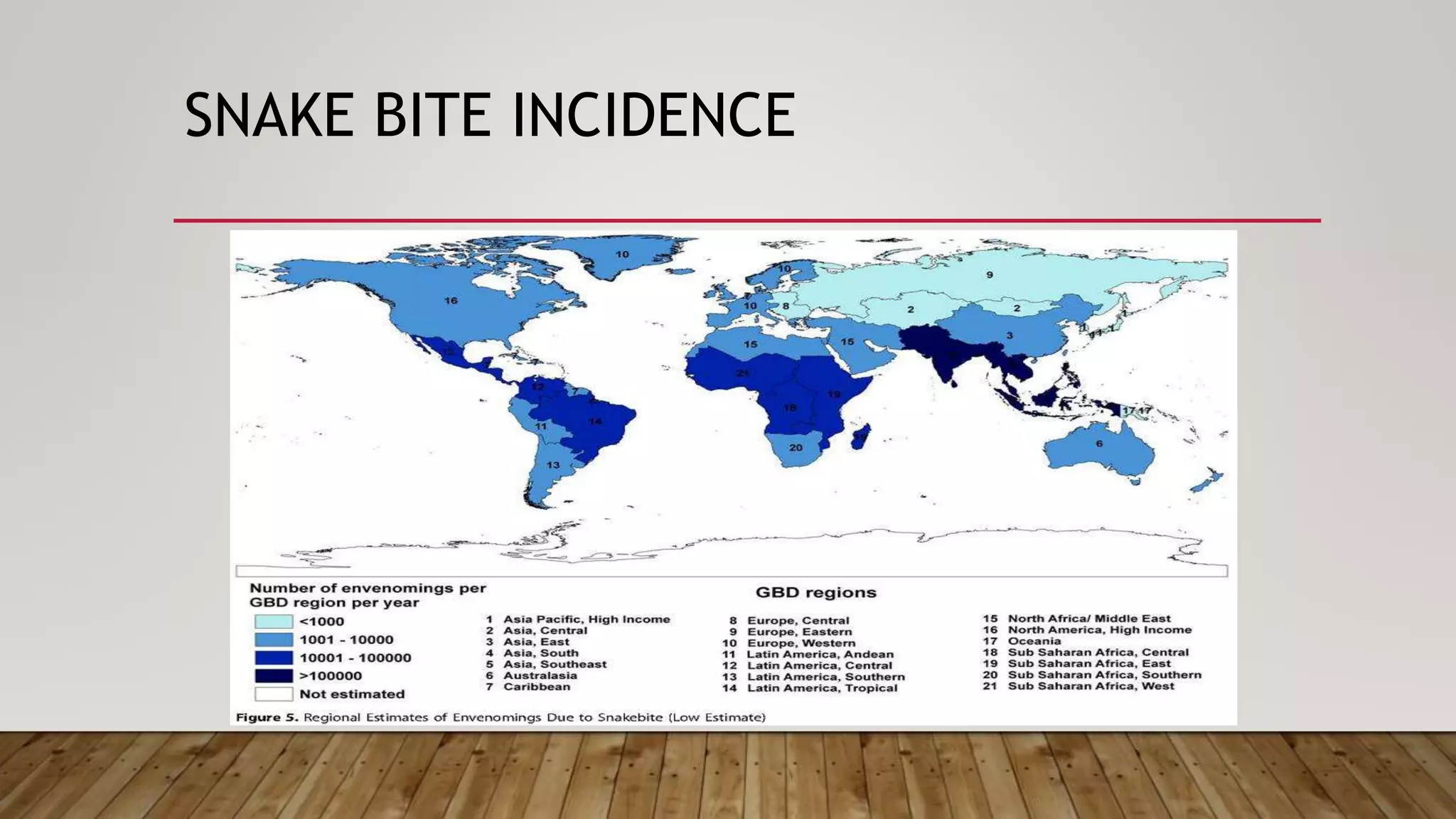
Snake bites are a major public health problem in tropical areas. They most commonly affect agricultural workers in rural parts of Africa, Asia, and Latin America. The two main families of venomous snakes are vipers and elapids. Viper venom causes hemorrhagic effects and elapid venom causes neurotoxic effects. Snake bites result in millions of deaths and amputations worldwide each year. Clinical features of snake bites include pain, swelling, blistering at the wound site, and symptoms varying by snake species such as ptosis and coagulopathy. Treatment involves wound cleaning, immobilization, antivenom administration for systemic effects, and supportive care. Antivenom is an immunoglobulin purified from animals and works by neutral