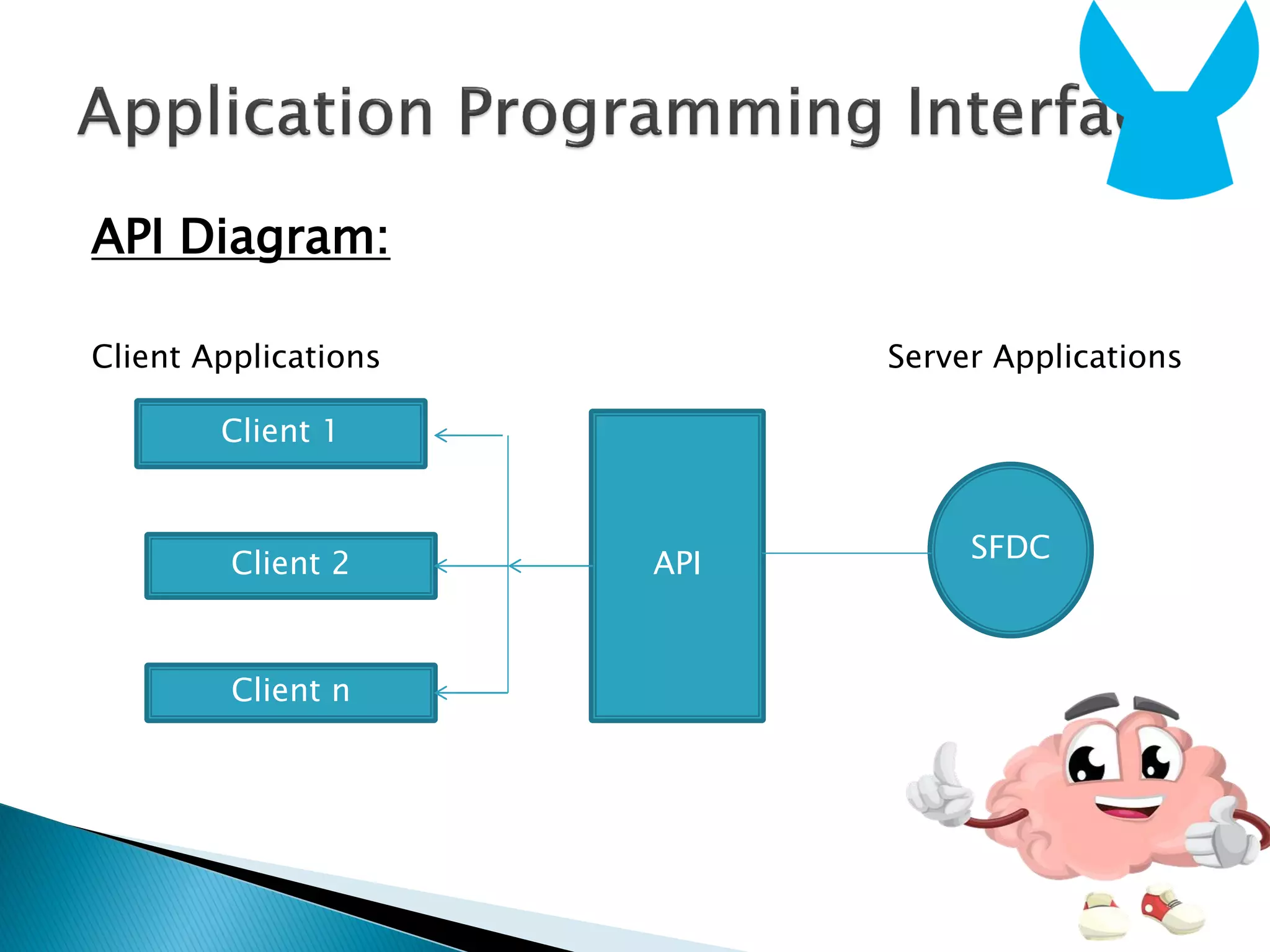
The document discusses APIs, defining them as interfaces that allow applications to communicate and share data over a network. It notes that APIs act as an interface between clients and servers, exposing backend data through operations, inputs, outputs, and data types. The document also outlines the benefits of APIs in standardizing communication and enabling reusability. It introduces common API terminology and types, focusing on web APIs which are the most widely used.