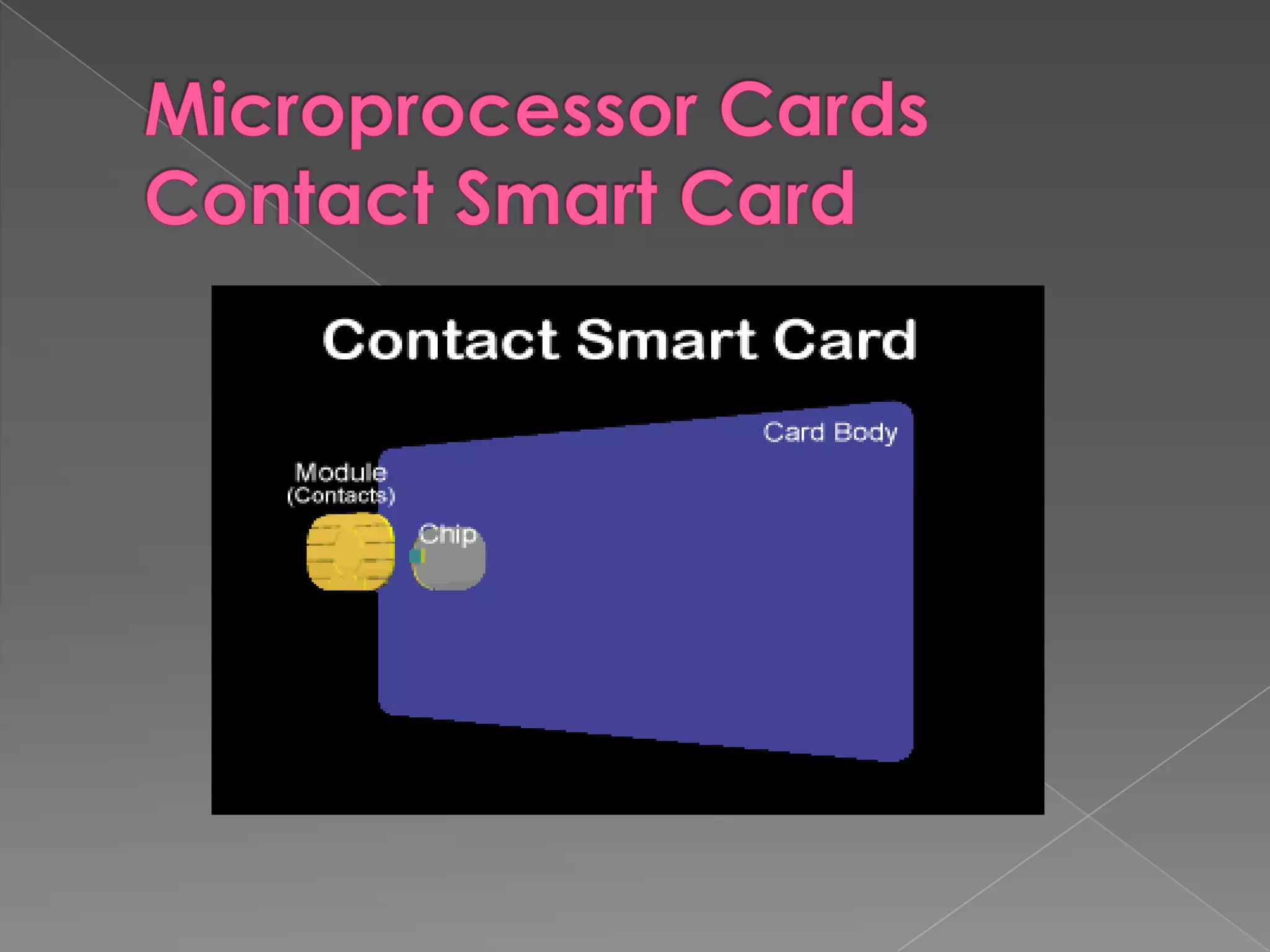
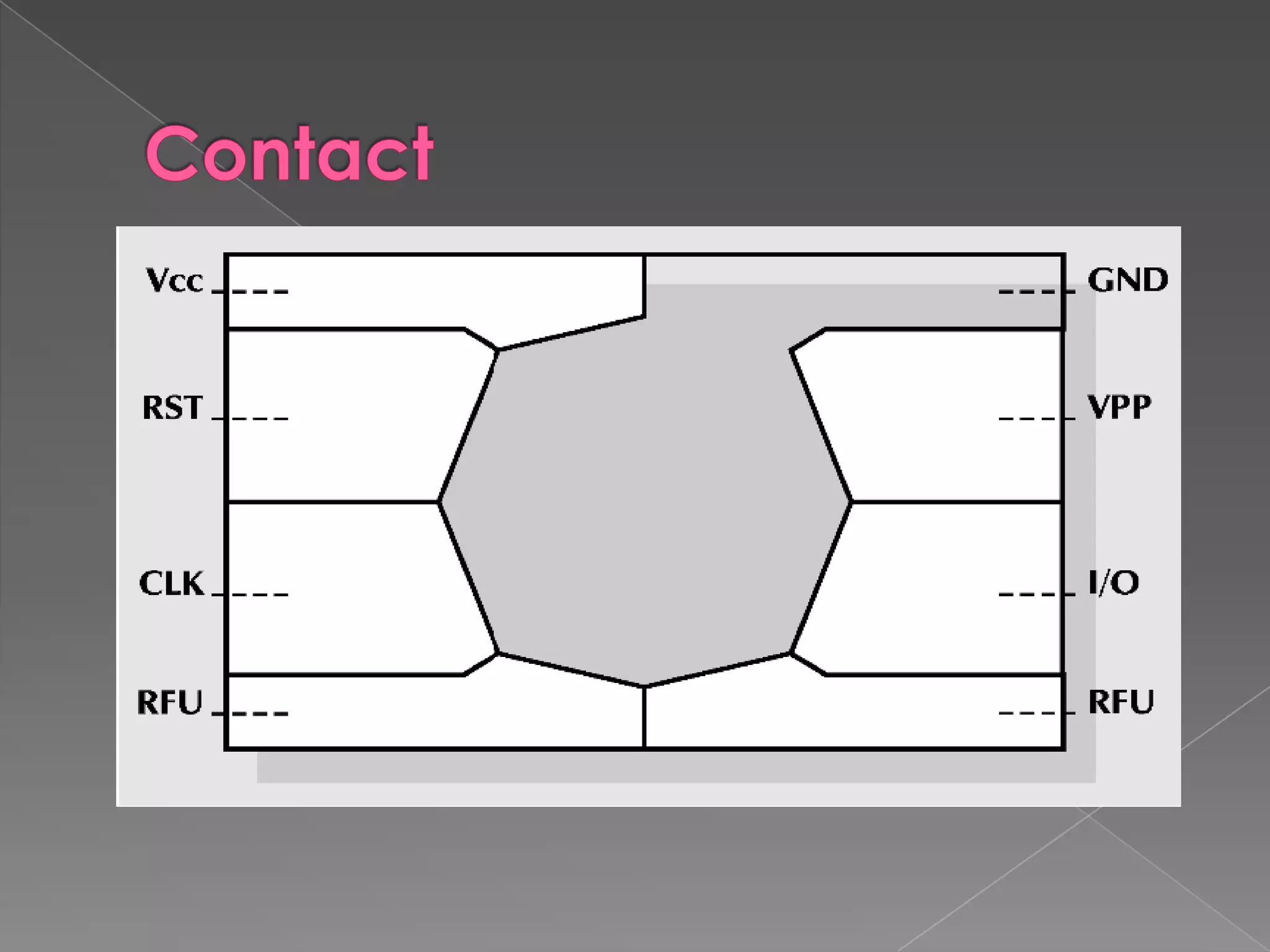
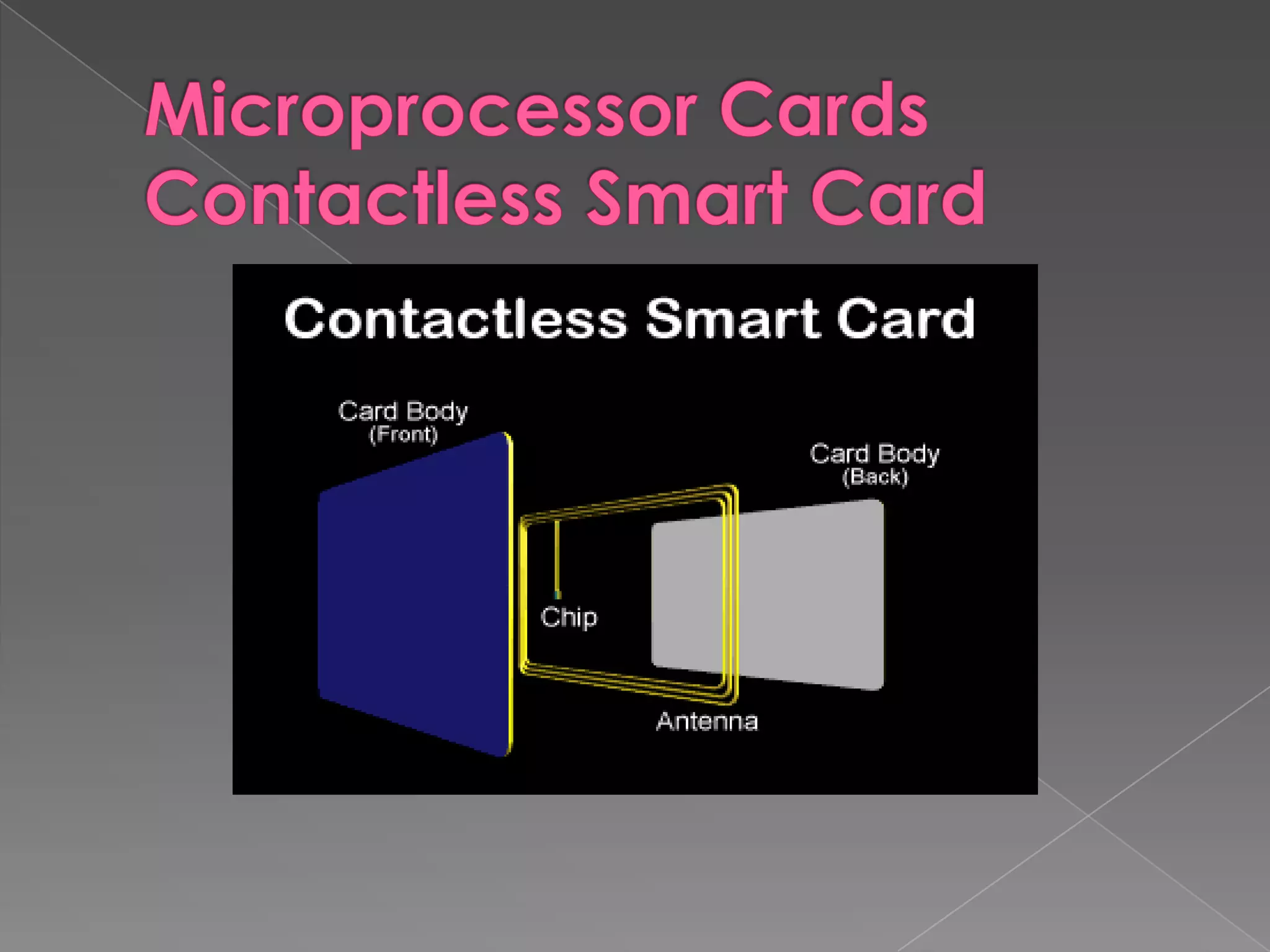
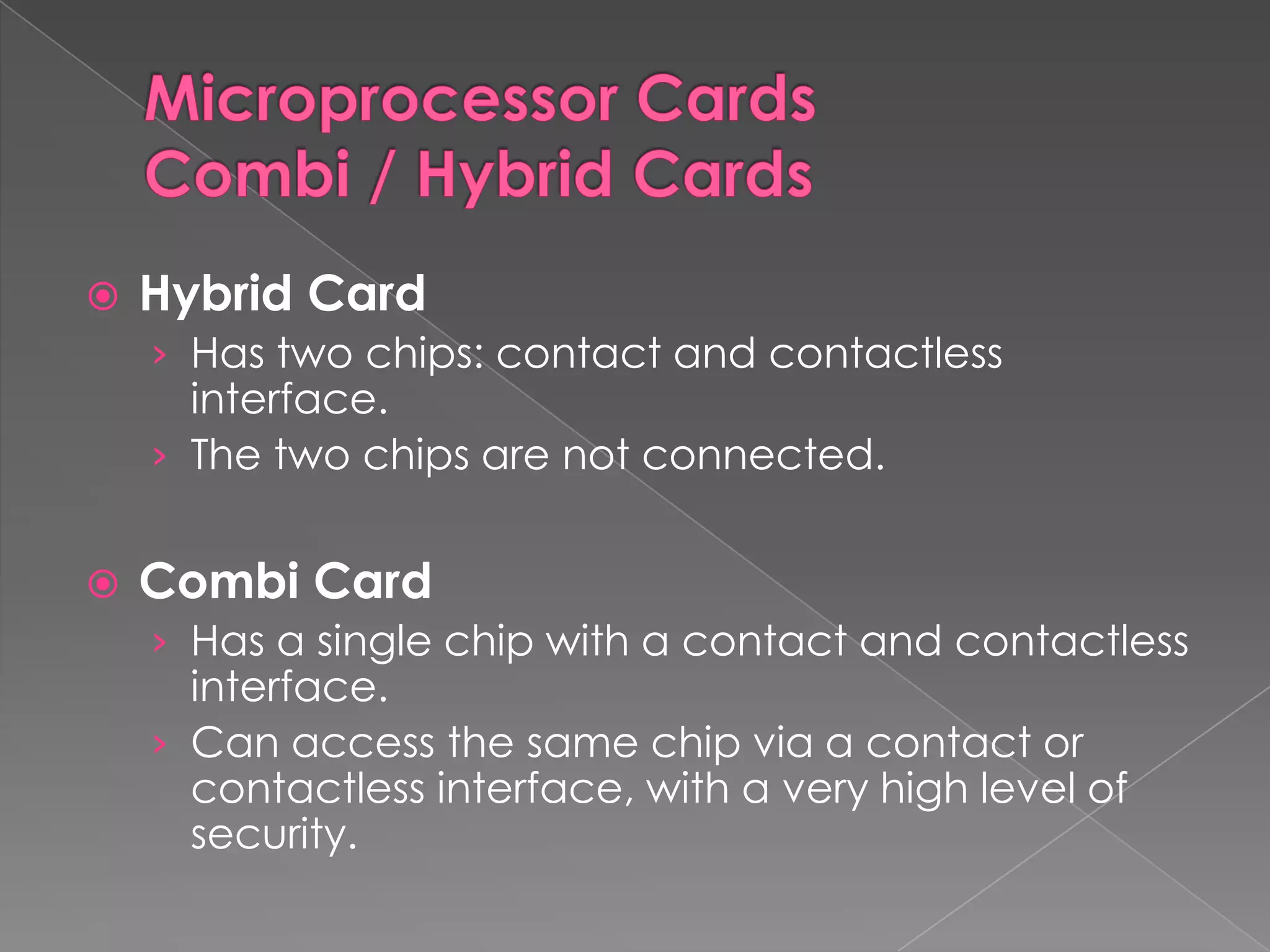
