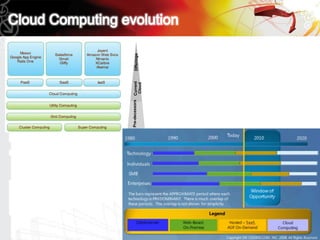
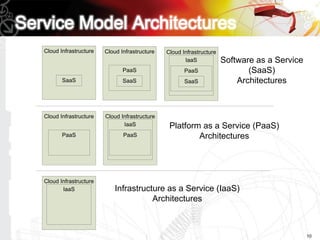
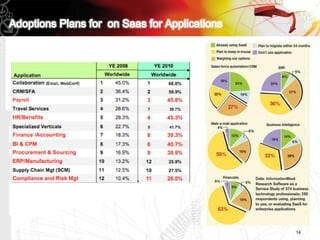
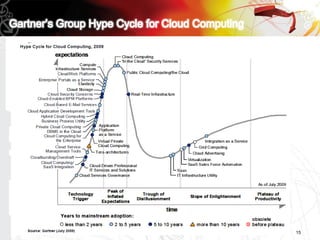
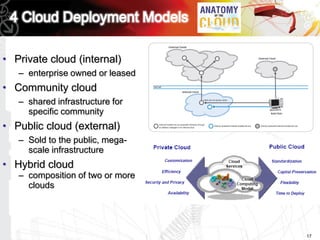
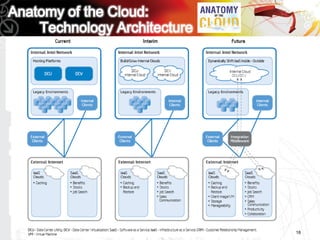
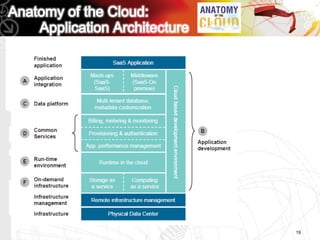
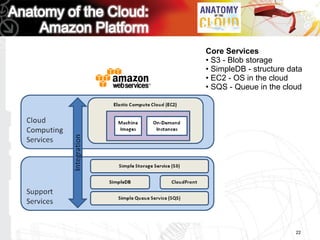
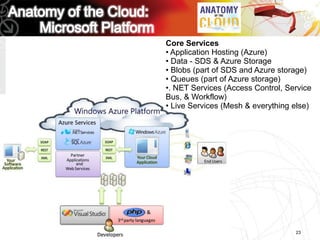
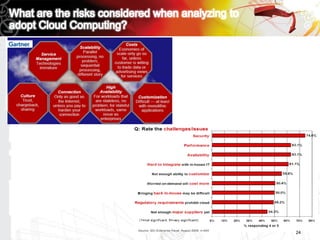
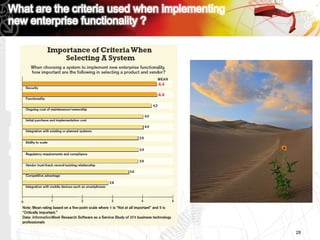
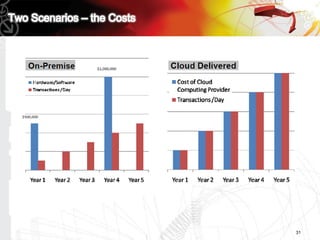
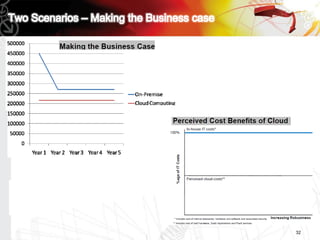
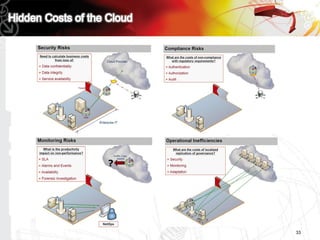
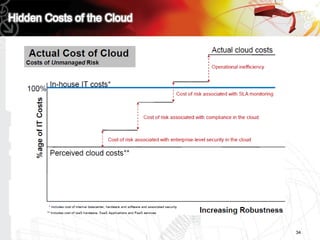
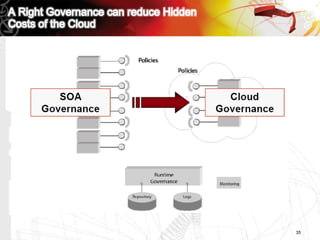
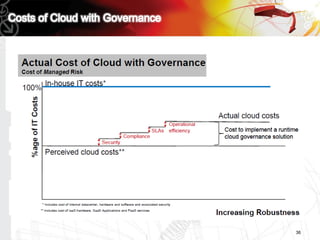
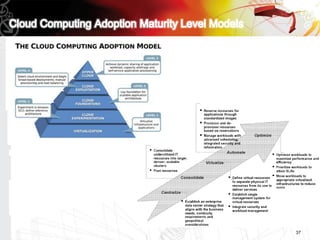
This document discusses key questions about cloud computing including: the main challenges companies face with applications that make them consider adopting cloud; current cloud computing provider offers; customer acceptance plans for cloud offers; risks of adopting cloud; criteria for evaluating cloud providers; benefits companies can expect from using cloud; how to build a business case for cloud; and whether cloud is a viable long-term strategy or a passing fad invented by tech providers. It seeks to provide answers to these questions about cloud computing challenges, offerings, adoption, risks, evaluation, benefits and business case development.