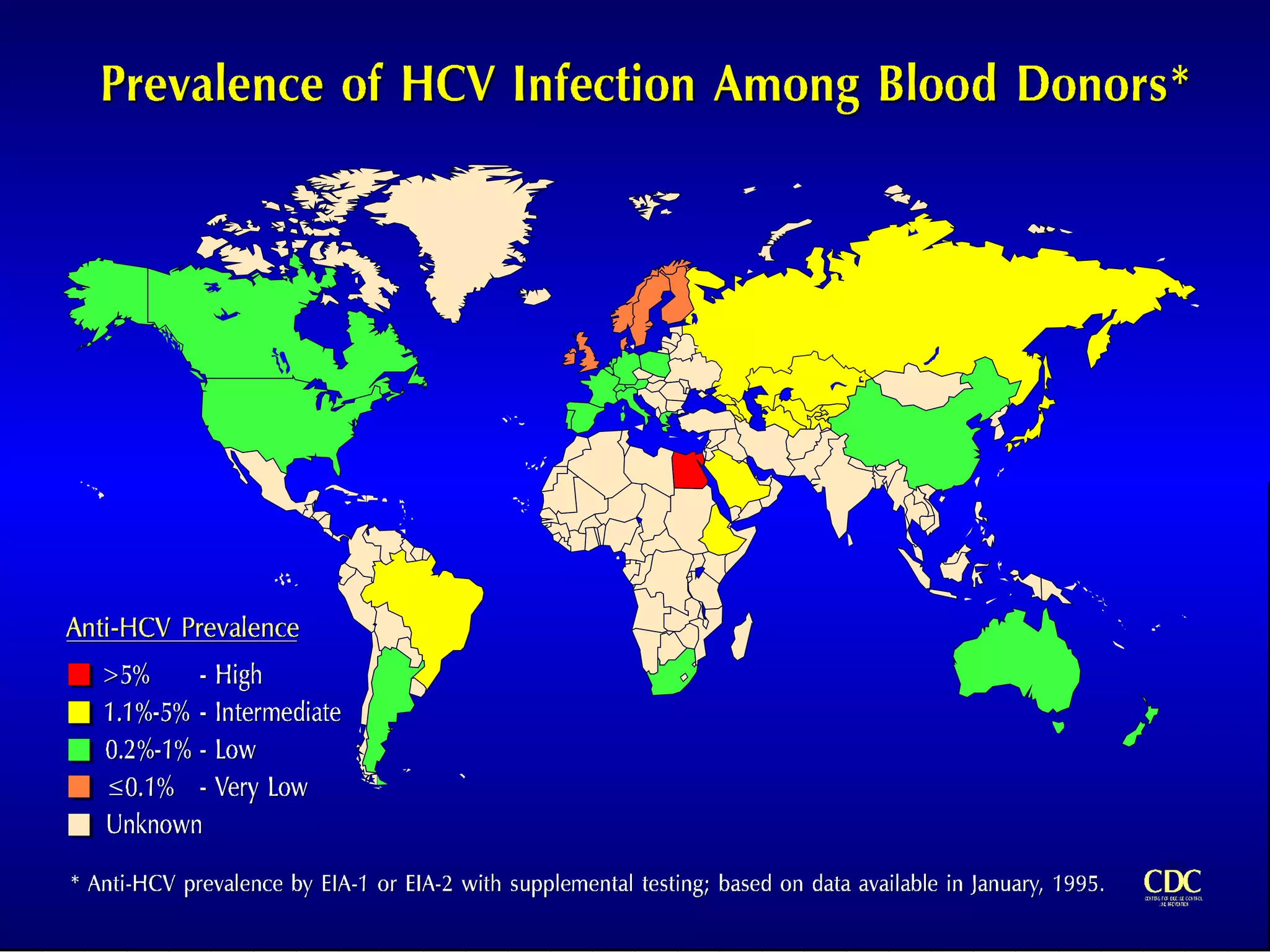
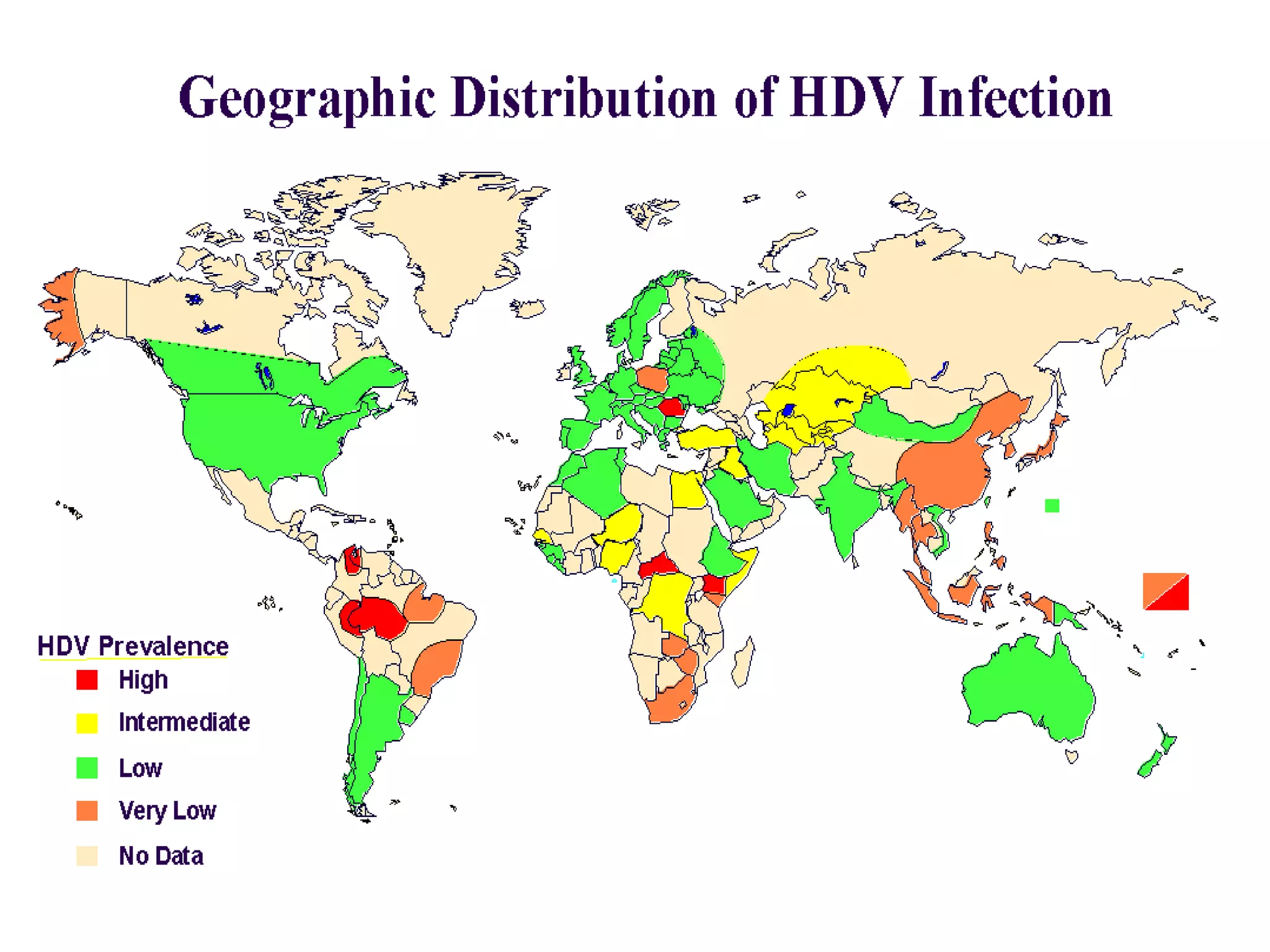
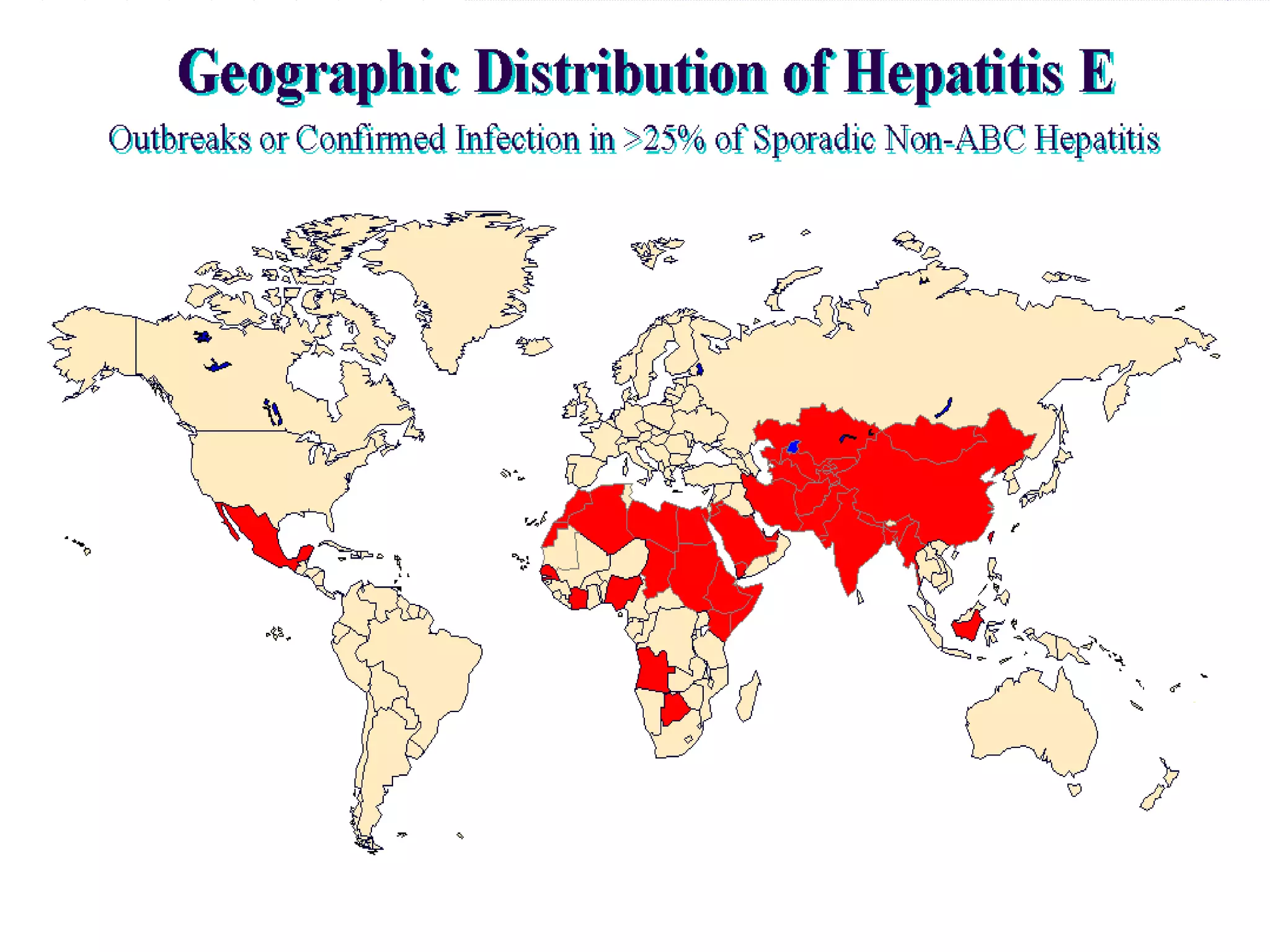
