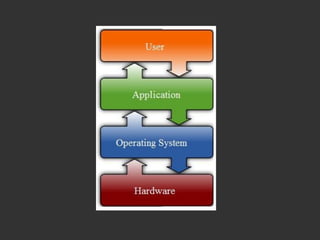
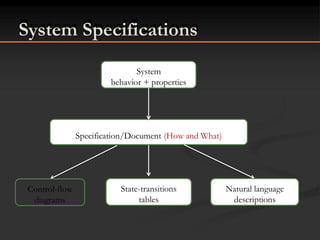
This document discusses software development and a software development process. It begins by defining software as a collection of computer programs and data that provide instructions for what a computer should do. It then describes different types of software like systems software and application software. The document outlines the typical stages of a software development process including specification, design, coding, testing, and evolution. It provides examples of system failures caused by software bugs. The remainder of the document discusses the contents of a textbook on C programming, outlining chapters that will cover topics like the programming environment, basic building blocks, loops, decisions, functions, arrays, strings, pointers, files and larger programs. It concludes with information on tests, labs, and the paper format for the course