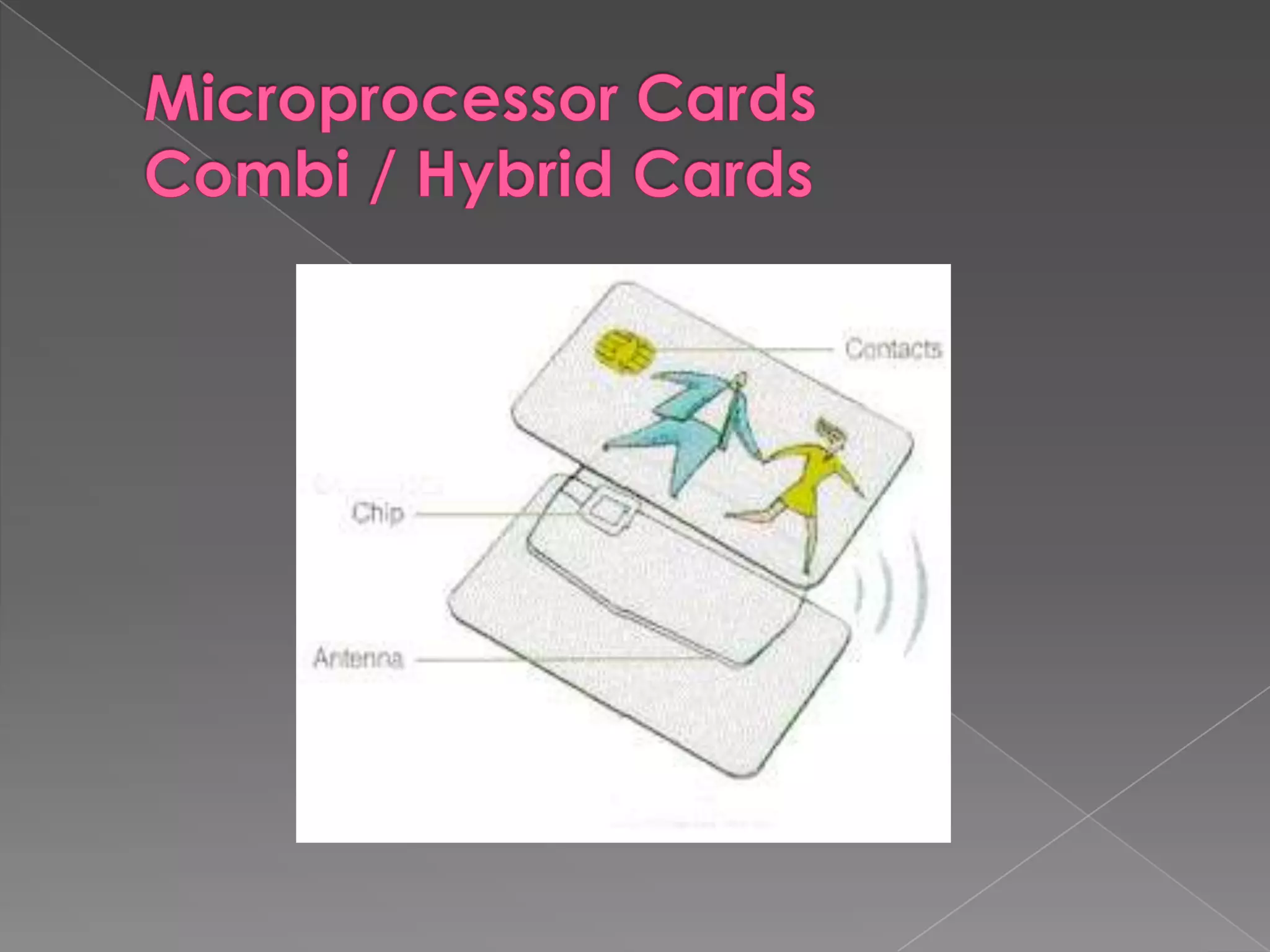
A smart card is a pocket-sized card with embedded integrated circuits that can securely store and process information. Smart cards can function like magnetic stripe cards for applications such as banking, identification, and ticketing while offering enhanced security features like the ability to encrypt data, perform calculations, and require PIN codes to access information. Common uses of smart cards include SIM cards in mobile phones, secure login credentials, and health records storage. While more secure than magnetic stripe cards, smart cards still have limitations such as requiring readers and potential loss or theft.