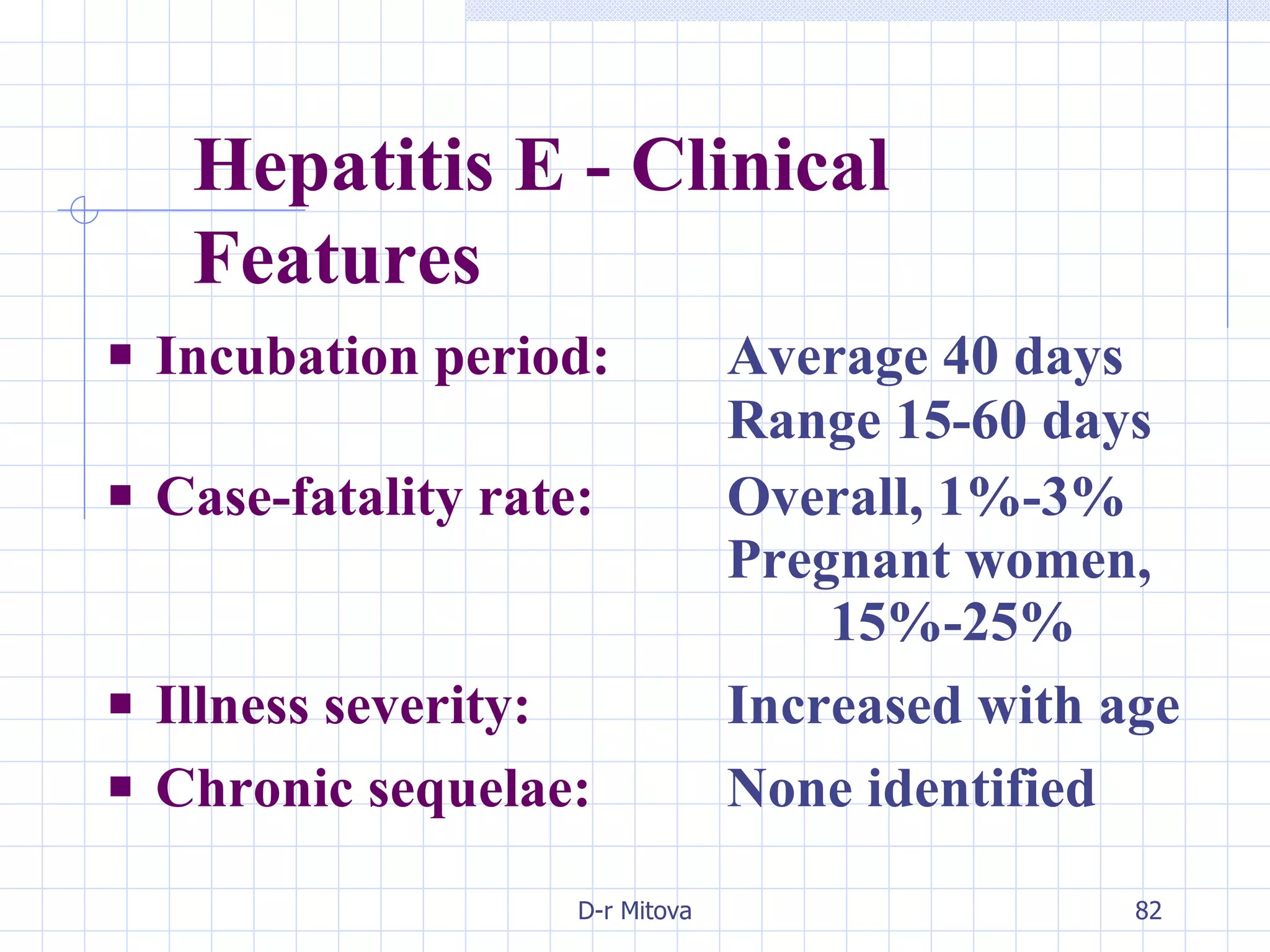
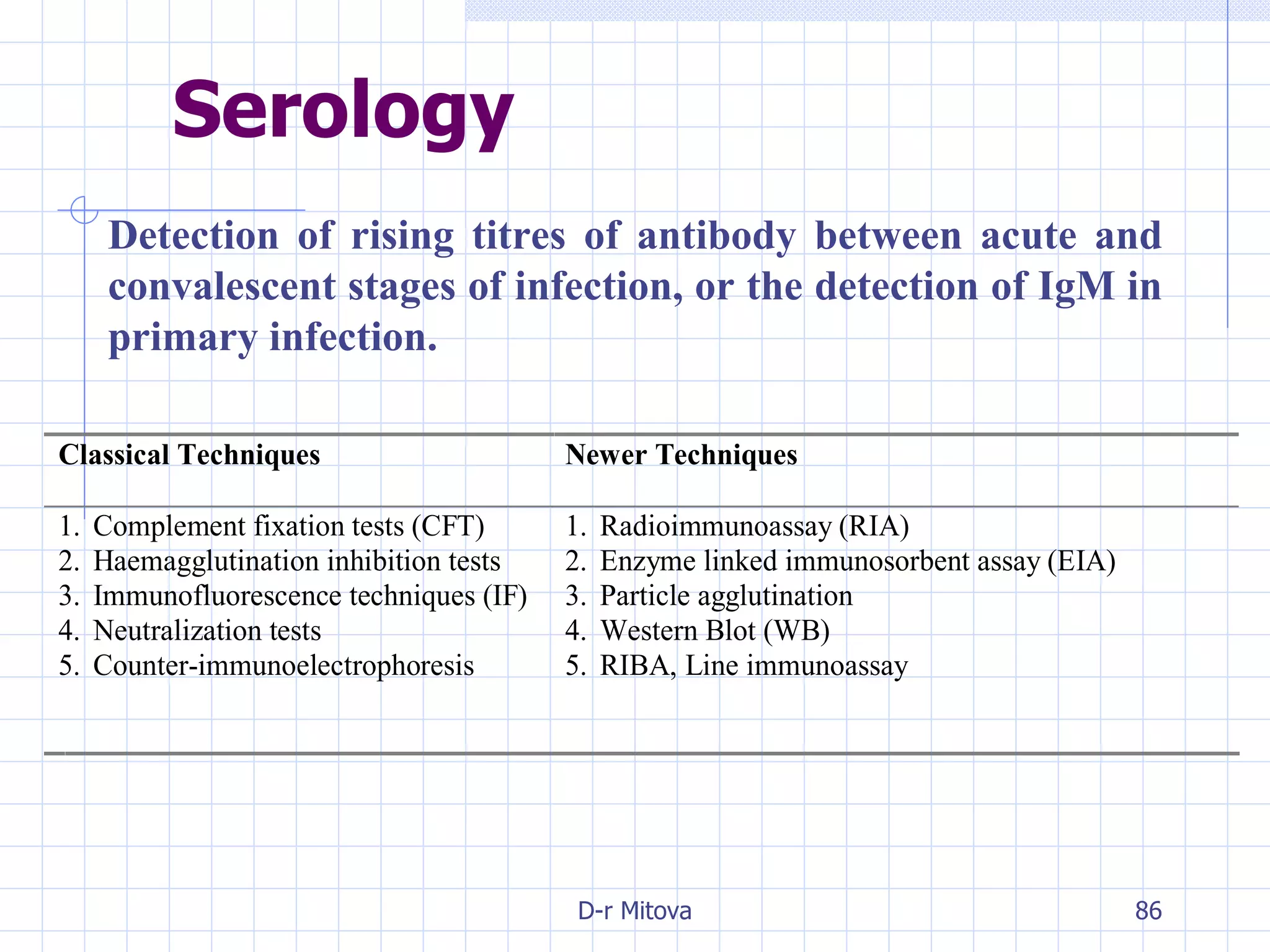
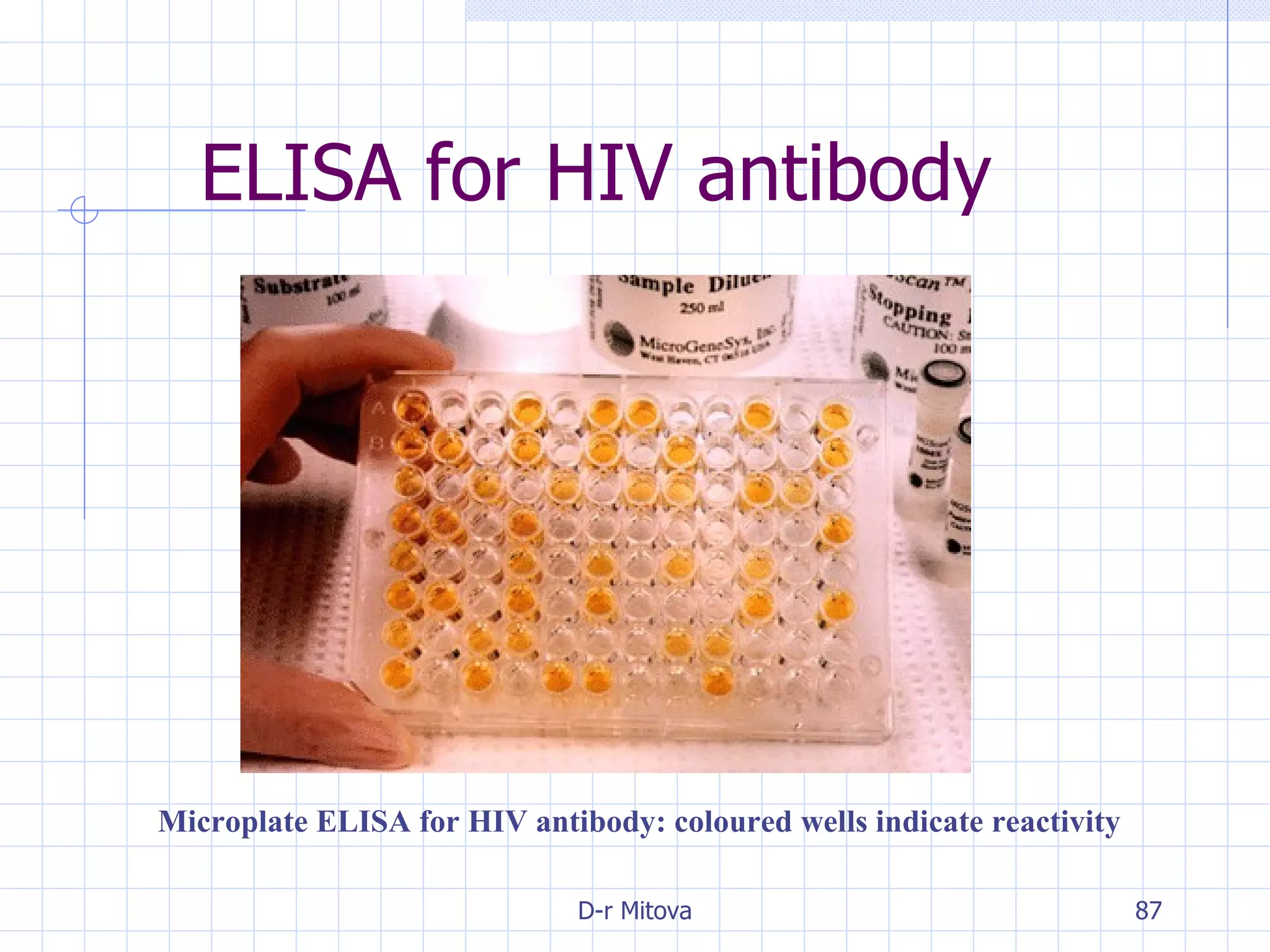
