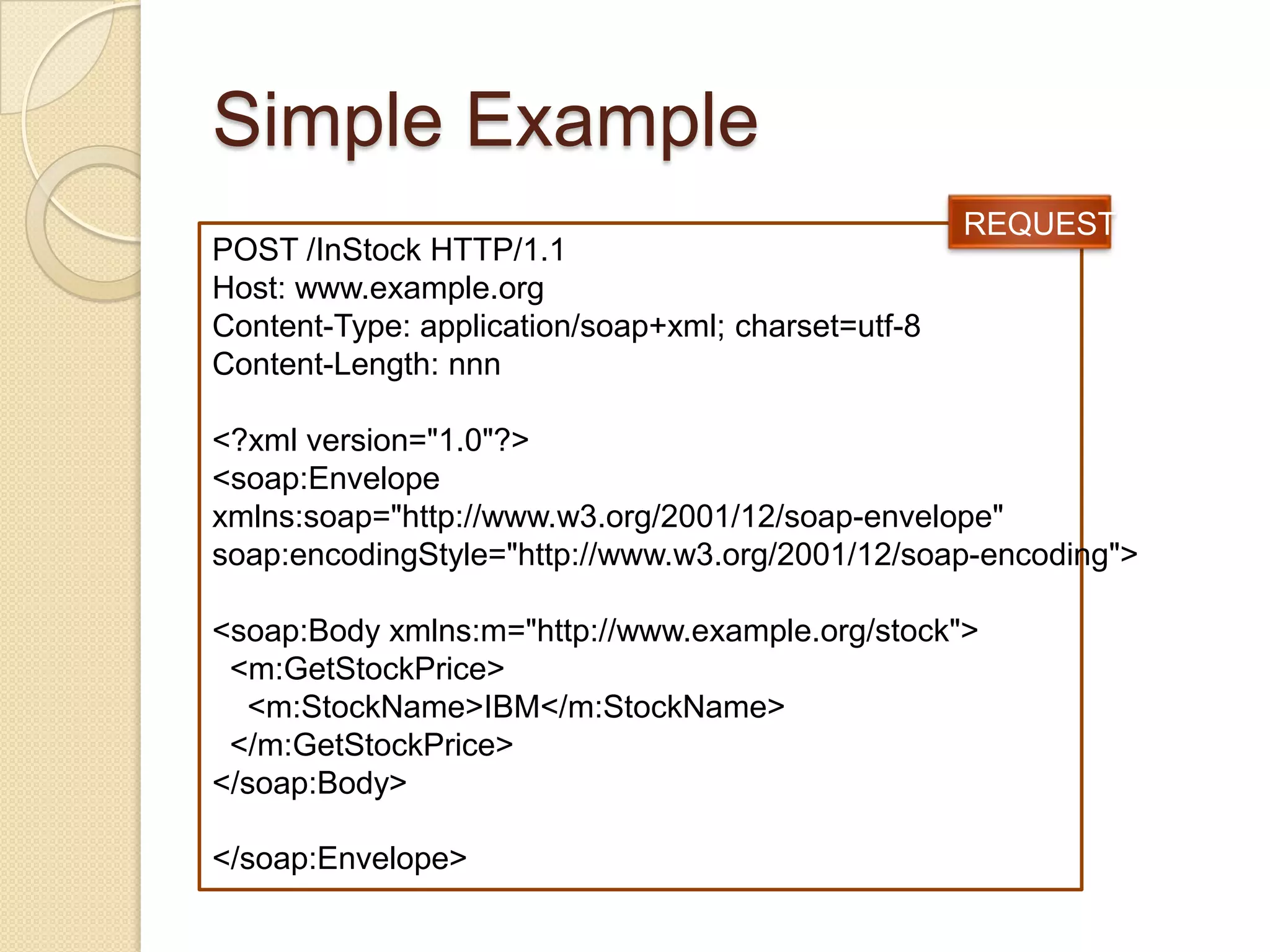
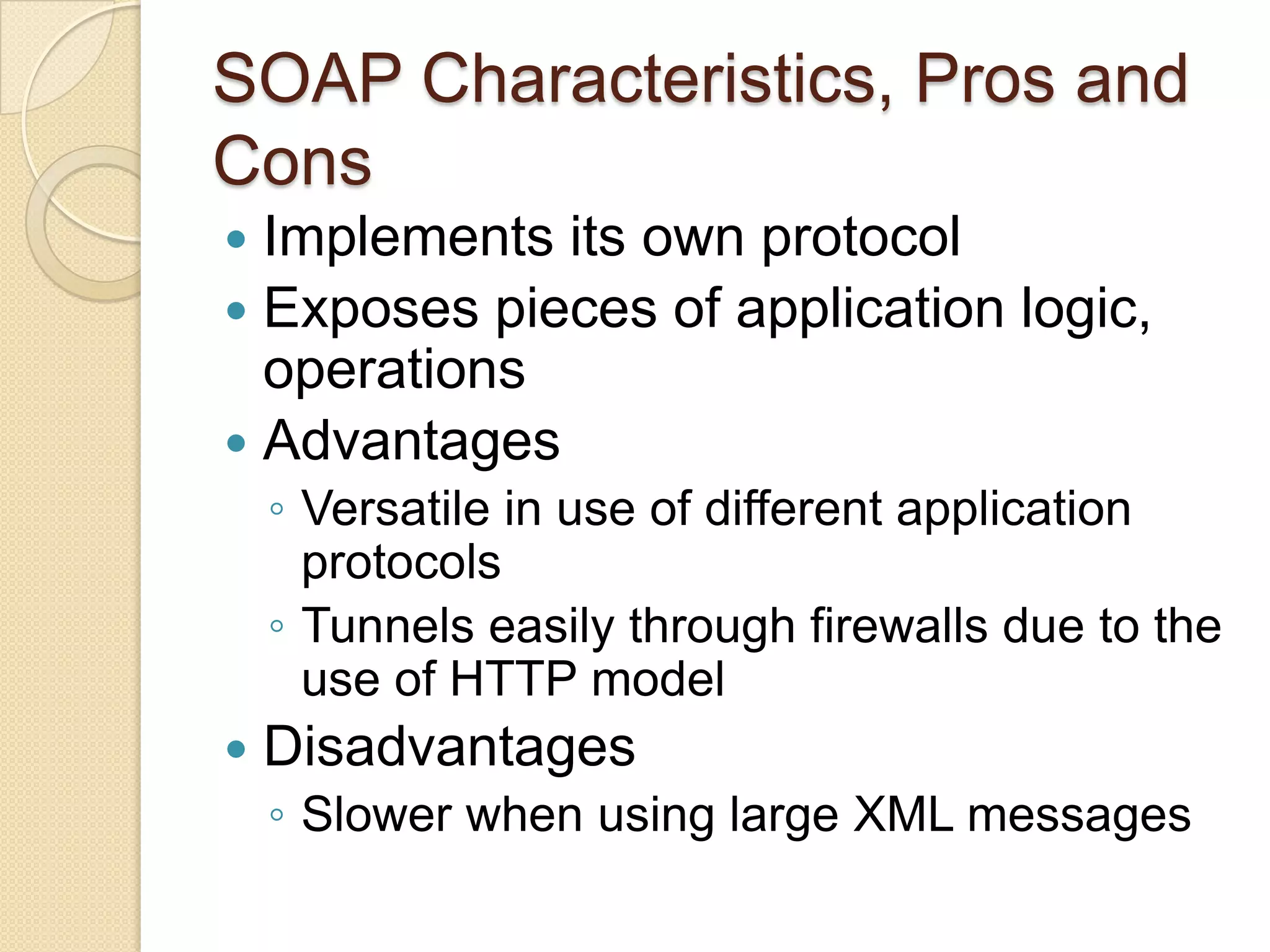
SOAP is a protocol for exchanging structured information in a decentralized, distributed environment using XML. It uses RPC and HTTP. REST focuses on accessing named resources through a consistent interface and represents resource state. SOAP is better for enterprise security and transactions while REST is lighter weight and less complex, using standard HTTP and supporting JSON. The choice depends on needs - SOAP for banking apps, REST for simpler web services.