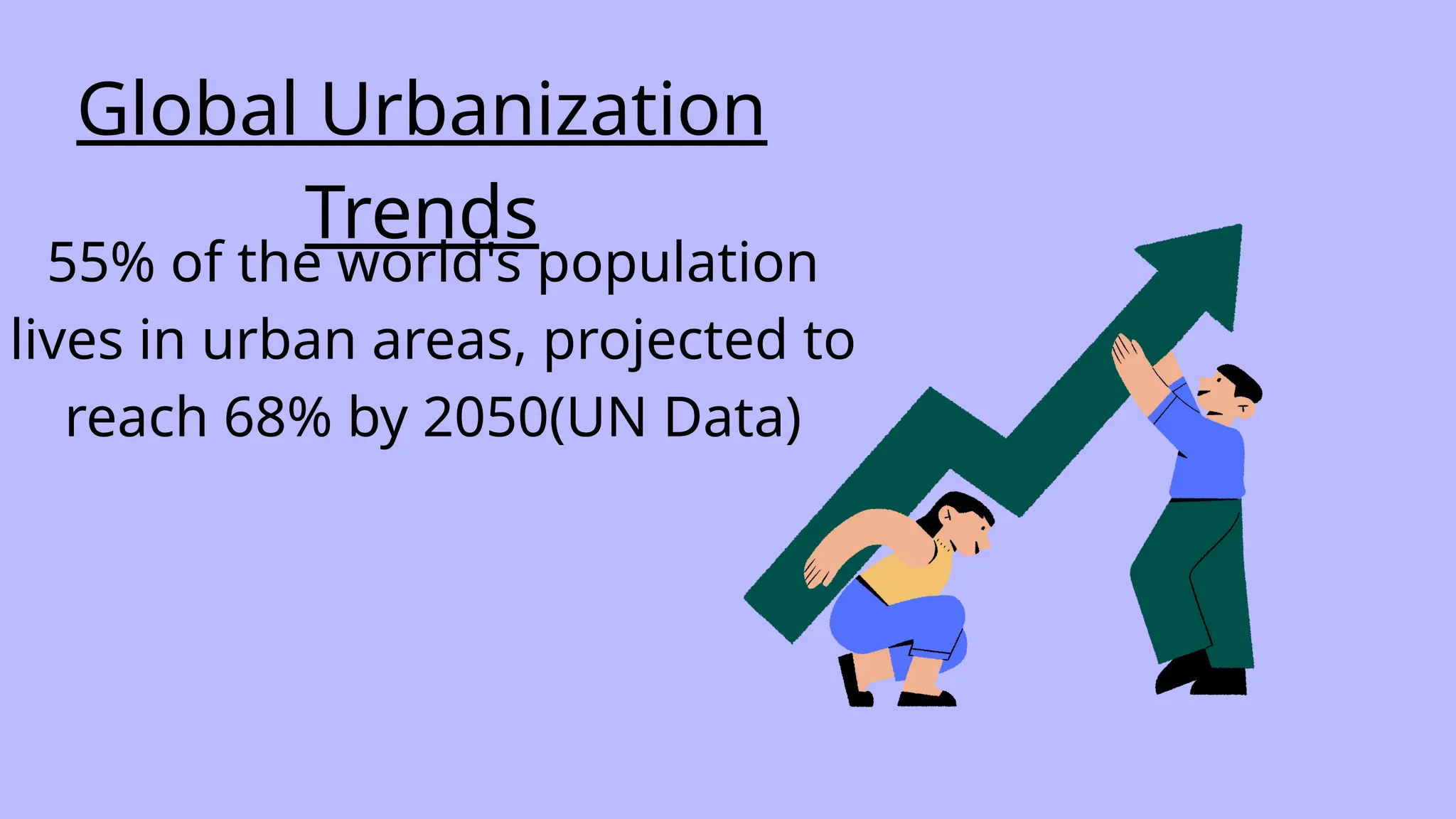
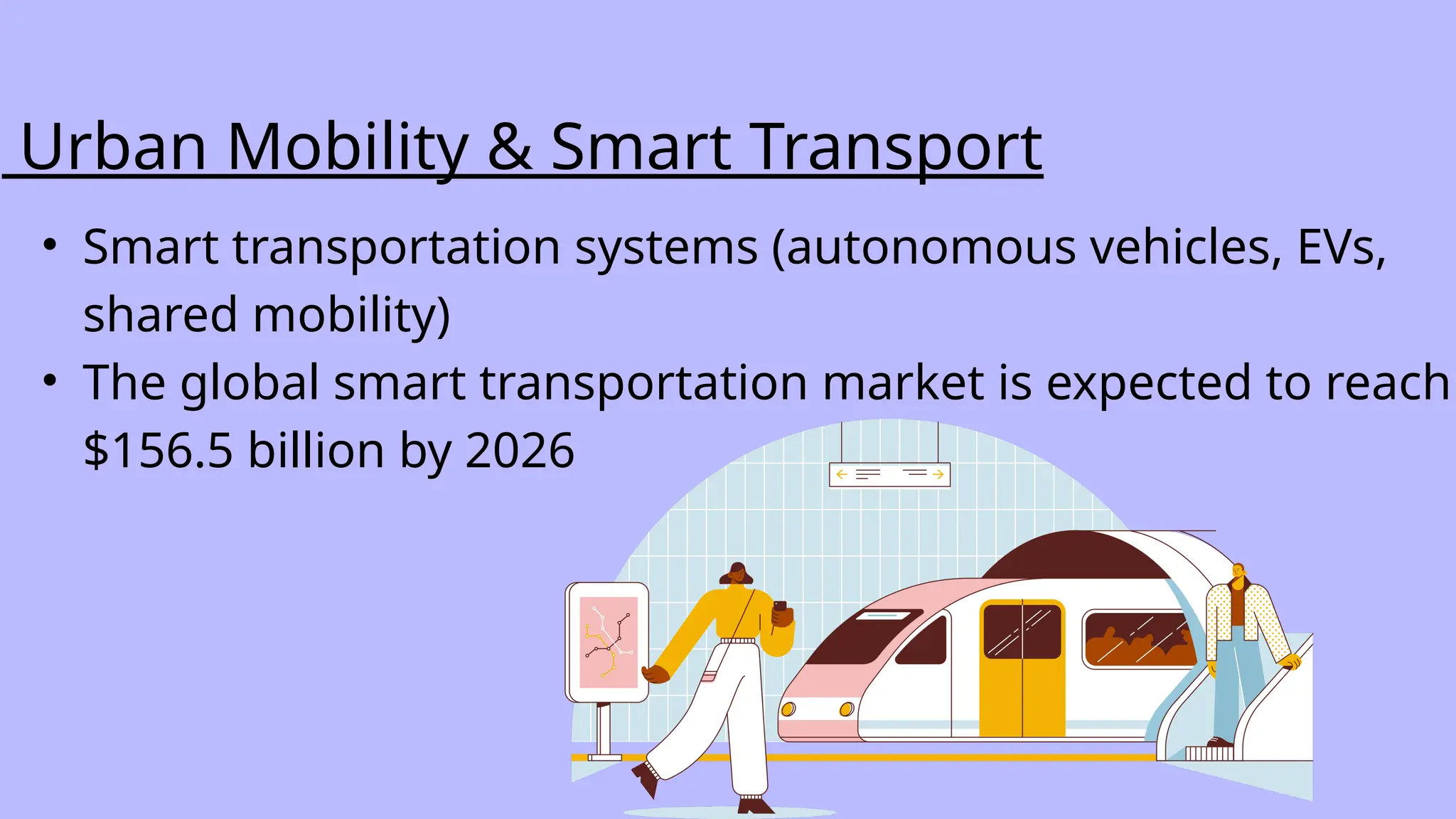
Smart cities utilize technology and data to enhance urban services and quality of life, focusing on innovation, efficiency, and sustainability. Key components include IoT, AI, big data, and smart governance which improve transport, public services, and energy management. Despite challenges like financial constraints and workforce shortages, smart city solutions can significantly reduce emissions and drive economic growth.