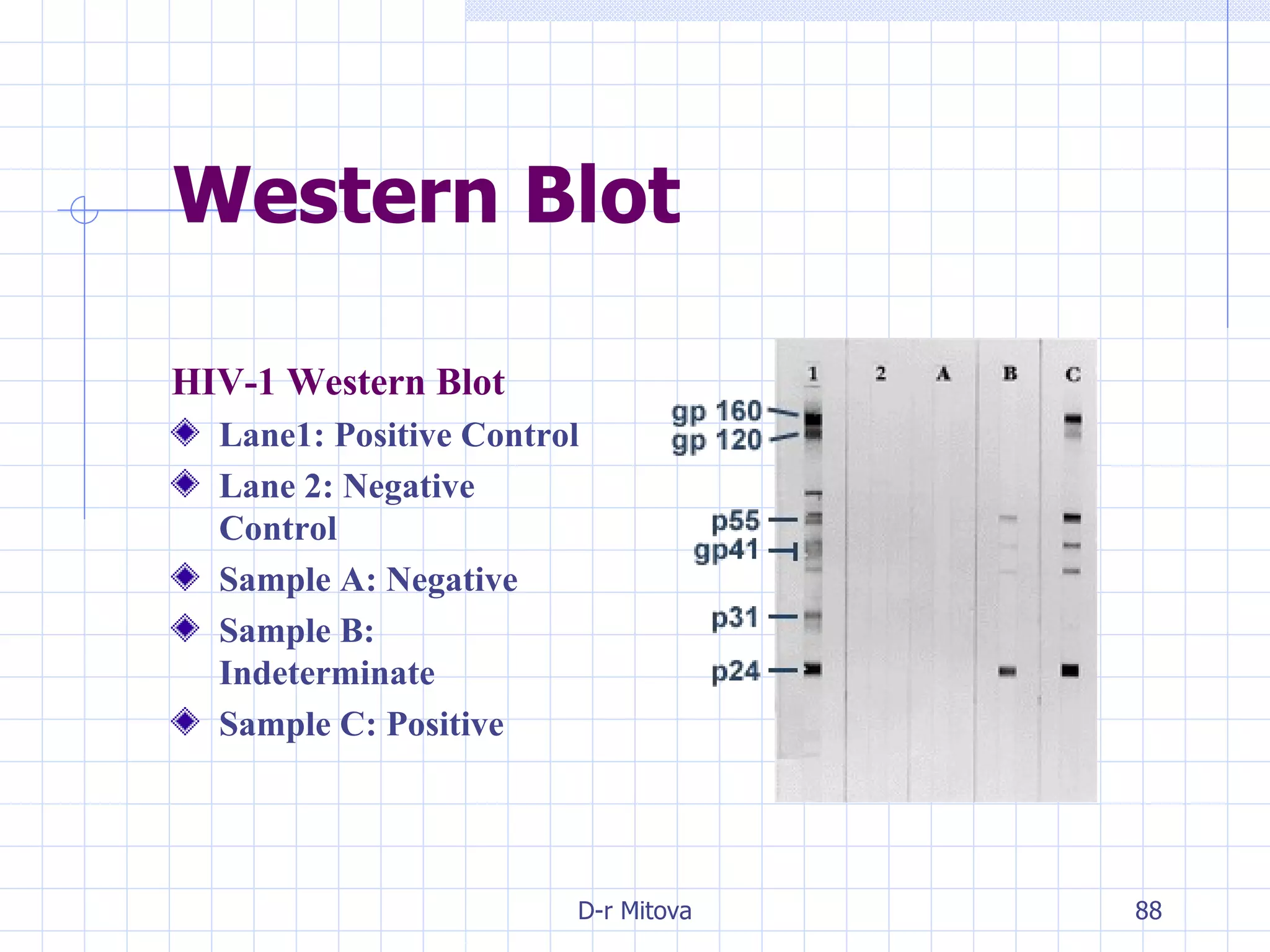
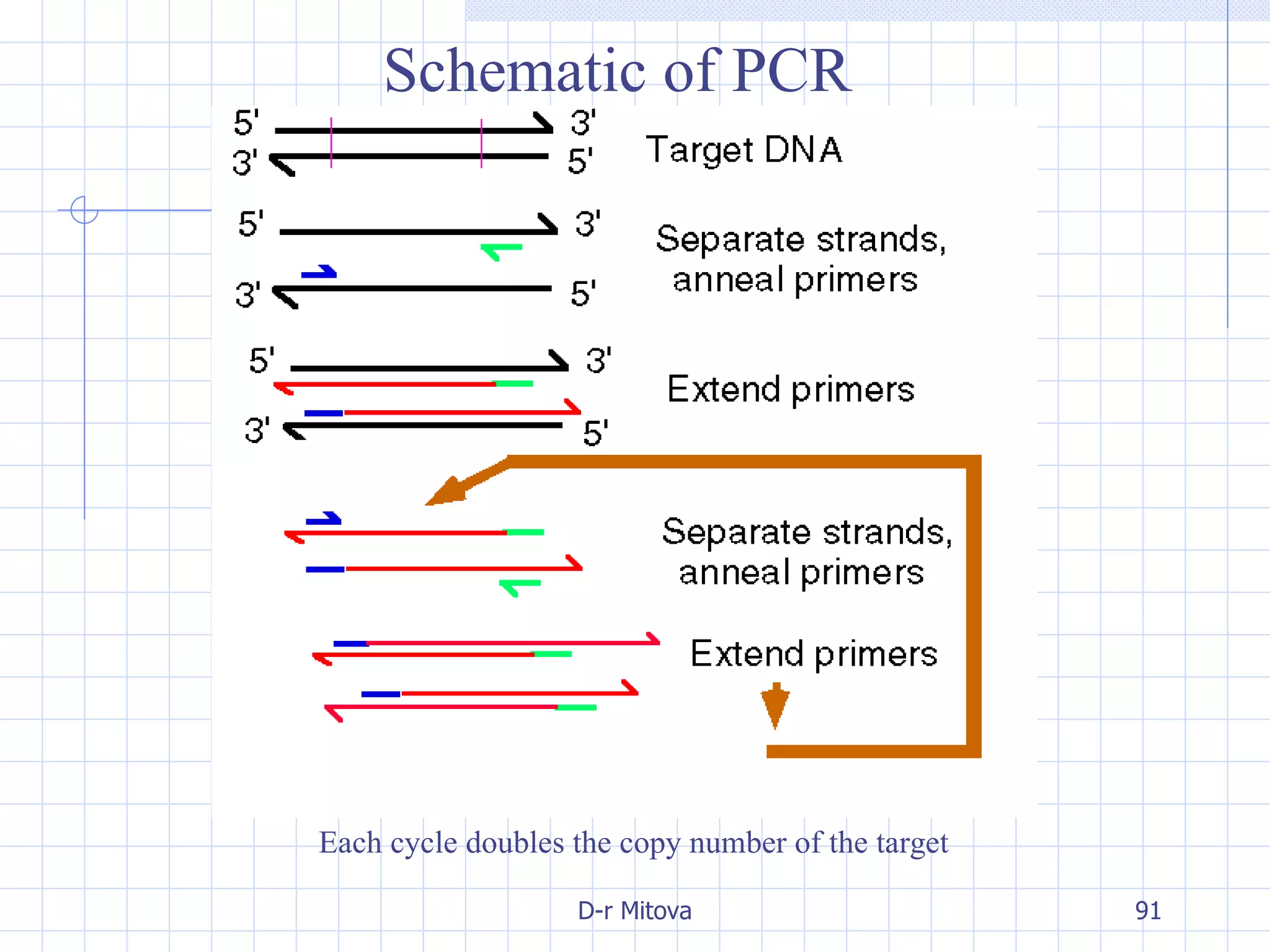
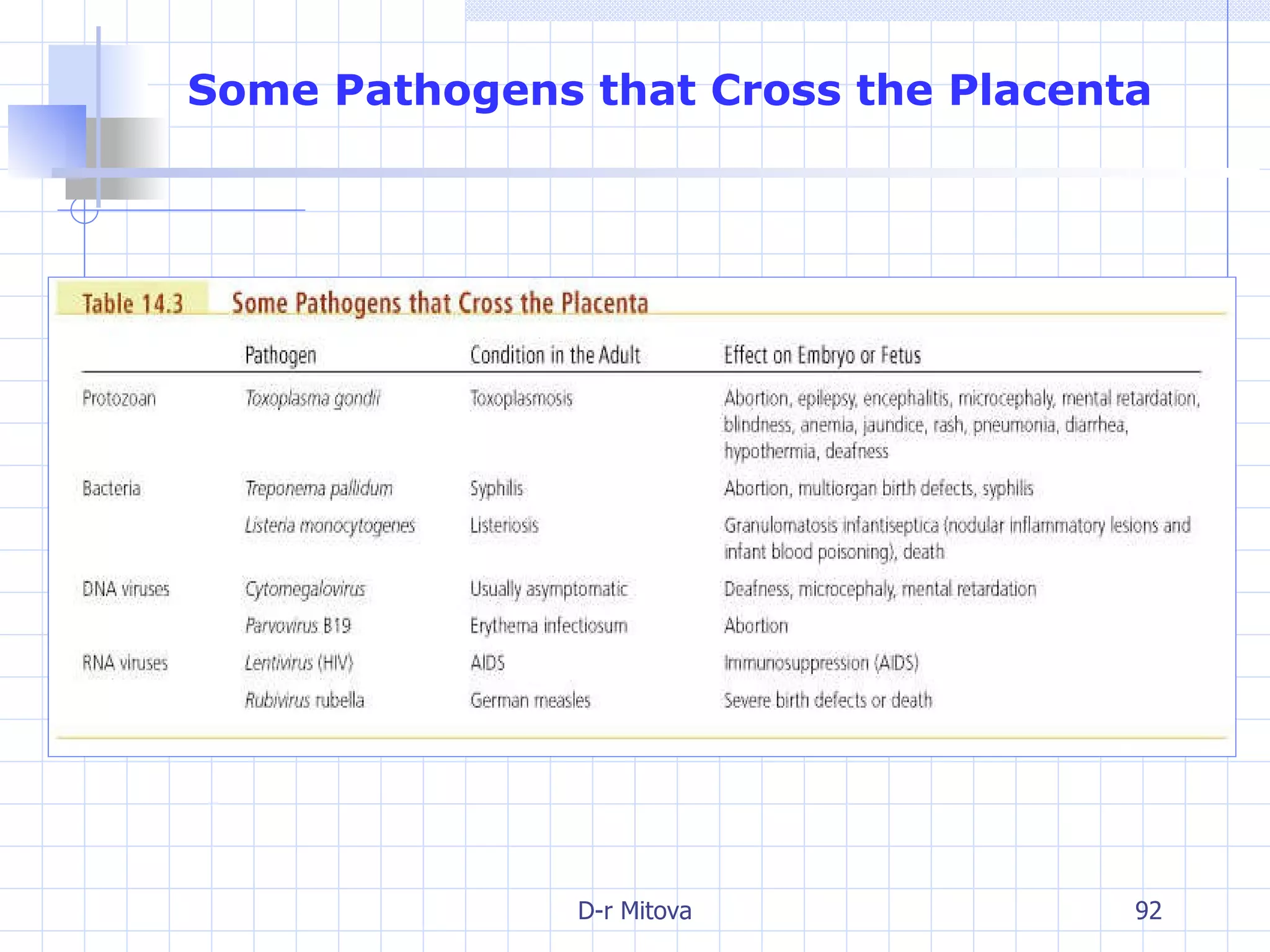
Infectious disease epidemiology studies the distribution and transmission of infectious diseases. It is a fundamental part of epidemiology, which originally developed from the study of infectious disease epidemics. There are different levels of infection including colonization, subclinical infection, latent infection, and clinical infection. Infectious diseases are transmitted from a source or reservoir of infection to a susceptible host through various modes of transmission. Carriers and subclinical cases are important in maintaining disease transmission within a population even without displaying symptoms.